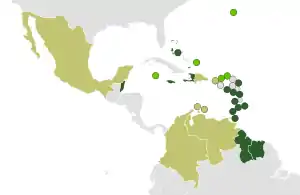
Caribbean Community
The Caribbean Community (CARICOM or CC) is an organisation of fifteen states and dependencies throughout the Caribbean having primary objectives to promote economic integration and cooperation among its members, to ensure that the benefits of integration are equitably shared, and to coordinate foreign policy.[10] The organisation was established in 1973. Its major activities involve coordinating economic policies and development planning; devising and instituting special projects for the less-developed countries within its jurisdiction; operating as a regional single market for many of its members (Caricom Single Market); and handling regional trade disputes. The secretariat headquarters is in Georgetown, Guyana. CARICOM is an official United Nations Observer.[11]
CARICOM was established by the English-speaking parts of the Caribbean, and currently includes all the independent anglophone island countries plus Belize, Guyana and Montserrat, as well as all other British Caribbean territories and Bermuda as associate members. English was its sole working language into the 1990s. The organization has become multilingual with the addition of Dutch-speaking Suriname in 1995 and the French-speaking Haiti in 2002. Furthermore, it has added Spanish as the fourth official language in 2003.[2] In July 2012, CARICOM announced that they were considering making French and Dutch official languages.[12] In 2001, the heads of government signed a revised Treaty of Chaguaramas that cleared the way to transform the idea of a common market CARICOM into a Caribbean (CARICOM) Single Market and Economy. Part of the revised treaty establishes and implements the Caribbean Court of Justice.
Membership
Currently CARICOM has 15 full members, 5 associate members and 8 observers. All of the associate members are British Overseas Territories, and it is currently not established what the role of the associate members will be. The observers are states which engage in at least one of CARICOM's technical committees. Although the group has close ties with Cuba, that nation was excluded due to lack of full democratic internal political arrangement. In 2017 the Republic of Cuba and the Caribbean Community (CARICOM) bloc signed the "CARICOM-Cuba Trade and Economic Cooperation Agreement"[13] to facilitate closer ties.
| Status | Name | Join date | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full member | 4 July 1974 | ||
| 4 July 1983 | Not a part of the customs union | ||
| 1 August 1973 | One of the four founding members | ||
| 1 May 1974 | |||
| 1 May 1974 | |||
| 1 May 1974 | |||
| 1 August 1973 | One of the four founding members | ||
| 2 July 2002 | Provisional membership on 4 July 1998 | ||
| 1 August 1973 | One of the four founding members | ||
| 1 May 1974 | British overseas territory | ||
| 26 July 1974 | Joined as Saint Christopher-Nevis-Anguilla | ||
| 1 May 1974 | |||
| 1 May 1974 | |||
| 4 July 1995 | |||
| 1 August 1973 | One of the four founding members | ||
| Associate | July 1999 | British overseas territory | |
| 2 July 2003 | British overseas territory | ||
| July 1991 | British overseas territory | ||
| 16 May 2002 | British overseas territory | ||
| July 1991 | British overseas territory | ||
| Observer | Constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands | ||
| Constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands | |||
| Unincorporated territory of the United States | |||
| Constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands | |||
Organisational structure
Structures comprised by the overall Caribbean Community (CARICOM).[15]
Under Article 4 CARICOM breaks its 15 member states into two groups: Less Developed Countries (LDCs) and More Developed Countries (MDCs).[16]
The countries of CARICOM which are designated as Less Developed Countries (LDCs) are:[16]
- Antigua and Barbuda
- Belize
- Commonwealth of Dominica
- Grenada
- Republic of Haiti
- Montserrat
- Federation of St. Kitts and Nevis
- St Lucia
- St Vincent and the Grenadines
The countries of CARICOM which are designated as More Developed Countries (MDCs) are:[16]
- Commonwealth of the Bahamas
- Barbados
- Co-operative Republic of Guyana
- Jamaica
- Republic of Suriname
- Republic of Trinidad and Tobago
Chairmanship
The post of Chairman (Head of CARICOM) is held in rotation by the regional Heads of State (for the republics) and Heads of Government (for the realms) of CARICOM's 15 member states. These include: Antigua and Barbuda, Belize, Dominica, Grenada, Haiti, Montserrat, St. Kitts and Nevis, St. Lucia, St. Vincent and the Grenadines, Bahamas, Barbados, Guyana, Jamaica, Suriname, Trinidad and Tobago.
Heads of government
CARICOM contains a quasi-Cabinet of the individual Heads of Government. These heads are given specific specialised portfolios of responsibility for overall regional development and integration.[17]
Secretariat
- Secretariat of the Caribbean Community, The term of office of the Secretary-General is five years, which may be renewed. (Chief Administrative Organ)
- Secretary-General of the Caribbean Community, the CARICOM Secretary General (Chief Executive) handles foreign and community relations.
- Deputy Secretary-General of the Caribbean Community, handles human and social Development.
- General Counsel of the Caribbean Community, handles trade and economic integration.
The goal statement of the CARICOM Secretariat is:
To provide dynamic leadership and service, in partnership with Community institutions and Groups, toward the attainment of a viable, internationally competitive and sustainable Community, with improved quality of life for all.
