Grassland
Grasslands are areas where the vegetation is dominated by grasses (Poaceae). However, sedge (Cyperaceae) and rush (Juncaceae) can also be found along with variable proportions of legumes, like clover, and other herbs. Grasslands occur naturally on all continents except Antarctica and are found in most ecoregions of the Earth. Furthermore, grasslands are one of the largest biomes on earth and dominate the landscape worldwide.[1] They cover 31-43% of the Earth's land area. There are different types of grasslands: natural grasslands, semi-natural grasslands, and agricultural grasslands.[1]


Definitions

There are a variety of definitions for "grasslands":
- "...any plant community, including harvested forages, in which grasses and/or legumes make up the dominant vegetation."[1]
- "...terrestrial ecosystems dominated by herbaceous and shrub vegetation, and maintained by fire, grazing, drought and/or freezing temperatures." (Pilot Assessment of Global Ecosystems, 2000)[1]
- "A region with sufficient average annual precipitation (25-75 cm) to support grass..." (Stiling, 1999)[1]
Semi-natural grasslands are a very common subcategory of the grasslands biome.[2] These can be defined as:
- Grassland existing as a result of human activity (mowing or livestock grazing), where environmental conditions and the species pool are maintained by natural processes.[3]
They can also be described as the following:
- "Semi-natural grasslands are one of the world's most biodiverse habitats on a small spatial scales."[4]
- "Semi-natural grasslands belong to the most species rich ecosystems in the world."[5]
- "...have been formed over the course of centuries through extensive grazing and mowing."[4]
- "...without the use of pesticides or fertilisers in modern time."[6]
There are many diiferent types types of semi-natural grasslands, e.g. hay meadows.[6]
Types of grassland

Classifications of grasslands
Grassland types by Schimper (1898, 1903):[7]
- Meadow (hygrophilous or tropophilous grassland)
- Steppe (xerophilous grassland)
- Savannah (xerophilous grassland containing isolated trees)
 Steppe family: a common grassland animal, the swift fox
Steppe family: a common grassland animal, the swift fox
Grassland types by Ellenberg and Mueller-Dombois (1967):[8]
Formation-class V. Terrestrial herbaceous communities
- Savannas and related grasslands (tropical or subtropical grasslands and parklands)
- Steppes and related grasslands (e.g. North American "prairies" etc.)
- Meadows, pastures or related grasslands
- Sedge swamps and flushes
- Herbaceous and half-woody salt swamps
- Forb vegetation
.jpg.webp) A hike through the Tallgrass Prairie Heritage Park in Canada
A hike through the Tallgrass Prairie Heritage Park in Canada
Grassland types by Laycock (1979):[9]
- Tallgrass (true) prairie
- Shortgrass prairie
- Mixed-grass prairie
- Shrub steppe
- Annual grassland
- Desert (arid) grassland
- High mountain grassland
Tropical and subtropical
These grasslands can be classified as the tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas and shrublands biome. The rainfall level for that grassland type is between 90-150 centimeters per year. Grasses and scattered trees are common for that ecoregion, as well as large mammals, such as wildebeest (Connochaetes taurinus) and zebra (Equus zebra). Notable tropical and subtropical grasslands include the Llanos grasslands of South America.[10]

Temperate
Mid-latitude grasslands, including the prairie and Pacific grasslands of North America, the Pampas of Argentina, Brazil and Uruguay, calcareous downland, and the steppes of Europe. They are classified with temperate savannas and shrublands as the temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome. Temperate grasslands are the home to many large herbivores, such as bison, gazelles, zebras, rhinoceroses, and wild horses. Carnivores like lions, wolves, cheetahs and leopards are also found in temperate grasslands. Other animals of this region include deer, prairie dogs, mice, jack rabbits, skunks, coyotes, snakes, foxes, owls, badgers, blackbirds, grasshoppers, meadowlarks, sparrows, quails, hawks and hyenas.[11]
Flooded
Grasslands that are flooded seasonally or year-round, like the Everglades of Florida, the Pantanal of Brazil, Bolivia and Paraguay or the Esteros del Ibera in Argentina, are classified with flooded savannas as the flooded grasslands and savannas biome and occur mostly in the tropics and subtropics. The species that live in these grasslands are well adapted to the hydrologic regimes and soil conditions. The Everglades - the world's largest rain-fed flooded grassland - is rich in 11,000 species of seed-bearing plants, 25 species of orchids, 300 bird species, and 150 fish species.
