Union territory
A union territory (Hindi: kendraśāsit pradeś, lit. 'centrally administered province') is a type of administrative division in the Republic of India. Unlike the states of India, which have their own governments, union territories are federal territories governed, in part or in whole, by the Central Government of India.[1][2][3]
| Union territory | |
|---|---|
| Category | Federated states |
| Location | Republic of India |
| Number | 8 |
| Populations | Lakshadweep - 64,473 (lowest); Delhi - 16,787,941 (highest) |
| Areas | 32 km2 (12 sq mi) Lakshadweep – 59,146 km2 (22,836 sq mi) Ladakh |
| Government | Union government |
| Subdivisions | Districts, Divisions |
History
 |
|---|
| This article is part of a series on the politics and government of India |
|
|
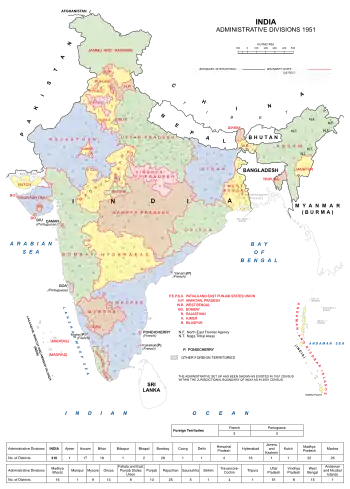
When the Constitution of India was adopted in 1949, the Indian federal structure included:
- Part C states, which were chief commissioners' provinces and some princely states, each governed by a chief commissioner appointed by the President of India. The ten Part C states were Ajmer, Bhopal, Bilaspur, Coorg, Delhi, Himachal Pradesh, Cutch, Manipur, Tripura and Vindhya Pradesh.
- One Part D state (Andaman and Nicobar Islands) administered by a lieutenant governor appointed by the central government.[4]
After the States Reorganisation Act, 1956, Part C and Part D states were combined into a single category of "Union territory". Due to various other reorganisations, only 6 union territories remained:
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Laccadive, Minicoy & Amindivi Islands (later renamed Lakshadweep)
- Delhi
- Manipur
- Tripura
- Himachal Pradesh
By early 1970s, Manipur, Tripura, and Himachal Pradesh had become full-fledged states, and Chandigarh became a union territory. Another three (Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu and Puducherry) were formed from acquired territories that formerly belonged to non-British colonial powers (Portuguese India and French India respectively).
In August 2019, the Parliament of India passed Jammu and Kashmir Reorganisation Act, 2019. The act contains provisions to reconstitute the state of Jammu and Kashmir into two union territories, one to be eponymously called Jammu and Kashmir, and the other Ladakh on 31 October 2019.
In November 2019, the Government of India introduced legislation to merge the union territories of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu into a single union territory to be known as Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu.[5][6][7]
Administration
The Parliament of India can pass a law to amend the constitution and provide a Legislature with elected Members and a Chief Minister for a union territory, as it has done for Delhi and Puducherry. In general, the President of India appoints an administrator or lieutenant governor for each UT.[1]
Delhi, Puducherry and Jammu and Kashmir operate differently from the other five. They were given partial statehood and Delhi was redefined as the National Capital Territory (NCT) and incorporated into a larger area known as the National Capital Region (NCR). Delhi, Puducherry and Jammu and Kashmir have an elected legislative assembly and an executive council of ministers with partially state-like function.
Due to existence of union territories, many critics have resolved India into a semi-federal nation, as the central and state governments each have their own domains and territories of legislation. Union territories of India have special rights and status due to their constitutional formation and development. The status of "union territory" may be assigned to an Indian sub-jurisdiction for reasons such as safeguarding the rights of indigenous cultures, averting political turmoil related to matters of governance, and so on. These union territories could be changed to states in the future for more efficient administrative control.[8]
The Constitution does not stipulate how tax revenue is to be devolved to the union territories, unlike for the states. The funds devolution to union territories by the union government have no criteria where all the revenue goes to the union government. Some union territories are provided more funds, while others are given less, in an arbitrary manner by the union government.[9] As union territories are directly ruled by the union government, some union territories get more funds from the union government than entitled on per capita and backwardness basis when compared to states.
After the introduction of GST, UT-GST is applicable in union territories which are not having legislative assembly. UT-GST is levied at par with the applicable state GST in rest of the country which would eliminate the previous lower taxation in the union territories.[10]
Constitutional status
Article 1 (1) of the Indian constitution says that India shall be a "Union of States", which are elaborated under Parts V (The Union) and VI (The States) of the constitution. Article 1 (3) says the territory of India comprises the territories of the states, the union territories and other territories that may be acquired. The concept of union territories was not in the original version of the constitution, but was added by the Constitution (Seventh Amendment) Act, 1956.[11] In the constitution wherever it refers to Territories of India, it is applicable to whole country including union territories. Where it refers to only India, it is applicable to all states only but not to union territories. Thus, citizenship (part II), fundamental rights (part III), Directive Principles of State Policy (part IV), Judiciary role, the Union Territories (part VIII), Article 245, etc. are applicable to union territories as it refers specifically to Territories of India. The executive power of Union (i.e. union of states only) rests with President of India. President of India is also chief administrator of union territories per Article 239. Union public service commission role is not applicable to all territories of India as it refers to India only in Part XIV.
