Nîmes
Nîmes (/niːm/ NEEM, French: [nim] (![]() listen); Occitan: Nimes [ˈnimes]; Latin: Nemausus) is the prefecture of the Gard department in the Occitanie region of Southern France. Located between the Mediterranean Sea and Cévennes, the commune of Nîmes has an estimated population of 150,610 (2017).[3]
listen); Occitan: Nimes [ˈnimes]; Latin: Nemausus) is the prefecture of the Gard department in the Occitanie region of Southern France. Located between the Mediterranean Sea and Cévennes, the commune of Nîmes has an estimated population of 150,610 (2017).[3]
Nîmes
| |
|---|---|
Prefecture and commune | |
.jpg.webp)   _(46785244294).jpg.webp) From top to bottom, left to right: city view from Tour Magne, Fontaine Pradier, Arena of Nîmes and Maison Carrée at night | |
.svg.png.webp) Coat of arms | |
Location of Nîmes 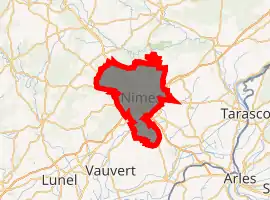
| |
 Nîmes  Nîmes | |
| Coordinates: 43°50′17″N 4°21′40″E | |
| Country | France |
| Region | Occitanie |
| Department | Gard |
| Arrondissement | Nîmes |
| Canton | Nîmes-1, 2, 3 and 4 and Saint-Gilles |
| Intercommunality | CA Nîmes Métropole |
| Government | |
| • Mayor (2020–2026) | Jean-Paul Fournier[1] (LR) |
| Area 1 | 161.85 km2 (62.49 sq mi) |
| Population (2017-01-01)[2] | 150,610 |
| • Density | 930/km2 (2,400/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| INSEE/Postal code | 30189 /30000 and 30900 |
| Elevation | 21–215 m (69–705 ft) (avg. 39 m or 128 ft) |
| 1 French Land Register data, which excludes lakes, ponds, glaciers > 1 km2 (0.386 sq mi or 247 acres) and river estuaries. | |
Dubbed the most Roman city outside Italy,[4] Nîmes has a rich history dating back to the Roman Empire when the city was a regional capital, and home to 50,000–60,000 people.[5][6][7][8] Several famous monuments are in Nîmes, such as the Arena of Nîmes and the Maison Carrée. Because of this, Nîmes is often referred to as the French Rome.
Origins
The site on which the built-up area of Nîmes has become established in the course of centuries is part of the edge of the alluvial plain of the Vistrenque River which butts up against low hills: to the northeast, Mont Duplan; to the southwest, Montaury; to the west, Mt. Cavalier and the knoll of Canteduc.
Its name appears in inscriptions in Gaulish as dede matrebo Namausikabo = "he has given to the mothers of Nîmes" and "toutios Namausatis" = "citizen of Nîmes".[9]
Nemausus was the god of the local Volcae Arecomici tribe.
History

.jpg.webp)
4000–2000 BC
The Neolithic site of Serre Paradis reveals the presence of semi-nomadic cultivators in the period 4000 to 3500 BC on the site of Nîmes.
The menhir of Courbessac (or La Poudrière) stands in a field, near the airstrip. This limestone monolith of over two metres in height dates to about 2500 BC, and is considered the oldest monument of Nîmes.
1800–600 BC
The Bronze Age has left traces of villages that were made out of huts and branches. The population of the site increased during the Bronze Age.
600–121 BC
The hill of Mt. Cavalier was the site of the early oppidum which gave birth to the city. During the third and 2nd centuries BC a surrounding wall was built with a dry-stone tower at the summit which was later incorporated into the Tour Magne. The Volcae Arecomici people settled around the spring at the foot of Mount Cavalier and build a sanctuary to Nemausus there.
The Warrior of Grezan is considered to be the most ancient indigenous sculpture in southern Gaul.