Water-meadows are grasslands that are deliberately flooded for short periods.[12]

Montane
High-altitude grasslands located on high mountain ranges around the world, like the Páramo of the Andes Mountains. They are part of the montane grasslands and shrublands biome and can be tropical, subtropical, and temperate. The plants and animals, that can be found in the tropical montane, are able to adapt to cool, wet conditions as well as intense sunlight.[13]
Tundra grasslands
Similar to montane grasslands, polar Arctic tundra can have grasses, but high soil moisture means that few tundras are grass-dominated today. However, during the Pleistocene glacial periods (commonly referred to as ice ages), a grassland known as steppe-tundra or mammoth steppe occupied large areas of the Northern Hemisphere. These areas were very cold and arid and featured sub-surface permafrost (hence tundra) but were nevertheless productive grassland ecosystems supporting a wide variety of fauna. As the temperature increased and the climate became wetter at the beginning of the Holocene much of the mammoth steppe transitioned to forest, while the drier parts in central Eurasia remained as a grassland, becoming the modern Eurasian steppe.[14]
Desert and xeric
Also called desert grasslands, they are composed of sparse grassland ecoregions located in the deserts and xeric shrublands biome. Temperature extremes and low amount of rainfall characterise these kinds of grasslands. Therefore, plants and animals are well adapted to minimize water loss.[15]
Evolutionary history
The graminoids are among the most versatile life forms. They became widespread toward the end of the Cretaceous period, and coprolites of fossilized dinosaur feces have been found containing phytoliths of a variety of grasses that include grasses that are related to modern rice and bamboo.[16]
The appearance of mountains in the western United States during the Miocene and Pliocene epochs, a period of some 25 million years, created a continental climate favourable to the evolution of grasslands.[17]
Around 5 million years ago during the Late Miocene in the New World and the Pliocene in the Old World, the first true grasslands occurred. Existing forest biomes declined, and grasslands became much more widespread. It is known that grasslands have existed in Europe throughout the Pleistocene (the last 1.8 million years).[6] Following the Pleistocene ice ages (with their glacials and interglacials), grasslands expanded in the hotter, drier climates, and began to become the dominant land feature worldwide.[17] Since the grasslands have existed for over 1.8 million years, there is high variability. For example steppe-tundra dominated in Northern and Central Europe whereas a higher amount of xerothermic grasslands occurred in the Mediterranean area.[6] Within temperate Europe, the range of types is quite wide and also became unique due to the exchange of species and genetic material between different biomes.
The semi-natural grasslands probably first appeared with the human starting farming. So for the use of agriculture, forests got cleared in Europe. Ancient meadows and pastures were the parts that were suitable for cultivation. The semi-natural grasslands were formed from these areas.[6] The removal of the plants by the grazing animals and later the mowing farmers led to co-existence of other plant species around. In the following, the biodiversity of the plants evolve. Also, the species that already lived there adapted to the new conditions.[6]
Most of the grassland areas have been turned to arable fields and disappeared again.
Nowadays, semi-natural grasslands are rather located in areas that are unsuitable for agricultural farming.[6]
Ecology
Biodiversity and conservation
Grasslands dominated by unsown wild-plant communities ("unimproved grasslands") can be called either natural or "semi-natural" habitat. Although their plant communities are natural, their maintenance depends upon anthropogenic activities such as grazing and cutting regimes. The semi-natural grasslands contain many species of wild plants, including grasses, sedges, rushes, and herbs; 25 plant-species per 100 square centimeters can be found.[6] A European record that was found on a meadow in Estonia described 76 species of plants in one square meter.[6] Chalk downlands in England can support over 40 species per square meter.
