Arameans
The Arameans (Old Aramaic: 𐤀𐤓𐤌𐤉𐤀, Āramayē) were an ancient Semitic-speaking people in the Near East, first recorded in historical sources from the late 12th century BC. At the beginning of the 1st millennium BC, a number of Aramean states were established throughout the Levant and Upper Mesopotamia. Local Aramean kingdoms were subsequently conquered by the Neo-Assyrian Empire. During the period of Assyrian rule, policy of population displacement and relocation, that was applied throughout the Assyrian domains, also affected Arameans. As a result of wider dispersion of Aramean communities, speaking areal of Aramaic language was also widened, gradually gaining significance and eventually becoming the common language of public life and administration, particularly during the periods of Neo-Babylonian Empire (612–539), and later Achaemenid Empire (539–330). As a result of linguistic aramization, a wider Aramaic-speaking areal was created throughout the central regions of the Near East, exceeding the boundaries of Aramean ethnic communities. During the later Hellenistic and Roman periods, minor Aramean states emerged, most notable of them being the Kingdom of Osroene, centered in Edessa, the birthplace of Edessan Aramaic, that later came to be known as Syriac language.[1][2][3]
| Arameans |
|---|
| Syro-Hittite states |
| Aramean kings |
| Aramean cities |
| Sources |
From the 1st century CE onward, the process of Christianization was initiated throughout the ancient Near East, encompassing various Aramaic-speaking communities, including Arameans, thus resulting in the creation of Aramean Christianity,[4] represented by prominent Christian leaders and authors, who created their theological and literary works in Aramaic language, most notable of them being saint Ephrem of Edessa (d. 373). In the following period, two consecutive processes have affected Christian Arameans. First process was initiated during the 5th century, when ancient Greek custom of using Syrian/Syriac labels for Arameans and their language, started to gain acceptance among Aramean literary and ecclesiastical elites. Second process was initiated after the Arab conquest in the 7th century, that was followed by Islamization and gradual Arabization of Aramean communities throughout the Near East, ultimately resulting in their fragmentation and acculturation.[5][6]
History


Origins
The toponym A-ra-mu appears in an inscription at the East Semitic speaking kingdom of Ebla listing geographical names, and the term Armi, which is the Eblaite term for nearby Idlib, occurs frequently in the Ebla tablets (c. 2300 BC). One of the annals of Naram-Sin of Akkad (c. 2250 BC) mentions that he captured "Dubul, the ensí of A-ra-me" (Arame is seemingly a genitive form), in the course of a campaign against Simurrum in the northern mountains.[7] Other early references to a place or people of "Aram" have appeared at the archives of Mari (c. 1900 BC) and at Ugarit (c. 1300 BC). However, there are no historical, archaeological or linguistic evidences that those early uses of the terms Aramu, Armi or Arame were actually referring to the Arameans. The earliest undisputed historical attestation of Arameans as a people appears much later, in the inscriptions of Tiglath Pileser I (c. 1100 BC).[8][9][10]
Nomadic pastoralists have long played a prominent role in the history and economy of the Middle East, but their numbers seem to vary according to climatic conditions and the force of neighbouring states inducing permanent settlement. The period of the Late Bronze Age seems to have coincided with increasing aridity, which weakened neighbouring states and induced transhumance pastoralists to spend longer and longer periods with their flocks. Urban settlements (hitherto largely Amorite, Canaanite, Hittite, Ugarite inhabited) in The Levant diminished in size, until eventually fully nomadic pastoralist lifestyles came to dominate much of the region. These highly mobile, competitive tribesmen with their sudden raids continually threatened long-distance trade and interfered with the collection of taxes and tribute.
The people who had long been the prominent population within what is today Syria (called the Land of the Amurru during their tenure) were the Amorites, a Canaanite speaking group of Semites who had appeared during the 25th century BC, destroying the hitherto dominant East Semitic speaking state of Ebla, founding the powerful state of Mari in the Levant, and during the 19th century BC founding Babylonia in southern Mesopotamia. However, they seem to have been displaced or wholly absorbed by the appearance of a people called the Ahlamu by the 13th century BC, disappearing from history.
Ahlamû appears to be a generic term for a new wave of Semitic wanderers and nomads of varying origins who appeared during the 13th century BC across the Near East, Arabian Peninsula, Asia Minor, and Egypt. The presence of the Ahlamû is attested during the Middle Assyrian Empire (1365–1020 BC), which already ruled many of the lands in which the Ahlamû arose, in the Babylonian city of Nippur and even at Dilmun (modern Bahrain). Shalmaneser I (1274–1245 BC) is recorded as having defeated Shattuara, King of the Mitanni and his Hittite and Ahlamû mercenaries. In the following century, the Ahlamû cut the road from Babylon to Hattusas, and Tukulti-Ninurta I (1244–1208 BC) conquered Mari, Hanigalbat and Rapiqum on the Euphrates and "the mountain of the Ahlamû", apparently the region of Jebel Bishri in northern Syria.
The Arameans would appear to be one part of the larger generic Ahlamû group rather than synonymous with the Ahlamu.
Aramean states
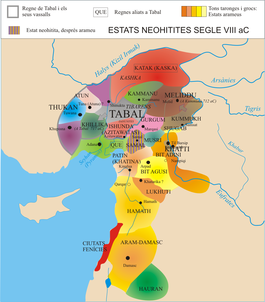
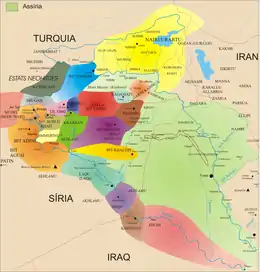
The emergence of the Arameans occurred during the Bronze Age collapse (1200–900 BC), which saw great upheavals and mass movements of peoples across the Middle East, Asia Minor, The Caucasus, East Mediterranean, North Africa, Ancient Iran, Ancient Greece and Balkans, leading to the genesis of new peoples and polities across these regions.