In 123 BC the Roman general Quintus Fabius Maximus campaigned against Gallic tribes in the area and defeated the Allobroges and the Arverni, while the Volcae offered no resistance. The Roman province Gallia Transalpina was established in 121 BC[10] and from 118 BC the Via Domitia was built through the later site of the city.
Roman period





The city arose on the important Via Domitia which connected Italy with Hispania.
Nîmes became a Roman colony as Colonia Nemausus sometime before 28 BC, as witnessed by the earliest coins, which bear the abbreviation NEM. COL, "Colony of Nemausus".[11] Veterans of Julius Caesar's legions in his Nile campaigns were given plots of land to cultivate on the plain of Nîmes.[12]
Augustus started a major building program in the city, as elsewhere in the empire. He also gave the town a ring of ramparts 6 km (3.7 miles) long, reinforced by 14 towers; two gates remain today: the Porta Augusta and the Porte de France.
The Maison Carrée dating from the late 1st c. BC is one of the best-preserved temples to be found anywhere in the former Roman Empire, and appears to be almost totally intact.
The great Nimes Aqueduct, many of whose remains can be seen today outside of the city, was built to bring water from the hills to the north. Where it crossed the River Gard between Uzès and Remoulins, the spectacular Pont du Gard was built. This is 20 km (12 mi) north east of the city.
The museum contains many fine objects including mosaic floors, frescoes and sculpture from rich houses and buildings found in excavations in and near the city. It is known that the town had a civil basilica, a curia, a gymnasium and perhaps a circus. The amphitheatre is very well preserved, dates from the end of the 2nd century and was one of the largest amphitheatres in the Empire. The so-called Temple of Diana dating from Augustus and rebuilt in the 2nd century was not a temple but was centred on a nymphaeum located within the Fontaine Sanctuary dedicated to Augustus and may have been a library.
The city was the birthplace of the family of emperor Antoninus Pius (138-161).
Emperor Constantine (306-337) endowed the city with baths.
It became the seat of the Diocesan Vicar, the chief administrative officer of southern Gaul.
The town was prosperous until the end of the 3rd century when successive barbarian invasions slowed its development. During the 4th and 5th centuries, the nearby town of Arles enjoyed more prosperity. In the early 5th century the Praetorian Prefecture was moved from Trier in northeast Gaul to Arles.
The Visigoths captured the city in 472.


Obverse: Back to back head of Agrippa left wearing rostral crown, and laureate head of Augustus right; on either side, inscription. Above and below, inscription. Border of dots. Lettering: "IMP P P DIVI F" ("IMPerator DIVI Filius Pater Patriæ", Emperor, Son of the Divine Father of the Nation).
Reverse: Crocodile to right, chained by neck to a palm-tree with tip bending left, two short palms on either side of trunk; on right, inscription; on left, inscription surmounted by a crown with two long tails to right. Border of dots. Lettering: "COL NEM" ("Colonia Nemausus", Colony of Nemausus)Finds from Roman Nimes in the Musée de la Romanité
 Mosaic of Europa and Zeus
Mosaic of Europa and Zeus Mosaic of still life
Mosaic of still life Pentheus mosaic
Pentheus mosaic Fresco of war galleys
Fresco of war galleys
4th–13th centuries
After the Roman period the Christian Church, already established in Gaul since the 1st century AD, appeared to be the last refuge of classical civilisation, as it was organised and directed by a series of Gallo-Roman aristocrats. When the Visigoths were accepted into the Roman Empire, Nîmes was included in their territory in 472, even after the Frankish victory at the Battle of Vouillé (507). The urban landscape went through transformation with the Goths, but much of the heritage of the Roman era remained largely intact.