In many parts of the world, few examples have escaped agricultural improvement (fertilizing, weed killing, plowing, or re-seeding). For example, original North American prairie grasslands or lowland wildflower meadows in the UK are now rare and their associated wild flora equally threatened. Associated with the wild-plant diversity of the "unimproved" grasslands is usually a rich invertebrate fauna; there are also many species of birds that are grassland "specialists", such as the snipe and the little bustard.[18] Due to semi-natural grasslands being referred to as one of the most-species rich ecosystems in the world and essential habitat for many specialists, also including pollinators,[5] there are many approaches to conservation activities lately.
Agriculturally improved grasslands, which dominate modern intensive agricultural landscapes, are usually poor in wild plant species due to the original diversity of plants having been destroyed by cultivation and by the use of fertilizers.
Almost 90% of the European semi-natural grasslands do not exist anymore due to political and economic reasons. This loss only took place during the 20th century.[4] The ones in Western and Central Europe have almost disappeared completely. There are a few left in Northern Europe.[4]
Unfortunately, a large amount of red-listed species are specialists of semi-natural grasslands and are affected by the landscape change due to agriculture of the last century.[19]
The original wild-plant communities having been replaced by sown monocultures of cultivated varieties of grasses and clovers, such as perennial ryegrass and white clover. In many parts of the world, "unimproved" grasslands are one of the most threatened types of habitat, and a target for acquisition by wildlife conservation groups or for special grants to landowners who are encouraged to manage them appropriately.

Vegetation
.jpeg.webp)
Grassland vegetation can vary considerably depending on the grassland type and on how strong it is affected by human impact. Dominant trees for the semi-natural grassland are Quercus robur, Betula pendula, Corylus avellana, Crataegus and many kinds of herbs.[20]
In chalk grassland, the plants can vary from height to very short. Quite tall grasses can be found in North American tallgrass prairie, South American grasslands, and African savanna. Woody plants, shrubs or trees may occur on some grasslands – forming savannas, scrubby grassland or semi-wooded grassland, such as the African savannas or the Iberian deheza.[21]
As flowering plants and trees, grasses grow in great concentrations in climates where annual rainfall ranges between 500 and 900 mm (20 and 35 in).[22] The root systems of perennial grasses and forbs form complex mats that hold the soil in place.


Fauna
Grasslands support the greatest aggregations of large animals on earth, including jaguars, African wild dogs, pronghorn, black-footed ferret, plains bison, mountain plover, African elephant, Sunda tiger, black rhino, white rhino, savanna elephant, greater one-horned rhino, Indian elephant and swift fox. Grazing animals, herd animals, and predators in grasslands, like lions and cheetahs live in the grasslands of the African savanna.[23] Mites, insect larvaenematodes, and earthworms inhabit deep soil, which can reach 6 meters underground in undisturbed grasslands on the richest soils of the world. These invertebrates, along with symbiotic fungi, extend the root systems, break apart hard soil, enrich it with urea and other natural fertilizers, trap minerals and water and promote growth. Some types of fungi make the plants more resistant to insect and microbial attacks.[24]
Grassland in all its form supports a vast variety of mammals, reptiles, birds, and insects. Typical large mammals include the blue wildebeest, American bison, giant anteater, and Przewalski's horse.[25]
Threats
Grasslands are very sensitive to disturbances, such as people hunting and killing key species, or plowing the land to make more space for farms.
