Maralbexi County
Maralbexi County[4][5] (Maralbeshi,[6] Maralbishi,[7][8][9] transliterated from Uighur: مارالبېشى ناھىيىسى; Chinese: 玛热勒巴什县), Bachu County (Chinese: 巴楚县), and Chinese: 巴尔楚克县) the former long Chinese name as well, is located in the southwest of the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region of the People's Republic of China and is under the administration of the Kashgar Prefecture. It has an area of 18,491 km2 (7,139 sq mi), and surrounds, but does not administer, the sub-prefecture-level city of Tumxuk. According to the 2002 census, it has a population of 380,000.
Maralbexi County
مارالبېشى ناھىيىسى 巴楚县 Bachu; Maralbashi; Maralbeshi; Pachu | |
|---|---|
 | |
.png.webp) Location of the county (red) within Kashgar Prefecture (yellow) and Xinjiang | |
 Maralbexi Location of the seat in Xinjiang | |
| Coordinates: 39°46′43″N 78°34′30″E | |
| Country | People's Republic of China |
| Autonomous region | Xinjiang |
| Prefecture | Kashgar Prefecture |
| Area | |
| • Total | 18,490.59 km2 (7,139.26 sq mi) |
| Population (2002) | |
| • Total | 380,000 |
| • Density | 21/km2 (53/sq mi) |
| Ethnic groups | |
| • Major ethnic groups | Uyghur[2][3] |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (China Standard) |
| Postal code | 843800 |
| Website | bachu |
| Maralbexi County | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Uyghur name | |||||||||||
| Uyghur | مارالبېشى ناھىيىسى | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Chinese name | |||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 巴楚縣 | ||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 巴楚县 | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Alternative Chinese name | |||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 巴爾楚克縣 | ||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 巴尔楚克县 | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Second alternative Chinese name | |||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 瑪熱勒巴什縣 | ||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 玛热勒巴什县 | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
History
In 1913, Maralbexi County was established.[1][10]
In September 1937, two regiments of Soviet Kirghiz troops and one regiment of Russian troops equipped with forty airplanes and twenty tanks entered Sinkiang from Atushe and attacked Maralbexi, dividing Ma Hushan's 36th Corps into two sections.[11]
In February 2002, a 6.7 magnitude earthquake killed 267 people in Maralbexi County and Payzawat County.[12]
On February 24, 2003, the 2003 Bachu earthquake occurred.
In April 2013, twenty-one died in an incident in Seriqbuya.[13][14]
In October 2014, twenty-two died in an incident at a farmer's market in the county.[15]
According to her husband, in May-June 2017, Mailikemu Maimati / Malika Mamiti, in her 30s, native of the county and wife of businessman Mirza Imran Baig of Pakistan, in his 40s, was detained in the county's re-education camp. After her release, she and their young son were not given their passports by Chinese authorities.[16][17]
Administrative divisions
Maralbexi County includes four towns, eight townships and other areas:[1][2][18][19][20]
Towns (بازىرى / 镇)
- Maralbeshi (Bachu Town; مارالبېشى بازىرى / 巴楚镇), Seriqbuya (Serikbuya, Selibuya; سېرىقبۇيا بازىرى / 色力布亚镇), Awat (Awati; ئاۋات بازىرى / 阿瓦提镇), Achal (Sanchakou; ئاچال بازىرى / 三岔口镇)
Townships (يېزىسى / 乡)
- Charbagh Township (Qia'erbage; چارباغ يېزىسى / 恰尔巴格乡), Doletbagh Township (Duolaitibage; دۆلەتباغ يېزىسى / 多来提巴格乡), Anarkol Township (Anakule; ئاناركۆل يېزىسى / 阿纳库勒乡), Shamal Township (Xiamale; شامال يېزىسى / 夏玛勒乡), Aqsaqmaral Township (Akesakemarele; ئاقساقمارال يېزىسى / 阿克萨克马热勒乡 / 阿克萨克玛热勒乡), Alaghir Township (Alage'er; ئالاغىر يېزىسى / 阿拉格尔乡 / 阿拉根乡), Chongqurchaq (Qiongku'erqiake; چوڭقۇرچاق يېزىسى / 琼库尔恰克乡 / 琼库恰克乡), Yengiosteng Township (Yingwusitang; يېڭىئۆستەڭ يېزىسى / 英吾斯塘乡)
Others
- Xiahe Forest Plantation (下河林场), 兵团48团, 兵团52团
Transportation
Bachu is served by the Southern Xinjiang Railway and G3012 Turpan–Hotan Expressway.