The constitutional status of a union territory is similar to a state under the perennial president's rule per Article 356 subject to specific exemptions to few union territories with legislative assembly. Per Article 240 (2), supreme power is accorded to the president in regulating the affairs of all the union territories except Chandigarh, NCT and Puducherry, including powers to override the laws made by Parliament and the constitution of India. Article 240 (2) allows to implement tax haven laws in these union territories to attract foreign capital and investments in to India instead of depending on foreign tax haven countries.
Three of the union territories have representation in the upper house of the Indian Parliament, the Rajya Sabha. Delhi, Jammu and Kashmir, and Puducherry which are also exceptional among union territories in that each has its own locally elected legislative assembly and government.
Current union territories
| Union territory | ISO 3166-2:IN | Vehicle code |
Zone | Capital | Largest city | UT established | Population | Area (km2) |
Official languages |
Additional official languages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Andaman and Nicobar Islands | IN-AN | AN | Southern | Port Blair | 1 November 1956 | 380,581 | 8,249 | English, Hindi | Bengali, Malayalam, Tamil, Telugu | |
| Chandigarh | IN-CH | CH | Northern | Chandigarh | — | 1 November 1966 | 1,055,450 | 114 | English, Hindi, Punjabi | — |
| Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu | IN-DH | DD | Western | Daman | 26 January 2020 | 586,956 | 603 | English, Gujarati, Hindi | Konkani, Marathi | |
| Delhi | IN-DL | DL | Northern | New Delhi | — | 1 November 1956 | 16,787,941 | 1,490 | English, Hindi | Punjabi, Urdu[12] |
| Jammu and Kashmir | IN-JK | JK | Northern | Srinagar (Summer) Jammu (Winter) |
Srinagar | 31 October 2019 | 12,258,433 | 55,538 | English, Hindi, Urdu | Dogri, Kashmiri |
| Ladakh | IN-LA | LA | Northern | Leh (Summer) Kargil (Winter)[13] |
Leh | 31 October 2019 | 290,492 | 174,852 | English, Ladakhi, Urdu | Balti, Purgi |
| Lakshadweep | IN-LD | LD | Southern | Kavaratti | 1 November 1956 | 64,473 | 32 | English, Malayalam | — | |
| Puducherry | IN-PY | PY | Southern | Puducherry | 16 August 1962 | 1,247,953 | 492 | English,[14] Tamil | Malayalam, Telugu | |
Former union territories
| Map | Name | Zone | Capital | Area | UT established | UT disestablished | Today part of |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
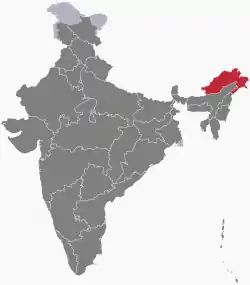 |
Arunachal Pradesh | North-Eastern | Itanagar | 83,743 km2 (32,333 sq mi) | 21 January 1972 | 20 February 1987 | As an Indian state |
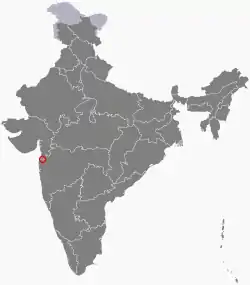 |
Dadra and Nagar Haveli | Western | Silvassa | 491 km2 (190 sq mi) | 11 August 1961 | 26 January 2020 | Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu union territory |
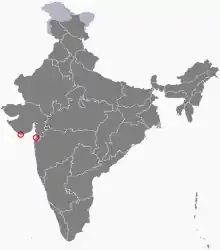 |
Daman and Diu | Western | Daman | 112 km2 (43 sq mi) | 30 May 1987 | 26 January 2020 | Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu union territory |
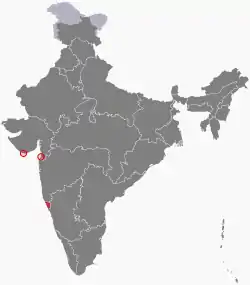 |
Goa, Daman and Diu | Western | Panaji | 3,814 km2 (1,473 sq mi) | 19 December 1961 | 30 May 1987 | Goa state and Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu union territory |
