Forgottonia
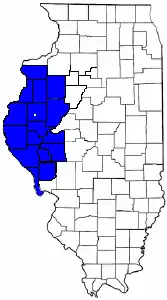
Forgottonia (/ˈfɔːrɡɒˌtoʊniə/), also spelled Forgotonia, is the name given to a 16-county region in Western Illinois in the late 1960s and early 1970s. This geographic region forms the distinctive western bulge of Illinois (area west of 90° Longitude West) that is roughly equivalent to "The Tract", the Illinois portion of the Military Tract of 1812, along and west of the Fourth Principal Meridian (see Principal meridian). Since this wedge-shaped region lies between the Illinois and Mississippi rivers, it has historically been isolated (river bridge access) from the eastern portion of Central Illinois.
The name Forgottonia was created by Jack Horn, son of civically minded Coca-Cola regional bottler Frank "Pappy" Horn; John Armstrong, Macomb Chamber of Commerce Board Member; and Neil Gamm, a Western Illinois University theatre student and a graduate of VIT (Vermont-Ipava-Table Grove) High School.[1][2] The initiative grew from frustration among the citizens and public officials of western Illinois due to the lack of support for regional transportation and infrastructure projects. Federal funding for a highway from Chicago to Kansas City routed through the heart of western Illinois was defeated by the U.S. Congress (1955, 1968, 1972), passenger rail service from Quincy and Macomb to Chicago was dropped in 1970. Carthage College packed up and moved to Kenosha, Wisconsin in 1964.
The term ‘’Forgottonia’’ was used again in 1980s by Congressman Dick Durbin, who represented the southern portion of the region, in stump speeches as he ran as a Democrat for the U.S. House of Representatives seat held by Paul Findley of Pittsfield for 22 years. He expanded the definition to include communications (educational television, fiber-optic routes, etc.) and infrastructure services (private and public). While the region's name is less popular today, the exodus of population and industries has continued. Some counties in this region have reached federal poverty levels, for the first time in the state's history.[3][4]
In the 1970s, there were six Illinois River highway bridge crossings south of Peoria (Pekin, Havana, Beardstown, Meredosia, Florence, and Hardin), plus two free Illinois River ferries at Kampsville, and Brussels. The Valley City Eagle bridge for the Central Illinois Expressway in the southern section of the region was not completed until the late 1980s. There were issues with eagles nesting in the Ray Norbut State Fish and Wildlife Area, through which the highway passes. The Mississippi River highways bridges at that time were toll bridges with a few exceptions, and owned by railroads or cities along the river. The toll ferry across the Mississippi River at Canton, Missouri served Adams County, Illinois; it was closed in 2014.[5]
Origin, coining of the name
Forgottonia represented a protest against inequalities in state and federal funding of infrastructure (e.g. transportation), communications and economic development in the region after World War II.[2]
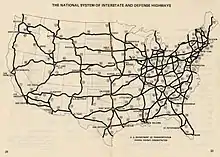
In 1955, during the formation of the Federal Aid Highway Act of 1956, the Chicago to Kansas City interstate route through the heart of this region was eliminated due to objections from Iowa and St. Louis as well as various granger railroads serving this region. In 1956, Missouri selected St. Louis based corridors to Joplin (US 66), Will Rogers Turnpike and Kansas City (US 40), Kansas Turnpike. A northern Missouri corridor (US 36) was viewed as a St. Louis by-pass and not supported. Carthage College, in Hancock County, relocated its educational campus to Kenosha, Wisconsin in 1964.[6]
Federal highway bills throughout the 1960s that included funding for a Chicago–Kansas City Expressway were defeated and removed from the Federal-Aid Highway Act of 1968. which added 1500 miles (2400 km) to the Interstate system (Interstate 15E in southern CA and Interstate 27 in northwest Texas). George H. Mahon, Texas member of the U.S. House of Representatives from 1935 to 1979 and chairman of the House Appropriations Committee after 1964, helped secure funding for the Interstate 27 route. The reintroduction of the Chicago to Kansas City Expressway was again defeated in the US Congress in 1972. These political and congressional actions resulted in the exodus of the region's businesses, long-time industries, and population by 1970. Those significant events were the catalysts for more vocal public protests by residents.
