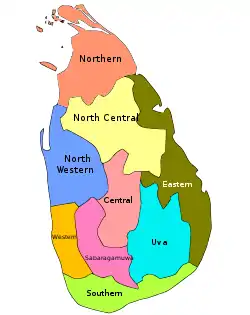
Provinces of Sri Lanka
In Sri Lanka, provinces (Sinhala: පළාත, romanized: Paḷāta; Tamil: மாகாணம், romanized: Mākāṇam) are the first level administrative division. They were first established by the British rulers of Ceylon in 1833. Over the next century most of the administrative functions were transferred to the districts, the second level administrative division. By the middle of the 20th century the provinces had become merely ceremonial. This changed in 1987 when, following several decades of increasing demand for a decentralization, the 13th Amendment to the 1978 Constitution of Sri Lanka established provincial councils.[1][2] Currently there are nine provinces.
| Province පළාත மாகாணம் | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Category | First level administrative division |
| Location | Sri Lanka |
| Created | 1 October 1833 |
| Number | 9 (as of 1 January 2007) |
| Populations | 1,061,315–5,851,130 |
| Areas | 3,684–10,472 km² |
| Government | Provincial council |
| Subdivisions | District |
| Administrative divisions of Sri Lanka |
|---|
| First level |
| Provinces |
| Second level |
| Districts |
| Third level |
| Divisional Secretary's Divisions |
| Fourth level |
| Grama Niladhari Divisions |
History
British Ceylon
 |
|---|
| This article is part of a series on the politics and government of Sri Lanka |
|
|
After the British took control of the entire island of Ceylon in 1815 it was divided into three ethnic based administrative structures: Low Country Sinhalese, Kandyan Sinhalese and Tamil. In 1829 the British established the Colebrooke–Cameron Commission to review the colonial government of Ceylon, including its administrative structures.[3] The Commission recommended that the existing three ethnic based administrations be unified into a single administration divided into five geographic provinces.[3] Accordingly, on 1 October 1833 five provinces under one administration came into being:[4][5][6][7]
- Central Province – composed of the central Kandyan provinces.
- Eastern Province – composed of the maritime districts of Batticaloa and Trincomalee, and the Kandyan provinces of Bintenna and Tamankaduwa.
- Northern Province – composed of the maritime districts of Jaffna, Mannar and Vanni, and the Kandyan province of Nuwara Kalawiya.
- Southern Province – composed of the maritime districts of Galle, Hambantota, Matara and Tangalle, and the Kandyan provinces of Lower Uva, Saffragam and Wellassa.
- Western Province – composed of the maritime districts of Colombo, Chilaw and Puttalam, and the Kandyan provinces of Three Korales, Four Korales, Seven Korales and Lower Bulathgama.
Over the next fifty years four additional provinces were created, taking the total number to nine:[6][7][8]
- North Western Province was created in 1845 from northern Western Province (districts of Chilaw, Puttalam and Seven Korales).[9]
- North Central Province was created in 1873 from southern Northern Province (district of Nuwara Kalawiya) and north-western Eastern Province (district of Tamankaduwa).[10]
- Uva Province was created in 1886 from parts of Central Province, Eastern Province (district of Bintenna) and Southern Province (district of Wellassa).[10]
- Sabaragamuwa Province was created in 1889.[11]
Sri Lanka

The number of provinces remained static until September 1988 when, in accordance with the Indo-Lanka Accord, President Jayewardene issued proclamations enabling the Northern and Eastern provinces to be one administrative unit administered by one elected Council, creating the North Eastern Province.[12] The proclamations were only meant to be a temporary measure until a referendum was held in the Eastern Province on a permanent merger between the two provinces. However, the referendum was never held and successive Sri Lankan presidents issued proclamations annually extending the life of the "temporary" entity.[13] The merger was bitterly opposed by Sri Lankan nationalists. On 14 July 2006, after a long campaign against the merger, the JVP filed three separate petitions with the Supreme Court of Sri Lanka requesting a separate Provincial Council for the East.[12] On 16 October 2006 the Supreme Court ruled that the proclamations issued by President Jayewardene were null and void and had no legal effect.[12] The North-East Province was formally de-merged into the Northern and Eastern provinces on 1 January 2007.