The first certain reference to the Arameans appears in an inscription of Tiglath-Pileser I (1115–1077 BC), which refers to subjugating the "Ahlamû-Aramaeans" (Ahlame Armaia). Shortly after, the Ahlamû disappear from Assyrian annals, to be replaced by the Aramaeans (Aramu, Arimi). This indicates that the Arameans had risen to dominance amongst the nomads. Among scholars, the relationship between the Akhlame and the Aramaeans is a matter of conjecture.[11] By the late 12th century BC, the Arameans were firmly established in Syria; however, they were conquered by the Middle Assyrian Empire, as had been the Amorites and Ahlamu before them.
The Middle Assyrian Empire (1365–1050 BC), which had dominated the Near East and Asia Minor since the first half of the 14th century BC, began to shrink rapidly after the death of Ashur-bel-kala, its last great ruler in 1056 BC, and the Assyrian withdrawal allowed the Arameans and others to gain independence and take firm control of what was then Eber-Nari (and is today Syria) during the late 11th century BC. It is from this point that the region was called Aramea.
Some of the major Aramean speaking kingdoms included: Aram-Damascus,[12][13] Hamath,[14][15] Bet-Adini,[16][17] Bet-Bagyan,[18] Bit-Hadipe, Aram-Bet Rehob,[19] Aram-Zobah, Bet-Zamani,[20] Bet-Halupe,[21] and Aram-Ma'akah, as well as the Aramean tribal polities of the Gambulu, Litau and Puqudu.[3]
Later Biblical sources tell us that Saul, David and Solomon (late 11th to 10th centuries) fought against the small Aramean kingdoms ranged across the northern frontier of Israel: Aram-Sôvah in the Beqaa, Aram-Bêt-Rehob (Rehov) and Aram-Ma'akah around Mount Hermon, Geshur in the Hauran, and Aram-Damascus. An Aramean king's account dating at least two centuries later, the Tel Dan Stele, was discovered in northern Israel, and is famous for being perhaps the earliest non-Israelite extra-biblical historical reference to the Israelite royal dynasty, the House of David. In the early 11th century BC, much of Israel came under Aramean rule for eight years according to the Biblical Book of Judges, until Othniel defeated the forces led by Chushan-Rishathaim, the King of Aram-Naharaim.[22]
Further north, the Arameans gained possession of Post-Hittite Hamath on the Orontes and were soon to become strong enough to dissociate with the Indo-European speaking Post-Hittite states.
During the 11th and the 10th centuries BCE, the Arameans conquered Sam'al (modern Zenjirli), also known as Yaudi, the region from Arpad to Aleppo, which they renamed Bît-Agushi,[23] and Til Barsip, which became the chief town of Bît-Adini, also known as Beth Eden. North of Sam'al was the Aramean state of Bit-Gabbari, which was sandwiched between the Syro-Hittite states of Carchemish, Gurgum, Khattina, Unqi and the Georgian state of Tabal.
At the same time, Arameans moved to the east of the Euphrates, where they settled in such numbers that, for a time, the whole region became known as Aram-Naharaim or "Aram of the two rivers". Eastern Aramaean tribes spread into Babylonia and an Aramaean usurper was crowned king of Babylon under the name of Adad-apal-iddin.[24] One of their earliest semi-independent kingdoms in southern Mesopotamia was Bît-Bahiâni (Tell Halaf).
Under Neo-Assyrian rule


Assyrian annals from the end of the Middle Assyrian Empire c. 1050 BC and the rise of the Neo-Assyrian Empire in 911 BC contain numerous descriptions of battles between Arameans and the Assyrian army.[3] The Assyrians would launch repeated raids into Aramea, Babylonia, Ancient Iran, Elam, Asia Minor, and even as far as the Mediterranean, in order to keep its trade routes open. The Aramean kingdoms, like much of the Near East and Asia Minor, were subjugated by the Neo Assyrian Empire (911–605 BC), beginning with the reign of Adad-nirari II in 911 BC, who cleared Arameans and other tribal peoples from the borders of Assyria, and began to expand in all directions (See Assyrian conquest of Aram). This process was continued by Ashurnasirpal II, and his son Shalmaneser III, who between them destroyed many of the small Aramean tribes, and conquered the whole of Aramea (modern Syria) for the Assyrians. In 732 BC Aram-Damascus fell and was conquered by the Assyrian king Tiglath-Pileser III. The Assyrians named their Aramean colonies Eber Nari, whilst still using the term Aramean to describe many of its peoples. The Assyrians conducted forced deportations of hundreds of thousands Arameans into both Assyria and Babylonia (where a migrant population already existed).[25][26] Conversely, the Aramaic language was adopted as the lingua franca of the Neo-Assyrian Empire in the 8th century BC, and the native Assyrians and Babylonians began to make a gradual language shift towards Aramaic as the most common language of public life and administration.
The Neo Assyrian Empire descended into a bitter series of brutal internal wars from 626 BC, weakening it greatly. This allowed a coalition of many its former subject peoples; the Babylonians, Chaldeans, Medes, Persians, Parthians, Scythians, Sargatians and Cimmerians to attack Assyria in 616 BC, sacking Nineveh in 612 BC, and finally defeating it between 605 and 599 BC. During the war against Assyria, hordes of horse borne Scythian and Cimmerian marauders ravaged through Aramea and all the way into Egypt.