Variously described as a new U.S. state or an independent republic, Forgottonia eventually became a fictional political secession movement in the early 1970s conceived by residents of McDonough County, in the heart of this region. Western Illinois University student Neil Gamm was named governor, and the hamlet of Fandon near Colchester was to be Forgottonia's capital. The name would catch on because the region appeared to be "forgotten" by politicians and business developers.[7]
Due to the loss of train service in 1971, with the creation of Amtrak, the State of Illinois intervened at the request of the region's residents, Quincy University, Western Illinois University and public officials. This became part of the 1971 "Illinois Service" initiative and is partially funded by the Illinois Department of Transportation.
Forgottonia counties
These are the 16 counties from Neal Gamm's original list. These Illinois county governments joined the movement in 1972.
The unincorporated village of Bernadotte, in Fulton County, which is four miles north of Ipava on the Spoon River, has the distinction of having once been considered as the site for the capital of Illinois, prior to the capital being located at Vandalia in 1820. Vandalia was selected over Bernadotte by the difference of one vote. The 2010 US Census population of Forgottonia (16 counties) is 354,709 residents.[8][9]
Transportation projects and proposals since 1972
Avenue of the Saints (1956, 1991−2010)

An Avenue of the Saints (St. Paul, Minnesota to St. Louis, Missouri) Expressway was proposed in 1955 during the formation of the Federal Aid Highway Act of 1956. That route would have followed U.S. Route 61 from St. Paul through La Crosse, Wisconsin, and Dubuque, Iowa, to Davenport, Iowa, and then following U.S. Route 67 from Davenport through western Illinois crossing the new Clark Bridge at Alton to St. Louis. This routing would have been along U.S. Route 67, the major north–south arterial highway in the Western Illinois region. The Mississippi River barge companies raised political objections for a new federally funded competitor. This route was not selected in 1956.
In the 1980s, this north–south arterial highway for an Avenue of the Saints was revived by Mt. Pleasant, Iowa elected officials, led by Ernie Hayes, owner of a local insurance agency, with support from the state of Missouri, led by Dick Gephardt, House majority leader in 1989. Future Iowa governor and US Department of Agriculture (USDA) Secretary Tom Vilsack, mayor of Mt. Pleasant from 1987 to 1992, was a strong supporter. This highway proposal was included as Corridor 2 in the Intermodal Surface Transportation Efficiency Act of 1991 (Public Law 102–240; ISTEA, pronounced "Ice-Tea") as a high priority North-South NAFTA corridor.
By the end of 1989, four possible routes for the Avenue of the Saints were under consideration by the Federal Highway Administration. Two of the rejected routes would have followed U.S. Route 52 and U.S. Route 63 from St. Paul through Rochester, Minnesota, to Waterloo, Iowa. The other route rejected was the 1955 proposed route following U.S. Route 67 through the heart of the Forgottonia region.
In 1990, the FHWA chose its route for the Avenue of the Saints: The Expressway would follow Interstate 35 from St. Paul to a point south of Clear Lake, Iowa; U.S. Route 18 to Charles City, Iowa; U.S. Route 218 to Cedar Falls, Iowa; Iowa Highway 58 and U.S. Route 20 around Cedar Falls and Waterloo, Iowa; Interstate 380 from Waterloo through Cedar Rapids to Interstate 80 near Coralville, Iowa and Iowa City, Iowa; U.S. 218 to Donnellson, Iowa; Iowa Highway 394 and Route B to Wayland, Missouri; and following U.S. 61 and Interstate 64 from Wayland through Missouri, west of the Mississippi River, to St. Louis. The route exclusively serves Iowa and Missouri, using existing interstates in Minnesota and St. Louis area for routing to terminus "Saint" cities.
This routing provides Quincy, IL with access to the Avenue of the Saints via a 10-mile segment of U.S. Route 24 from Taylor, Missouri.
Amtrak service and expansion (1971−present)
Denied access to the US Interstate highway network, the "Illinois Service" initiative for Amtrak rail service was approved in 1971. It is partially funded by the Illinois Department of Transportation.[10] The Illinois Zephyr began daily round-trip service from Chicago to Quincy in 1971, through the heart of the region. Amtrak's Southwest Chief and California Zephyr share trackage with the Illinois Zephyr as far as Galesburg. The state of Missouri's "Missouri Service" only funded the extension of the Ann Rutledge to provide daily service between Kansas City and St. Louis with continuing services to Chicago via Springfield.