To feed a growing human population, most of the world's grasslands, including the American prairies, are converted from natural landscapes to fields of corn, wheat or other crops. Grasslands that have remained largely intact thus far, like East African savannas, are in danger of being lost to agriculture.[23]
The plants and animals that live in grasslands are connected through an unlimited web of interactions. But the removal of key species—such as buffalo and prairie dogs within the American West—and introduction of invasive species, like cane toads in northern Australia, have disrupted the balance in these ecosystems and damaged a number of other species.[23]
Grasslands are home to a number of the foremost magnificent animals on the planet—elephants, bison, lions—and hunters have found them to be enticing prey. But when hunting isn't controlled or is conducted illegally, species can become extinct.[23]
Effects of climate change
Grasslands often occur in areas with annual precipitation is between 600 mm (24 in) and 1,500 mm (59 in) and average mean annual temperatures ranges from −5 and 20 °C.[26] However, some grasslands occur in colder (−20 °C) and hotter (30 °C) climatic conditions. Grassland can exist in habitats that are frequently disturbed by grazing or fire, as such disturbance prevents the encroachment of woody species.[27] Species richness is particularly high in grasslands of low soil fertility such as serpentine barrens and calcareous grasslands, where woody encroachment is prevented as low nutrient levels in the soil may inhibit the growth of forest and shrub species. Another common predicament often experienced by the ill-fated grassland creatures is the constant burning of plants, fueled by oxygen and many expired photosynthesizing organisms, with the lack of rain pushing this problem to further heights.[28] When not limited by other factors, increasing CO2 concentration in the air increases plant growth, similarly as water use efficiency, which is very important in drier regions. However, the advantages of elevated CO2 are limited by factors including water availability and available nutrients, particularly nitrogen. Thus effects of elevated CO2 on plant growth will vary with local climate patterns, species adaptations to water limitations, and nitrogen availability. Studies indicate that nutrient depletion may happen faster in drier regions, and with factors like plant community composition and grazing. Nitrogen deposition from air pollutants and increased mineralization from higher temperatures can increase plant productivity, but increases are often among a discount in biodiversity as faster-growing plants outcompete others. A study of a California grassland found that global change may speed reductions in diversity and forb species are most prone to this process.[29]
Human impact and economic importance
The grasslands we see today have an extensive history of human activity and disturbance.[29]
Grassland vegetation is often a plagioclimax; it remains dominant in a particular area usually due to grazing, cutting, or natural or man-made fires, all discouraging colonization by and survival of tree and shrub seedlings.[30] Some of the world's largest expanses of grassland are found in the African savanna, and these are maintained by wild herbivores as well as by nomadic pastoralists and their cattle, sheep or goats. Grasslands have an impact on climate change by slower decomposition rates of litter compared to forest environments.[31]
Herbaceous (non-wooded) vegetation dominates grasslands and, unlike forests, carbon is stored in the roots and soil underground. Furthermore, this above-ground biomass carbon is relatively short-lived due to grazing, fire, and senescence. In contrast, grassland species have an extensive fibrous root system, with grasses often accounting for 60-80% of the biomass carbon in this ecosystem. This underground biomass can extend several meters below the surface and store abundant carbon into the soil, resulting in deep, fertile soils with high organic matter content. For this reason, soil carbon accounts for about 81% of the total ecosystem carbon in grasslands. The close link between soil carbon and underground biomass leads to similar responses of these carbon pools to fluctuations in annual precipitation and temperature on a broad spatial scale. Because plant productivity is limited by grassland precipitation, carbon stocks are highest in regions where precipitation is heaviest, such as the high grass prairie in the humid temperate region of the United States. Similarly, as annual temperatures rise, grassland carbon stocks decrease due to increased evapotranspiration.[32]
Grasslands have suffered large losses of organic carbon due to soil disturbances, vegetation degradation, fires, erosion, nutrient deficiencies, and water shortages. The type, frequency and intensity of the disturbance can play a key role in the soil organic carbon (SOC) balance of grasslands. Bedrock, irrigation practices, soil acidification, liming, and pasture management can all have potential impacts on grassland organic carbon stocks.[33]
