Nevers
Nevers (/nəˈvɛər/ nə-VAIR, French: [nəvɛʁ] (![]() listen); Latin: Noviodunum, later Nevirnum and Nebirnum) is the prefecture of the Nièvre department in the Bourgogne-Franche-Comté region in central France. It was the principal city of the former province of Nivernais. It is 260 km (160 mi) south-southeast of Paris.
listen); Latin: Noviodunum, later Nevirnum and Nebirnum) is the prefecture of the Nièvre department in the Bourgogne-Franche-Comté region in central France. It was the principal city of the former province of Nivernais. It is 260 km (160 mi) south-southeast of Paris.
Nevers | |
|---|---|
Prefecture and commune | |
 Panoramic view of Nevers, France. | |
 Coat of arms | |
Location of Nevers 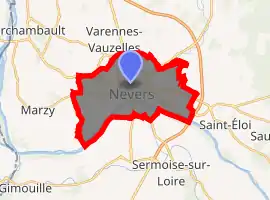
| |
 Nevers  Nevers | |
| Coordinates: 46°59′36″N 3°09′26″E | |
| Country | France |
| Region | Bourgogne-Franche-Comté |
| Department | Nièvre |
| Arrondissement | Nevers |
| Canton | Nevers-1, 2, 3 and 4 |
| Intercommunality | CA Nevers |
| Government | |
| • Mayor (2020–2026) | Denis Thuriot |
| Area 1 | 17.33 km2 (6.69 sq mi) |
| Population (2017-01-01)[1] | 32,990 |
| • Density | 1,900/km2 (4,900/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| INSEE/Postal code | 58194 /58000 |
| Elevation | 167–238 m (548–781 ft) (avg. 180 m or 590 ft) |
| 1 French Land Register data, which excludes lakes, ponds, glaciers > 1 km2 (0.386 sq mi or 247 acres) and river estuaries. | |
History
Nevers first enters written history as Noviodunum, a town held by the Aedui at Roman contact. The quantities of medals and other Roman antiquities found on the site indicate the importance of the place,[2] and in 52 BCE, Julius Caesar made Noviodunum, which he describes as in a convenient position on the banks of the Loire, a depot (B. G. vii. 55). There he had his hostages, corn, his military chest, with the money in it allowed him from home for the war, his own and his army's baggage and a great number of horses which had been bought for him in Spain and Italy. After his failure before Gergovia, the Aedui at Noviodunum massacred those who were there to look after stores, the negotiators, and the travelers who were in the place. They divided the money and the horses among themselves, carried off in boats all the corn that they could, and burned the rest or threw it into the river. Thinking they could not hold the town, they burned it. This was a great loss to Caesar; and it may seem that he was imprudent in leaving such great stores in the power of treacherous allies. But he was in straits during this year, and probably he could not have done other than he did. Dio Cassius (xl. 38) tells the story of Caesar out of the affair of Noviodunum. He states incorrectly what Caesar did on the occasion, and he shows that he neither understood his original nor knew what he was writing about.
The city was later called Nevirnum, as the name appears in the Antonine Itinerary. In the Tabula Peutingeriana, it is corrupted into Ebrinum. In still other sources the name appears as Nebirnum or Nivernum.
It became the seat of a bishopric at the end of the 5th century. The county dates at least from the beginning of the 10th century. The citizens of Nevers obtained charters in 1194 and in 1231. For a short time in the 14th century the town was the seat of a university, transferred from Orléans, to which it was restored.[2]
In 1565 the town became the seat of a branch of the Gonzaga family, who in 1627 succeeded to the Duchy of Mantua. This line of the Gonzaga Dukes of Nevers itself died out in 1708.