By 725, the Muslim Umayyads had conquered the whole Visigothic territory of Septimania including Nîmes. In 736–737, Charles Martel and his brother led an expedition to Septimania and Provence, and largely destroyed the city (in the hands of Umayyads allied with the local Gallo-Roman and Gothic nobility), including the amphitheatre, thereafter heading back north. The Muslim government came to an end in 752, when Pepin the Short captured the city. In 754, an uprising took place against the Carolingian king, but was put down, and count Radulf, a Frank, appointed as master of the city. After the events connected with the war, Nîmes was now only a shadow of the opulent Roman city it had once been. The local authorities installed themselves in the remains of the amphitheatre. Islamic burials have been found in Nîmes.[13][14][15][16]
Carolingian rule brought relative peace, but feudal times in the 12th century brought local troubles, which lasted until the days of St. Louis. During that period Nîmes was jointly administered by a lay power resident in the old amphitheatre, where lived the Viguier and the Knights of the Arena, and the religious power based in the Bishop's palace complex, around the cathedral, its chapter and the Bishop's house; meanwhile the city was represented by four Consuls, who sat in the Maison Carrée.
Despite incessant feudal squabbling, Nîmes saw some progress both in commerce and industry as well as in stock-breeding and associated activities.
After the last effort by Raymond VII of Toulouse, St. Louis managed to establish royal power in the region which became Languedoc. Nîmes thus finally came into the hands of the King of France.
Period of invasions
During the 14th and 15th centuries the Rhone Valley underwent an uninterrupted series of invasions which ruined the economy and caused famine. Customs were forgotten, religious troubles developed (see French Wars of Religion) and epidemics, all of which affected the city. Nîmes, which was one of the Protestant strongholds, felt the full force of repression and fratricidal confrontations (including the Michelade massacre) which continued until the middle of the 17th century, adding to the misery of periodic outbreaks of plague.
17th century to the French Revolution

In the middle of the 17th century Nîmes experienced a period of prosperity. Population growth caused the town to expand, and slum housing to be replaced. To this period also belong the reconstruction of Notre-Dame-Saint-Castor, the Bishop's palace and numerous mansions (hôtels). This renaissance strengthened the manufacturing and industrial potential of the city, the population rising from 21,000 to 50,000 inhabitants.
In this same period the Fountain gardens, the Quais de la Fontaine, were laid out, the areas surrounding the Maison Carrée and the Amphitheatre were cleared of encroachments, whilst the entire population benefited from the atmosphere of prosperity.
From the French Revolution to the present
Following a European economic crisis that hit Nîmes with full force, the Revolutionary period awoke the slumbering demons of political and religious antagonism. The White Terror added to natural calamities and economic recession, produced murder, pillage and arson until 1815. Order was however restored in the course of the century, and Nîmes became the metropolis of Bas-Languedoc, diversifying its industry into new kinds of activity. At the same time the surrounding countryside adapted to market needs and shared in the general increase of wealth.
During the Second World War, the Maquis resistance fighters Jean Robert and Vinicio Faïta were executed at Nîmes on 22 April 1943. The Nîmes marshalling yards were bombed by American bombers in 1944.
The 2º Régiment Étranger d'Infanterie (2ºREI), the main motorised infantry regiment of the French Foreign Legion, has been garrisoned in Nîmes since November 1983.[17]
Geography
Climate
Nîmes is one of the warmest cities in France. The city has a Mediterranean climate (Köppen: Csa), being wetter than a typical Mediterranean climate, especially for its moderately rainy summers. It's slightly inland, southerly location results in hot air over the city during summer months, temperatures above 34 °C are common in July and August, whereas winters are cool but not cold. Night temps under 0 °C are common from December to February, while snowfall occurs every year.
