Wind power in Pennsylvania
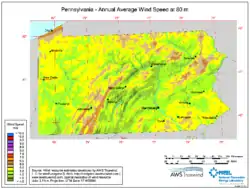
There are more than twenty wind power projects operating in the commonwealth of Pennsylvania. The most productive wind energy regions generally fall in mountain or coastal terrains. The northern portion of the Appalachian chain, including most of Southwestern Pennsylvania, is one of the areas with the highest potential for wind energy in the Eastern United States. The mountain ridges of central and northeastern Pennsylvania, including the Poconos in the eastern part of the state, offer some of the best wind resources in the region.[1]

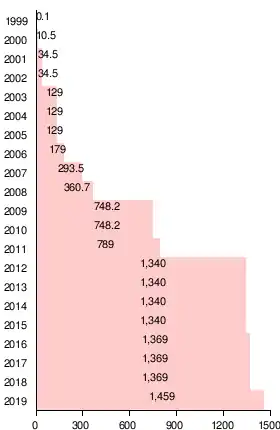
If all wind energy potential in Pennsylvania was developed with utility-scale wind turbines, the power produced each year would be enough to supply 6.4% of the state's current electricity consumption.[2] In 2016 the state had 1369 megawatts (MW) of wind powered electricity generating capacity, responsible for 1.6% of in-state electricity production.[3] This increased to 1459 MW in 2019.[4]
History

In 2006, Pennsylvania's legislature ruled that wind turbines and related equipment may not be included in property-tax assessments. Instead, the sites of wind facilities are assessed for their income-capitalization value.
In 2007, Montgomery County became the first wind-powered county in the nation, with a two-year commitment to buy 100 percent of its electricity from a combination of wind energy and renewable energy credits derived from wind energy.[5]
In 2009, the Environmental Protection Agency honored Swarthmore, Pennsylvania as a Green Power Community — the only one in the Eastern United States - for its commitment to buy clean energy generated from wind turbines in mountainous region of western Pennsylvania.[6]
In 2012, a coalition of wind farm developers, owner, operators, their supporters, and retail suppliers joined together to form ChoosePAWind. This coalition's goal is to educate Pennsylvanians about the environmental and economic benefits of supplying energy from local wind farms.
Many smaller wind farms in Pennsylvania are operated by NextEra Energy Resources, based in Florida.[7]
Wind farms
| Name | Turbines | Capacity (MW) | Power (MW·hr/yr) | Location (county) | Year Operational |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Allegheny Ridge Wind Farm | 40 | 80 | 210,240[8] | Blair and Cambria | 2007 |
| Armenia Mountain Wind Farm | 67 | 101 | unknown | Tioga and Bradford | 2010[9] |
| Bear Creek Wind Power Project | 12 | 24 | 70,000[10] | Luzerne | 2006 |
| Big Level Project | 25 | 90 | 2019 | ||
| Casselman Wind Power Project | 23 | 34.5 | 90,666[8] | Somerset | 2007 |
| Chestnut Flats Wind Farm | 19 | 38 | unknown | Blair and Cambria | 2011 |
| Forward Wind Project | 14 | 29.4 | 77,263[8] | Somerset | 2008 |
| Green Mountain Wind Energy Center | 8 | 10.4 | 27,331[8] | Somerset | 2000 |
| Highland Wind Farm | 25 | 62.5 | unknown | Cambria | 2009[11] |
| Highland North Wind Farm | 30 | 75 | unknown | Cambria | 2012 |
| Kimberly Run Wind Project | 40 | 80 | unknown[12] | Somerset | Proposed |
| Laurel Hill Wind Energy Project | 30 | 69 | unknown | Lycoming | 2012 |
| Locust Ridge I | 13 | 26 | 68,328[13] | Schuylkill | 2004 |
| Locust Ridge II | 51 | 102 | 268,056[8][14] | Columbia and Schuylkill | 2008 |
| Lookout Wind Project | 18 | 37.8 | 99,338[8] | Somerset | 2008 |
| Mason Dixon Wind Project | 30 | 60 | unknown[15] | Somerset | Proposed |
| Mehoopany Wind Farm | 88[16] | 140.8[16] | Unknown | Wyoming | 2012 |
| Meyersdale Wind Power Project | 20 | 30 | 78,840[8] | Somerset | 2003 |
| Mill Run Wind Energy Center | 10 | 15 | 39,420[8] | Fayette | 2001 |
| North Allegheny Wind Farm | 35 | 70[17] | unknown | Blair and Cambria | 2009 |
| Patton Wind Farm | 15[18] | 30 | unknown | Cambria | 2012 |
| Ringer Hill Wind Farm | 14 | 39.9[19] | unknown | Somerset | 2016 |
| Sandy Ridge Wind Farm | 25 | 50[20] | unknown | Centre | 2012 |
| Somerset Wind Farm | 6 | 9 | 23,652[8] | Somerset | 2001 |
| South Chestnut Wind Project | 23 | 46 | unknown | Fayette | 2011 |
| Stonycreek Wind Farm | 35 | 52.5[21] | unknown | Somerset | 2009 |
| Twin Ridges Wind Farm | 68[22] | 140 | unknown | Somerset | 2012 |
| Waymart Wind Farm | 43 | 64.5 | 169,506[8][23] | Wayne | 2003 |
Location map
Installed capacity and wind resources
The graph at left shows the end of year wind generation capacity growth from 1999 through 2019.