As a result of migratory processes, various Aramean groups were settled throughout the Ancient Near East, and their presence is recorded in the regions of Assyria,[27] Babylonia,[28] Anatolia,[29] Phoenicia,[30] Palestine,[31] Egypt,[32] and Northern Arabia.[33]
Population transfers, conducted during the Neo-Assyrian Empire and followed by gradual linguistic aramization of non-Aramean populations, created a specific situation in the regions of Assyria proper, among ancient Assyrians, who originally spoke ancient Assyrian language (a dialect of Akkadian), but later accepted Aramaic language.[34]
Under Neo-Babylonian rule
Aramea/Eber-Nari was then ruled by the succeeding Neo-Babylonian Empire (612–539 BC), initially headed by a short lived Chaldean dynasty. The Aramean regions became a battleground between the Babylonians and the Egyptian 26th Dynasty, which had been installed by the Assyrians as vassals after they had conquered Egypt, ejected the previous Nubian dynasty and destroyed the Kushite Empire. The Egyptians, having entered the region in a belated attempt to aid their former Assyrian masters, fought the Babylonians (initially with the help of remnants of the Assyrian army) in the region for decades before being finally vanquished.
The Babylonians remained masters of the Aramean lands only until 539 BC, when the Persian Achaemenid Empire overthrew Nabonidus, the Assyrian born last king of Babylon, who had himself previously overthrown the Chaldean dynasty in 556 BC.
Under Achaemenid rule
The Arameans were later conquered by the Achaemenid Empire (539–332 BCE). However, little changed from the Neo-Assyrian and Neo-Babylonian times, as the Persians, seeing themselves as successors of previous empires, maintained Imperial Aramaic language as the main language of public life and administration.[1][2] Provincial administrative structures also remainde the same, and the name Eber Nari still applied to the region.
Under Seleucid and Ptolemaic rule
Conquests of Alexander the Great (336-323 BCE) marked the beginning of a new era in the history of the entire Near East, including regions inhabited by Arameans. By the end of the 4th century BCE, two newly created Hellenistic states emerged as main pretenders for regional supremacy: the Seleucid Empire (305–64 BCE), and the Ptolemaic Empire (305–30 BCE). Several conflicts, known in historiography as the Syrian Wars, were fought durig the 3rd and the 2nd century BCE between those two powers, over the control of regions that came to be known as "Coele Syria" (meaning: the whole Syria), a term derived from an older Aramean designation (the whole Aram). Since earlier times, ancient Greeks were commonly using "Syrian" labels as designations for Arameans and heir lands, but is during the Hellenistic (Seleucid-Ptolemaic) period that the term Syria was finally defined, as designation for regions western of Euphrates, as opposed to the term Assyria, that designated regions further to the east.[35][36][37]
During the 3rd century BCE, various narratives related to the history of earlier Aramean kingdoms became accessible to wider audiences after the translation of Hebrew Bible into Greek language. Known as Septuagint, the translation was created in Alexandria, capital city of Ptolemaic Egypt, that was the most important city of the Hellenistic world, and also one of the main centers of Hellenization. Influenced by Greek terminology,[38] translators decided to adopt ancient Greek custom of using "Syrian" labels as designations for Arameans and their lands, thus abandoning endonymic (native) terms, that were used in the Hebrew Bible. In the Greek translation (Septuagint), the region of Aram was commonly labeled as "Syria", while Arameans were labeled as "Syrians".[39] Such promotion of exonymic (foreign) terms had far-reaching influence on later terminology.[40]
Under Roman and Parthian rule
After the establishment of Roman rule in the region of Syria proper (western of Euphrates) during the 1st century BC, Aramean lands became the frontier region between two empires, Roman and Parthian, and later between their successor states, Byzantine and Sasanid empires. Several minor states also existed in frontier regions, most notable of them being the Kingdom of Osroene, centered in the city of Edessa, known in Aramaic language as Urhay.[41]
Greek geographer and historian Strabo (d. in 24 CE) wrote about contemporary Arameans, mentioning them on several instances in his "Geography". Showing particular interest for names of peoples, Strabo recorded that Arameans are using term Aramaians (their native name) as a self-designation, and also noted that Greeks are commonly labeling them as "Syrians". He stated that "those whom we call Syrians are called Aramaians by the Syrians themselves", also recognizing "Syrians as the Arimians, now called the Aramaians", and mentioning "Syria itself, for those there are Aramaians".[42]
Between the 1st and the 3rd centuries AD, ancient Arameans adopted Christianity, thus replacing the old polytheistic Aramean religion. In the same tame, Christian Bible was translated into Aramaic, and by the 4th century local Aramaic dialect of Edessa (Urhay) developed into a literary language, known as Edessan Aramaic (Urhaya).[43][44]
One of the most prominent Christian authors from that period was saint Ephrem of Edessa (d. 373), whose works contain several endonymic (native) references to his language (Aramaic), homeland (Aram) and people (Arameans).[45][46][47][48]
Syrianization and Arabization
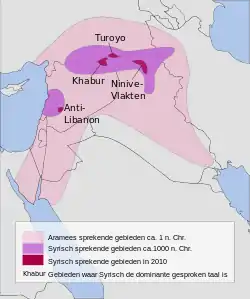
During the Late Antiquity, and the Early Middle Ages, two consecutive processes: Syrianization and Arabization, were initiated among Arameans, affecting their self-identification, and ethnolinguistic identity.