| Climate data for Nîmes (Météo France Office-Courbessac), elevation: 59 m or 194 ft, 1981–2010 normals, extremes 1922–present | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 21.5 (70.7) |
23.8 (74.8) |
27.3 (81.1) |
30.7 (87.3) |
34.7 (94.5) |
44.4 (111.9) |
38.8 (101.8) |
41.6 (106.9) |
35.4 (95.7) |
31.9 (89.4) |
26.1 (79.0) |
20.6 (69.1) |
44.4 (111.9) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 11.0 (51.8) |
12.4 (54.3) |
16.0 (60.8) |
18.6 (65.5) |
23.0 (73.4) |
27.5 (81.5) |
31.0 (87.8) |
30.5 (86.9) |
25.7 (78.3) |
20.4 (68.7) |
14.5 (58.1) |
11.3 (52.3) |
20.2 (68.4) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 6.8 (44.2) |
7.8 (46.0) |
10.9 (51.6) |
13.5 (56.3) |
17.5 (63.5) |
21.7 (71.1) |
24.9 (76.8) |
24.4 (75.9) |
20.3 (68.5) |
16.0 (60.8) |
10.5 (50.9) |
7.4 (45.3) |
15.2 (59.4) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 2.7 (36.9) |
3.2 (37.8) |
5.8 (42.4) |
8.3 (46.9) |
12.1 (53.8) |
15.8 (60.4) |
18.7 (65.7) |
18.4 (65.1) |
14.9 (58.8) |
11.5 (52.7) |
6.5 (43.7) |
3.6 (38.5) |
10.2 (50.4) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −12.2 (10.0) |
−14.0 (6.8) |
−6.8 (19.8) |
−2.0 (28.4) |
1.1 (34.0) |
5.4 (41.7) |
10.0 (50.0) |
9.2 (48.6) |
5.4 (41.7) |
−1.0 (30.2) |
−4.8 (23.4) |
−9.7 (14.5) |
−14.0 (6.8) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 64.7 (2.55) |
47.3 (1.86) |
40.4 (1.59) |
65.1 (2.56) |
58.5 (2.30) |
40.9 (1.61) |
28.2 (1.11) |
53.3 (2.10) |
96.4 (3.80) |
119.2 (4.69) |
83.1 (3.27) |
65.8 (2.59) |
762.9 (30.04) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 5.7 | 5.2 | 4.9 | 6.8 | 5.9 | 4.4 | 2.8 | 3.8 | 5.2 | 7.0 | 6.8 | 5.8 | 64.2 |
| Average snowy days | 0.8 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 2.4 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 141.6 | 166.3 | 222.2 | 229.8 | 262.0 | 311.0 | 341.1 | 301.6 | 239.0 | 166.6 | 147.9 | 134.0 | 2,662.9 |
| Source: Météo France[18][19][20] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Nîmes (Météo France Office-Courbessac), elevation: 59 m or 194 ft, 1961–1990 normals and extremes | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 20.1 (68.2) |
22.7 (72.9) |
27.3 (81.1) |
27.9 (82.2) |
30.6 (87.1) |
37.4 (99.3) |
38.0 (100.4) |
38.2 (100.8) |
34.7 (94.5) |
28.7 (83.7) |
26.1 (79.0) |
20.6 (69.1) |
38.2 (100.8) |
| Mean maximum °C (°F) | 13.2 (55.8) |
15.8 (60.4) |
18.1 (64.6) |
20.7 (69.3) |
24.8 (76.6) |
29.5 (85.1) |
33.0 (91.4) |
31.5 (88.7) |
28.8 (83.8) |
22.2 (72.0) |
16.4 (61.5) |
13.5 (56.3) |
33.0 (91.4) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 10.3 (50.5) |
12.1 (53.8) |
14.9 (58.8) |
18.0 (64.4) |
21.6 (70.9) |
26.1 (79.0) |
29.8 (85.6) |
28.9 (84.0) |
25.6 (78.1) |
20.3 (68.5) |
14.3 (57.7) |
11.3 (52.3) |
19.4 (67.0) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 6.3 (43.3) |
8.0 (46.4) |
10.0 (50.0) |
12.8 (55.0) |
16.4 (61.5) |
20.5 (68.9) |
23.7 (74.7) |
22.9 (73.2) |
20.1 (68.2) |
15.8 (60.4) |
10.0 (50.0) |
7.3 (45.1) |
14.5 (58.1) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 2.4 (36.3) |
3.6 (38.5) |
5.2 (41.4) |
7.8 (46.0) |
11.1 (52.0) |
14.8 (58.6) |
17.6 (63.7) |
16.9 (62.4) |
15.0 (59.0) |
11.0 (51.8) |
5.9 (42.6) |
3.3 (37.9) |
9.6 (49.2) |
| Mean minimum °C (°F) | −1.7 (28.9) |
−0.5 (31.1) |