Grasslands may occur naturally or as a result of human activity. Hunting cultures around the world often set regular fires to maintain and extend grasslands and prevent fire-intolerant trees and shrubs from taking hold. The tallgrass prairies in the U.S. Midwest may have been extended eastward into Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio by human agency. Much grassland in northwest Europe developed after the Neolithic Period when people gradually cleared the forest to create areas for raising their livestock.[34]
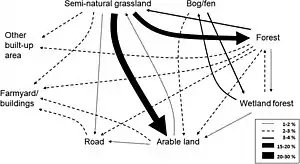
Land cover has always changed during the years. The following relates to the changes between 1960 and 2015. There has been a decrease in semi-natural grasslands and an increase in areas with arable land, forest and land used for infrastructure and buildings. The line style and relative thickness of the lines indicates the percentage of the total area that changed. Changes less than 1% and land-cover classes with all changes less than 1% (i.e. semi-natural wetlands and water) are not included.[19]
In 1960 most of the land, 49.7%, was covered with forest and there was also more semi-natural grassland (18.8%) than arable land (15.8%). In 2015 this has changed drastically. The forest cover has increased (50.8%) and arable land has also increased (20.4%), but the semi-natural grassland cover has decreased. Although it still covers a large area of the earth (10.6%).[19]
A quarter of semi-natural grassland was lost through intensification, i.e. it was converted into arable or pasture land and forests.[35] It is more likely that intensification will occur in flat semi-natural grasslands, especially if the soil is fertile. On the other hand, grasslands, where the land is drought-prone or less productive, are more likely to persist as semi-natural grasslands than grasslands with fertile soil and low gradient of the terrain.[36] Furthermore, the accessibility of the land is also important, as it is then easier to fertilize, for example. For instance, if it is located near a road. With the development of technology, it is becoming increasingly easy to cultivate land with a steeper gradient, to the detriment of grasslands. The management of grasslands is also changing permanently. There is increased use of mineral fertilizers, furthermore borders and field edges are removed to enlarge fields and leveling the terrain to facilitate the use of agricultural machinery.[19]
The professional study of dry grasslands falls under the category of rangeland management, which focuses on ecosystem services associated with the grass-dominated arid and semi-arid rangelands of the world. Rangelands account for an estimated 70% of the earth's landmass; thus, many cultures including those of the United States are indebted to the economics that the world's grasslands have to offer, from producing grazing animals, tourism, ecosystems services such as clean water and air, and energy extraction.[37]
Temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands ecoregions
The grassland ecoregions of the temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome are:
| Canterbury-Otago tussock grasslands | New Zealand |
| Eastern Australia mulga shrublands | Australia |
| Southeast Australia temperate savanna | Australia |
| Argentine Espinal | Argentina |
| Argentine Monte | Argentina |
| Humid Pampas | Argentina, Uruguay |
| Patagonian grasslands | Argentina |
| Patagonian steppe | Argentina |
| Semi-arid Pampas | Argentina |
Tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands ecoregions
| Arnhem Land tropical savanna | Australia |
| Brigalow tropical savanna | Australia |
| Cape York Peninsula tropical savanna | Australia |
| Carpentaria tropical savanna | Australia |
| Einasleigh Uplands savanna | Australia |
| Kimberley tropical savanna | Australia |
| Mitchell grass downs | Australia |
| Trans-Fly savanna and grasslands | Indonesia, Papua New Guinea |
| Victoria Plains tropical savanna | Australia |
| Terai-Duar savanna and grasslands | Bhutan, India, Nepal |
| Western Gulf coastal grasslands | Mexico, United States |
| Beni savanna | Bolivia |
| Campos rupestres | Brazil |
| Cerrado | Bolivia, Brazil, Paraguay |
| Clipperton Island shrub and grasslands | Clipperton Island is an overseas territory of France |
| Córdoba montane savanna | Argentina |
| Guianan savanna | Brazil, Guyana, Venezuela |
| Gran Chaco | Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, Bolivia |
| Llanos | Venezuela, Colombia |
| Uruguayan savanna | Argentina, Brazil, Uruguay |
| Hawaiian tropical high shrublands | Hawaiʻi |
| Hawaiian tropical low shrublands | Hawaiʻi |
| Northwestern Hawaii scrub | Hawaiʻi, Midway Atoll |
References
- Gibson, David J. (2009). Grasses and grassland ecology. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-154609-9. OCLC 308648056.