Geography
Nevers is situated on the slope of a hill on the right bank of the Loire River.[2]
Climate
| Climate data for Nevers (1981–2010 averages) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 17.2 (63.0) |
23.5 (74.3) |
26.7 (80.1) |
30.0 (86.0) |
31.0 (87.8) |
39.0 (102.2) |
38.7 (101.7) |
39.2 (102.6) |
35.1 (95.2) |
30.2 (86.4) |
23.5 (74.3) |
19.5 (67.1) |
39.2 (102.6) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 6.7 (44.1) |
8.3 (46.9) |
12.4 (54.3) |
15.4 (59.7) |
19.4 (66.9) |
22.8 (73.0) |
25.5 (77.9) |
25.2 (77.4) |
21.4 (70.5) |
16.7 (62.1) |
10.5 (50.9) |
7.1 (44.8) |
16.0 (60.8) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 0.2 (32.4) |
−0.1 (31.8) |
1.8 (35.2) |
3.9 (39.0) |
7.9 (46.2) |
10.9 (51.6) |
12.8 (55.0) |
12.3 (54.1) |
9.1 (48.4) |
7.0 (44.6) |
2.8 (37.0) |
0.8 (33.4) |
5.8 (42.4) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −25 (−13) |
−21.8 (−7.2) |
−13.8 (7.2) |
−7.5 (18.5) |
−4.8 (23.4) |
0.2 (32.4) |
3.4 (38.1) |
0.3 (32.5) |
−1.2 (29.8) |
−8.9 (16.0) |
−12.3 (9.9) |
−16.8 (1.8) |
−21.8 (−7.2) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 62.0 (2.44) |
57.8 (2.28) |
54.3 (2.14) |
68.7 (2.70) |
80.1 (3.15) |
70.1 (2.76) |
61.8 (2.43) |
60.9 (2.40) |
67.5 (2.66) |
77.6 (3.06) |
70.1 (2.76) |
73.2 (2.88) |
804.1 (31.66) |
| Average precipitation days | 12.0 | 10.0 | 10.3 | 10.7 | 11.5 | 8.8 | 8.3 | 8.3 | 8.4 | 11.0 | 11.6 | 11.7 | 122.7 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 87 | 82 | 78 | 74 | 77 | 76 | 74 | 77 | 80 | 85 | 87 | 87 | 80.3 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 65.5 | 85.6 | 147.7 | 170.3 | 197.9 | 223.2 | 235.0 | 227.5 | 180.0 | 121.0 | 65.4 | 54.9 | 1,774 |
| Source 1: Météo France[3][4] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Infoclimat.fr (humidity, 1961–1990)[5] | |||||||||||||
Main sights


Narrow winding streets lead from the quay through the town where there are numerous old houses dating from the 14th to the 17th century.[2]
Among the ecclesiastical buildings the most important is the Cathédrale of Saint Cyr-Sainte Julitte, dedicated to Saint Quiricus and Saint Julietta, which is a combination of two buildings, and possesses two apses. The apse and transept at the west end are the remains of a Romanesque church, while the nave and eastern apse are in the Gothic style and belong to the 14th century. There is no transept at the eastern end. The lateral portal on the south side belongs to the late 15th century; the massive and elaborately decorated tower which rises beside it to the early 16th century.[2]
The church of Saint Etienne is a specimen of the Romanesque style of Auvergne of which the disposition of the apse with its three radiating chapels is characteristic. It was consecrated at the close of the 9th century, and belonged to a priory affiliated to Cluny.[2]
The Ducal Palace (now occupied by the courts of justice and an important ceramic museum) was built in the 15th and 16th centuries and is one of the principal feudal edifices in central France. The façade is flanked at each end by a turret and a round tower. A middle tower containing the great staircase has its windows adorned by sculptures relating to the history of the House of La Marck by the members of which the greater part of the palace was built.[2]
Behind the palace lies an open space with a fine view over the valley of the Loire. The Porte du Croux, a square tower, with corner turrets, dating from the end of the 14th century, is among the remnants of the old fortifications; it now contains a collection of sculptures and Roman antiquities.[2]
A triumphal arch from the 18th century, commemorating the victory of Fontenoy and the hotel de ville, a modern building which contains the library, are of some interest. The Loire is crossed by a modern stone bridge, and by an iron railway bridge.[2]
At the Chapel of Saint Bernadette at the mother house of the Sisters of Charity of Nevers, it is possible to view the incorrupt body of Saint Bernadette Soubirous, the famous seer of Our Lady of Lourdes apparitions, which are presented in a gold and crystal reliquary.