Economy
Agricultural products include corn, cotton, wheat and others as well as sword-leaf dogbane. The central and eastern parts of the county have old desert poplar forests. Animal herding is prominent and rock salt and phosphate fertilizer are produced in the county. Industries include food processing, plastics, rug making, electricity and construction.[10]
As of 1885, there was about 30,600 acres (202,728 mu) of cultivated land in Maralbexi.[21]
Demographics
| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 375,883 | — |
| 2010 | 336,274 | −1.11% |
| [1] | ||
As of 2015, 363,488 of the 382,186 residents of the county were Uyghur, 17,816 were Han Chinese and 882 were from other ethnic groups.[22]
As of 2019, the population of Maralbexi County was 95.13% Uyghur.[2]
As of 1999, 83.12% of the population of Maralbexi (Bachu) County was Uyghur and 16.41% of the population was Han Chinese.[23]
Geography
Climate
| Climate data for Maralbexi County (1971−2000) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 0.9 (33.6) |
6.4 (43.5) |
14.6 (58.3) |
23.8 (74.8) |
28.6 (83.5) |
32.1 (89.8) |
33.8 (92.8) |
32.3 (90.1) |
27.9 (82.2) |
20.8 (69.4) |
11.0 (51.8) |
2.4 (36.3) |
19.6 (67.2) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −12.2 (10.0) |
−7.4 (18.7) |
1.4 (34.5) |
9.0 (48.2) |
14.0 (57.2) |
17.4 (63.3) |
19.5 (67.1) |
18.5 (65.3) |
13.1 (55.6) |
4.8 (40.6) |
−3.4 (25.9) |
−10.1 (13.8) |
5.4 (41.7) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 0.4 (0.02) |
1.3 (0.05) |
2.5 (0.10) |
2.9 (0.11) |
7.8 (0.31) |
13.8 (0.54) |
13.2 (0.52) |
11.7 (0.46) |
4.3 (0.17) |
2.1 (0.08) |
0.3 (0.01) |
0.7 (0.03) |
61.0 (2.40) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 1.0 | 1.1 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 2.6 | 4.7 | 5.5 | 4.1 | 2.3 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 0.9 | 24.8 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 61 | 50 | 41 | 33 | 36 | 39 | 43 | 47 | 49 | 51 | 56 | 65 | 48 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 180.6 | 177.8 | 194.5 | 229.3 | 267.5 | 301.7 | 308.1 | 285.4 | 265.4 | 258.1 | 212.8 | 177.8 | 2,859 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 61 | 59 | 53 | 58 | 61 | 68 | 68 | 67 | 71 | 75 | 71 | 61 | 64 |
| Source: China Meteorological Administration | |||||||||||||
Notable persons
Historical maps
Historical English-language maps including Maralbexi:
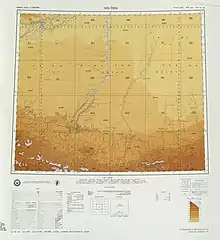 Map including Maralbexi (labeled as PA-CH'U (MARAL BASHI)) (USATC, 1971)[lower-alpha 1]
Map including Maralbexi (labeled as PA-CH'U (MARAL BASHI)) (USATC, 1971)[lower-alpha 1]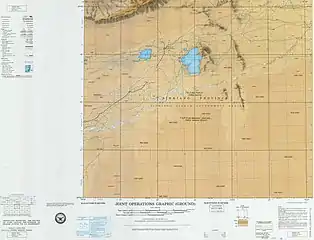 Map including Maralbexi (labeled as PA-CH'U (MARAL BASHI)) (ATC, 1971)
Map including Maralbexi (labeled as PA-CH'U (MARAL BASHI)) (ATC, 1971)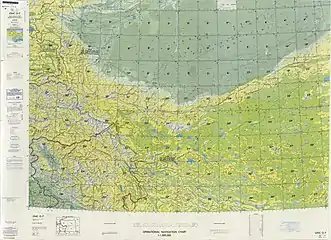 From the Operational Navigation Chart; map including Maralbexi (labeled as BACHU (PA-CH'U)) (DMA, 1980)[lower-alpha 2]
From the Operational Navigation Chart; map including Maralbexi (labeled as BACHU (PA-CH'U)) (DMA, 1980)[lower-alpha 2] Map including Maralbexi (labeled as BACHU (PA-CH'U)) (DMA, 1984)[lower-alpha 3]
Map including Maralbexi (labeled as BACHU (PA-CH'U)) (DMA, 1984)[lower-alpha 3]
See also
Notes
- From map: "DELINEATION OF INTERNATIONAL BOUNDARIES MUST NOT BE CONSIDERED AUTHORITATIVE".
