Otsego County, New York
Otsego County is a county in the U.S. state of New York. As of the 2010 census, the population was 62,259.[1] The county seat is Cooperstown.[2] The name Otsego is from a Mohawk or Oneida word meaning "place of the rock."[3]
Otsego County | |
|---|---|
 Original Otsego County Bank, in Cooperstown | |
 Flag  Seal | |
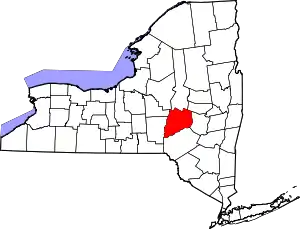 Location within the U.S. state of New York | |
 New York's location within the U.S. | |
| Coordinates: 42°38′N 75°02′W | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| Founded | February 16, 1791 |
| Seat | Cooperstown |
| Largest city | Oneonta |
| Area | |
| • Total | 1,016 sq mi (2,630 km2) |
| • Land | 1,002 sq mi (2,600 km2) |
| • Water | 14 sq mi (40 km2) 1.4% |
| Population (2010) | |
| • Total | 62,259 |
| • Density | 62/sq mi (24/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC−5 (Eastern) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) |
| Congressional district | 19th |
| Website | www |
History
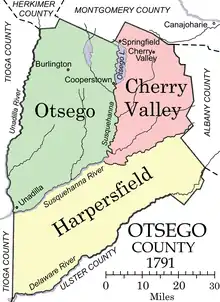
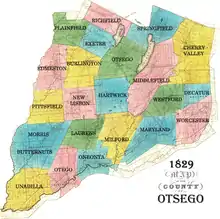
In 1789, Ontario County was split off from Montgomery. The area split off from Montgomery County was much larger than the present county, as it included the present Allegany, Cattaraugus, Chautauqua, Erie, Genesee, Livingston, Monroe, Niagara, Orleans, Steuben, Wyoming, Yates, and part of Schuyler and Wayne counties.
Formation
Otsego County was one of three early counties split off from Montgomery (the other two being Herkimer and Tioga) after the American Revolutionary War. Otsego County was officially established on February 16, 1791, with Cooperstown as its county seat, although at the time the village of Cherry Valley was much larger. The original county consisted of three large townships:
- Cherry Valley in the northeast,
- Otsego in the northwest, and
- Harpersfield in the south.
Otsego and Cherry Valley together roughly covered the area of modern Otsego County, while Harpersfield covered the area south of the current county as far as the Delaware River.
The original appointments to Otsego County government positions, made by Governor George Clinton included:
- Richard R. Smith, county sheriff, from Otsego township,
- Jacob Morris, county clerk, from Otsego township,
- William Cooper, chief judge, from Otsego township,
- Jedediah Peck, associate justice from Otsego township,
- Edward Griswold, associate justice from Cherry Valley
- Platt Townsend, associate justice from Harpersfield,
- Alexander Harper, commander of the county militia, from Harpersfield.
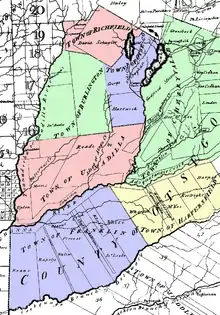
New towns
By 1793, four towns had been added to the county by division of the existing towns:
- The Otsego township had been divided into the towns of:
- Burlington in the west,
- Otsego in the northeast,
- Richfield in the north, and
- Unadilla in the south.
- Harpersfield had been divided into the towns of:
- Franklin in the west and
- Harpersfield in the east.
In 1795, a piece of Otsego County was joined with a portion taken from Albany County to create Schoharie County.
In 1797, a piece of Otsego County was joined with a portion taken from Ulster County to create Delaware County.
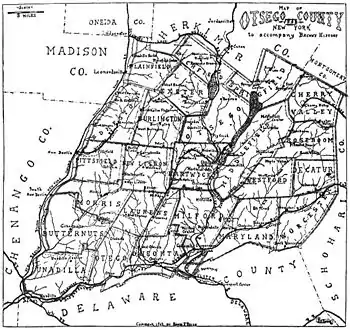
Geography
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 1,016 square miles (2,630 km2), of which 1,002 square miles (2,600 km2) is land and 14 square miles (36 km2) (1.4%) is water.[4]
Otsego County is in central New York State, to the west of Albany, southeast of Utica, and northeast of Binghamton. The county is part of the Central New York Region and Mohawk Valley Region of New York State. The county is considered by some to belong to the Southern Tier region of New York State, and is the northernmost county of the Appalachian Region.