First process (Syrianization) was initiated during the 5th century,[49] when ancient Greek custom of using Syrian labels for Arameans and their language, started to gain acceptance among Aramean literary and ecclesiastical elites. The practice of using Syrian labels as designations for Arameans and their language was very common among ancient Greeks, and under their influence it also became common among Romans and Byzantines.[50]
The initial vessel of Syrianization was the Septuagint (Greek translation of the Hebrew Bible),[39] later accompanied by Greek books of the New Testament, that also used Syrian labels as designations for Arameans and their land (Aram). By the beginning of the 5th century, that practice also started to affect terminology of Aramean ecclesiastical and literary elites, and Syrian labels started to gain frequency and acceptance not only in Aramean translations of Greek works, but also in original works of Aramean writers. Following the example of their elites, it became common among Arameans to use not only endonymic (native), but also exonymic (foreign) designations, thus creating a specific duality that persisted throughout the Middle Ages, as attested in works of prominent writers, who used both designations, Aramean/Aramaic and Syrian/Syriac.[51][52]
Since Edessan Aramaic language (Urhaya) was the main liturgical language of Aramaic Christianity,[53][54][4] it also became known as Edessan Syriac, later defined by western scholars as Classical Syriac, thus creating a base for the term Syriac Christianity.[55][56][57]
The second process (Arabization) was initiated after the Arab conquest in the 7th century. In the religious sphere of life, Christian Arameans were exposed to Islamization, that created a base for gradual acceptance of Arabic language, not only as the dominant language of Islamic prayer and worship, but also as a common language of public and domestic life. Acceptance of Arabic language became the main vessel of gradual Arabization of Aramean communities throughout the Near East, ultimately resulting in their fragmentation and acculturation. Those processes affected not only Islamized Arameans, but also some of those who remained Christians, thus creating local communities of Arabic-speaking Christians of Aramean origin, who spoke Arabic in their public and domestic life, but continued to belong to Churches that used liturgical Aramaic/Syriac language.[58][5][6]
Legacy and modern Aramean identity
Legacy of ancient Arameans became of particular interest for scholars during the Early Modern period, resulting in the emergence of Aramaic studies, as a distinctive field dedicated to the study of Aramaic language and Aramean cultural heritage in general.[59] By the 19th century, the Aramean question was formulated, and several scholarly theses were proposed regarding the development of Aramaic language, and the history of Arameans.[60]
Some of those questions were focused on contemporary issues, related to the uses of Aramean/Aramaic, Syrian/Syriac, Assyrian and Chaldean designations. In 1875, Henry Van-Lennep (d. 1889), who was working as an American missionary among Eastern Christians in the Ottoman Near East, stated that Arameans are "better known as the Syrians, the Assyrians, and the Chaldeans", and also added: "The name Aramean is generally applied to all the inhabitants of the country which extends from the eastern boundary of Assyria to the Mediterranean, exclusive of Asia Minor proper and Palestine". Van-Lennep also stated that Arameans are divided in two branches, eastern ("the Eastern Arameans, or Assyrians, now called Chaldeans"), and western ("the Western Arameans, or modern Syrians").[61] Some of those pan-Aramean views were later accepted by other western researchers, who also held that modern Syrians are descendants of Arameans.[62] Reflecting on traditional influences of Greek terminology on English translations of the Septuagint, American orientalist Robert W. Rogers (d. 1930) noted in 1921: "it is most unfortunate that Syria and Syrians ever came into the English versions. It should always be Aram and the Aramaeans".[63]
During the 20th century, the notion of Aramean continuity clashed with the notion of Assyrian continuity, resulting in a series of disputes that remain unresolved. In modern times, Aramean identity is mainly held by a number of Syriac Christians in southeastern Turkey, parts of Syria and Lebanon, and in the Aramean diaspora, especially in Germany and Sweden.[64] In 2014, Israel officially recognized Arameans as a distinctive minority.[65] Questions related to minority rights of Arameans in some other countries were also brought to international attention.[66]
Culture
Language
Arameans were mostly defined by their use of the West Semitic Old Aramaic language (1100 BC – AD 200), first written using the Phoenician alphabet, over time modified to a specifically-Aramaic alphabet.
As early as the 8th century BC, Aramaic competed with the East Semitic Akkadian language and script in Assyria and Babylonia, and it spread then throughout the Near East in various dialects. By around 800 BC, Aramaic had become the lingua franca of the Neo-Assyrian Empire, continuing during the Achaemenid period as Imperial Aramaic. Although marginalized by Greek in the Hellenistic period, Aramaic in its varying dialects remained unchallenged as the common language of all Semitic peoples of the region until the Arab Islamic conquest of Mesopotamia in the 7th century AD, when it became gradually superseded by Arabic.
The late Old Aramaic language of the Neo-Assyrian Empire, Neo-Babylonian Empire and Achaemenid Persian Empire developed into the Middle Aramaic Syriac language of Persian Assyria, which would become the liturgical language of Syriac Christianity. The descendant dialects of this branch of Eastern Aramaic, which still retains Akkadian loanwords, still survive as the spoken and written language of the Assyrian people. It is found mostly in northern Iraq, northwestern Iran, southeastern Turkey and northeastern Syria and, to a lesser degree, in migrant communities in Armenia, Georgia, southern Russia, Lebanon, Israel, Jordan and Azerbaijan as well as in diaspora communities in the West, particularly the United States, Canada, Great Britain, Sweden, Australia and Germany. A small number of Israeli Jews, particularly those originating from Iraq and, to a lesser degree, Iran and eastern Turkey, still speak Eastern Aramaic, but it is largely being eroded by Hebrew, especially within the Israeli-born generations.
The Western Aramaic dialect is now only spoken by Muslims and Christians in Ma'loula, Jubb'adin and Bakhah. Mandaic is spoken by up to 75,000 speakers of the ethnically-Mesopotamian Gnostic Mandaean sect, mainly in Iraq and Iran.
