List of National Historic Landmarks in Oregon
This is a complete List of National Historic Landmarks in Oregon. The United States National Historic Landmark (NHL) program is operated under the auspices of the National Park Service, and recognizes buildings, structures, districts, objects, and similar resources nationwide according to a list of criteria of national significance.[1] The state of Oregon is home to 17 of these landmarks, two of which extend beyond Oregon's borders into other states, as well as one site from which NHL status was withdrawn upon its destruction.
Background
Historic context
Programmatic context
The National Historic Landmark program is administered by the National Park Service, a branch of the U.S. Department of the Interior. The National Park Service determines which properties meet NHL criteria and makes nomination recommendations after an owner notification process.[1] The Secretary of the Interior reviews nominations and, based on a set of predetermined criteria, makes a decision on NHL designation or a determination of eligibility for designation.[2] Both public and privately owned properties are designated as NHLs. This designation provides indirect, partial protection of the historic integrity of the properties, via tax incentives, grants, monitoring of threats, and other means.[1] Owners may object to the nomination of the property as a NHL; when this is the case the Secretary of the Interior can only designate a site as eligible for designation.[2]
NHLs are also included on the National Register of Historic Places (NRHP), which are historic properties that the National Park Service deems to be worthy of preservation. The primary difference between a NHL and a NRHP listing is that the NHLs are determined to have particular national significance, while other NRHP properties may be deemed significant at the local or state level.[1] The NHLs in Oregon comprise 0.8% of the approximately 1,900 properties and districts listed on the NRHP in Oregon.
Current National Historic Landmarks
| [3] | Landmark name | Image | Date designated[4] | Location | County | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Bonneville Dam Historic District |  Bonneville Dam Historic District |
June 30, 1987 (#86000727) |
Bonneville 45°38′29″N 121°56′41″W |
Multnomah and Skamania (Washington) | Built in the 1930s to harness the Columbia River for power generation, this was the first hydroelectric dam with a hydraulic drop sufficient to produce 500,000 kW of hydropower. The NHL district covers the dam and other elements of the federal dam project, including the #1 powerhouse, navigation lock, fish ladder, and hatchery. |
| 2 | Columbia River Highway |  Columbia River Highway |
May 16, 2000 (#83004168) |
Troutdale to Mosier[5] 45°37′27″N 121°44′51″W |
Multnomah, Hood River, and Wasco | Constructed between 1913 and 1922, this was the first scenic highway in the United States. Designed specifically to provide visitors access to the most outstanding of the scenic features of the Columbia River Gorge, the highway is also an outstanding example of modern highway development for its pioneering advances in road engineering, and is the single most important contribution to the fields of civil engineering and landscape architecture by Samuel C. Lancaster. |
| 3 | Crater Lake Superintendent's Residence |  Crater Lake Superintendent's Residence |
May 28, 1987 (#87001347) |
Crater Lake National Park 42°54′03″N 122°08′16″W |
Klamath | The 1930s-era Munson Valley development was originally one of the best-designed rustic installations in a U.S. national park. This is the only building in the group to remain in near-original condition, and it employed unusual construction methods in response to the very short Crater Lake building season. |
| 4 | Deady and Villard Halls, University of Oregon |  Deady and Villard Halls, University of Oregon |
May 5, 1977 (#72001082) |
Eugene 44°02′48″N 123°04′35″W |
Lane | Completed in 1876 and 1886, respectively, Deady and Villard Halls are the first and second buildings of the University of Oregon. Deady Hall is simplified Italianate in design with mansarded main roof and towers; Villard Hall has Second Empire touches, and is one of the few surviving academic buildings of its era in the Western United States. |
| 5 | Fort Astoria Site | 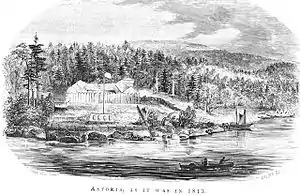 Fort Astoria Site |