The Illinois Zephyr has become one of Amtrak's most successful routes, and is the longest continuously-operated state-supported route in the Amtrak network. As part of the Midwest Regional Rail Initiative and Illinois's partnership with Amtrak an additional daily train service on this Chicago-Quincy line was added on October 30, 2006. This service expansion is part of the state sponsorship for increasing round-trip train service between Chicago and downstate cities from three daily to seven daily schedules. The new Carl Sandburg train joined the existing Illinois Zephyr to provide both a morning and evening train in each direction. Proposals have been considered to extend the two routes across the Mississippi River to Hannibal and/or St. Louis.
In February 2009, Thomas C. Carper, mayor of Macomb from 1991 to 2003, was elected as Chairman of Amtrak's Board of Directors for a 4-year term, until February 2013.[11] Mr. Carper rejoined the Amtrak Board of Directors on August 15, 2013 for a five-year term.[12]
During fiscal year 2011, both the Illinois Zephyr and Carl Sandburg carried a combined 225,000 passengers, a 6.9% increase over FY2010.[13] The two trains had a total revenue of $5,580,227 in FY2011, a 10.6% increase over FY2010.[13]
Central Illinois Expressway / Interstate 72 (1978−2010)
The Central Illinois Expressway, the Interstate 72 (I-72) Purple Heart Memorial Highway began in the late 1970s and was completed in 1991.[14] The Interstate 172 spur for Quincy access to the Expressway was completed in 1995. This provided some relief for the southern counties and enabled Interstate access to the cities of Quincy, Pittsfield and Jacksonville from Springfield, Central Illinois and Indiana.
Two decades later, the Missouri Department of Transportation, as part of NAFTA High Priority Corridor 61 - Missouri corridors, completed their Interstate 72 and U.S. Route 36 Northern Missouri segment from Hannibal, MO through Cameron to St. Joseph, MO in August 2010. In coordination with Illinois DOT, the route from Cameron, MO to Hannibal, MO is marked as Chicago-Kansas City - Missouri Route 110.
Chicago-Kansas City Tollway (1989 studies)
In 1989, the idea of a Chicago to Kansas City expressway was revisited. A tri-state economic and highway study was performed and found that a full, limited-access tollway running from the Kansas Turnpike at Kansas City to the Indiana Toll Road at Gary or Tri-State Tollway near the Joliet area would cost $2 to $2.5 billion, if funded entirely by private investors.[15]
The study was useful in providing an expenditure number (1989 dollars) to Illinois and Missouri legislatures and public officials for building the highway. Missouri DOT's higher priority from 1989 to 2000 was completing their section of the Avenue of the Saints and 2000 to 2010 for completing the Missouri portion of Interstate 72. Illinois DOT was struggling in 1990s with funding to finish existing highway upgrade projects (Interstate 39, Interstate 172) from the 1980s.
Illinois Route 336 (2001−present)
In 2009, the construction of Illinois Route 336 from Quincy was extended from Carthage to Macomb partially built along with former U. S. Route 136 alignment, on which it runs concurrently, and a new alignment bypassing Tennessee and Colchester to end temporarily west of Macomb. This provides these communities (Quincy, Carthage, Macomb) with a southwestern connection (Kansas City and St. Joseph, MO) to Interstate 72. A bypass around Macomb was under construction, with funding secured in 2014.[16] It was eventually completed in 2018 but only opened one lane in each direction.[17]
Cannon Ball Route / Illinois Route 110 (1917−1941; 2010)
The Cannon Ball Trail Association, which was based in Leon, Iowa, marked the Missouri and Iowa portions of the route in 1912.[18] The Chicago Auto Club marked the Illinois segment of the highway in 1913.[19] By 1915, the route was considered "one of the best-marked highways between Quincy... and Chicago", and an extension from Quincy to the St. Louis – Kansas City highway at Monroe City was posted.[20]
In 1917 the Illinois State Highway Department, a precursor to the modern-day Illinois Department of Transportation, produced a Map of Marked Routes for the new automotive owner. The route from Hannibal, MO to Chicago, IL roughly paralleling the Chicago, Burlington and Quincy Railroad, was marked as the Cannon Ball Route.