Religion
It appears from their inscriptions as well as from their names that Arameans worshipped Mesopotamian gods such as Haddad (Adad), Sin, Ishtar (whom they called Astarte), Shamash, Tammuz, Bel and Nergal, and Canaanite-Phoenician deities such as the storm-god, El, the supreme deity of Canaan, in addition to Anat (‘Atta) and others.
The Arameans who lived outside their homelands apparently followed the traditions of the country where they settled. The King of Damascus, for instance, employed Phoenician sculptors and ivory-carvers. In Tell Halaf-Guzana, the palace of Kapara, an Aramean ruler (9th century BC), was decorated with orthostats and with statues that display a mixture of Mesopotamian, Hittite, and Hurrian influences.
Between the 1st and 4th centuries AD, the Arameans began to adopt Christianity in place of the polytheist Aramean religion, and the regions of the Levant and Mesopotamia became an important centre of Syriac Christianity, along with the Aramean kingdom Osroene to the east from where the Syriac language and Syriac script emerged.
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Arameans. |
References
- Lipiński 2000.
- Gzella 2015.
- Younger 2016.
- Healey 2019, p. 433–446.
- Messo 2017, p. 41-57.
- Frenschkowski 2019, p. 457–484.
- "Cuneiform Digital Library Initiative: Year names". UCLA.
- Lipiński 2000, p. 25–27.
- Gzella 2015, p. 56.
- Younger 2016, p. 35-108.
- "Akhlame". Encyclopædia Britannica.
- Lipiński 2000, p. 347.
- Younger 2016, p. 549-654.
- Lipiński 2000, p. 249.
- Younger 2016, p. 425-500.
- Lipiński 2000, p. 163.
- Younger 2016, p. 307-372.
- Lipiński 2000, p. 119.
- Lipiński 2000, p. 319.
- Lipiński 2000, p. 135.
- Lipiński 2000, p. 78.
- Boling, Robert G., revised by Richard D. Nelson, Harper Collins Study Bible: The Book of Judges
- Younger 2016, p. 501-548.
- "Aramaean (people)". Encyclopaedia Britannica.
- Wunsch 2013, p. 247–260.
- ^ "The destruction of the Assyrian Empire did not wipe out its population. They were predominantly peasant farmers, and since Assyria contains some of the best wheat land in the Near East, descendants of the Assyrian peasants would, as opportunity permitted, build new villages over the old cities and carried on with agricultural life, remembering traditions of the former cities. After seven or eight centuries, and after various vicissitudes, these people became Christians. These Christians, and the Jewish communities scattered amongst them, not only kept alive the memory of their Assyrian predecessors but also combined them with traditions from the Bible." - H. W. F. Saggs. The Might That Was Assyria. pp. 290
- Nissinen 2014, p. 273-296.
- Streck 2014, p. 297-318.
- Lemaire 2014, p. 319-328.
- Niehr 2014b, p. 329-338.
- Berlejung 2014, p. 339-365.
- Botta 2014, p. 366-377.
- Niehr 2014c, p. 378-390.
- Millard 1983, p. 106-107.
- Frye 1992, p. 281–285.
- Heinrichs 1993, p. 106-107.
- Joseph 1997, p. 37–43.
- Joosten 2010, p. 53–72.
- Wevers 2001, p. 237-251.
- Messo 2011, p. 113-114.
- Harrak 1992, p. 209–214.
- Roller 2014, p. 71, 594, 730.
- Brock 1992, p. 16.
- Brock 1999, p. 105.
- Griffith 2002, p. 15, 20.
- Palmer 2003, p. 3.
- Debié 2009, p. 103.
- Messo 2011, p. 119.
- Minov 2020, p. 256-257.
- Messo 2011, p. 118.
- Messo 2011, p. 118-123.
- Minov 2020, p. 255-263.
- Aufrecht 2001, p. 149.
- Quispel 2008, p. 80.
- Griffith 2002, p. 5–20.
- Healey 2007, p. 115–127.
- Healey 2014, p. 391–402.
- Bcheiry 2015, p. 455-475.
- Burnett 2005, p. 421-436.
- Nöldeke 1871, p. 113-131.
- Van-Lennep 1875, p. 341, 358.
- Wells 1920, p. 192.
- Rogers 1921, p. 139.
- Woźniak 2015, p. 483–496.
- Eti Weissblei (2017): Arameans in the Middle East and Israel: Historical Background, Modern National Identity,and Government Policy
- Sommer 2012, p. 157-170.
Sources
- Akopian, Arman (2013). Introduction to Aramean and Syriac Studies: A Manual. Piscataway, NJ: Gorgias Handbooks.
- Arav, Rami (2013). "Geshur: The Southwesternmost Aramean Kingdom". Arameans, Chaldeans, and Arabs in Babylonia and Palestine in the First Millennium B.C. Wiesbaden: Harrassowitz Verlag. pp. 1–29. ISBN 9783447065443.
- Arnold, Bill T. (2011). "Aramean Origins: The Evidence from Babylonia". Archiv für Orientforschung. 52: 179–185.
- Aufrecht, Walter E. (2001). "A Legacy of Syria: The Aramaic Language". Bulletin of the Canadian Society for Mesopotamian Studies. 36: 145–155.
- Bcheiry, Iskandar (2015). "The Arabization Process in Upper Mesopotamia in the Eighth Century A.D.: The Case of the Mosulis in the Chronicle of Zūqnīn". Parole de l'Orient. 40: 455–475.
- Beaulieu, Paul-Alain (2013). "Arameans, Chaldeans, and Arabs in Cuneiform Sources from the Late Babylonian Period". Arameans, Chaldeans, and Arabs in Babylonia and Palestine in the First Millennium B.C. Wiesbaden: Harrassowitz Verlag. pp. 31–55.
