Mahdavia
Mahdavia (Arabic: مهدوي mahdawi) or Mahdavism, known as Zikri in Pakistan, is a Mahdiist Muslim sect founded by Syed Muhammad Jaunpuri in India in the late 15th century. Syed Muhammad declared himself to be Imam Mahdi at the holy city of Mecca, in front of the Kaaba in 1496 and is revered as such by the Mahdavia community throughout the world, most of which is in India, Pakistan, USA, Canada and UK.
| Part of a series on |
| Islam |
|---|
 |
|
Beliefs
Mahdavis believe in the following: 1)oneness of Allah, 2) The prophethood of Muhammad as the last messenger of Allah, 3) The Quran as their holy book.
They strictly adhere to the five pillars of Islam, sunnah tradition, and sharia, while having high respect and reverence for the House of Muhammad and his immediate progeny (ahl-e bayt), the Rashidun caliphs, and the companions of Muhammad (sahaba).
Mahdavis also respect all four schools of Islamic jurisprudence, but widely follow the traditions similar to Hanafi jurisprudence.
They offer prayers five times a day led by their murshids, or spiritual guides; fast during Ramadan; offer special thanks on Dugana Laylat al-Qadr past midnight between 26 and 27 Ramadan; perform hajj; and pay zakat. They also attach great significance to zikr (remembrance of Allah), after dawn (fajr) prayers, and in the evening after asr prayer.
Mahdavis, besides following the five pillars of Islam, also follow the seven obligations of sainthood, known as faraiz-e wilaya Muhammadiya. These obligations are: renunciation (tark-e dunya), quest for divine vision (talab didar-e Ilahi), company of truthfuls and ascetics (sohbat-e sadiqan), migration (hijrah), retreat and solitude (uzlat az khalq), absolute dependence on Allah (tawakkul), constant remembrance of Allah (zikr-e Ilahi) and distributing tithe (ushr). Followers of Jaunpuri strictly follow some of these obligations in their day-to-day life. Most of them initiate renunciation in the advanced stage of their lives, after getting retirement from the jobs or by handing over business to their heirs. Their renunciation is in any way not related to celibacy, because almost all of them get married.[1]
Mohammad Jaunpuri declared himself to be Promised Mahdi, and as such a "caliph of Allah". He claimed to teach the true inner meaning of the Qur'an and strictly adhere to the Sunnah of Muhammad. Jaunpuri's declaration was ignored by the ulema of Mecca, but after he repeated his declaration in Ahmedabad, Gujarat, he gained a group of followers and established a line of caliphs who led the movement after his death.
After Jaunpuri's demise in 1505, the Mahdavi movement went through a militant phase, lasting during the reign of the first five Mahdavi caliphs. The movement was persecuted under the Sultan Muzaffar Shah II (r. 1511–1526) of Gujarat Sultanate.
The second Mahdavi caliph, Bandagi Miyan Syed Khundmir and his fukhra disciples (the persons who renounce the world and keep remembering Allah with zikr), faced organised persecution by the regime of Muzaffar at the behest of his court-appointed Mullas and was killed in 1523 along with hundreds of unarmed and peaceful disciples. Syed Khundmir's tomb is located in the town of Champaner in the Panchmahal district of the western Indian state Gujarat, where thousands of seekers and followers, from different parts of India and other countries, arrive to pay tribute.
After failure to re-appear in that year, the movement lost much of its fervor and entered a "quietist" phase, which lasted throughout the 17th century. In the 18th century, the movement mostly died out in northern India.[2]
After the 1799 siege of Seringapatam, the British government invited the Mahdavis to re-settle in Mysore.[3]
Mahdavis
| Part of a series on Islam Sufism |
|---|
|
|
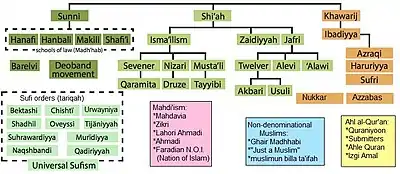
Zikris
Zikris are an offshoot of the Mahdavi movement found mostly in the Balochistan region of western Pakistan.
"Mahdavis are estimated to number over 750,000 people. They live mostly in Makran and Las Bela in southern Pakistan, and are followers of a 15th-century mahdi, an Islamic messiah, called Nur Pak ('Pure Light'). Mahdavis practices and rituals differ from those of orthodox Islam..."[4]
The content of their prayer, which they call Zikr-e-Elahi, refers to the worship of God. In addition to the Hajj, Zikris also visit (ziyarat) to the Koh-e-Murad ("Mountain of Desire" in Balochi), where their Promised Imam al-Mahdi Syed Muhammad Jaunpuri is believed to have stayed and in 1504 AD, he offered two Raka'as (cycles) special thanks giving prayers Dougana Laylat al-Qadr in the midnight of 27th Ramadan 908 Hijri. Following his tradition, including Zikris all Mahdavis offer Dougna Laylathu'l-Qadr prayers on 27th Ramadan midnight every year, under the leadership of their murshid. Thus, Mahdavis are a sect who follow the Sufi order, defined by the medieval saint Syed Muhammad Jaunpuri of the capital city of the Sharqi dynasty. This city was also known as The Shiraz of the East, due to its academic and intellectual eminence and the presence of many Islamic scholars in that era.
