Alphaproteobacteria
Alphaproteobacteria is a class of bacteria in the phylum Proteobacteria (See also bacterial taxonomy).[17] Its members are highly diverse and possess few commonalities, but nevertheless share a common ancestor. Like all Proteobacteria, its members are gram-negative and some of its intracellular parasitic members lack peptidoglycan and are consequently gram variable.[17][18]
| Alphaproteobacteria | |
|---|---|
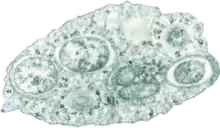 | |
| Transmission electron micrograph of Wolbachia within an insect cell. Credit:Public Library of Science / Scott O'Neill | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Bacteria |
| Phylum: | Proteobacteria |
| Class: | Alphaproteobacteria Garrity et al. 2006 |
| Subclasses | |
| |
Characteristics
The Alphaproteobacteria are a diverse taxon and comprises several phototrophic genera, several genera metabolising C1-compounds (e.g., Methylobacterium spp.), symbionts of plants (e.g., Rhizobium spp.), endosymbionts of arthropods (Wolbachia) and intracellular pathogens (e.g. Rickettsia). Moreover, the class includes (as an extinct member) the protomitochondrion, the bacterium that was engulfed by the eukaryotic ancestor and gave rise to the mitochondria, which are organelles in eukaryotic cells (See endosymbiotic theory).[7] A species of technological interest is Rhizobium radiobacter (formerly Agrobacterium tumefaciens): scientists often use this species to transfer foreign DNA into plant genomes.[19] Aerobic anoxygenic phototrophic bacteria, such as Pelagibacter ubique, are alphaproteobacteria that are a widely distributed and may constitute over 10% of the open ocean microbial community.
Evolution and genomics
There is some disagreement on the phylogeny of the orders, especially for the location of the Pelagibacterales, but overall there is some consensus. The discord stems from the large difference in gene content (e.g. genome streamlining in Pelagibacter ubique) and the large difference in GC-richness between members of several orders.[7] Specifically, Pelagibacterales, Rickettsiales and Holosporales contain species with AT-rich genomes. It has been argued that it could be a case of convergent evolution that would result in an artefactual clustering.[20][21][22] However, several studies disagree.[7][23][24][25]
Furthermore, it has been found that the GC-content of ribosomal RNA (the traditional phylogenetic marker for prokaryotes) little reflects the GC-content of the genome. One example of this atypical decorrelation of ribosomal GC-content with phylogeny is that members of the Holosporales have a much higher ribosomal GC-content than members of the Pelagibacterales and Rickettsiales, even though they are more closely related to species with high genomic GC-contents than to members of the latter two orders.[7]
The Class Alphaproteobacteria is divided into three subclasses Magnetococcidae, Rickettsidae and Caulobacteridae.[7] The basal group is Magnetococcidae, which is composed by a large diversity of magnetotactic bacteria, but only one is described, Magnetococcus marinus.[26] The Rickettsidae is composed of the intracellular Rickettsiales and the free-living Pelagibacterales. The Caulobacteridae is composed of the Holosporales, Rhodospirillales, Sphingomonadales, Rhodobacterales, Caulobacterales, Kiloniellales, Kordiimonadales, Parvularculales and Sneathiellales.
Comparative analyses of the sequenced genomes have also led to discovery of many conserved insertion-deletions (indels) in widely distributed proteins and whole proteins (i.e. signature proteins) that are distinctive characteristics of either all Alphaproteobacteria, or their different main orders (viz. Rhizobiales, Rhodobacterales, Rhodospirillales, Rickettsiales, Sphingomonadales and Caulobacterales) and families (viz. Rickettsiaceae, Anaplasmataceae, Rhodospirillaceae, Acetobacteraceae, Bradyrhiozobiaceae, Brucellaceae and Bartonellaceae).
These molecular signatures provide novel means for the circumscription of these taxonomic groups and for identification/assignment of new species into these groups.[27] Phylogenetic analyses and conserved indels in large numbers of other proteins provide evidence that Alphaproteobacteria have branched off later than most other phyla and Classes of Bacteria except Betaproteobacteria and Gammaproteobacteria.[28][29]
Phylogeny
The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) [18] and National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI)[30] and the phylogeny is based on 16S rRNA-based LTP release 106 by 'The All-Species Living Tree' Project [31]
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Notes:
♠ Strains found at the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) but not listed in the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LSPN).
