List of Solar System objects most distant from the Sun
These Solar System minor planets are the farthest from the Sun as of March 2020. The objects have been categorized by their approximate heliocentric distance from the Sun, and not by the greatest calculated aphelion of their orbit. The list changes over time because the objects are moving. Some objects are inbound and some are outbound. It would be difficult to detect long-distance comets if it weren't for their comas, which become visible when heated by the Sun. Distances are measured in astronomical units (AU, Sun–Earth distances). The distances are not the minimum (perihelion) or the maximum (aphelion) that may be achieved by these objects in the future.
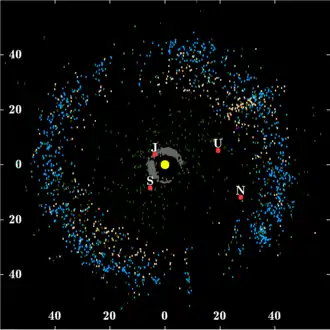
Jupiter trojans (6,178)
Scattered disc (>300) Giant planets: J · S · U · N
Centaurs (44,000)
Kuiper belt (>1,000)
(scale in AU; epoch as of January 2015; # of objects in parentheses)
This list does not include near-parabolic comets of which many are known to currently be more than 100 AU (15 billion km) from the Sun, but are too far away to currently be observed by telescope. Trans-Neptunian objects are typically announced publicly months or years after their discovery, so as to make sure the orbit is correct before announcing it. Due to their greater distance from the Sun and slow movement across the sky, trans-Neptunian objects with observation arcs less than several years often have poorly constrained orbits. Particularly distant objects discovered in 2020 may only be announced in 2022 or later.
Noted objects
One particularly distant body is 90377 Sedna, which was discovered in November 2003. Although it takes over 10,000 years to orbit, during the next 50 years it will slowly move closer to the Sun as it comes to perihelion at a distance of 76 AU from the Sun.[1] Sedna is the largest known sednoid, a class of objects that play an important role in the Planet Nine hypothesis.
Pluto (30–49 AU, about 34 AU in 2015) was the first Kuiper belt object to be discovered (1930) and is the largest known dwarf planet.
Images
- Some Notable Trans-Neptunian Objects
 This observation of Halley's Comet in 2003, when it was 28 AU from the Sun, illustrates some of the difficulty in observing objects as they grow more distant.
This observation of Halley's Comet in 2003, when it was 28 AU from the Sun, illustrates some of the difficulty in observing objects as they grow more distant.
 Makemake viewed with the Hubble Space Telescope, 2006
Makemake viewed with the Hubble Space Telescope, 2006 Sedna viewed with Hubble Space Telescope, 2004
Sedna viewed with Hubble Space Telescope, 2004

Known distant objects
This is a list of known objects at heliocentric distances of more than 60 AU. In theory, the Oort Cloud could extend over 120,000 AU (2 ly) from the Sun.
| Most-distant observable objects in the Solar System as of 1 March 2020[2] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Object name | Distance from the Sun (AU) | Radial velocity (AU/yr)[lower-alpha 1] | Apparent magnitude |
Absolute magnitude (H) |
Important Dates | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| June 2020 | December 2015 | Perihelion | Aphelion | Semimajor axis | Discovered | Announced | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Great Comet of 1680 (for comparison) |
257.6[3] | 255.4[3] | 0.47[3] | 0.006 | 889 | 444 | Unknown | Unknown | 1680-11-14 | n/a | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voyager 1 (for comparison) |
149.4[3] | 133.3[3] | 3.57[3] | 8.90 | ∞ Hyperbolic | −3.2[4] | ~50 | ~28 | n/a | n/a | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| "FarFarOut" | ~140?[lower-alpha 2] | ~140?[lower-alpha 3] | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | 2019-02-21 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pioneer 10 (for comparison) |