2.2 (36.0) |
6.0 (42.8) |
9.2 (48.6) |
13.2 (55.8) |
15.7 (60.3) |
15.5 (59.9) |
12.2 (54.0) |
5.6 (42.1) |
3.7 (38.7) |
−0.3 (31.5) |
−1.7 (28.9) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −12.2 (10.0) |
−10.5 (13.1) |
−6.4 (20.5) |
−1.1 (30.0) |
1.1 (34.0) |
5.4 (41.7) |
10.0 (50.0) |
9.3 (48.7) |
5.4 (41.7) |
0.9 (33.6) |
−3.3 (26.1) |
−9.7 (14.5) |
−12.2 (10.0) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 60.7 (2.39) |
58.6 (2.31) |
52.1 (2.05) |
62.8 (2.47) |
55.5 (2.19) |
26.3 (1.04) |
14.9 (0.59) |
50.7 (2.00) |
42.6 (1.68) |
96.3 (3.79) |
60.4 (2.38) |
60.1 (2.37) |
641 (25.26) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 6.9 | 6.4 | 6.7 | 6.7 | 5.8 | 4.8 | 3.1 | 3.8 | 4.7 | 6.7 | 5.5 | 6.2 | 67.3 |
| Average snowy days | 0.7 | 1.0 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 0.9 | 3.4 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 71 | 68 | 63 | 63 | 64 | 61 | 56 | 60 | 67 | 73 | 72 | 72 | 65.8 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 143.5 | 147.4 | 203.1 | 227.6 | 267.8 | 310.2 | 353.8 | 315.3 | 236.6 | 186.7 | 143.9 | 133.0 | 2,668.9 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 51 | 51 | 56 | 57 | 59 | 68 | 77 | 74 | 64 | 55 | 50 | 49 | 59 |
| Source 1: NOAA[21] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Infoclimat.fr (humidity)[22] | |||||||||||||
Sights


Several important remains of the Roman Empire can still be seen in and around Nîmes:
- The elliptical Roman amphitheatre, of the 1st or 2nd century AD, is the best-preserved Roman arena in France. It was filled with medieval housing, when its walls served as ramparts, but they were cleared under Napoleon. It is still used as a bull fighting and concert arena.
- The Maison Carrée (Square House), a small Roman temple dedicated to sons of Agrippa was built c. 19 BC. It is one of the best-preserved Roman temples anywhere. Visitors can watch a short film about the history of Nîmes inside.
- The 18th-century Jardins de la Fontaine (Gardens of the Fountain) built around the Roman thermae ruins.
- The nearby Pont du Gard, also built by Agrippa, is a well-preserved aqueduct that used to carry water across the small Gardon river valley.
- The nearby Mont Cavalier is crowned by the Tour Magne ("Great Tower"), a ruined Roman tower.[23]
Later monuments include:
- The cathedral (dedicated to Saint Castor of Apt, a native of the city), occupying, it is believed, the site of the temple of Augustus, is partly Romanesque and partly Gothic in style.
- The Musée des Beaux-Arts de Nîmes
There is modern architecture at Nîmes too: Norman Foster conceived the Carré d'art (1986), a museum of modern art and mediatheque, and Jean Nouvel designed the Nemausus, a post-modern residential ensemble.
Tree-shaded boulevards trace the foundations of its former city walls.
Economy and infrastructure
Nîmes is historically known for its textiles. Denim, the fabric of blue jeans, derives its name from this city (Serge de Nîmes). The blue dye was imported via Genoa from Lahore the capital of the Great Mughal.
Population
|
|
The population of Nîmes increased from 128,471 in 1990 to 146,709 in 2012, yet the biggest growth the city ever experienced happened in 1968, with a growth of +23.5% compared to 1962.