Sri Lanka currently has nine provinces, seven of which have had provincial councils from the start.[2]
- Evolution of Sri Lankan provinces since 1833
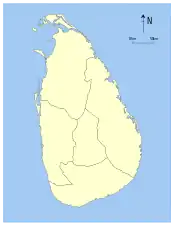 1833–1845
1833–1845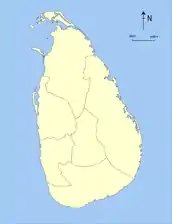 1845–1873
1845–1873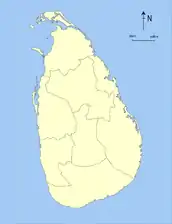 1873–1886
1873–1886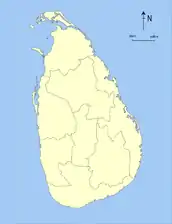 1886–1889
1886–1889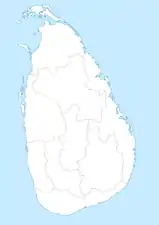 1889 – Present
1889 – Present
Provinces
Current
All population data are from the most recent census of Sri Lanka, in 2012.
| Province | Area map | Provincial capital |
Date Created |
Land area in km2 (mi2)[14] |
Inland water area in km2 (mi2)[14] |
Total area in km2 (mi2)[14] |
Population (2012)[15] |
Population density per km2 (per mi2)[lower-alpha 1] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
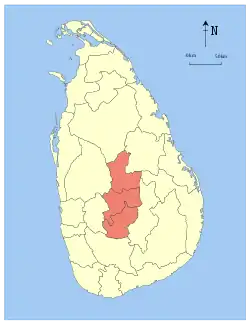 |
Kandy | 1 October 1833 | 5,575 (2,153) | 99 (38) | 5,674 (2,191) | 2,571,557 | 461 (1,190) | |
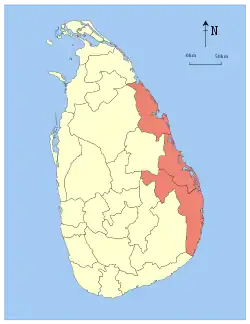 |
Trincomalee | 1 October 1833 | 9,361 (3,614) | 635 (245) | 9,996 (3,859) | 1,555,510 | 166 (430) | |
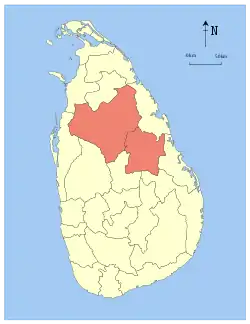 |
Anuradhapura | 1873 | 9,741 (3,761) | 731 (282) | 10,472 (4,043) | 1,266,663 | 130 (340) | |
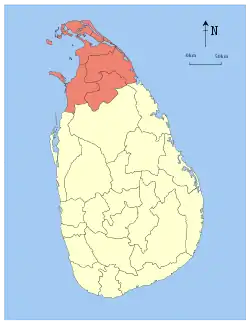 |
Jaffna | 1 October 1833 | 8,290 (3,200) | 594 (229) | 8,884 (3,430) | 1,061,315 | 128 (330) | |
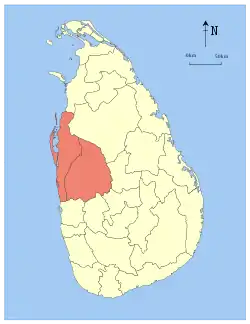 |
Kurunegala | 1845 | 7,506 (2,898) | 382 (147) | 7,888 (3,046) | 2,380,861 | 317 (820) | |
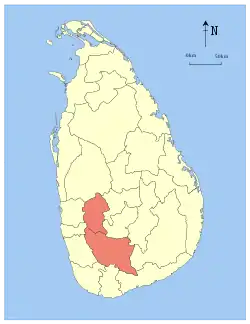 |
Ratnapura | 1889 | 4,921 (1,900) | 47 (18) | 4,968 (1,918) | 1,928,655 | 392 (1,020) | |
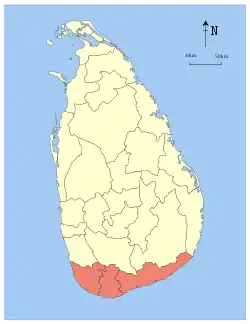 |
Galle | 1 October 1833 | 5,383 (2,078) | 161 (62) | 5,544 (2,141) | 2,477,285 | 460 (1,200) | |
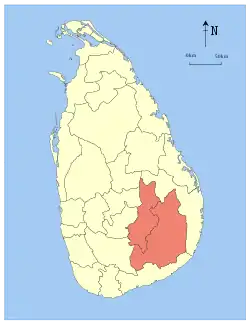 |
Badulla | 1886 | 8,335 (3,218) | 165 (64) | 8,500 (3,300) | 1,266,463 | 152 (390) | |
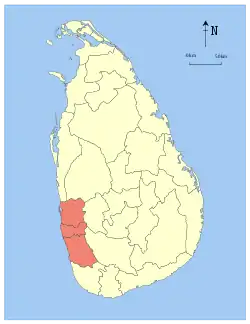 |
Colombo | 1 October 1833 | 3,593 (1,387) | 91 (35) | 3,684 (1,422) | 5,851,130 | 1,628 (4,220) | |