In a joint resolution between the Illinois House and Senate in late May 2010,[21] an expressway project connecting Chicago-to-Kansas City will be named Illinois Route 110. The path, 532 miles in total,[22] follows parts of the existing Illinois Route 336, Interstate 88, Interstate 172, Interstate 72, Interstate 74, U.S. Route 136, U.S. Route 67, and connect the cities of Quincy, Macomb, Galesburg, a number of communities of the Chicago metropolitan area, including Chicago itself on Interstate 290.[23][24][25]
River bridges
Since the 1970s, new Mississippi River highway bridges providing western access (Missouri, Iowa) to this region have been built: Mark Twain Memorial Bridge at Hannibal, Bayview Bridge at Quincy, Keokuk-Hamilton Bridge at Keokuk-Hamilton, and the Great River Bridge at Burlington. The 1928 Champ Clark Bridge at Louisiana, MO carrying U.S. Highway 54 was in poor condition and replaced by a new Champ Clark Bridge in 2019.[26] The railroads, serving the region, Kansas City Southern Railway, BNSF Railway, and Norfolk Southern Railway have replaced, performed major upgrades, or demolished their Mississippi and Illinois river bridges (Keithsburg Rail Bridge). Some of these railroad bridges require further upgrades, based on the increasing transcontinental rail traffic.
However, the Illinois River highway bridges providing eastern access to central Illinois, especially at Hardin, Florence, Meredosia, Beardstown, Havana, Lacon, and Henry are over 50 years old. While Illinois DOT has performed major maintenance on these structures, they are not currently funded for replacement.
The first bridge to be replaced, as funds become available, is the Florence drawbridge on Illinois 100/106, formerly US 36 and 54. A replacement highway bridge at Meredosia was completed in 2018. The next planned bridge replacement is for US 67 at Beardstown. This is planned for the eventual upgrade of US 67 to an expressway (four lanes) north from Chaplin, IL.
U.S. Route 67 in Illinois
In 1990, U.S. Route 67 in Missouri was designated as NAFTA Corridor 61, but north of St. Louis U.S. Route 67 in Illinois, through the heart of this region, does not carry this NAFTA priority designation. Portions of U. S. Route 67 in Illinois north of Macomb were upgraded to a four lane expressway with bypasses around Monmouth and Roseville. It is four-lane but with many at-grade intersections and a few signals. A bypass around Jacksonville has been completed which extends from near Chapin to the north to near Roodhouse to the south. Except for the expressway near Jacksonville, no other sections from Macomb extending south to Jerseyville have been completed. The 4 lane divided highway starts again at the Jersey County line, south to Godfrey where it intersects with Illinois 255. A new section of four-lane highway, near Chapin, is to open in 2013. Sections farther north have some studies completed and right-of-way bought; no funding is in place to upgrade or complete further studies.
U.S. Route 34 to Burlington
Since 1993, the Illinois portion of U.S. Route 34 has been incomplete between the new Great River Bridge at Gulfport, Illinois to the eastern edge of Monmouth, Illinois. If and when the 4-lane to Monmouth is complete, U.S. Route 34 would merge with U.S. Route 67 at the south western edge of Monmouth and a new limited access bypass south and southeast of Monmouth connecting with the existing 4-lane U.S. Route 34 and continuing east to Galesburg.[27]
The Great River Bridge at Burlington was completed and open to traffic on October 4, 1993. The Iowa Department of Transportation completed the Des Moines to Burlington "Super-4" expressway project, Iowa Highway 163, on November 18, 2008. This expressway intersects the Avenue of the Saints at Mt. Pleasant.
By 2020, U.S. Route 34 across southern Iowa between Ottumwa, Iowa and Plattsmouth, Nebraska is planned for Super-2 upgrades with a new bridge across the Missouri River bridge to Nebraska as part of these upgrades. Nebraska is studying an upgrade of their U.S. Route 34 section between Plattsmouth and Interstate 80, near Lincoln, Nebraska.