Adjacent counties
- Herkimer County - north
- Montgomery County - northeast
- Schoharie County - east
- Delaware County - south
- Chenango County - southwest
- Oneida County - northwest
- Madison County - northwest
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1800 | 21,343 | — | |
| 1810 | 38,802 | 81.8% | |
| 1820 | 44,856 | 15.6% | |
| 1830 | 51,372 | 14.5% | |
| 1840 | 49,628 | −3.4% | |
| 1850 | 48,638 | −2.0% | |
| 1860 | 50,157 | 3.1% | |
| 1870 | 48,967 | −2.4% | |
| 1880 | 51,397 | 5.0% | |
| 1890 | 50,861 | −1.0% | |
| 1900 | 48,939 | −3.8% | |
| 1910 | 47,216 | −3.5% | |
| 1920 | 46,200 | −2.2% | |
| 1930 | 46,710 | 1.1% | |
| 1940 | 46,082 | −1.3% | |
| 1950 | 50,763 | 10.2% | |
| 1960 | 51,942 | 2.3% | |
| 1970 | 56,181 | 8.2% | |
| 1980 | 59,075 | 5.2% | |
| 1990 | 60,517 | 2.4% | |
| 2000 | 61,676 | 1.9% | |
| 2010 | 62,259 | 0.9% | |
| 2018 (est.) | 59,749 | [5] | −4.0% |
| U.S. Decennial Census[6] 1790-1960[7] 1900-1990[8] 1990-2000[9] 2010-2013[1] | |||
As of the census[10] of 2000, there were 61,676 people, 23,291 households, and 15,115 families residing in the county. The population density was 62 people per square mile (24/km2). There were 28,481 housing units at an average density of 28 per square mile (11/km2). The racial makeup of the county was 95.80% White, 1.75% African American, 0.23% Native American, 0.63% Asian, 0.05% Pacific Islander, 0.50% from other races, and 1.05% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 1.90% of the population. 15.0% were of Irish, 14.9% English, 14.9% German, 11.3% Italian and 9.1% American ancestry according to Census 2000. 95.4% spoke English and 2.1% Spanish as their first language.
There were 23,291 households, out of which 29.60% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 51.10% were married couples living together, 9.50% had a female householder with no husband present, and 35.10% were non-families. 27.00% of all households were made up of individuals, and 11.60% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.43 and the average family size was 2.94.
In the county, the population was spread out, with 22.70% under the age of 18, 14.40% from 18 to 24, 24.30% from 25 to 44, 23.60% from 45 to 64, and 15.00% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 37 years. For every 100 females there were 93.10 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 90.00 males.
The median income for a household in the county was $33,444, and the median income for a family was $41,110. Males had a median income of $29,988 versus $22,609 for females. The per capita income for the county was $16,806. About 8.80% of families and 14.90% of the population were below the poverty line, including 15.80% of those under age 18 and 8.20% of those age 65 or over.
Government and politics
| Year | Republican | Democratic | Third parties |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 51.9% 13,308 | 40.7% 10,451 | 7.4% 1,909 |
| 2012 | 47.5% 11,461 | 50.2% 12,117 | 2.3% 561 |
| 2008 | 46.0% 12,026 | 52.0% 13,570 | 2.0% 525 |
| 2004 | 50.1% 13,342 | 47.7% 12,723 | 2.2% 587 |
| 2000 | 48.2% 12,219 | 45.2% 11,460 | 6.6% 1,679 |
| 1996 | 36.4% 8,774 | 47.5% 11,470 | 16.1% 3,882 |
| 1992 | 38.1% 10,141 | 39.4% 10,471 | 22.5% 5,994 |
| 1988 | 53.5% 13,021 | 45.5% 11,069 | 1.0% 245 |
| 1984 | 63.3% 16,777 | 36.1% 9,582 | 0.6% 152 |
| 1980 | 49.4% 11,814 | 36.8% 8,795 | 13.8% 3,298 |
| 1976 | 59.8% 14,796 | 39.5% 9,787 | 0.7% 171 |
| 1972 | 68.6% 17,364 | 31.2% 7,898 | 0.2% 59 |
| 1968 | 59.7% 13,543 | 35.2% 7,981 | 5.2% 1,172 |
| 1964 | 36.2% 8,643 | 63.7% 15,190 | 0.1% 26 |
| 1960 | 68.7% 17,422 | 31.2% 7,899 | 0.1% 26 |
| 1956 | 77.5% 19,484 | 22.5% 5,644 | 0.0% 0 |
| 1952 | 76.8% 20,304 | 23.1% 6,115 | 0.1% 27 |
| 1948 | 66.6% 15,437 | 30.9% 7,174 | 2.5% 586 |
| 1944 | 66.2% 15,427 | 33.7% 7,849 | 0.2% 37 |
| 1940 | 68.0% 16,771 | 31.6% 7,798 | 0.3% 78 |
| 1936 | 67.4% 16,682 | 31.5% 7,807 | 1.1% 276 |
| 1932 | 64.1% 14,904 | 34.9% 8,114 | 1.1% 247 |
| 1928 | 74.3% 18,286 | 24.4% 6,006 | 1.3% 314 |
| 1924 | 65.7% 13,573 | 28.3% 5,841 | 6.1% 1,256 |
| 1920 | 63.9% 12,112 | 33.1% 6,275 | 3.0% 574 |
| 1916 | 48.2% 5,926 | 48.6% 5,975 | 3.3% 403 |
| 1912 | 40.7% 5,138 | 42.2% 5,338 | 17.1% 2,165 |
| 1908 | 53.4% 7,459 | 42.8% 5,975 | 3.9% 543 |
| 1904 | 55.4% 7,770 | 40.9% 5,725 | 3.7% 519 |
| 1900 | 54.8% 7,893 | 42.7% 6,142 | 2.5% 359 |