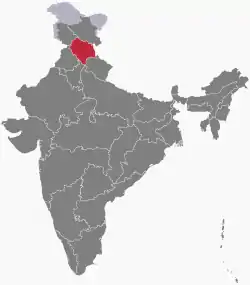 |
Himachal Pradesh | Northern | Shimla | 55,673 km2 (21,495 sq mi) | 1 November 1956 | 25 January 1971 | As an Indian state |
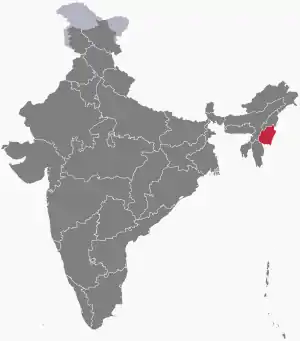 |
Manipur | North-Eastern | Imphal | 22,327 km2 (8,621 sq mi) | 1 November 1956 | 21 January 1972 | As an Indian state |
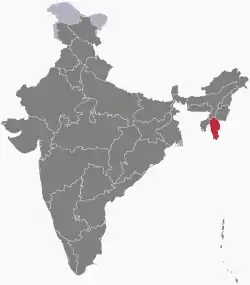 |
Mizoram | North-Eastern | Aizawl | 21,087 km2 (8,142 sq mi) | 21 January 1972 | 20 February 1987 | As an Indian state |
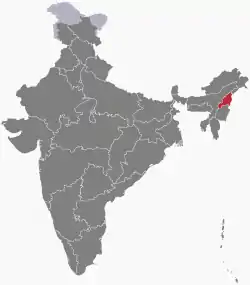 |
Nagaland | North-Eastern | Kohima | 16,579 km2 (6,401 sq mi) | 29 November 1957 | 1 December 1963 | As an Indian state |
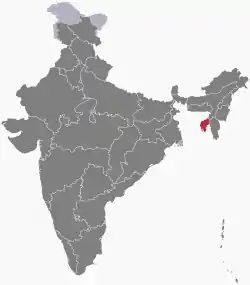 |
Tripura | North-Eastern | Agartala | 10,491.65 km2 (4,050.85 sq mi) | 1 November 1956 | 21 January 1972 | As an Indian state |
Proposed union territories
Mahe
Mahe district is one of the four districts of Puducherry, lying completely opposite to Puducherry district on Kerala coast. It is argued by many advocating the adjoining of Mahe with Lakshadweep or Kerala or make a separate union territory because of a perceived lack of development compared to the rest of Puducherry.
Panun Kashmir
Panun Kashmir is a superficial proposed union territory in the Kashmir Valley which is advocated by the Kashmiri Pandit Network as a homeland for Kashmiri Hindus who have fled the Kashmir valley as a result of ongoing violence and hope to return.[15]
See also
Notes
References
- Union Territories. Know India: National Portal of India Archived 2012-11-26 at the Wayback Machine
- "States and Union Territories". KnowIndia.gov.in. Archived from the original on 24 October 2013. Retrieved 17 November 2013.
- "Union Territories of India".
- "The Constitution (Seventh Amendment) Act, 1956". Archived from the original on 1 May 2017. Retrieved 19 November 2011.
- Dutta, Amrita Nayak (10 July 2019). "There will be one UT less as Modi govt plans to merge Dadra & Nagar Haveli and Daman & Diu". New Delhi. The Print. Retrieved 22 August 2019.
- "Govt plans to merge 2 UTs -- Daman and Diu, Dadra and Nagar Haveli". Press Trust of India. 22 November 2019. Retrieved 22 November 2019.
- "Bill No. 366 of 2019" [THE DADRA AND NAGAR HAVELI AND DAMAN AND DIU (MERGER OF UNION TERRITORIES) BILL, 2019]. Article 240 (2), of 21 November 2019 (PDF). Lok Sabha.
- "Supreme Court judgement, New Delhi Municipal Corporation ... vs State Of Punjab Etc.Etc on 19 December, 1996". Retrieved 17 September 2017.
- "Puducherry CM N Rangasamy seeks 'clear formula' for devolution of Central funds". Retrieved 17 September 2017.
- "Why Union Territory GST law (UTGST) is important?". Retrieved 17 September 2017.
- "The Constitution (Seventh Amendment) Act, 1956". Archived from the original on 1 May 2017. Retrieved 17 September 2017.
- "Official Language Act 2000" (PDF). Government of Delhi. 2 July 2003. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 17 July 2015.
- Excelsior, Daily (12 November 2019). "LG, UT Hqrs, Head of Police to have Sectts at both Leh, Kargil: Mathur". Retrieved 17 December 2019.
- "Regional data" (PDF). lawsofindia.org.
- http://www.panunkashmir.org/
External links
 Media related to Union territories of India at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Union territories of India at Wikimedia Commons

.svg.png.webp)
.svg.png.webp)