Macomb to Peoria Expressway
By 2003, the Macomb to Peoria Expressway, through the former coal mining regions of Fulton County was planned and routes proposed, but is not currently funded (DOT Job No. P94-025-00 URS Job No. 25364560; July 7, 2003). Hence, Peoria and Fulton Counties have no direct (short distance) highway route to Hannibal/Quincy or NAFTA trade routes to southwestern USA and Mexico. There are Fulton county opponents for improved highway access. The interchange (Exit 3) at Interstate 474 for this expressway segment was completed in the late 1970s. Currently, it is a partial cloverleaf to a short spur to the west that ends on Maxwell Road leading one mile south to Illinois 116.[28]
Peoria to Chicago Highway
Peoria, Illinois, at the eastern edge of the region, failed in the 1990s to gain central Illinois support for completing the Peoria-to-Chicago Highway, which was the eastern segment for the original 1955 routing of the Chicago–Kansas City Expressway. This highway segment upgrade is tabled indefinitely (low priority). Peoria was bypassed in the 2010 Chicago–Kansas City Expressway / Illinois Route 110 alignment by the Illinois legislature.
Culture
Colleges and universities
- Western Illinois University (WIU) is a public university located in Macomb.
- Knox College is a private liberal arts college located in Galesburg.
- Carl Sandburg College is a two-year community college based in Galesburg with a branch campus located in Carthage and an extension center located in Bushnell.
- Quincy University is a private liberal arts Catholic university in the Franciscan tradition located in Quincy.
- John Wood Community College is a two-year community college located in Quincy with educational centers in Pittsfield, Perry, and Mt. Sterling.
- Spoon River College is a two-year community college located near Canton with a second campus in Macomb and learning centers in Havana and Rushville.
- Illinois College is a private liberal arts college located in Jacksonville, affiliated with the United Church of Christ and the Presbyterian Church (USA).
- MacMurray College is a private liberal arts college located in Jacksonville.
- Monmouth College is a private liberal arts college located in Monmouth.
Public television
In 1970, the west-central region of Illinois was one of the few areas in the United States without a PBS station.[29] Fringes of this region were served from PBS stations outside the region or state: WILL-TV in Urbana; WTVP in Peoria; and KIIN in West Branch, Iowa. Cable television networks in north-central Illinois communities and Macomb carried Iowa Public Television or WTVP PBS programming to their residents.
How the States Got Their Shapes
In 2011, The History Channel series How the States Got Their Shapes focused its first season, second episode, The Great Plains, Trains, and Automobiles to the historic inequality given to this western Illinois region, as a result of Federal-Aid Highway Act of 1956, popularly known as the National Interstate and Defense Highways Act (Public Law 84-627) and later legislation. Neil Gamm, governor of Forgottonia, was interviewed by host Brian Unger in 2011 for the series.[30] Neil Gamm died on November 16, 2012 at the age of 65.[31][32]
Businesses
Forgottonia Brewing, opened in Macomb, Illinois in 2019, is named after the Forgottonia social movement.[33]
See also
- Conch Republic, similar movement covering the Florida Keys
- Category:Secession in the United States
Notes
- "Gone, But not Forgottonia". Peoria Journal Star. December 31, 2010. Retrieved October 11, 2012.
- Nathan Woodside (December 28, 2010). "When we seceded: Remembering Forgottonia". McDonough County Voice. Archived from the original on January 28, 2013. Retrieved July 8, 2012.
- "M-R238 Strategic Plan: Is Wheaton-Warrenville an Appropriate Comparison?". Blogging Forgottonia. January 28, 2011. Archived from the original on January 18, 2013. Retrieved July 20, 2012.
- Sue Ebetsch, Coordinator (2011). "2000 & 2010 Census Comparisons". Illinois Department of Commerce & Economic Opportunity. Retrieved July 1, 2012.
- "Canton Ferry to close permanently". WGEM-TV. April 16, 2014. Retrieved March 7, 2016.
- Carthage College history Archived January 18, 2010, at the Wayback Machine
- "How the States Got Their Shapes Full Episodes, Video & More - HISTORY".