Aquaspirillum is now regarded to belong to Betaproteobacteria. A newer tree based on 16S and 23S rRNA (and other data) is given by Ferla et al. (2013) as follows:
| Schematic ribosomal RNA phylogeny of Alphaproteobacteria | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The cladogram of Rickettsidae has been inferred by Ferla et al. [7] from the comparison of 16S + 23S ribosomal RNA sequences. |
An updated phylogeny of the alphaproteobacteria was published in which the position of the Mitochondria is not clear yet. [32]
Natural genetic transformation
Although only a few studies have been reported on natural genetic transformation in the Alphaproteobacteria, this process has been described in Agrobacterium tumefaciens,[33] Methylobacterium organophilum,[34] and Bradyrhizobium japonicum.[35] Natural genetic transformation is a sexual process involving DNA transfer from one bacterial cell to another through the intervening medium, and the integration of the donor sequence into the recipient genome by homologous recombination.
References
- Grote J, Thrash JC, Huggett MJ, Landry ZC, Carini P, Giovannoni SJ, Rappé MS (2012). "Streamlining and core genome conservation among highly divergent members of the SAR11 clade". mBio. 3 (5): e00252-12. doi:10.1128/mBio.00252-12. PMC 3448164. PMID 22991429.
- Breoghania, on: NCBI Taxonomy Browser
- Hartmannibacter, on: NCBI Taxonomy Browser
- La Scola B, Barrassi L, Raoult D (2004). "A novel alpha-Proteobacterium, Nordella oligomobilis gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated by using amoebal co-cultures". Research in Microbiology. 155 (1): 47–51. doi:10.1016/j.resmic.2003.09.012.
- Nordella, on: NCBI Taxonomy Browser]
- Geminicoccus, on: NCBI Taxonomy Browser
- Ferla MP, Thrash JC, Giovannoni SJ, Patrick WM (2013). "New rRNA gene-based phylogenies of the Alphaproteobacteria provide perspective on major groups, mitochondrial ancestry and phylogenetic instability". PLOS One. 8 (12): e83383. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0083383. PMC 3859672. PMID 24349502.
- Reyranella, on: NCBI Taxonomy Browser
- Elioraea tepidiphila (SPECIES), on: UniProt Taxonomy
- Elioraea tepidiphila, on: NCBI Taxonomy Broeser
- Eilatimonas, on: NCBI Taxonomy Browser
- Rhizomicrobium, on: NCBI Taxonomy Browser
- Subaequorebacter, on: NCBI Taxonomy Browser
- Rose, A.H.; Tempest, D.W.; Morris, J.G. (1983). Advances in Microbial Physiology. 24. Academic Press. p. 111. ISBN 0-12-027724-7.
- Tuberoidobacter, on: IniProt Taxonomy
- Tuberoidobacter, on: NCBI Taxonomy Browser
- Brenner, Don J.; Krieg, Noel R.; Staley, James T. (July 26, 2005) [1984(Williams & Wilkins)]. George M. Garrity (ed.). The Proteobacteria. Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology. 2C (2nd ed.). New York: Springer. p. 1388. ISBN 978-0-387-24145-6. British Library no. GBA561951.
- J.P. Euzéby. "Alphaproteobacteria". List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN). Archived from the original on 2013-01-27. Retrieved 2011-11-17.
- Chilton MD, Drummond MH, Merio DJ, Sciaky D, Montoya AL, Gordon MP, Nester EW (1977). "Stable incorporation of plasmid DNA into higher plant cells: the molecular basis of crown gall tumorigenesis". Cell. 11 (2): 263–71. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(77)90043-5. PMID 890735.
- Rodríguez-Ezpeleta N, Embley TM (2012). "The SAR11 group of alpha-proteobacteria is not related to the origin of mitochondria". PLOS ONE. 7 (1): e30520. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0030520. PMC 3264578. PMID 22291975.

