Administrative division
Administrative division, subnational entity, first-level subdivision, administrative region, constituent unit, as well as many similar terms, are generic names for a discrete, officially-delineated geographical area within a particular, independent sovereign state (country). Such a division is created to enhance, in some way, the responsiveness of a national administration (government) to sub-national affairs. As such, an administrative division is granted a certain degree of administrative autonomy,[1] which in some countries is regarded as form of limited self-government.
| Part of the Politics series | ||||
| Basic forms of government | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
.svg.png.webp) | ||||
| Power source | ||||
|
|
||||
| Power ideology | ||||
|
|
||||
| Power structure | ||||
|
|
||||
|
| ||||
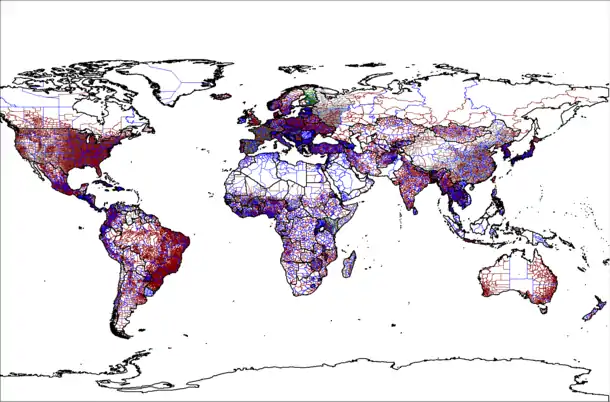
The names given to such divisions include: states (i.e. "federated states", rather than sovereign states), provinces, lands, oblasts, governorates, wilayahs, prefectures, regions, departments, and cantons. Larger countries are usually divided into two or more such administrative divisions. These, in turn, are usually divided in whole or in part into multiple, second-tier local governments, which are usually known by names such as circuits, counties, comarcas, raions, judets, administrative districts, parishes, municipalities, communes or communities. (In smaller countries, or in particular historical periods, first-level divisions carry a name from the latter group and/or are regarded as "local governments".)
Administrative divisions are conceptually separate from dependent territories, with the former being an integral part of the state and the other being only under some lesser form of control. However, the term "administrative division" can include dependent territories as well as accepted administrative divisions (for example, in geographical databases).
For clarity and convenience the standard neutral reference for the largest administrative division of a country is called the "first-level administrative division" or "first administrative level". Next smaller is called "second-level administrative division" or "second administrative level".[2][3]
Examples of administrative divisions
English terms
In many of the following terms originating from British cultural influence, areas of relatively low mean population density might bear a title of an entity one would expect to be either larger or smaller. There is no fixed rule, for "all politics is local" as is perhaps well demonstrated by their relative lack of systemic order. In the realm of self-government, any of these can and does occur along a stretch of road—which for the most part is passing through rural unsettled countryside. Since the terms are administrative political divisions of the local regional government their exact relationship and definitions are subject to home rule considerations, tradition, as well as state statute law and local governmental (administrative) definition and control. In British cultural legacy, some territorial entities began with fairly expansive counties which encompass an appreciably large area, but were divided over time into a number of smaller entities. Within those entities are the large and small cities or towns, which may or may not be the county seat. Some of the world's larger cities culturally, if not officially, span several counties, and those crossing state or provincial boundaries have much in common culturally as well, but are rarely incorporated within the same municipal government. Many sister cities share a water boundary, which quite often serves as a border of both cities and counties. For example, Cambridge and Boston, Massachusetts appear to the casual traveler as one large city, while locally they each are quite culturally different and occupy different counties.
List
- Area
- Autonomous community
- Banner
- Barony
- Capital city
- Canton
- County
- Community
- Constituency
- Crown dependency
- Department
- District
- Division
- Duchy
- Governorate
- Legal entity
- Hundred
- Federal subjects
- Kingdom
- Local council
- Municipality
- Oblast
- Parish
- Prefecture
- Principality
- Province
- Public body
- Region
- Republic
- Riding
- State
- Special administrative region
- Territory
- Theme
- Voivodeship
Urban or rural regions
General terms for these incorporated places include "municipality," "settlement," "locality," and "populated place."
Indigenous
Non-English terms
Due to variations in their use worldwide, consistency in the translation of terms from non-English to English is sometimes difficult to maintain.
Comparison
- Sovereign state, a national or supra-national division.
- Country, a national or sub-national division.
- Empire, a supra-national division.
See also
- GADM, a high-resolution database of country administrative areas.
- ISO 3166-2, specifically Codes for the representation of names of countries and their subdivisions — Part 2.
- List of administrative division name changes
- List of etymologies of country subdivision names
- List of administrative divisions by country
References
- "What does Administration mean?". The STANDS4 Network.
- "Global Administrative Unit Layers (GAUL)". FAO. Archived from the original on 24 September 2015.
- "Core Geo-Database". United Nations Geographic Information Working Group (UNGIWG). Archived from the original on 1 May 2014. Retrieved 1 May 2014.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Administrative territorial entities. |
- SALB Second Administrative Level Boundaries (SALB) programme of the United Nations.
- Statoids, an international convention with standardized two-letter-based multi-level summaries of administrative divisions worldwide (e.g. GH.AH.AS represents Adansi South (AE) in the Accra Home (AH) region of Ghana (GH)).