- https://www.usatoday.com/news/nation/census/profile/IL Illinois 2010 Census profile, by county
- http://www2.illinois.gov/census/Pages/Census2010Data.aspx Illinois 2010 Census Data
- Sanders, Craig (2006). Amtrak in the Heartland. Bloomington, Indiana: Indiana University Press. ISBN 978-0-253-34705-3.
- "Former Macomb mayor to chair Amtrak board". Chicago Tribune. February 2, 2009. Retrieved July 9, 2012.
- "Tom Carper Rejoins Amtrak Board of Directors" (PDF). Amtrak. August 15, 2013.
- "Amtrak Ridership Rolls Up Best-Ever Records" (PDF). Amtrak. October 13, 2011. Retrieved February 7, 2012.
- Wes Smith (February 21, 1993). "It Was A Long, Hard-built Road Out of Forgottonia". Chicago Tribune. Retrieved October 12, 2012.
- Krasnowski, Matt (December 22, 1989). "Chicago-Kansas City Expresway Cost Set At $2.5 Billion". The State Journal-Register (Springfield, IL). Retrieved August 19, 2010.
- "ILDOT press release". Illinois Department of Transportation. October 10, 2014. Retrieved March 7, 2016.
- Boyer, Emily. "Macomb Bypass Now Open to Traffic". www.tspr.org. Retrieved September 25, 2020.
- "Association Posting Trail". Automobile Journal. 34. 1912.
- Clarke, Dave (January 8, 2013). "Cannon Ball Trail was early attempt at self-guided travel". Star Courier. Retrieved February 25, 2013.
- "To Extend Cannon Ball Trail". Motor Age. 27. 1915.
- "Senate Joint Resolution 118". May 27, 2010. Archived from the original on October 22, 2012. Retrieved 2010-08-19., 96th Illinois General Assembly.
- Hilkevitch, John (August 22, 2010). "Getting Around: By the numbers". Chicago Tribune. Archived from the original on July 23, 2012. Retrieved August 23, 2010.
- WGEM. "Connecting Quincy to the Country". WGEM. Archived from the original on September 28, 2011. Retrieved May 8, 2012.
- "Chicago-Kansas City Expressway corridor becomes a reality". Daily Gate City (Keokuk, IA). July 1, 2010. Retrieved August 19, 2010.
- Wilson, Doug (June 30, 2010). "Chicago-Kansas City Expressway a reality after six-decade effort". Quincy Herald Whig. Archived from the original on August 26, 2010. Retrieved 2010-08-19.
- https://www.stltoday.com/news/local/metro/new-champ-clark-bridge-at-louisiana-mo-opens/article_f68f9fcd-8c5f-59ca-a227-4297329b2a7a.html
- "The Highway 34 Coalition". Retrieved August 21, 2013.
- http://www.tricountyrpc.org/land-use-documents Archived July 23, 2014, at the Wayback Machine Fulton County Corridor Study
- "Television on the United States, Educational Television". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved May 1, 2012.
- "How the States Got Their Shapes Full Episodes, Video & More - HISTORY".
- ""Neil Gamm, Forgottonia's former governor, passes"".
- BIBO, TERRY. "Neal Gamm gone, but not 'Forgottonia'".
- Faust, Spencer. "Craft brewery named for social movement opens its doors to Macomb". Aledo Times Record.
Bibliography
- Gutfreund, Owen D. (2004). Twentieth Century Sprawl: Highways and the Reshaping of the American Landscape. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780195141412.
- Rose, Mark H. & Mohl, Raymond A. (2012). Interstate: Highway Politics and Policy Since 1939. Knoxville, TN: University of Tennessee Press. ISBN 9781572337251.
- Swift, Earl (2011). The Big Roads: The Untold Story of the Engineers, Visionaries, and Trailblazers Who Created the American Superhighways. Boston: Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. ISBN 9780618812417.
References
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Forgottonia. |
- Nowlan, J.D. 1998. From Lincoln to Forgottonia. Illinois Issues 24(9):27-30.
- Outfitters.com. McDonough County, Illinois, USA.
- Wilson, Doug (2010-06-30). "Chicago-Kansas City Expressway a reality after six-decade effort". Quincy Herald Whig. Retrieved 2010-08-19
- History Channel, 2011. "The Great Plains, Trains, & Automobiles" Season 1, episode 3 of How The States Got Their Shapes