Culture
From 1810 to 1822, Joseph Gergonne published a scientific journal specializing in mathematics from Nîmes called Annales de Gergonne.
In the famous novel The Count of Monte Cristo by Alexander Dumas, in Nîmes, the procureur du roi Villefort kills the older brother of Bertuccio, a soldier in Napoleon's army, as he is en route to his home in Corsica in 1829. Bertuccio declares a vendetta on Villefort and stabs him; Villefort survives and asks for a transfer out of the city. Bertuccio later becomes a servant to the Count.
The asteroid 51 Nemausa was named after Nîmes, where it was discovered in 1858.
Two times per year, Nîmes hosts one of the main French bullfighting events, Feria de Nîmes (festival), and several hundreds of thousands gather in the streets.
In 2005 Rammstein filmed their #1 live Album Völkerball in Nîmes, and are returning in 2017.
Metallica's live DVD Français Pour une Nuit (English: French for One Night) was recorded in Nîmes, France, in the Arena of Nîmes on 7 July 2009, during the World Magnetic Tour.
Transportation
Nîmes-Alès-Camargue-Cévennes Airport serves the city. The Gare de Nîmes is the central railway station, offering connections to Paris (high-speed rail), Marseille, Montpellier, Narbonne, Toulouse, Perpignan, Figueras and Barcelona in Spain and several regional destinations. The motorway A9 connects Nîmes with Orange, Montpellier, Narbonne, and Perpignan, the A54 with Arles and Salon-de-Provence.
Work is almost complete on the construction of a high-speed TGV line, Contournement Nîmes – Montpellier bypassing Nîmes and Montpellier with the LGV Méditerranée.[24]
The new line opened to passenger service on 15 December 2019 together with a new TGV station at NIMES-PONT DU GARD, (a confusing name as it located some 12km from the city itself and 20km from the Pont du Gard).[25]
A new station is also to be opened at the same time on the existing route between Nìmes and Avignon, thus providing connections between the new line and local rail service.
Nîmes bus station is adjacent to the city centre railway station. Buses connect the city with nearby towns and villages not served by rail. https://www.laregion.fr/transports-gard-regulier
Sport
The association football club Nîmes Olympique who has recently achieved promotion to Ligue 1 is based in Nîmes. World Archery Indoor World Cup takes place in Nîmes each year in mid January The local rugby union team is RC Nîmes.
There is a professional volleyball team located here.
Olympic swimming champion Yannick Agnel was born in Nîmes.
The city hosted the opening stages of the 2017 Vuelta a España cycling race.
Mayors
- Émile Jourdan, PCF (1965–1983)
- Jean Bousquet, UDF (1983–1995)
- Alain Clary, PCF (1995–2001)
- Jean-Paul Fournier, LR (since 2001)
Twin towns – sister cities
Nîmes is twinned with:[26][27]
 Preston, United Kingdom, since 1955
Preston, United Kingdom, since 1955 Verona, Italy, since 1960
Verona, Italy, since 1960 Braunschweig, Germany, since 1962
Braunschweig, Germany, since 1962 Prague 1, Czech Republic, since 1967
Prague 1, Czech Republic, since 1967 Frankfurt (Oder), Germany, since 1976
Frankfurt (Oder), Germany, since 1976 Córdoba, Spain
Córdoba, Spain Rishon LeZion, Israel, since 1986
Rishon LeZion, Israel, since 1986 Meknes, Morocco, since 2005
Meknes, Morocco, since 2005 Fort Worth, United States, since 2019
Fort Worth, United States, since 2019
See also
References
- "Répertoire national des élus: les maires". data.gouv.fr, Plateforme ouverte des données publiques françaises (in French). 2 December 2020. Retrieved 11 December 2020.
- "Populations légales 2017". INSEE. Retrieved 6 January 2020.
- Téléchargement du fichier d'ensemble des populations légales en 2017, INSEE
- "Nîmes, the most Roman city outside Italy, just got more Roman". The Telegraph. Retrieved 30 July 2018.