126.1[3] | 114.8[3] | 2.51[3] | 4.94 | ∞ Hyperbolic | ~49 | ~29 | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2018 VG18 | 124.1 | 123.2 | 0.03 | 35.9 | 146.1 | 91.0 | 24.5 | 3.7 | 2018-11-10 | 2018-12-17 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voyager 2 (for comparison) |
124.0[3] | 109.7[3] | 3.17[3] | 21.2 | ∞ Hyperbolic | −4.0[4] | ~48 | ~28 | n/a | n/a | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pioneer 11 (for comparison) |
103.1[3] | 92.5[3] | 2.35[3] | 9.45 | ∞ Hyperbolic | ~48 | ~29 | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Eris 136199 |
96.0 | 96.3 | -0.07 | 38.3 | 97.5 | 67.9 | 18.8 | −1.1 | 2003-10-21 | 2005-07-29 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2015 TH367 | 90.0 | 88.2 | 0.42 | 28.9 | 136.4 | 82.6 | 26.3 | 6.6 | 2015-10-13 | 2018-03-13 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2014 UZ224 | 90.0 | 91.9 | -0.45 | 38.4 | 175.7 | 107.0 | 23.2 | 3.4 | 2014-10-21 | 2016-08-28 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gonggong 225088 |
88.5 | 87.4 | 0.23 | 33.7 | 101.2 | 67.5 | 21.1 | 1.6 | 2007-07-17 | 2009-01-07 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2015 FG415 | 87.4 | 36.2 | 92.1 | 64.1 | 25.4 | 6.0 | 2015-03-17 | 2019-03-27 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2014 FC69 | 85.3 | 84.1 | 0.25 | 40.4 | 103.8 | 72.1 | 24.0 | 4.6 | 2014-03-25 | 2015-02-11 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sedna 90377 |
84.5 | 85.8 | -0.29 | 76.3 | 892.6 | 484.4 | 20.7 | 1.3 | 2003-11-14 | 2004-03-15 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2006 QH181 | 84.4 | 83.3 | 0.22 | 37.5 | 96.7 | 67.1 | 23.7 | 4.3 | 2006-08-21 | 2006-11-05 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2012 VP113 | 84.0 | 83.3 | 0.16 | 80.4 | 442.6 | 261.5 | 23.4 | 4.0 | 2012-11-05 | 2014-03-26 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2015 VO166 | 84.0 | 38.3 | 113.2 | 75.8 | 25.3 | 5.9 | 2015-11-06 | 2018-10-02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2013 FS28 | 83.5 | 85.9 | -0.62 | 34.2 | 358.2 | 196.2 | 24.2 | 4.9 | 2013-03-16 | 2016-08-29 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2017 SN132 | 82.0 | 42.0 | 110.0 | 76.0 | 25.1 | 5.8 | 2017-09-16 | 2019-02-10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2015 UH87 | 81.5 | 82.3 | -0.20 | 34.3 | 90.0 | 62.2 | 25.2 | 6.0 | 2015-10-16 | 2018-03-12 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2013 FY27 532037 |
79.9 | 80.3 | -0.10 | 35.2 | 82.1 | 58.7 | 22.2 | 3.2 | 2013-03-17 | 2014-03-31 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2015 TJ367 | 79.0 | 88.2 | 0.42 | 33.6 | 128.1 | 80.9 | 25.8 | 6.7 | 2015-10-13 | 2018-03-13 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2017 FO161 | 78.3 | 34.1 | 85.4 | 59.8 | 23.2 | 4.3 | 2017-03-23 | 2018-04-02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Leleākūhonua 541132 |
78.0 | 79.8 | -0.40 | 65.2 | 2106 | 1085 | 24.5 | 5.5 | 2015-10-13 | 2018-10-01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2015 VJ168 | 73.2 | 37.6 | 81.5 | 59.5 | 24.6 | 5.8 | 2015-11-06 | 2018-10-03 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2010 GB174 | 73.1 | 70.6 | 0.54 | 48.6 | 636.0 | 342.3 | 25.2 | 6.5 | 2010-04-12 | 2013-04-30 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2014 FJ72 | 72.2 | 70.1 | 0.46 | 38.4 | 148.2 | 93.3 | 24.2 | 5.6 | 2014-03-24 | 2016-08-31 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2016 TS97 | 71.3 | 36.2 | 71.7 | 54.0 | 24.8 | 6.1 | 2016-10-06 | 2018-04-02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2015 GN55 | 71.2 | 32.5 | 78.4 | 55.5 | 24.4 | 5.8 | 2015-04-13 | 2018-19-02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2015 