| 1896 | 56.4% 8,161 | 40.2% 5,820 | 3.4% 496 |
| 1892 | 49.5% 7,095 | 44.7% 6,408 | 5.8% 833 |
| 1888 | 51.0% 7,829 | 45.4% 6,972 | 3.7% 565 |
| 1884 | 43.8% 6,871 | 52.9% 8,307 | 3.3% 516 |
Otsego County is a true swing county and bellwether; it has chosen the winner of the presidency for the last three decades. In 2004, Otsego County voted 51–48 percent in favor of George W. Bush. In 2008 and 2012, Otsego County voted in favor of Barack Obama. Democrats are prevalent in the City of Oneonta and Village of Cooperstown, whereas the majority of voters in many of the surrounding towns are registered Republicans.
Otsego County is the only county in New York that names its legislative body the Board of Representatives. It consists of fourteen members elected from single-member districts. The Board Chair is David Bliss (R). The county also has an elected District Attorney, County Treasurer, County Clerk, and County Sheriff.
Media
Along with Herkimer County and the eastern portion of Oneida County, northern Otsego County is considered part of the Utica television market, while the Southern half of the county, including the city of Oneonta, is considered to be in the Binghamton television market.[12]
Economy
The Village of Cooperstown (home of James Fenimore Cooper, whose father William Cooper founded it) is located at the south end of Otsego Lake. It attracts many tourists to the Baseball Hall of Fame and the New York State Historical Association museums. Cultural attractions also include the Glimmerglass Opera, with a summer season that draws many repeat visitors for stays.
The primary contributor to the economy is healthcare: Bassett Medical Center, the headquarters of Bassett Healthcare Network and its more than 3,000 employees, is located here.
The City of Oneonta has two institutions of higher education: Hartwick College and the State University of New York at Oneonta; A.O. Fox Memorial Hospital, an affiliate of the Bassett Network; major retail activity; and numerous small businesses. The county as a whole remains relatively rural, with dairy farming a contributing industry that has consolidated employment in recent years, although production has remained steady.
Communities
City
Towns
Villages
- Cherry Valley
- Cooperstown (county seat)
- Gilbertsville
- Laurens
- Milford
- Morris
- Otego
- Richfield Springs
- Unadilla
Census-designated places
See also
References
- "State & County QuickFacts". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on June 7, 2011. Retrieved October 12, 2013.
- "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Retrieved 2011-06-07.
- Beauchamp, William Martin (1907). Aboriginal Place Names of New York (New York State Museum Bulletin, Volume 108). New York State Education Department. p. 174. Retrieved August 12, 2015.
- "2010 Census Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. August 22, 2012. Archived from the original on May 19, 2014. Retrieved January 6, 2015.
- "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". Retrieved December 20, 2019.
- "U.S. Decennial Census". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 6, 2015.
- "Historical Census Browser". University of Virginia Library. Retrieved January 6, 2015.
- "Population of Counties by Decennial Census: 1900 to 1990". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 6, 2015.
- "Census 2000 PHC-T-4. Ranking Tables for Counties: 1990 and 2000" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 6, 2015.
- "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2008-01-31.
- Leip, David. "Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections". uselectionatlas.org. Retrieved 2018-10-24.
- "WKTV.com | WKTV bringing CBS affiliation to Utica". WKTV.com. 2015-10-26. Archived from the original on 2015-10-27. Retrieved 2015-10-27.
Further reading
- Butterfield, Lyman H. "Cooper's Inheritance: The Otsego Country and its Founders", New York History, Vol. 35, No. 4 (October, 1954), pp. 374–411.
- Sullivan, Dr. James (editor). "Otsego County", The History of New York State, Lewis Historical Publishing Company, Inc., 1927
- French, J. H. "Otsego County", Gazetteer of the State of New York, Syracuse, New York: R. Pearsall Smith, 1860
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Otsego County, New York. |
- Official Otsego County Government site
- Otsego County at Curlie
- Henderson Scout Reservation - Boy Scout Camp serving Otsego County