- "Landscape images from the Nordic countries". 2015-08-19. doi:10.6027/9789289342414-11-en. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Rūsiņa, Solvita (2012-09-10). "Semi-natural Grassland Vegetation Database of Latvia". Biodiversity & Ecology. 4: 409. doi:10.7809/b-e.00197. ISSN 1613-9801.
- Waldén, Emelie 1984- (2018). Restoration of semi-natural grasslands Impacts on biodiversity, ecosystem services and stakeholder perceptions. Lindborg, Regina., Helm, Aveliina., Landscape Ecology. Stockholm: Department of Physical Geography, Stockholm University. ISBN 978-91-7797-172-6. OCLC 1038678595.
- Johansen, Line; Westin, Anna; Wehn, Sølvi; Iuga, Anamaria; Ivascu, Cosmin Marius; Kallioniemi, Eveliina; Lennartsson, Tommy (April 2019). "Traditional semi-natural grassland management with heterogeneous mowing times enhances flower resources for pollinators in agricultural landscapes". Global Ecology and Conservation. 18: e00619. doi:10.1016/j.gecco.2019.e00619.
- Pärtel, M. (2005). "Biodiversity in temperate European grasslands: origin and conservation". Grassland Science in Europe. 10: 1–14.
- Schimper, A. F. W. 1898. Pflanzen-Geographie auf physiologischer Grundlage. Fisher, Jena. 876 pp. English translation, 1903.
- Ellenberg, H. & D. Mueller-Dombois. 1967. Tentative physiognomic-ecological classification of plant formations of the Earth [based on a discussion draft of the UNESCO working group on vegetation classification and mapping.] Berichte des Geobotanischen Institutes der Eidg. Techn. Hochschule, Stiftung Rübel, Zürich 37 (1965-1966): 21—55, .
- Laycock, W.A. 1979. Introduction, pp. 1-2, in: French. N R. (ed.). Perspectives in Grassland Ecology. Springer, New York, 204 pp., .
- "Tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas and shrublands | Biomes | WWF". World Wildlife Fund. Retrieved 2020-05-20.
- "Temperate grasslands, savannas and shrublands | Biomes | WWF". World Wildlife Fund. Retrieved 2020-05-20.
- "Flooded grasslands and savannas | Biomes | WWF". World Wildlife Fund. Retrieved 2020-05-20.
- "Montane grasslands and shrublands | Biomes | WWF". World Wildlife Fund. Retrieved 2020-05-20.
- "Tundra | Biomes | WWF". World Wildlife Fund. Retrieved 2020-05-20.
- "Deserts and xeric shrublands | Biomes | WWF". World Wildlife Fund. Retrieved 2020-05-20.
- Piperno, D. R.; Sues, HD (2005). "Dinosaurs Dined on Grass". Science. 310 (5751): 1126–8. doi:10.1126/science.1121020. PMID 16293745. S2CID 83493897.
- "University of California Museum of Paleontology Grasslands website". Ucmp.berkeley.edu. Retrieved 2011-12-01.
- Kunz, Werner, 1940- (2016). Species conservation in managed habitats : the myth of a pristine nature with a preamble by Josef H. Reichholf. Weinheim, Germany. ISBN 978-3-527-68884-5. OCLC 948690426.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Aune, Sigrun; Bryn, Anders; Hovstad, Knut Anders (2018-07-04). "Loss of semi-natural grassland in a boreal landscape: impacts of agricultural intensification and abandonment". Journal of Land Use Science. 13 (4): 375–390. doi:10.1080/1747423X.2018.1539779. ISSN 1747-423X.
- Wahlman, Henrik; Milberg, Per (2002). "Management of semi-natural grassland vegetation: evaluation of a long-term experiment in southern Sweden". Annales Botanici Fennici. 39 (2): 159–166. ISSN 0003-3847. JSTOR 23726791.
- "University of California Museum of Paleontology". ucmp.berkeley.edu. Retrieved 2020-05-20.
- "NASA Earth Observatory webpage". Earthobservatory.nasa.gov. Retrieved 2011-12-01.