Economy
Nevers is the seat of a bishopric, of tribunals of first instance and of commerce and of a Cour d'assises and has a chamber of commerce and a branch of the Bank of France. Its educational institutions include several lycées, a training college for female teachers, ecclesiastical seminaries, a school of art of the automotive engineering college Institut supérieur de l'automobile et des transports. The town manufactures porcelain, agricultural implements, chemical manures, glue, boilers and iron goods, boots and shoes and fur garments, and has distilleries, tanneries and dye works. Its trade is in iron and steel, wood, wine, grain, livestock, etc. hydraulic lime, kaolin and clay for the manufacture of faience are worked in the vicinity.[2]
Transport
The Gare de Nevers railway station offers connections to Paris, Dijon, Lyon, Clermont-Ferrand and several regional destinations. The A77 motorway connects Nevers with Paris.
Population
|
|
Notable people
- Marie Louise Gonzaga, Queen of Poland, born in Nevers in 1611
- Marie Casimire Louise de La Grange d'Arquien, Queen of Poland, born in Nevers in 1641
- Pierre Gaspard Chaumette, revolutionary, born in Nevers in 1763
- Bernadette Soubirous, better known as Saint Bernadette of Lourdes, died in Nevers in 1879 (aged 35).
- Anne Boutiaut, born in Nevers in 1851 and later known as La Mère Poulard in Mont St-Michel.
- Michel Vieuchange, Saharan explorer, adventurer and writer, born in Nevers in 1904, where there is a street named after him
- Jean Vieuchange, editor of Michel Vieuchange's travel notebooks, born in Nevers in 1906
- Pierre Bérégovoy, former Prime Minister of France, committed suicide in 1993 in Nevers
- Parfait Mandanda, footballer, born in Nevers in 1989
- Valérie Beauvais, politician, born in Nevers in 1963
- Benjamin "uNKOE" Chevasson, professional Overwatch player for the Dallas Fuel
Culture
Nevers has been known for several centuries for its Nevers faience.
The Formula One circuit of Magny-Cours is located near Nevers.
The anonymous French woman (played by Emmanuelle Riva) who is the main character in the film Hiroshima mon amour by Alain Resnais is from Nevers, and the film features many flashbacks to her youth there during World War II. In the final scene of the film, her Japanese lover tells her "You are Nevers". There is a lot of play on the English translation of the town's name throughout the film, with dialogue such as "Nevers ? Jamais !" ("Nevers? Never!")
Most of the scenes in the film Rosalie Blum were filmed in Nevers between March and April 2015, with the exception of the end scenes, which were filmed at Leffrinckoucke in the Nord.
Nevers is also the setting of most of the second half of Éric Rohmer's 1992 film, Conte d'Hiver.
International relations
 Koblenz, Germany
Koblenz, Germany Erzsébetváros (Budapest), Hungary
Erzsébetváros (Budapest), Hungary Mantua, Italy
Mantua, Italy St Albans, England, United Kingdom
St Albans, England, United Kingdom Lund, Sweden
Lund, Sweden Stavroupoli, Greece
Stavroupoli, Greece Curtea de Argeș, Romania
Curtea de Argeș, Romania Taizhou, China
Taizhou, China Charleville-Mézières, France
Charleville-Mézières, France Hammamet, Tunisia
Hammamet, Tunisia Neubrandenburg, Germany
Neubrandenburg, Germany
References
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Smith, William, ed. (1854–1857). "Noviodunum". Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography. London: John Murray.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Smith, William, ed. (1854–1857). "Noviodunum". Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography. London: John Murray.
- "Populations légales 2017". INSEE. Retrieved 6 January 2020.
-
 One or more of the preceding sentences incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Nevers". Encyclopædia Britannica. 19 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 456–457.
One or more of the preceding sentences incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Nevers". Encyclopædia Britannica. 19 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 456–457. - "Données climatiques de la station de Nevers" (in French). Meteo France. Retrieved 30 December 2015.
- "Climat Bourgogne" (in French). Meteo France. Retrieved 30 December 2015.
- "Normes et records 1961-1990: Nevers-Marzy (58) - altitude 175m" (in French). Infoclimat. Retrieved 30 December 2015.
- "Les villes jumelées". nevers.fr (in French). Nevers. Retrieved 16 November 2019.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Nevers. |
- Official website
- . The American Cyclopædia. 1879.
- . New International Encyclopedia. 1905.
- Nevers page on the site Bourgogne Romane
