Suea pat
The suea pat (Lao: ເສື້ອປັດ Lao pronunciation: [sɯ̏a.pát], Northern Thai: เสื้อปั๊ด Northern Thai pronunciation: [sɯ̋a.pát]) or suea pai (Lao: ເສື້ອປ້າຍ Lao pronunciation: [sɯ̏a.pâaj], Northern Thai: เสื้อป้าย Northern Thai pronunciation: [sɯ̋a.pa̋aj]) [1][2] is a type of shirt worn by women from different ethnic backgrounds in Laos and Northern Thailand and other areas in Southeast Asia. These ethnic groups typically include the Lao, the Tai Lue, and the Tai Yuan etc.


The suea pat is a long-sleeved shirt with no buttons. It is worn by wrapping the right side of the front panel of the shirt over the left side of the front panel, and the two panels are tied together via strings. Suea pats from Luang Prabang, Laos typically have large golden collars.
Etymology
The words "suea pat" and "suea pai" are made up of words of Tai origin. "Suea pat" and "suea pai" literally mean "wrapping shirt"; suea (Thai: เสื้อ, Lao: ເສື້ອ) means "shirt", while pat (Thai: ปัด, Lao: ປັດ) and pai (Thai: ป้าย, Lao: ປ້າຍ) mean "to wrap sideways, to smear."
In Laos
In present-day Laos, women wear suea pats to ceremonial events such as weddings.[3] Each year in Luang Prabang, the winner of the Miss Songkran contest who becomes the next Miss Songkran, or nang sangkhane (Lao: ນາງສັງຂານ Lao pronunciation: [náaŋ.sǎŋ.kʰǎan]), gets to wear a suea pat underneath a pha biang which is a scarf-like cloth that wraps diagonally from the lower right waist to the upper left shoulder.
Design
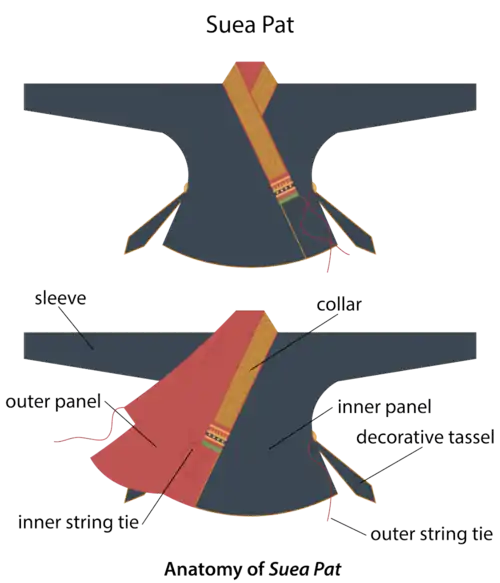
Suea pat is traditionally made with indigo-dyed cotton, silk or velvet. There are different variations of the suea pat among various Tai-speaking people.
Basic components of the suea pat include a collar, front panels, back panels, sleeves, and tie strings. There are tassels at the side of the garment, though not always present. Modern versions typically of Lao design may use fasteners or buttons in lieu of strings. The collar can be done with intricate goldwork or be left plain. A cuff matching the collar is sometimes present and the sleeves can be full or three-quarters length.
The cross-collar design is likely an influence of Chinese fashion as late as the Ming Dynasty.