- "Grasslands | Habitats | WWF". World Wildlife Fund. Retrieved 2020-05-20.
- Menta, Cristina (2012-08-29), Lameed, Gbolagade Akeem (ed.), Biodiversity Conservation and Utilization in a Diverse World, InTech, doi:10.5772/51091, ISBN 978-953-51-0719-4, retrieved 2020-05-20 Missing or empty
|title=(help);|chapter=ignored (help) - "44.3D: Temperate Grasslands". Biology LibreTexts. 2018-07-17. Retrieved 2020-05-20.
- "EO Experiments: Grassland Biome". Earthobservatory.nasa.gov. Retrieved 2011-12-01.
- "GEOGRAPHICAL INQUIRY". GEOGRAPHICAL INQUIRY. Retrieved 2020-05-20.
- Craven, Dylan; Isbell, Forest; Manning, Pete; Connolly, John; Bruelheide, Helge; Ebeling, Anne; Roscher, Christiane; van Ruijven, Jasper; Weigelt, Alexandra; Wilsey, Brian; Beierkuhnlein, Carl (2016-05-19). "Plant diversity effects on grassland productivity are robust to both nutrient enrichment and drought". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 371 (1694): 20150277. doi:10.1098/rstb.2015.0277. ISSN 0962-8436. PMC 4843698. PMID 27114579.
- "Grasslands and Climate Change | Climate Change Resource Center". www.fs.usda.gov. Retrieved 2020-05-20.
- Ochoa-Hueso, R; Delgado-Baquerizo, M; King, PTA; Benham, M; Arca, V; Power, SA (2019). "Ecosystem type and resource quality are more important than global change drivers in regulating early stages of litter decomposition". Soil Biology and Biochemistry. 129: 144–152. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2018.11.009.
- Liu, Jun; Feng, Chao; Wang, Deli; Wang, Ling; Wilsey, Brian J.; Zhong, Zhiwei (August 2015). Firn, Jennifer (ed.). "Impacts of grazing by different large herbivores in grassland depend on plant species diversity". Journal of Applied Ecology. 52 (4): 1053–1062. doi:10.1111/1365-2664.12456.
- "Grassland Carbon Management | Climate Change Resource Center". www.fs.usda.gov. Retrieved 2020-05-20.
- Lorenz, Klaus; Lal, Rattan (2018), "Carbon Sequestration in Grassland Soils", Carbon Sequestration in Agricultural Ecosystems, Springer International Publishing, pp. 175–209, doi:10.1007/978-3-319-92318-5_4, ISBN 978-3-319-92317-8
- "Grasslands Information and Facts". National Geographic. 2019-03-15. Retrieved 2020-05-20.
- Monteiro, Antonio T.; Fava, Francesco; Hiltbrunner, Erika; Della Marianna, Giampaolo; Bocchi, Stefano (April 2011). "Assessment of land cover changes and spatial drivers behind loss of permanent meadows in the lowlands of Italian Alps". Landscape and Urban Planning. 100 (3): 287–294. doi:10.1016/j.landurbplan.2010.12.015. ISSN 0169-2046.
- Cousins, Sara A. O.; Auffret, Alistair G.; Lindgren, Jessica; Tränk, Louise (January 2015). "Regional-scale land-cover change during the 20th century and its consequences for biodiversity". AMBIO. 44 (S1): 17–27. doi:10.1007/s13280-014-0585-9. ISSN 0044-7447. PMC 4288995. PMID 25576277.
- "Grassland of the world". www.fao.org. Retrieved 2020-05-20.
Further reading
- Courtwright, Julie. 2011. Prairie Fire: A Great Plains History. University Press of Kansas. 274 pp.
- French, N. R. (ed.). 1979. Perspectives in Grassland Ecology. Springer, New York, 204 pp., .
- Suttie, J. M.; Reynolds, S. G.; C. Batello. 2005. Grasslands of the world. Rome: FAO. .
- Wilsey, B.J. 2018. Biology of Grasslands. Oxford University Press
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Grasslands. |