In a 2010 report, the National Renewable Energy Laboratory stated that Pennsylvania had potential to install up to about 3,300 MW of onshore wind power nameplate capacity at 80m, which would generate enough clean power annually to meet the energy needs of 1,168,000 homes, or 7,200 MW at 100m, capable of generating 21,200 GWh/year.[28][29]
Despite the state's limited shoreline, on Lake Erie, Pennsylvania has the potential to install up to 5,670 MW of offshore wind turbines in an area of 1,135 square kilometres (438 sq mi), capable of generating 23,571 GWh/year.[30] Offshore wind turbines tend to have a higher capacity factor than onshore wind turbines.
Wind generation
| Pennsylvania Wind Generation (GWh, Million kWh) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Total | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sept | Oct | Nov | Dec |
| 2011 | 1,968 | 171 | 206 | 202 | 226 | 146 | 130 | 79 | 107 | 87 | 144 | 195 | 205 |
| 2012 | 2,129 | 252 | 194 | 207 | 209 | 107 | 150 | 106 | 76 | 120 | 206 | 207 | 294 |
| 2013 | 3,352 | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 3,564 | ||||||||||||
| 2015 | 3,353 | 391 | 314 | 416 | 348 | 206 | 230 | 132 | 118 | 156 | 317 | 363 | 361 |
| 2016 | 3,476 | ||||||||||||
| 2017 | 3,590 | ||||||||||||
| 2018 | 3,566 | ||||||||||||
| 2019 | 3,548 | ||||||||||||
See also
References
- A new crop takes root accessed March 1, 2010.
- State wind energy fact sheet - Pennsylvania, American Wind Energy Association, Dec. 2011
- "Pennsylvania Wind Energy" (PDF). U.S. Wind Energy State Facts. American Wind Energy Association. Retrieved 27 December 2017.
- Wind Energy in Pennsylvania
- Pennsylvania profile ((secondary source)) Natural Resources Defense Council, accessed March 1, 2010.
- Town in Pennsylvania Catches Wind of Clean Energy Future April 7, 2009. Accessed March 2, 2010.
- Wind Farms in Pennsylvania Pennsylvania Wind Working Group, accessed March 1, 2010.
- Wind farms in Pennsylvania Penn Futures: Citizens for Pennsylvania's Future, accessed March 3, 2010.
- AES Wind Generation Announces Commercial Operation of Armenia Mountain Wind Farm, U.S. AES press release, January 4, 2010. Accessed March 6, 2010.
- Wind Farms in Pennsylvania accessed March 2, 2010.
- "Highland Wind Farm". White Construction. Retrieved 31 July 2019.
- Everpower Wind Holdings, accessed January 28, 2015.
- Locust Ridge Wind Farm in Pennsylvania accessed March 1, 2010.
- 51 windmills will top local mountain; Massive project to stretch 10 miles March 23, 2008. Accessed March 1, 2010.
- Everpower Wind Holdings, accessed February 9, 2015.
- Renewable Energy Systems America, accessed July 28, 2013
- Duke Energy steps up US wind farm development July 6, 2009. Accessed March 30, 2010.
- Patton Wind Farm Accessed August 26, 2011.
- NJR completes Ringer Hill Wind Farm
- Gamesa moves turbine blades Gamesa moves turbine blades. Accessed August 26, 2012.
- U.S Wind Energy Projects, Pennsylvania American Wind Energy Association, December 31, 2009. Accessed March 30, 2010.
- 68-turbine wind farm to be constructed in Somerset Co. , accessed August 26, 2012.
- Waymart Wind Farm Safeway Wind Energy, accessed March 1, 2010.
- "Wind Powering America: Installed U.S. Wind Capacity and Wind Project Locations". U.S. Department of Energy. 19 January 2012. Retrieved 19 January 2012.
- "AWEA 4th quarter 2011 Public Market Report" (PDF). American Wind Energy Association(AWEA). January 2012. Retrieved 3 February 2012.
- "WINDExchange: Installed Wind Capacity". U.S. Department of Energy. 29 December 2016. Retrieved 29 December 2016.
- "WINDExchange: U.S. Installed and Potential Wind Power Capacity and Generation". U.S. Department of Energy. 3 March 2019. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- "Estimates of Windy Land Area and Wind Energy Potential by State for Areas >= 30% Capacity Factor at 80m" (XLS). National Renewable Energy Laboratory. 2010-02-04. Retrieved 2010-03-29.
- "Pennsylvania Wind Activities". National Renewable Energy Laboratory. 2010-02-19. Retrieved 2010-03-29.
- Renewable Energy Technical Potential
- EIA (July 27, 2012). "Electric Power Monthly Table 1.17.A." United States Department of Energy. Retrieved 2012-08-15.
- EIA. "EIA Electricity Data Browser". United States Department of Energy. Retrieved 2016-12-30.
- Wind Energy in Pennsylvania
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Wind power in Pennsylvania. |
- Pennsylvania Wind Working Group
- Penn Future: Citizens for Pennsylvania's Future profile on Wind farms in Pennsylvania.