- Berlejung, Angelika (2014). "Palestine". The Aramaeans in Ancient Syria. Leiden: Brill. pp. 339–365. ISBN 9789004229433.
- Beyer, Klaus (1986). The Aramaic Language: Its Distribution and Subdivisions. Göttingen: Vandenhoeck & Ruprecht. ISBN 9783525535738.
- Bonatz, Dominik (2014). "Art". The Aramaeans in Ancient Syria. Leiden: Brill. pp. 205–253. ISBN 9789004229433.
- Botta, Alejandro F. (2014). "Egypt". The Aramaeans in Ancient Syria. Leiden: Brill. pp. 366–377. ISBN 9789004229433.
- Bowman, Raymond A. (1948). "Arameans, Aramaic, and the Bible". Journal of Near Eastern Studies. 7 (2): 65–90. doi:10.1086/370861. JSTOR 542672. S2CID 162226854.
- Brinkman, John A. (1968). A Political History of Post-Kassite Babylonia, 1158-722 B.C. Roma: Pontificium Institutum Biblicum.
- Brinkman, John A. (1977). "Notes on Arameans and Chaldeans in Southern Babylonia in the Early Seventh Century B.C." Orientalia. 46 (2): 304–325. JSTOR 43074768.
- Brock, Sebastian P. (1989). "Three Thousand Years of Aramaic Literature". Aram Periodical. 1 (1): 11–23.
- Brock, Sebastian P. (1992) [1985]. The Luminous Eye: The Spiritual World Vision of Saint Ephrem (2nd revised ed.). Kalamazoo: Cistercian Publications. ISBN 9780879075248.
- Brock, Sebastian P. (1999). From Ephrem to Romanos: Interactions Between Syriac and Greek in Late Antiquity. Aldershot: Ashgate. ISBN 9780860788003.
- Burnett, Stephen G. (2005). "Christian Aramaism: The Birth and Growth of Aramaic Scholarship in the Sixteenth Century" (PDF). Seeking Out the Wisdom of the Ancients. Winona Lake: Eisenbrauns. pp. 421–436.
- Coyne, John J. A. (1914). "Hellenism and the Aramean People". Studies: An Irish Quarterly Review. 3 (10): 64–91. JSTOR 30092466.
- Courtois, Sebastien de (2004). The Forgotten Genocide: Eastern Christians, the Last Aramaeans. Piscataway, NJ: Gorgias Press. ISBN 9781593330774.
- D'Agostino, Anacleto (2009). "The Assyrian-Aramaean interaction in the upper Khabur: The archaeological evidence from Tell Barri Iron Age layers". Syria. 86 (86): 17–41. doi:10.4000/syria.507. JSTOR 20723917.
- Debié, Muriel (2009). "Syriac Historiography and Identity Formation". Church History and Religious Culture. 89 (1–3): 93–114. doi:10.1163/187124109X408014.
- Drijvers, Hendrik J. W. (1980). Cults and Beliefs at Edessa. Leiden: Brill. ISBN 9004060502.
- Fales, Frederick M. (2011). "Moving around Babylon: On the Aramean and Chaldean Presence in Southern Mesopotamia". Babylon: Wissenskultur in Orient und Okzident. Berlin-Boston: Walter de Gruyter. pp. 91–112.
- Fales, Frederick M. (2017). "Ethnicity in the Assyrian Empire: A View from the Nisbe (III): Arameans and Related Tribalists". At the Dawn of History: Ancient Near Eastern Studies in Honour of J. N. Postgate. Eisenbrauns: Penn State University Press. pp. 133–178. ISBN 9781575064710.
- Frame, Grant (2013). "The Political History and Historical Geography of the Aramean, Chaldean, and Arab Tribes in Babylonia in the Neo-Assyrian Period". Arameans, Chaldeans, and Arabs in Babylonia and Palestine in the First Millennium B.C. Wiesbaden: Harrassowitz Verlag. pp. 87–121.
- Frenschkowski, Marco (2019). "Are Syrians Arameans? Some Preliminary Remarks on Syriac Ethnic Identity in Late Antiquity". Research on Israel and Aram: Autonomy, Independence and Related Issues. Tübingen: Mohr Siebeck. pp. 457–484. ISBN 9783161577192.
- Frye, Richard N. (1992). "Assyria and Syria: Synonyms". Journal of Near Eastern Studies. 51 (4): 281–285. doi:10.1086/373570. JSTOR 545826. S2CID 161323237.
- Greenfield, Jonas C. (1976). "The Aramean God Rammān/Rimmōn". Israel Exploration Journal. 26 (4): 195–198. JSTOR 27925588.
- Gzella, Holger (2014). "Language and Script". The Aramaeans in Ancient Syria. Leiden: Brill. pp. 71–107. ISBN 9789004229433.
- Gzella, Holger (2015). A Cultural History of Aramaic: From the Beginnings to the Advent of Islam. Leiden-Boston: Brill. ISBN 9789004285101.
- Gzella, Holger (2017). "New Light on Linguistic Diversity in Pre-Achaemenid Aramaic: Wandering Arameans or Language Spread?". Wandering Arameans: Arameans Outside Syria: Textual and Archaeological Perspectives. Wiesbaden: Harrassowitz Verlag. pp. 19–38.
- Griffith, Sidney H. (2002). "Christianity in Edessa and the Syriac-Speaking World: Mani, Bar Daysan, and Ephraem, the Struggle for Allegiance on the Aramean Frontier". Journal of the Canadian Society for Syriac Studies. 2: 5–20.
- Harrak, Amir (1992). "The Ancient Name of Edessa" (PDF). Journal of Near Eastern Studies. 51 (3): 209–214. doi:10.1086/373553. S2CID 162190342. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-08-09.
- Hausleiter, Arnulf (2016). "The Middle Euphrates, Iraq: Assyrian-Babylonian interactions in an Aramaean territory in the early 1st millennium BC". Parcours d'Orient: Recueil de textes offert à Christine Kepinski. Oxford: Archaeopress publishing. pp. 107–120.
- Healey, John F. (2007). "The Edessan Milieu and the Birth of Syriac" (PDF). Hugoye: Journal of Syriac Studies. 10 (2): 115–127.
- Healey, John F. (2014). "Aramaean Heritage". The Aramaeans in Ancient Syria. Leiden: Brill. pp. 391–402. ISBN 9789004229433.
- Healey, John F. (2019). "Arameans and Aramaic in Transition – Western Influences and the Roots of Aramean Christianity". Research on Israel and Aram: Autonomy, Independence and Related Issues. Tübingen: Mohr Siebeck. pp. 433–446. ISBN 9783161577192.
- Heinrichs, Wolfhart (1993). "The Modern Assyrians - Name and Nation". Semitica: Serta philologica Constantino Tsereteli dicata. Torino: Zamorani. pp. 99–114. ISBN 9788871580241.
- Hasegawa, Shuichi (2012). Aram and Israel during the Jehuite Dynasty. Berlin-Boston: Walter de Gruyter. ISBN 9783110283488.
- Jarjour, Tala (2016). "Chant as the Articulation of Christian Aramean Spirithood". The Oxford Handbook of Music and World Christianities. Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 187–207. ISBN 9780199859993.
- Joosten, Jan (2010). "The Aramaic Background of the Seventy: Language, Culture and History". Bulletin of the International Organization for Septuagint and Cognate Studies. 43: 53–72.
- Joseph, John B. (1997). "Assyria and Syria: Synonyms?" (PDF). Journal of Assyrian Academic Studies. 11 (2): 37–43. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2020-07-15.
- Kühn, Dagmar (2014). "Society, Institutions, Law, and Economy". The Aramaeans in Ancient Syria. Leiden: Brill. pp. 37–70. ISBN 9789004229433.
- Levin, Yigal (2017). "My Father was a Wandering Aramean: Biblical Views of the Ancestral Relationship between Israel and Aram". Wandering Arameans: Arameans Outside Syria: Textual and Archaeological Perspectives. Wiesbaden: Harrassowitz Verlag. pp. 39–52.
- Lemaire, André (2014). "Anatolia". The Aramaeans in Ancient Syria. Leiden: Brill. pp. 319–328. ISBN 9789004229433.
- Lipiński, Edward (2000). The Aramaeans: Their Ancient History, Culture, Religion. Leuven: Peeters Publishers. ISBN 9789042908598.
- Lipiński, Edward (2013). "The Aramaeans in the West (13th–8th centuries)". Arameans, Chaldeans, and Arabs in Babylonia and Palestine in the First Millennium B.C. Wiesbaden: Harrassowitz Verlag. pp. 123–147. ISBN 9783447065443.
- Mazar, Benjamin (1962). "The Aramean Empire and Its Relations with Israel". The Biblical Archaeologist. 25 (4): 97–120. doi:10.2307/3210938. JSTOR 3210938. S2CID 165844359.
- Merlo, Paolo (2014). "Literature". The Aramaeans in Ancient Syria. Leiden: Brill. pp. 109–125. ISBN 9789004229433.
- Messo, Johny (2011). "The Origin of the Terms Syria(n) and Suryoyo: Once Again". Parole de l'Orient. 36: 111–125.
- Messo, Johny (2017). Arameans and the Making of Assyrians: The Last Aramaic-speaking Christians of the Middle East. Aramaic Press.
- Millard, Alan R. (1980). "A Wandering Aramean". Journal of Near Eastern Studies. 39 (2): 153–155. doi:10.1086/372792. JSTOR 545123. S2CID 161083532.
- Millard, Alan R. (1983). "Assyrians and Arameans". Iraq: British Institute for the Study of Iraq. 45 (1): 101–108. JSTOR 4200184.
- Minov, Sergey (2020). Memory and Identity in the Syriac Cave of Treasures: Rewriting the Bible in Sasanian Iran. Leiden-Boston: Brill. ISBN 9789004445512.
- Mutlu-Numansen, Sofia; Ossewaarde, Marinus (2019). "A Struggle for Genocide Recognition: How the Aramean, Assyrian, and Chaldean Diasporas Link Past and Present" (PDF). Holocaust and Genocide Studies. 33 (3): 412–428. doi:10.1093/hgs/dcz045.
- Niehr, Herbert (2014a). "Religion". The Aramaeans in Ancient Syria. Leiden: Brill. pp. 127–203. ISBN 9789004229433.
- Niehr, Herbert (2014b). "Phoenicia". The Aramaeans in Ancient Syria. Leiden: Brill. pp. 329–338. ISBN 9789004229433.
- Niehr, Herbert (2014c). "Northern Arabia". The Aramaeans in Ancient Syria. Leiden: Brill. pp. 378–390. ISBN 9789004229433.
- Nissinen, Martti (2014). "Assyria". The Aramaeans in Ancient Syria. Leiden: Brill. pp. 273–296. ISBN 9789004229433.
- Nöldeke, Theodor (1871). "Die Namen der aramäischen Nation und Sprache". Zeitschrift der Deutschen Morgenländischen Gesellschaft. 25 (1–2): 113–131. JSTOR 43366019.
- Novák, Mirko (2014). "Architecture". The Aramaeans in Ancient Syria. Leiden: Brill. pp. 255–271. ISBN 9789004229433.