- From map: "The representation of international boundaries is not necessarily authoritative."
- From map: "The representation of international boundaries is not necessarily authoritative"
External links
- Introduction to Maralbishi County, official website of Kashgar Prefecture government.
References
- 巴楚县历史沿革. XZQH.org. 14 November 2014. Retrieved 25 February 2020.
2000年第五次人口普查,巴楚县常住总人口375883人,{...}2003年,巴楚县总面积18490.59平方千米,{...}2010年第六次人口普查,巴楚县常住总人口336274人,其中:巴楚镇47704人,色力布亚镇44642人,阿瓦提镇22232人,三岔口镇737人,恰尔巴格乡27816人,多来提巴格乡28158人,阿纳库勒乡26408人,夏马勒乡10174人,阿克萨克玛热勒乡30858人,阿拉根乡29412人,琼库恰克乡37197人,英吾斯坦乡24480人,兵团四十八团6456人。
- 巴楚县概况. 巴楚县人民政府网 (in Chinese). 8 December 2019. Retrieved 25 February 2020.
巴楚县辖8乡4镇1个良种繁育场,229个村(社区),总人口38.51万人,其中农村户籍人口29.91万人,有汉族、维吾尔族、回族、哈萨克族等31个民族,维吾尔族占95.13%。
- 1997年巴楚县行政区划 [1997 Maralbexi County Administrative Divisions]. XZQH.org. 18 January 2011. Retrieved 4 April 2020.
喀什地区辖县。位于喀什地区东部。面积21741.8平方千米,人口33.1万,有维吾尔、汉、 回等民族,其中维吾尔族占83.03%,汉族占16.4%,辖4镇8乡。
- Zhang Dongmiao, ed. (5 March 2017). "Xinjiang finishes first round of universal health checks". Xinhua News Agency. Retrieved 23 February 2020.
Thanks to the first universal health check in northwest China's Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, Mtailipu Rosuli, 65, a Uygur man in Bachu (Maralbexi) County, had his first health examination of his life.
- Ben Blanchard (30 April 2013). Stephen Coates (ed.). "China says detains 19, seizes weapons after Xinjiang unrest". Reuters. Retrieved 23 February 2020.
The government has labeled the violence in Kashgar’s Maralbexi county as a “terrorist attack”, though the exiled World Uyghur Congress has said the shooting and killing of a young Uighur by “Chinese armed personnel” prompted the Uighurs to retaliate.
- Joshua Lipes (22 November 2019). "Xinjiang Authorities Undermine Muslim Abstention From Pork in Bid to Assimilate Uyghurs". Radio Free Asia. Translated by Elise Anderson. Retrieved 23 February 2020.
In October 2018, a photo was posted online by the government of Kashgar (in Chinese, Kashi) prefecture’s Maralbeshi (Bachu) county, which portrayed a Uyghur village head eating a piece of pork and calling on other Uyghurs to join him. The photo was taken down shortly after publishing.
RFA recently spoke with a village head in Maralbeshi who confirmed that the photo was real, and that local authorities are teaching people to eat pork as well. - "Kashgar Tourism". Archived from the original on 22 August 2012. Retrieved 6 April 2020 – via Internet Archive.
Maralbishi County
- Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development (2010). 建筑抗震设计规范 [GB50011-2010: Code for Seismic Design of Buildings] (in English and Chinese). Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press. p. 203 – via Google Books.
Marabishi [sic] County
- "Project Beauty Unveils China's Ugly Side". Newsweek Pakistan. 25 November 2013. Retrieved 7 April 2020.
But they also argue that some officials’ aggressive approach sparked resentment and violence, including an April attack by Uighurs on police in Maralbishi outside Kashgar that left 21 people dead. Beijing blamed “terrorists” who “regularly watched video clips advocating religious extremism.”