The population
The number of Mahdavis is not known with any confidence. Gall (1998) stated that they were "estimated to number over 750,000 people",[5] while the United States Senate Committee on Foreign Relations in 2004 stated that there were "approximately 200,000".[6] The Mahdavis form a local majority in Pakistan's Gwadar District,[6] and there are sizable communities in Karachi, the Pakistani part of Makran, Lasbela District, and Quetta, and in Pakistan's Sindh province. Their concentration in urban Karachi is due to many Mahdavis having relocated to the city, especially the neighborhood of Lyari Town.
With the general rise of Islamic extremism and jihadism in the region since the 1980s, Mahdavis have been discriminated against, targeted, and killed by Sunni militants in Pakistan.[7][8][9][10][11] As a result, the Mahdavis community has been shrinking and becoming less visible, with many killed by terrorists. Non-governmental organizations including the Human Rights Commission of Pakistan (HRCP) are working with local activists to create a greater awareness of the Mahdavis predicament. Recently, police protection has been provided to some Mahdavis pilgrims.
The persecution of Mahdavis by Sunni militants as of 2014 has been part of the larger backlash against religious minorities in Pakistani Balochistan, targeting Hindus, Hazaras, Shias, and Zikris, resulting in the migration of over 300,000 Shias, Zikris, and Hindus from Pakistani Balochistan. The persecutions were due both to banned militant organizations such as Lashkar-i-Jhangvi and Pakistani Taliban.[8][9][10][11]
Mahdavia community in India
Anjuman E Mahdavia is a Mahdavia community center in Hyderabad Telangana, India, established in 1902.[12] L. K. A. Iyer in 1930 reports the existence of a community of "Mahdavia Musalmans" in Mysore Donabaghatta, Channapatna, Kirugavalu. There is a village named Donabaghatta in Karnataka. Large groups of Mahdavis resided in Gujarat, Rajasthan, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka-Bengaluru, etc. The 1962 Gazette of Karnataka State has recorded the Mahadavia Sect of Islam in the state.[13]
See also
Others who claimed to be Mahdi
References
- "Khalifatullah Mehdi (AHS)". www.khalifatullahmehdi.info.
- Timothy R. Furnish, Holiest Wars: Islamic Mahdis, their Jihads, and Osama bin Laden, Greenwood Publishing Group, 2005, pp 38–41.
- L. K. A. Iyer, The Mysore: Tribes and Castes, Vol IV (1930), p. 383: "the benign British government issued a proclamation assuring peace and inviting all the Mahdavis to the territory of Mysore to resettle there, and they then settled in different places after their exile."
- Gall, Timothy L. (ed). Worldmark Encyclopedia of Culture & Daily Life. Vol. 3, Asia & Oceania. Cleveland, OH: Eastword Publications Development (1998); pg. 85
- " Mahdavis are estimated to number over 750,000 people. They live mostly in Makran and Las Bela in southern Pakistan, and are followers of a 15th-century mahdi, an Islamic messiah, called Nur Pak ('Pure Light'). Mahdavis practices and rituals differ from those of orthodox Islam... " Gall, Timothy L. (ed). Worldmark Encyclopedia of Culture & Daily Life. Vol. 3, Asia & Oceania. Cleveland, OH: Eastword Publications Development (1998); pg. 85 cited after adherents.com.
- Senate Committee on Foreign Relations, Annual Report on International Religious Freedom (2004), p. 656.
- "The Zikri question has become one of the leading issues during last few years which mobilized enormous resistance by the religious groups, particularly the Jamiat Ulema-e-Islam (JUI), in Balochistan" Mansoor Akbar Kundi, Balochistan, a socio-cultural and political analysis, Qasim Printers, 1993, p. 83.
- "Human Rights Commission of Pakistan worried over mass migration of Hindus from Balochistan". DNA. 13 October 2014. Retrieved 23 July 2019.
- "Meanwhile, in Balochistan". Epaper.dawn.com. Retrieved 3 January 2015.
- "Pro-Taliban takfiris hail ISIS: Zikri-Balochs, Hindus threatened to death". The Shia Post. Archived from the original on 3 September 2014. Retrieved 3 January 2015.
- "Gunmen target minority sect in Pakistan". Aljazeera.com. Retrieved 3 January 2015.
- "Hyderabad: The State government has declared April 19 as optional holiday on the occasion of 'Hazrat Syed Mohd. Juvanpuri Mahdi Ma'ud (AS)' instead of April 20". Hyderabadcircle.com. Retrieved 3 January 2015.
- The Mysore. 1965. Retrieved 3 January 2015.
Other sources
- Ziaullah Yadullahi (trans.). "Maulud Sharif". Jamiat-e-Mahdavia, Bangalore (2007).
- Azhar Munīr, I. A. Rehman. Zikris in the light of history & their religious beliefs, Izharsons, 1998.
External links
- "Mahdavia"
- "Ishqnama" Quran software with tafseer from Noor e Imaan
- "Mehdavia Times"
- "Khalifatullah Mehdi"
- Hazrat Muhammad Nooruddin Arabi Saheb, "Mahdaviat in the light of sayings of Imamana"
- "Mahdavia Foundation"
- "Jamiat-e-Mahdavia, Bangalore"