November 5, 1961 (#66000639) |
Astoria 46°11′16″N 123°49′39″W |
Clatsop | John Jacob Astor attempted to break the British monopoly on the Pacific Northwest fur trade starting with construction of this fortified trading post in 1811. The fort subsequently became an important part of the American territorial claim to the Oregon Country. Astor sold the fort to the British North West Company in 1813. |
| 6 | Fort Rock Cave |  Fort Rock Cave |
January 20, 1961 (#66000641) |
Fort Rock 43°21′22″N 121°03′13″W |
Lake | This cave yielded to archeologists the "Fort Rock sandals", the oldest manufactured articles found in the Americas, which demonstrated the early development of weaving among Native Americans. Occupation of the site has been dated to 11,000 BCE. |
| 7 | Jacksonville Historic District | 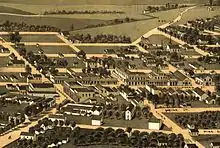 Jacksonville Historic District |
November 13, 1966 (#66000950) |
Jacksonville 42°18′45″N 122°58′04″W |
Jackson | Founded in 1852 as a mining town, Jacksonville became the principal financial and commercial center of southern Oregon until it was bypassed by the railroad. Its group of surviving, unaltered commercial and residential buildings spans the full range of architectural styles employed in the West between 1850 and 1890. The town's unusual state of preservation and completeness make it a uniquely intact example of a mid-19th century inland commercial town.[6] |
| 8 | Kam Wah Chung Company Building |  Kam Wah Chung Company Building |
September 20, 2005 (#73001575) |
John Day 44°25′07″N 118°57′25″W |
Grant | This building is the best known example of a Chinese mercantile and herb store in the United States. It embodies the role of immigrant Chinese in the post-Civil War expansion period of the western United States. |
| 9 | Lightship WAL-604, "Columbia" |  Lightship WAL-604, "Columbia" |
December 20, 1989 (#89002463) |
Astoria 46°11′25″N 123°49′27″W |
Clatsop | Retired in 1979 as the last lightship to be stationed at the Columbia River Bar — or anywhere on the Pacific coast of the United States — WAL-604 retains the best historic integrity of the last generation of U.S. Coast Guard lightships after 1939. WAL-604, built in 1950, and its relatives closely resembled earlier lightship types in external appearance, but were a distinct departure in their overall design. |
| 10 | Lower Klamath National Wildlife Refuge |  Lower Klamath National Wildlife Refuge |
January 12, 1965 (#66000238) |
Dorris, California 41°56′48″N 121°39′57″W |
Klamath and Siskiyou (California) | This national wildlife refuge, established in 1908, was the first large block of public land set aside for wildlife management purposes. Because of the refuge's extensive overlap with the Klamath Basin water reclamation project, it has become an ongoing example of the tensions between conservation and economic demands in public land management. |
| 11 | Oregon Caves Chateau |  Oregon Caves Chateau |
May 28, 1987 (#87001346) |
Oregon Caves National Monument 42°05′54″N 123°24′27″W |
Josephine | This rustically intimate site features a shaggy bark finish, stone retaining walls, fishponds, waterfalls, and walkways. Built in 1934, the structure makes use of a very limited site over a canyon, and retains a high degree of integrity in its design, furnishings, and setting. |
| 12 | Pioneer Courthouse |  Pioneer Courthouse |
May 5, 1977 (#73001582) |
Portland 45°31′08″N 122°40′40″W |
Multnomah | Built in 1875 and restored in the 1970s, this was one of the first monumental buildings in the Pacific Northwest. It has served as a U.S. courthouse, a customhouse, and a post office. It underwent another rehabilitation in the 2000s. |
| 13 | Skidmore/Old Town Historic District |  Skidmore/Old Town Historic District |
May 5, 1977 (#75001597) |
Portland 45°31′21″N 122°40′18″W |
Multnomah | One of the most impressive historic commercial districts on the West Coast, this is where Portland began and first flourished. The buildings, which date from the mid-to-late-19th century, were built in a variety of High Victorian architectural styles, and many feature cast iron fronts. |
| 14 | Sunken Village Archeological Site |  Sunken Village Archeological Site |
December 20, 1989 (#89002455) |
Sauvie Island[7] 45°41′49″N 122°50′20″W |
