Maputaland-Pondoland-Albany Hotspot
The Maputaland-Pondoland-Albany Hotspot (MPA) is a biodiversity hotspot, a biogeographic region with significant levels of biodiversity, in Southern Africa. It is situated near the south-eastern coast of Africa, occupying an area between the Great Escarpment and the Indian Ocean.[1] The area is named after Maputaland, Pondoland and Albany. It stretches from the Albany Centre of Plant Endemism in the Eastern Cape Province of South Africa, through the Pondoland Centre of Plant Endemism and KwaZulu-Natal Province, the eastern side of Eswatini (known as Swaziland until 2018) and into southern Mozambique and Mpumalanga. The Maputaland Centre of Plant Endemism is contained in northern KwaZulu-Natal and southern Mozambique.
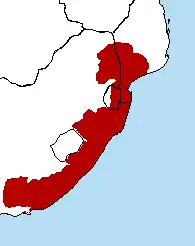
Geography
This ecoregion covers globally all the humid subtropical climate zones of Africa (the latter being located almost exclusively in South Africa), an area of 274,136 km2 (105,845 sq mi). It forms a broad coastal strip extending from the extreme south of Mozambique and north-east of Mpumalanga to the east of Eastern Cape Province in South Africa, including the Wild Coast. It also includes eastern Swaziland and borders southern and eastern Lesotho. It consists of three regions more or less biologically close but each with its own characteristics. Maputaland (also known as Tongaland) refers to the southern part of Mozambique, Swaziland and northern KwaZulu-Natal, Pondoland includes central and southern KwaZulu-Natal, and Albany is the eastern part of Eastern Cape.[2]
The terrain in this region is complex, providing a great diversity of landscapes with varied reliefs. It encompasses the southeast of the Great Escarpment and down to the edge of the Indian Ocean. As a result, this ecoregion includes much of the Drakensberg range, especially in the south and centre of the area. One of the best-watered areas in South Africa, a large part of the area receives on average between 750 and 1,000 mm (30 and 39 in) per year and the Kwazulu-Natal coasts as well as parts of the Drakensberg exceed the annual 1,000 mm (39 in).[3] The northern part of the area consists mainly of medium and lowland plains with areas of ancient sand dunes, while the southern part has more rugged terrain with many cliffs cut by multiple streams. Inland, there are several ranges of mountain which include Sneeuberge, Winterberg, Amathole Mountains, Ngeli Range, Lebombo Mountains and Ngoye Range.[4]

Biodiversity
The vegetation cover is mainly composed of forests, shrubland, bushveld and meadows. About 80% of the remaining forests of South Africa occur in this region, and nearly 600 species of trees are represented here, the highest diversity of any temperate forest in the world. Among the large number of plants in this ecoregion, about 1900 are endemic. The Albany region also has a great diversity of succulent plants, notably arborescent plants, differing from the leafy succulent species of the Karoo desert.[4]
Although the hotspot was originally envisaged as referring to the wide diversity of vascular plant species, the pattern of plant endemism is matched by numerous endemic vertebrates. The degree of endemism among plants in this hotspot is 23.5% whereas the degree of endemism among vertebrates is 5.1% and near-endemism 4.9%. If the area of the hotspot was redefined as the "Greater Maputaland-Pondoland-Albany" area, an increase of 73%, to include the Great Escarpment area, the vertebrate endemism would total 146 species (19 freshwater fishes, 29 amphibians, 75 reptiles, 15 birds and 8 mammals), a figure 135% higher than the 62 vertebrate species for the MPA as presently defined.[5]
Most of the endemic vertebrates in the ecoregion inhabit the forests and grasslands, and many have niche habitat requirements such as rocky outcrops or marshy areas within these larger biomes; the Sloggett's vlei rat and the Natal red rock hare are quite widespread in the area while the woodbush legless skink and the robust golden mole have narrower habitat requirements.[6]
List of endemic plants (incomplete)
The endemic plants found in the Maputaland-Pondoland-Albany Hotspot include:[7]
- Albizia suluensis
- Allophylus natalensis
- Aloe thraskii
- Atalaya alata
- Atalaya natalensis
- Baphia racemosa
- Brachylaena discolor
- Deinbollia oblongifolia
- Encephalartos natalensis
- Encephalartos woodii
- Ficus bizanae
- Isoglossa woodii
- Jubaeopsis caffra
- Millettia grandis
- Raphia australis
- Stangeria eriopus
- Tephrosia pondoensis
Gallery
 Erythrina caffra; endemic to the Maputaland-Pondoland-Albany Hotspot
Erythrina caffra; endemic to the Maputaland-Pondoland-Albany Hotspot Aloe thraskii; endemic to the Maputaland-Pondoland-Albany Hotspot
Aloe thraskii; endemic to the Maputaland-Pondoland-Albany Hotspot Hibiscus pedunculatus; near-endemic to the Maputaland-Pondoland-Albany Hotspot
Hibiscus pedunculatus; near-endemic to the Maputaland-Pondoland-Albany Hotspot Dracaena aletriformis (near-endemic) and Isoglossa woodii (endemic)
Dracaena aletriformis (near-endemic) and Isoglossa woodii (endemic)
See also
- Maputaland-Pondoland bushland and thickets – Montane shrubland ecoregion in South Africa
- Maputaland – Natural region in South Africa in northern KwaZulu-Natal
- EmaMpondweni, also known as Pondoland
- Albany, South Africa
- Forests of KwaZulu-Natal – Forest vegetation type in South Africa
- Ezemvelo KZN Wildlife – Governmental organisation managing wildlife conservation areas and biodiversity in KwaZulu-Natal Province, South Africa
References
- Biodiversity Archived 2010-03-23 at the Wayback Machine
- Philip's (1994). Atlas of the World. Reed International. pp. 104–105. ISBN 0-540-05831-9.
- "CEPF Final Project Completion Report" (PDF). Critical Ecosystem Partnership Fund. July 1, 2016. Retrieved July 6, 2019.
- "Maputaland-Pondoland-Albany". Biodiversity hotspots. Conservation International. Archived from the original on March 23, 2010. Retrieved July 6, 2019.
- Perera, Sandun J.; Ratnayake-Perera, Dayani; Procheş. Şerban (2011). "Vertebrate distributions indicate a greater Maputaland-Pondoland-Albany region of endemism". South African Journal of Science. 107 (7–8). doi:10.4102/sajs.v107i7/8.462.
- Perera, Sandun J. (2011). "Veretbrate distributions indicate a greater Maputaland-Pondoland-Albany region of endemism". South African Journal of Science. Retrieved July 6, 2019.
- Van Wyk, A.E.; Smith, G.F. (2001). Regions of floristic endemism in southern Africa. Umdaus Press. pp. 82–109. ISBN 978-1-919766-18-8.