| Total | 62,705 (24,211) | 2,905 (1,122) | 65,610 (25,330) | 20,359,439 | 325 (840) |
Notes
- Population density has been calculated using the land area rather than the total area.
References
- Law, Gwillim (2010). "Provinces of Sri Lanka". statoids.com. Retrieved 19 January 2010.
- "Introduction". Provincial Councils. Government of Sri Lanka. Archived from the original on 7 July 2009. Retrieved 16 January 2010.
- "The Colebrooke-Cameron Reforms". Sri Lanka. Library of Congress. Retrieved 16 August 2009.
- Mills, Lennox A. (1933). Ceylon Under British Rule 1795–1932. London: Oxford University Press/Humphrey S. Milford. p. 68. Retrieved 16 August 2009.
- Mendis 1946, p. 39.
- Samarasinghe, L. M. (21 March 2003). "River basins as administrative divisions". Daily News (Sri Lanka).
- "Sinhala Colonisation in the Hereditary Tamil Regions of the Island of Sri Lanka". UN Commission on Human Rights 56th Sessions: March/April 2000. Tamil Nation. Retrieved 16 August 2009.
- Karalliyadda, S. B. (4 February 2009). "Independence Struggle for a Hundred and Thirty Three Years". Daily News (Sri Lanka). Retrieved 16 August 2009.
- Mendis 1946, p. 51.
- Mendis 1946, p. 84.
- Mendis 1946, p. 85.
- Selvanayagam, S. S. (17 October 2006). "North-East merger illegal: SC". The Daily Mirror (Sri Lanka). Archived from the original on 3 April 2013.
- Sambandan, V. S. (14 November 2003). "Sri Lanka's North-East to remain united for another year". The Hindu.
- "Table 1.1: Area of Sri Lanka by province and district" (PDF). Statistical Abstract 2014. Department of Census and Statistics, Sri Lanka.
- "Census of Population and Housing of Sri Lanka, 2012 – Table A1: Population by district, sex and sector" (PDF). Department of Census & Statistics, Sri Lanka.
Bibliography
- Mendis, G. C. (1946). Ceylon Under the British (2nd (Revised) ed.). Colombo: Colombo Apothecaries' Company.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Provinces of Sri Lanka. |
- "Provinces of Sri Lanka". Statoids.