Multnomah | The archeological remains of this Chinookan village, dating from the mid-13th to the mid-18th centuries CE, are unusually well preserved. This cosmopolitan people's complex hunter-gatherer economy and extensive trade network allowed them to establish one of the highest population densities in aboriginal North America, yet they left very few physical remains.[8] The site has been subject to erosion and looting, problems which have been ameliorated by a protective layer of riprap.[7] |
| 15 | Timberline Lodge |  Timberline Lodge |
December 22, 1977 (#73001572) |
Government Camp 45°19′52″N 121°42′41″W |
Clackamas | President Franklin D. Roosevelt dedicated this lodge at an elevation of 6,000 feet (1,830 m) on the south slope of Mount Hood in 1937. It is considered the finest example of 1930s-era "mountain architecture" by the Works Progress Administration. |
| 16 | Wallowa Lake Site |  Wallowa Lake Site |
May 5, 1989 (#89001082) |
Joseph 45°20′11″N 117°13′20″W |
Wallowa | The religious and cultural values associated with this traditional Nez Perce campground have persisted for over a century since Chief Joseph the Younger and his band of nontreaty Nez Perce were driven out. It provides a view of high, glaciated lake and mountain country,[9] and includes the final resting place of Chief Joseph the Elder. It is a unit within the Nez Perce National Historical Park.[10] |
| 17 | Aubrey Watzek House | .jpg.webp) Aubrey Watzek House |
July 25, 2011 (#74001715) |
Portland 45°30′56″N 122°43′39″W |
Multnomah | John Yeon's 1937 house for a lumber magnate combined the International Style with regional preferences to create the Northwest Style |
Former National Historic Landmark
| Site name | Image | Date designated | Date withdrawn | Locality | County | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Samuel Elmore Cannery |  |
November 13, 1966 | July 16, 1993[11] | Astoria 46°11′30″N 123°50′45″W |
Clatsop | The home of "Bumble Bee" brand tuna, this was the longest continuously-operated salmon cannery in the United States, from its construction in 1898 until decommissioning in 1980. The canned salmon industry was a cornerstone of the Northwest's resource-based economy from the late 1860s until after World War II. Amid seasonal and declining salmon stocks, the cannery diversified into tuna in the 1930s. Because of structural deterioration, the building was slated for demolition in 1991, and it burned in 1993.[12] |
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to National Historic Landmarks in Oregon. |
References
- National Park Service. "National Historic Landmarks Program: Frequently Asked Questions". Retrieved 2013-08-07.
- "Title 36 of the Code of Federal Regulations, Part 65". US Government Printing Office. Archived from the original on 2012-02-17. Retrieved 2008-04-05.
- Numbers represent an alphabetical ordering by significant words. Various colorings, defined here, differentiate National Historic Landmarks and historic districts from other NRHP buildings, structures, sites or objects.
- The eight-digit number below each date is the number assigned to each location in the National Register Information System database, which can be viewed by clicking the number.
- National Park Service. "National Register Information System". Archived from the original on June 11, 2007. Retrieved 2009-05-18.
- McKithan, Cecil (September 12, 1977), National Register of Historic Places Invenory — Nomination Form: Jacksonville Historic District (PDF), retrieved September 22, 2013.
- Bogan, David (2006). "Sauvie Island's "Sunken Village" — A Special Place Forever Preserved?" (PDF). Cultural Heritage Courier. 2006 (2). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2007-02-07. Retrieved 2007-10-06..
- National Park Service. "National Historic Landmark Program: NHL Database". Archived from the original on 2004-06-06. Retrieved 2009-05-26.
- National Park Service. "National Historic Landmark Program: NHL Database". Archived from the original on March 1, 2007. Retrieved August 30, 2013.
- National Park Service. "Nez Perce NHP - Oregon and Washington Sites". Retrieved August 30, 2013. This source refers to the landmark as "Old Chief Joseph's Gravesite".
- National Park Service (July 23, 1993), Weekly List of Actions Taken on Properties: 7/12/93 through 7/16/93 (PDF), retrieved September 25, 2015.
- National Park Service, National Historic Landmark Program: Samuel Elmore Cannery, archived from the original on September 26, 2015, retrieved September 26, 2015.