VL168 | 70.1 | 37.7 | 136.0 | 86.8 | 24.7 | 6.1 | 2015-11-07 | 2018-10-03 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2012 FH84 | 69.0 | 68.8 | 0.07 | 41.9 | 70.1 | 56.0 | 25.6 | 7.2 | 2012-03-25 | 2016-06-07 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2015 RZ277 | 69.0 | 34.7 | 90.5 | 62.6 | 25.3 | 6.8 | 2015-09-08 | 2018-10-01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2015 GR50 | 68.5 | 68.4 | 0.07 | 38.2 | 69.7 | 54.0 | 25.0 | 6.6 | 2015-04-13 | 2016-08-31 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2013 FQ28 | 68.2 | 67.8 | 0.19 | 45.6 | 80.0 | 62.7 | 24.4 | 6.0 | 2013-03-17 | 2016-06-07 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2015 GP50 | 67.7 | 68.0 | 0.10 | 40.4 | 70.0 | 55.2 | 24.9 | 6.5 | 2015-04-14 | 2016-06-07 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2016 CD289 | 67.0 | 65.8 | 0.18 | 37.5 | 74.0 | 55.8 | 25.6 | 7.3 | 2016-02-05 | 2018-03-13 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2016 GZ276 | 66.7 | 38.6 | 253.6 | 146.1 | 25.4 | 7.0 | 2016-04-10 | 2020-06-03 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2016 GB277 | 66.6 | 40.0 | 119.4 | 79.7 | 25.6 | 7.3 | 2016-04-10 | 2020-06-04 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2014 UD228 | 66.5 | 66.1 | 0.18 | 3 6.7 | 73.3 | 55.0 | 24.5 | 6.1 | 2014-10-22 | 2017-12-07 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2014 FL72 | 65.5 | 38.0 | 167.1 | 102.5 | 25.0 | 6.8 | 2014-03-26 | 2016-08-31 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2016 TQ120 | 65.4 | 42.3 | 114.3 | 78.3 | 25.0 | 6.7 | 2016-10-06 | 2020-06-04 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2018 VO35[3] | 65.3 | 67.9 | -0.60 | 33.5 | 218.2 | 125.9 | 24.9 | 6.6 | 2018-11-10 | 2019-02-10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2013 UJ15 | 65.2 | 37.2 | 67.4 | 52.3 | 25.3 | 7.0 | 2013-10-28 | 2016-08-31 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2015 RQ281 | 65.2 | 62.7 | 36.9 | 210.6 | 123.8 | 25.0 | 6.8 | 2015-09-05 | 2019-03-27 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2015 KV167 | 65.1 | 38.0 | 65.3 | 51.6 | 25.4 | 7.2 | 2015-05-18 | 2018-03-13 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2018 AZ18 | 65.1 | 39.1 | 70.5 | 54.8 | 26.0 | 7.7 | 2018-01-15 | 2019-03-27 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2014 FD70 | 64.9 | 35.9 | 78.6 | 57.3 | 25.0 | 6.9 | 2014-03-25 | 2018-04-02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2014 SU349 | 64.5 | 28.5 | 157.0 | 92.8 | 25.4 | 7.2 | 2014-09-18 | 2016-08-31 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2015 KG172 | 64.3 | 41.2 | 70.1 | 55.7 | 24.3 | 6.1 | 2015-05-20 | 2018-05-31 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2014 FE72 | 63.8 | 36.3 | 2682 | 1359 | 24.2 | 6.1 | 2014-03-26 | 2016-08-29 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2017 DO121 | 63.7 | 26.9 | 330.2 | 178.5 | 25.5 | 7.6 | 2017-02-24 | 2018-04-02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2013 AT183 | 63.3 | 35.5 | 87.7 | 61.6 | 23.0 | 4.9 | 2013-01-10 | 2016-07-26 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2015 RL258 | 63.1 | 34.4 | 67.5 | 50.9 | 24.6 | 6.5 | 2015-09-07 | 2018-03-12 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2000 CR105 148209 |
62.7 | 44.1 | 388.1 | 216.1 | 24.3 | 6.3 | 2000-02-06 | 2000-03-16 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2015 KF172 | 62.7 | 38.1 | 101.4 | 69.8 | 23.6 | 5.5 | 2015-05-20 | 2018-05-31 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2015 RR245 523794 |