- Öztemiz den Butter, Mutay (2017). "Cultural Boundaries and Homeland among the Arameans (Syriacs)". Parole de l'Orient. 43: 303–314.
- Palmer, Andrew N. (2003). "Paradise Restored". Oriens Christianus. 87: 1–46.
- Quispel, Gilles (2008). Gnostica, Judaica, Catholica: Collected Essays of Gilles Quispel. Leiden-Boston: Brill. ISBN 9789047441823.
- Rogers, Robert W. (1921). A Book of Old Testament Lessons for Public Reading in Churches. New York: Abingdon Press.
- Roller, Duane W., ed. (2014). The Geography of Strabo: An English Translation, with Introduction and Notes. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9781139952491.
- Sader, Hélène (1992). "The 12th Century B.C. in Syria: The Problem of the Rise of the Aramaeans". The Crisis Years: The 12th Century B.C. from beyond the Danube to the Tigris. Dubuque: Kendall-Hunt. pp. 157–164.
- Sader, Hélène (2000). "The Aramaean Kingdoms of Syria: Origin and Formation Processes". Essays on Syria in the Iron Age. Louvain: Peeters Press. pp. 61–76. ISBN 9789042908789.
- Sader, Hélène (2010). "The Aramaeans of Syria: Some Considerations on their Origin and Material Culture". The Books of Kings: Sources, Composition, Historiography and Reception. Leiden-Boston: Brill. pp. 273–300. ISBN 978-9004177291.
- Sader, Hélène (2014). "History". The Aramaeans in Ancient Syria. Leiden: Brill. pp. 11–36. ISBN 9789004229433.
- Sader, Hélène (2016). "The Formation and Decline of the Aramaean States in Iron Age Syria". State Formation and State Decline in the Near and Middle East. Wiesbaden: Harrassowitz Verlag. pp. 61–76. ISBN 9783447105651.
- Salvesen, Alison (2009). "Keeping it in the Family? Jacob and his Aramean Heritage according to Jewish and Christian Sources". The Exegetical Encounter between Jews and Christians in Late Antiquity. Leiden-Boston: Brill. pp. 205–220. ISBN 978-9004177277.
- Sato, Noriko (2018). "The Memory of Sayfo and Its Relation to the Identity of Contemporary Assyrian/Aramean Christians in Syria". Sayfo 1915: An Anthology of Essays on the Genocide of Assyrians/Arameans during the First World War. Piscataway, NJ: Gorgias Press. pp. 305–326. ISBN 9781463207304.
- Sergi, Omer (2017). "The Battle of Ramoth-gilead and the Rise of the Aramean Hegemony in the Southern Levant during the Second Half of the 9th Century BCE". Wandering Arameans: Arameans Outside Syria: Textual and Archaeological Perspectives. Wiesbaden: Harrassowitz Verlag. pp. 81–98.
- Sokoloff, Michael, ed. (1983). Arameans, Aramaic and the Aramaic Literary Tradition. Tel Aviv: Bar Ilan University Press.
- Soldi, Sebastiano (2009). "Aramaeans and Assyrians in North-Western Syria: Material Evidence from Tell Afis". Syria: Archéologie, Art et Histoire. 86: 97–118.
- Sommer, Renate (2012). "The Role of Religious Freedom in the Context of the Accession Negotiations between the European Union and Turkey - The Example of the Arameans". The Slow Disappearance of the Syriacs from Turkey and of the Grounds of the Mor Gabriel Monastery. Münster: LIT Verlag. pp. 157–170. ISBN 9783643902689.
- Spieckermann, Hermann (1999). "Arameans". The Encyclopedia of Christianity. 1. Grand Rapids: Eerdmans. pp. 114–115.
- Streck, Michael P. (2014). "Babylonia". The Aramaeans in Ancient Syria. Leiden: Brill. pp. 297–318. ISBN 9789004229433.
- Van-Lennep, Henry J. (1875). Bible Lands: Their Modern Customs and Manners Illustrative of Scripture. New York: Harper & Brothers.
- Vittmann, Günter (2017). "Arameans in Egypt". Wandering Arameans: Arameans Outside Syria: Textual and Archaeological Perspectives. Wiesbaden: Harrassowitz Verlag. pp. 229–280.
- Wells, Herbert G. (1920). The New and Revised Outline of History. 1. New York: Macmillan.
- Wevers, John W. (2001). "Aram and Aramaean in the Septuagint". The World of the Aramaeans. 1. Sheffield: Sheffield Academic Press. pp. 237–251. ISBN 9781841271583.
- Woźniak, Marta (2015). "The Modem Arameans: In Search for National Identity". Parole de l'Orient. 40: 483–496.
- Wunsch, Cornelia (2013). "Glimpses on the Lives of Deportees in Rural Babylonia.". Arameans, Chaldeans, and Arabs in Babylonia and Palestine in the First Millennium B.C. Wiesbaden: Harrassowitz Verlag. pp. 247–260.
- Younger, Kenneth Lawson (2016). A Political History of the Arameans: From Their Origins to the End of Their Polities. Atlanta: SBL Press. ISBN 9781628370843.
- Younger, Kenneth Lawson (2017). "Tiglath-Pileser I and the Initial Conflicts of the Assyrians with the Arameans". Wandering Arameans: Arameans Outside Syria: Textual and Archaeological Perspectives. Wiesbaden: Harrassowitz Verlag. pp. 195–228.
- Zadok, Ran (2013). "The Onomastics of the Chaldean, Aramean, and Arabian Tribes in Babylonia during the First Millennium". Arameans, Chaldeans, and Arabs in Babylonia and Palestine in the First Millennium B.C. Wiesbaden: Harrassowitz Verlag. pp. 261–336. ISBN 9783447065443.