- Frank Sear (1983). Roman Architecture. Cornell University Press. p. 213. ISBN 0-8014-9245-9.
- Trudy Ring; Noelle Watson; Paul Schellinger (28 October 2013). Northern Europe: International Dictionary of Historic Places. Taylor & Francis. p. 853. ISBN 978-1-136-63951-7.
- "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 March 2014. Retrieved 19 March 2014.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- MobileReference (1 January 2007). Travel Barcelona, Spain for Smartphones and Mobile Devices – City Guide, Phrasebook, and Maps. MobileReference. p. 428. ISBN 978-1-60501-059-5.
- Woodard, Roger D. (2008). The Ancient Languages of Europe. Cambridge University Press. p. 183. ISBN 978-1-139-46932-6.
- Maddison, Angus (2007), Contours of the World Economy 1–2030 AD: Essays in Macro-Economic History, Oxford: Oxford University Press, p. 41, ISBN 9780191647581
- Colin M. Kraay, "The Chronology of the coinage of Colonia Nemausus", Numismatic Chronicle 15 (1955), pp. 75–87.
- Alain Veyrac, "Le symbolisme de l'as de Nîmes au crocodile" Archéologie et histoire romaine vol. 1 (1998) (on-line text).
- Netburn, Deborah (24 February 2016). "Earliest Known Medieval Muslim Graves are Discovered in France". Los Angeles Times.
- Newitz, Annalee (24 February 2016). "Medieval Muslim Graves in France Reveal a Previously Unseen History". Ars Technica.
- "France's Earliest 'Muslim Burials' Found". BBC News. 25 February 2016.
- Gleize, Yves; Mendisco, Fanny; Pemonge, Marie-Hélène; Hubert, Christophe; Groppi, Alexis; Houix, Bertrand; Deguilloux, Marie-France; Breuil, Jean-Yves (24 February 2016). "Early Medieval Muslim Graves in France: First Archaeological, Anthropological and Palaeogenomic Evidence". PLOS ONE. 11 (2): e0148583. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0148583. PMC 4765927. PMID 26910855.
- Official Website of the 2nd Foreign Infantry Regiment, Historique du 2 REI, La Creation (Creation)
- "Données climatiques de la station de Nîmes" (in French). Meteo France. Retrieved 7 January 2016.
- "Climat Languedoc-Roussillon" (in French). Meteo France. Retrieved 7 January 2016.
- "Nimes–Courbessac (30)" (PDF). Fiche Climatologique: Statistiques 1981–2010 et records (in French). Meteo France. Archived from the original (PDF) on 30 March 2018. Retrieved 30 March 2018.
- "Nîmes (07645) – WMO Weather Station". NOAA. Retrieved 22 July 2019.
- "Normes et records 1961–1990: Nimes-Courbessac (30) – altitude 59m" (in French). Infoclimat. Archived from the original on 3 March 2016. Retrieved 7 January 2016.
- Giving rise to the example of rime richissime Gall, amant de la Reine, alla (tour magnanime)/ Gallament de l'Arène a la Tour Magne, à Nîmes, or "Gall, lover opf the Queen, passed (magnanimous gesture), gallantly from the Arena to the Tour Magne at Nîmes".
- "Railway Gazette: Southern LGV projects make progress". Retrieved 14 February 2011.
- https://www.sncf.com/en/passenger-offer/nimes-pont-du-gard-new-station-benefits
- "Jumelages". nimes.fr (in French). Nîmes. Retrieved 15 November 2019.
- "Official Nîmes Signing". fwsistercities.org. Fort Worth. Retrieved 15 November 2019.
Further reading
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Nîmes. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Nîmes. |
- 2° Régiment étranger d'infanterie
- Practical Guide to Nîmes Airport
- City council website
- The official Web site of Roman Nîmes
- Images of Roman remains of Nîmes
- Photogallery of Nîmes
- Regordane Info – The independent portal for The Regordane Way or St Gilles Trail The Regordane passes through Nîmes. (in English and French)