- 夏征农; 陈至立, eds. (September 2009). 辞海:第六版彩图本 [Cihai (Sixth Edition in Color)] (in Chinese). Shanghai: Shanghai Lexicographical Publishing House. p. 58. ISBN 9787532628599.
- Arthur C. Hasiotis, Jr. (1987). Soviet Political, Economic, and Military Involvement in Sinkiang from 1928 to 1949. Garland Publishing. pp. 102-103. ISBN 0-8240-8055-6.
- Nabijan Tursun (2007). Uyghur Reader. Dunwoody Press. p. 141. ISBN 978-1-931546-42-3.
- Luisetta Mudie, Parameswaran Ponnudurai. (24 April 2013). "Xinjiang Violence Leaves 21 Dead". Radio Free Asia. Retrieved 25 February 2020.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
- "Overview of the Maralbeshi Incident on 23 April 2013" (PDF). World Uyghur Congress. May 2013. Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 August 2016.
- Shohret Hoshur, Parameswaran Ponnudurai (18 October 2014). "22 Killed in Farmers' Market Attack in Xinjiang's Kashgar Prefecture". Radio Free Asia. Translated by Shohret Hoshur. Retrieved 25 February 2020.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
- Christian Shepherd, Philip Wen (25 September 2018). "'China's big mistake': Pakistanis lobby to free wives trapped in Xinjiang". Reuters. Retrieved 7 April 2020.
Mirza Imran Baig, 40, who trades between his home city of Lahore and Urumqui, the Xinjiang regional capital, said his wife was detained in a “re-education” camp in her native Bachu county for two months in May and June 2017 and had been unable to leave her hometown since her release.
CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link) - Linette Lopez (15 December 2019). "China's next gambit to save its economy will export dystopia worldwide". Business Insider. Retrieved 7 April 2020.
Pakistani businessman Mirza Imran Baig shows a picture with his Uighur wife, Malika Mamiti, outside the Pakistani embassy in Beijing. Mamiti, was sent to a political-indoctrination camp after returning to China's far west Xinjiang region in May 2017, Baig said. Scores of Pakistani men whose Muslim Uighur wives have disappeared into internment camps in China feel helpless, fighting a wall of silence as they struggle to reunite their families.
- 2018年统计用区划代码和城乡划分代码:巴楚县 (in Chinese). National Bureau of Statistics of the People's Republic of China. 2018. Retrieved 23 February 2020.
统计用区划代码 名称 653130100000 巴楚镇 653130101000 色力布亚镇 653130102000 阿瓦提镇 653130103000 三岔口镇 653130200000 恰尔巴格乡 653130201000 多来提巴格乡 653130202000 阿纳库勒乡 653130203000 夏马勒乡 653130204000 阿克萨克玛热勒乡 653130205000 阿拉根乡 653130206000 琼库恰克乡 653130207000 英吾斯坦乡 653130508000 兵团四十八团
- 行政区划. 巴楚县人民政府网 (in Chinese). 24 December 2019. Retrieved 23 February 2020.
巴楚县辖4个镇、8个乡:巴楚镇、色力布亚镇、阿瓦提镇、三岔口镇、恰尔巴格乡、多来提巴格乡、阿纳库勒乡、夏马勒乡、阿克萨克马热勒乡、阿拉格尔乡、琼库尔恰克乡、英吾斯塘乡。
- Xie Yuzhong 解玉忠 (2003). 地名中的新疆 (in Chinese). Ürümqi: 新疆人民出版社. pp. 230–233. ISBN 7-228-08004-1.
- Herold J. Wiens (November 1966). "Cultivation Development and Expansion in China's Colonial Realm in Central Asia". The Journal of Asian Studies. 26 (1): 75. JSTOR 2051832 – via JSTOR.
- 3-7 各地、州、市、县(市)分民族人口数 (in Chinese). شىنجاڭ ئۇيغۇر ئاپتونوم رايونى 新疆维吾尔自治区统计局 Statistic Bureau of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region. 15 March 2017. Archived from the original on 11 October 2017. Retrieved 3 September 2017.
- Morris Rossabi, ed. (2004). Governing China's Multiethnic Frontiers (PDF). University of Washington Press. p. 179. ISBN 0-295-98390-6.
| Look up Maralbexi, Bachu, or Pa-ch'u in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |