Birmingham metropolitan area, Alabama
The Birmingham metropolitan area, sometimes known as Greater Birmingham, is a metropolitan area in north central Alabama centered on Birmingham, Alabama.
Greater Birmingham | |
|---|---|
| Birmingham-Hoover MSA | |
     Clockwise from top: Downtown Birmingham, Alabama Theatre in Downtown Birmingham, Old Mill in Mountain Brook, Aerial picture of Samford University in Homewood, Vulcan statue in Birmingham | |
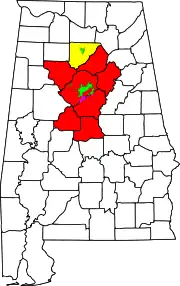 Birmingham–Hoover–Cullman Combined Statistical Area | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| Largest city | |
| Principal cities | - Hoover |
| Area | |
| • Total | 5,371 sq mi (13,910 km2) |
| Population (2010) | |
| • Total | 1,130,047 (49th) |
| • Density | 217/sq mi (84/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC−6 (Central Time Zone (CST)) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−5 (CDT) |
| Area code(s) | 205, 659 |
| Website | www |
As of 2013, the federal government defines the Birmingham–Hoover, AL Metropolitan Statistical Area as consisting of seven counties (Bibb, Blount, Chilton, Jefferson, St. Clair, Shelby, and Walker) centered on Birmingham.[1] The population of this metropolitan statistical area as of the 2010 census was 1,130,047, making it the 49th largest metropolitan statistical area in the United States as of that date. According to the United States Census 2013 estimate, the metro area has a population of 1,140,300.
The seven counties in the Birmingham–Hoover metropolitan statistical area are combined with the Cullman micropolitan area (Cullman County) and the Talladega–Sylacauga Micropolitan Statistical Area (Talladega County and Coosa County) to form the federally defined Birmingham–Hoover–Talladega, AL Combined Statistical Area.[1]
According to the United States Census 2013 estimate, the combined statistical area has a population of 1,313,105. It is the 42nd largest population sub-region in the United States, and the largest population region in Alabama, constituting roughly 1/4 of the state's population. It is the largest population region in Central Alabama. The northern counties of the metropolitan area overlap North Alabama known locally as the Tennessee Valley making it the largest metropolitan area in that region as well. Nearby counties Tuscaloosa, Etowah, and Calhoun, while not officially a part of Greater Birmingham, contribute significantly to the region's economy. The Birmingham media market covers these counties as well. Birmingham is part of the Piedmont Atlantic Megaregion containing an estimated 19 million people, while many residents also consider themselves part of the Deep South. It is classified as Southeast by the U.S. Census and also falls in the geographic area of the Upland South due to its location at the southern terminus of the Appalachian foothills. The entire MSA and CSA are within the congressional Appalachian Regional Commission's definition of Appalachia.
Counties
Counties marked with * are officially part of the Birmingham–Hoover–Talladega, AL Combined Statistical Area
Cities
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1900 | 140,420 | — | |
| 1910 | 226,476 | 61.3% | |
| 1920 | 310,054 | 36.9% | |
| 1930 | 431,493 | 39.2% | |
| 1940 | 459,930 | 6.6% | |
| 1950 | 556,926 | 21.1% | |
| 1960 | 812,094 | 45.8% | |
| 1970 | 833,075 | 2.6% | |
| 1980 | 930,281 | 11.7% | |
| 1990 | 956,844 | 2.9% | |
| 2000 | 1,052,238 | 10.0% | |
| 2010 | 1,061,024 | 0.8% | |
| 2019 (est.) | 1,090,435 | 2.8% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census[2] | |||
Anchor city
Principal cities
Suburbs with more than 10,000 inhabitants
Economy
The economy of Greater Birmingham is the most diversified of any metropolitan area in Alabama. Many of the region's major employers are located in Birmingham and Jefferson County. The economy of Birmingham ranges from service industries such as banking and finance to health-related technological research and heavy industry. The University of Alabama at Birmingham (UAB) is Alabama's largest employer as well as the area's largest, with some 20,000 employees. The area is world headquarters for Regions Financial, and Books-A-Million, the second largest book retailer in the United States.
Major employers
- Alabama Power
- AT&T (formerly BellSouth)
- Blue Cross/Blue Shield of Alabama
- Books-A-Million, Inc.
- BBVA (formerly Compass Bancshares)
- Drummond Company
- EBSCO Industries
- Encompass Health (formerly HealthSouth)
- Hibbett Sports, Inc.
- Liberty National Life Insurance Co. (part of Torchmark)
- McWane, Inc.
- Motion Industries
- Regions Financial Corporation (merged with AmSouth)
- Royal Cup Coffee, Inc.
- Shipt
- Sloss Industries
- Southern Research Institute
- Spire Inc (formerly Alagasco)
- Torchmark
- University of Alabama at Birmingham
- Vulcan Materials Company
- Wells Fargo (formerly SouthTrust and then Wachovia)
Retail
Birmingham is known as the shopping destination in the state of Alabama and a primary shopping hub of the Piedmont Atlantic Megaregion. It includes the major retail destination for the region, the Riverchase Galleria mall, along with several other shopping centers and malls.
Major Malls & Shopping Centers
- Riverchase Galleria, a 1,570,000 square foot, enclosed-mall in the southern suburb of Hoover. Anchors include Macy's, J. C. Penney, Belk, Von Maur, H&M, Forever 21, and Dave & Busters
- Brookwood Village, an 816,000-square-foot, enclosed mall in the suburbs of Homewood and Mountain Brook. It is anchored by Macy's and Target and also includes a 42,000-square-foot grocery-anchored retail component.
- The Summit, a large, upscale lifestyle center near the Cahaba Heights neighborhood. The center contains Saks Fifth Avenue, Belk, Barnes & Noble, Apple Store, Brooks Brothers, and local department store, Gus Mayer.
- Pinnacle at Tutwiler Farm, a lifestyle center in the eastern suburb of Trussville that is anchored by Belk, Best Buy, and J. C. Penney.
- The Shops At Grand River, an outlet mall in the eastern suburb of Leeds. Anchors include H&M and Old Navy. The development also contains a to-be-constructed residential area, Barber Motorsports Park, and a Bass Pro Shops.
Transportation
Road
Greater Birmingham is at the convergence of four major interstate highways: Interstate 65 (which connects with Mobile and Chicago); Interstate 20 (which connects with Dallas and Atlanta); Interstate 59 (which connects with New Orleans and Chattanooga); and Interstate 22 (which connects with Memphis). Interstate 459, completed in 1984, forms a southern bypass around Birmingham. It runs through portions of Bessemer, Vestavia Hills, and Trussville, and forms a main route through the primary city of Hoover. Interstate 422, the Birmingham Northern Bypass is planned to run from the current I-20/59/459 interchange near Bessemer to Interstate 59 and US Route 11 near Argo. It is planned to be completed by 2048.
Four U.S. highways, US-31, US-11, US-78, and US-280, run through Greater Birmingham. US-31 parallels Interstate 65 for its entire route, including Greater Birmingham. US-280 runs southeast of the city, connecting it with Auburn and Auburn University. The corridor through suburban Birmingham is notorious for its severe congestion as it carries about 200% of its traffic capacity. US-31 and 280 merge in Homewood to form the Elton B. Stephens Expressway known locally as the Red Mountain Expressway. This expressway goes through a geologic cut through Red Mountain, connecting downtown Birmingham to its southern suburbs. US-78 parallels Interstate 22 to the northwest of Birmingham, and Interstate 20 to the east. US-11 parallels Interstate 59 for its entire route. All four of these highways meet in downtown Birmingham.
Major highways
.svg.png.webp) Interstate 20
Interstate 20.svg.png.webp) Interstate 22
Interstate 22.svg.png.webp) Interstate 59
Interstate 59
.svg.png.webp) Interstate 65
Interstate 65 U.S. Highway 11
U.S. Highway 11 U.S. Highway 31
U.S. Highway 31 U.S. Highway 67
U.S. Highway 67 U.S. Highway 231
U.S. Highway 231 U.S. Highway 280
U.S. Highway 280 U.S. Highway 411
U.S. Highway 411
Mass transit
Birmingham received $87 million from the US Congress to help fund a regional transportation system. The city's new $30 million, three-block intermodal station brings Amtrak, Greyhound, the Birmingham-Jefferson County Transit Authority and automotive transportation together in one place.
Air
Greater Birmingham is served by Birmingham-Shuttlesworth International Airport with American Airlines, American Eagle, Southwest, United, Frontier, and Delta providing service to more than 40 cities. Established in 1931, BHM has been governed by the Birmingham Airport Authority since its establishment in 1986. In 2008, the airport was renamed Birmingham-Shuttlesworth International Airport in honor of late Birmingham civil rights activist Rev. Fred Shuttlesworth.
Education
Natural features
- Red Mountain
- Oak Mountain State Park
- Double Oak Mountain
- Ruffner Mountain
- Black Warrior River
- Cahaba River
- Cahaba River National Wildlife Refuge
- Talladega National Forest (Oakmulgee Division)
- Coosa River
Rivers
See also
- Piedmont Atlantic
- Table of United States Combined Statistical Areas
- Table of United States Metropolitan Statistical Areas
References
- "OMB Bulletin No. 13-01: Revised Delineations of Metropolitan Statistical Areas, Micropolitan Statistical Areas, and Combined Statistical Areas, and Guidance on Uses of the Delineations of These Areas" (PDF). United States Office of Management and Budget. February 28, 2013. Retrieved April 3, 2013.
- "U.S. Decennial Census". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on May 12, 2015. Retrieved May 28, 2013.