62.2 | 34.1 | 129.4 | 81.7 | 21.9 | 3.8 | 2015-09-09 | 2016-07-10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2015 VG157 | 62.1 | 39.0 | 68.9 | 54.0 | 25.6 | 7.5 | 2015-11-07 | 2018-03-14 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2017 VO34 | 62.1 | 35.2 | 68.8 | 52.0 | 25.4 | 7.3 | 2017-11-15 | 2019-03-27 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2018 AX18 | 62.1 | 36.8 | 67.4 | 52.1 | 24.7 | 6.6 | 2018-01-15 | 2019-02-10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2015 RH278 | 62.0 | 34.3 | 76.7 | 55.5 | 25.2 | 7.2 | 2015-09-08 | 2018-10-02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2008 ST291 528381 |
61.7 | 42.4 | 158.8 | 100.6 | 22.4 | 4.4 | 2008-09-24 | 2009-11-14 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2017 FD163 | 61.5 | 30.1 | 65.0 | 47.5 | 24.8 | 6.9 | 2017-03-25 | 2019-03-27 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2017 DP121 | 61.5 | 40.6 | 60.4 | 50.5 | 25.0 | 7.2 | 2017-02-24 | 2018-04-02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2011 GM89 | 61.5 | 36.5 | 68.8 | 52.7 | 25.6 | 7.1 | 2011-04-04 | 2016-08-31 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2016 TP120 | 61.1 | 39.9 | 307.0 | 173.4 | 25.1 | 7.1 | 2016-10-07 | 2020-06-04 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2014 FM72 | 61.1 | 34.1 | 76.8 | 55.5 | 24.1 | 6.2 | 2014-03-25 | 2016-08-31 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2014 SV349 | 61.0 | 34.0 | 90.0 | 62.0 | 23.2 | 5.2 | 2014-09-19 | 2016-08-31 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2018 JT6 | 60.7 | 61.1 | -0.10 | 42.8 | 63.8 | 53.3 | 24.7 | 6.8 | 2018-05-10 | 2019-03-27 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2016 TO120 | 60.6 | 40.1 | 80.5 | 60.3 | 25.3 | 7.3 | 2016-10-06 | 2020-06-03 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2015 GW55 | 60.5 | 34.0 | 136.7 | 85.3 | 24.6 | 6.7 | 2015-04-13 | 2018-10-03 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2014 FF72 | 60.5 | 36.7 | 64.0 | 50.4 | 24.8 | 6.9 | 2014-03-24 | 2016-08-31 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2017 OK69 | 60.4 | 36.3 | 65.1 | 50.7 | 23.8 | 5.8 | 2017-07-26 | 2019-03-27 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2003 QX113 | 60.3 | 59.9 | 37.5 | 62.3 | 49.9 | 23.0 | 5.1 | 2003-08-31 | 2006-04-22 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2015 FU403 | 60.3 | 35.2 | 80.8 | 58.0 | 25.4 | 7.5 | 2015-03-17 | 2018-03-12 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2016 TN120 | 60.3 | 43.7 | 61.8 | 52.8 | 24.4 | 6.4 | 2016-10-06 | 2020-06-03 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2015 KH162 | 60.2 | 41.6 | 82.5 | 62.1 | 22.0 | 4.1 | 2015-05-18 | 2016-02-23 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2013 JQ64 | 60.0 | 58.4 | 22.5 | 75.6 | 49.1 | 24.1 | 6.2 | 2013-05-08 | 2015-09-13 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| This table includes all observable objects currently located at least 60 AU from the Sun.[2] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
- AU/yr indicates if the object is moving inwards or outwards in its orbit, and the rate at which it does so.
- A crude estimate based on a short observation arc.
- A crude estimate based on a short observation arc.
See also
- List of artificial objects leaving the Solar System
- Lists of astronomical objects
- List of Solar System objects by greatest aphelion
- List of hyperbolic comets
- List of trans-Neptunian objects
- Objects with very large aphelia
References
- Most Distant Object In Solar System Discovered; NASA.gov; (2004)
- "AstDyS-2, Asteroids – Dynamic Site". Retrieved 1 March 2020.
Objects with distance from Sun over 50 AU
- JPL Horizons On-Line Ephemeris System. "JPL Horizons On-Line Ephemeris". Retrieved 4 June 2020.
Ephemeris Type: Vector; Observer Location: @sun; Time Span: Start=2015-12-01, Stop=2020-06-01, Intervals=1; Table Settings: quantities code=6 - https://voyager.jpl.nasa.gov/mission/science/hyperbolic-orbital-elements/