- Viklund J, Ettema TJ, Andersson SG (Feb 2012). "Independent genome reduction and phylogenetic reclassification of the oceanic SAR11 clade". Mol Biol Evol. 29 (2): 599–615. doi:10.1093/molbev/msr203. PMID 21900598.
- Viklund J, Martijn J, Ettema TJ, Andersson SG (2013). "Comparative and phylogenomic evidence that the alphaproteobacterium HIMB59 is not a member of the oceanic SAR11 clade". PLOS ONE. 8 (11): e78858. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0078858. PMC 3815206. PMID 24223857.

- Georgiades K, Madoui MA, Le P, Robert C, Raoult D (2011). "Phylogenomic analysis of Odyssella thessalonicensis fortifies the common origin of Rickettsiales, Pelagibacter ubique and Reclimonas americana mitochondrion". PLOS ONE. 6 (9): e24857. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0024857. PMC 3177885. PMID 21957463.

- Thrash JC, Boyd A, Huggett MJ, Grote J, Carini P, Yoder RJ, Robbertse B, Spatafora JW, Rappé MS, Giovannoni SJ (2011). "Phylogenomic evidence for a common ancestor of mitochondria and the SAR11 clade". Sci Rep. 1: 13. doi:10.1038/srep00013. PMC 3216501. PMID 22355532.
- Williams KP, Sobral BW, Dickerman AW (July 2007). "A robust species tree for the alphaproteobacteria". Journal of Bacteriology. 189 (13): 4578–86. doi:10.1128/JB.00269-07. PMC 1913456. PMID 17483224.
- Bazylinski DA, Williams TJ, Lefèvre CT, Berg RJ, Zhang CL, Bowser SS, Dean AJ, Beveridge TJ (2012). "Magnetococcus marinus gen. nov., sp. nov., a marine, magnetotactic bacterium that represents a novel lineage (Magnetococcaceae fam. nov.; Magnetococcales ord. nov.) at the base of the Alphaproteobacteria". Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 63: 801–808. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.038927-0. PMID 22581902.
- Gupta RS (2005). "Protein signatures distinctive of Alphaproteobacteria and its subgroups and a model for Alpha proteobacterial evolution". Crit Rev Microbiol. 31 (2): 135. doi:10.1080/10408410590922393. PMID 15986834.
- Gupta R.S. (2000). "Phylogeny of Proteobacteria: Relationships to other eubacterial phyla and to eukaryotes". FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 24 (4): 367–402. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6976.2000.tb00547.x. PMID 10978543.
- Gupta R.S.; Sneath P.H.A. (2007). "Application of the Character compatibility approach to generalized molecular sequence data: Branching order of the Proteobacterial subdivisions". J. Mol. Evol. 64 (1): 90–100. doi:10.1007/s00239-006-0082-2. PMID 17160641.
- Sayers; et al. "Alphaproteobacteria". National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) taxonomy database. Retrieved 2011-06-05.
- 'The All-Species Living Tree' Project."16S rRNA-based LTP release 106 (full tree)" (PDF). Silva Comprehensive Ribosomal RNA Database. Retrieved 2011-11-17.
- Roger, Andrew J.; Muñoz-Gómez, Sergio A.; Kamikawa, Ryoma (2017-11-01). "The Origin and Diversification of Mitochondria". Current Biology. 27 (21): R1177–R1192. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2017.09.015. ISSN 0960-9822.
- Demanèche S, Kay E, Gourbière F, Simonet P (2001). "Natural transformation of Pseudomonas fluorescens and Agrobacterium tumefaciens in soil". Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 67 (6): 2617–21. doi:10.1128/AEM.67.6.2617-2621.2001. PMC 92915. PMID 11375171.
- O'Connor M, Wopat A, Hanson RS (1977). "Genetic transformation in Methylobacterium organophilum". J. Gen. Microbiol. 98 (1): 265–72. doi:10.1099/00221287-98-1-265. PMID 401866.
- Raina JL, Modi VV (1972). "Deoxyribonucleate binding and transformation in Rhizobium jpaonicum". J. Bacteriol. 111 (2): 356–60. PMC 251290. PMID 4538250.
External links
- Alphaproteobacteria at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Bacterial (Prokaryotic) Phylogeny Webpage: Alpha Proteobacteria.