Organs and bodies
| Organ | Description |
|---|---|
| CARICOM Heads of Government | Consisting of the various heads of Government from each member state |
| Standing Committee of Ministers | Ministerial responsibilities for specific areas, for example the Standing Committee of Ministers responsible for Health will consist of Ministers of Health from each member state |
Community Council
The Community Council consists of ministers responsible for community affairs and any other Minister designated by the member states in their absolute discretion. It is one of the community's principal organs; the other is the Conference of the Heads of Government. It is supported by four other organs and three bodies.
| Secondary organ | Abbreviation |
|---|---|
| Council for Finance and Planning | COFAP |
| Council for Foreign and Community Relations | COFCOR |
| Council for Human and Social Development | COHSOD |
| Council for Trade and Economic Development | COTED |
| Body | Description |
|---|---|
| Legal Affairs Committee | provides legal advice |
| Budget Committee | examines the draft budget and work programme of the Secretariat and submits recommendations to the Community Council. |
| Committee of the Central Bank Governors | provides recommendations to the COFAP on monetary and financial matters. |
Institutions
The 25 designated institutions of CARICOM are as follows:
| Institution | Abbreviation |
|---|---|
| Caribbean Disaster Emergency Management Agency | CDEMA |
| Caribbean Meteorological Institute | CMI |
| Caribbean Meteorological Organisation | CMO |
| Caribbean Food Corporation | CFC |
| Caribbean Environment Health Institute | CEHI |
| Caribbean Agriculture Research and Development Institute | CARDI |
| Caribbean Regional Centre for the Education and training of Animal Health and Veterinary Public Health Assistants | REPAHA |
| Assembly of Caribbean Community Parliamentarians | ACCP |
| Caribbean Centre for Development Administration | CARICAD |
| Caribbean Food and Nutrition Institute | CFNI |
| Caribbean Agricultural Health and Food Safety Agency | CAHFSA |
| CARICOM Implementation Agency for Crime and Security | IMPACS |
| Caribbean Examinations Council | CXC |
| CARICOM Single Market and Economy | CSME |
| Caribbean Court of Justice | CCJ |
| Caribbean Community Administrative Tribunal | CCAT |
| CARICOM Competition Commission | CCC |
| Caribbean Regional Fisheries Mechanism | CRFM |
| Caribbean Regional Organisation for Standards and Quality | CROSQ |
| Caribbean Telecommunications Union | CTU |
| Caribbean Community Climate Change Centre | CCCCC |
| Caribbean Organisation of Tax Administrators | COTA |
| Council of Legal Education | CLE |
| Caribbean Aviation Safety and Securing Oversight System | CASSOS |
| Caribbean Regional Information and Translation Institute | CRITI |
The Caribbean Court of Justice (CCJ) is based in Port of Spain, Trinidad and Tobago and was chiefly developed to act as a settlement unit for disputes on the functioning of the Caribbean (CARICOM) Single Market and Economy (CSME) (known as "original jurisdiction"). In addition, some of the region's Commonwealth Caribbean member states of CARICOM have opted to supplement original jurisdiction with "appellate jurisdiction" which by practice replaces the Privy Council (in London, United Kingdom) with the CCJ.
The Caribbean Public Health Agency (CARPHA) is a regional public health agency headquartered in Trinidad and Tobago[18] which was established by CARICOM leaders in July 2011[19] and began operation in 2013.[18]
As of 2018, the majority of member states continue to utilize the Privy Council as their final appellate court and three member states do not use the CCJ for either its original jurisdiction or its appellate jurisdiction because they have either not signed the Revised Treaty of Chaguaramas (the Bahamas and Haiti) or are a current United Kingdom Overseas Territory (Montserrat). A handful of various public propositions have been held in several countries of CARICOM polling on public support for transitioning of appellate jurisdiction to the CCJ, and to date the majority of these measures held have failed.
Associate institutions
The seven designated associate institutions of CARICOM are as follows:
| Associate institution | Abbreviation |
|---|---|
| Caribbean Development Bank | CDB |
| University of Guyana | UG |
| University of the West Indies | UWI |
| Caribbean Law Institute / Caribbean Law Institute Centre | CLI / CLIC |
| Organisation of Eastern Caribbean States | OECS |
| West Indies Cricket Board | WICB |
| CARICOM Private Sector Organisation[20] | CPSO |
Symbols
Standard
The flag of the Caribbean Community was chosen and approved in November 1983 at the Conference of Heads of Government Meeting in Port of Spain, Trinidad. The original design by the firm of WINART Studies in Georgetown, Guyana was substantially modified at the July 1983 Meeting of the Conference of Heads of Government.[21] The flag was first flown on 4 July 1984 in Nassau, Bahamas at the fifth Meeting of the Conference of Heads of Government.[22]
The flag features a blue background, but the upper part is a light blue representing sky and the lower, a darker blue representing the Caribbean Sea. The yellow circle in the centre represents the sun on which is printed in black the logo of the Caribbean Community, two interlocking Cs. The two Cs are in the form of broken links in a chain, symbolising both unity and a break with the colonial past. The narrow ring of green around the sun represents the vegetation of the region.[21]
Song
For CARICOM's 40th anniversary, a competition to compose an official song or anthem for CARICOM was launched in April 2013[23] to promote choosing a song that promoted unity and inspired CARICOM identity and pride. A regional panel of judges comprising independent experts in music was nominated by member states and the CARICOM Secretariat. Three rounds of competition condensed 63 entries to a final three, from which judges chose Celebrating CARICOM by Michele Henderson of Dominica[23] in March 2014.[24] Henderson won a US$10,000 prize.[25] Her song was produced by her husband, Roland Delsol Jr., and arranged by Earlson Matthew. It also featured Michael Ferrol on drums and choral input from the St. Alphonsus Choir. It was re-produced for CARICOM by Carl Beaver Henderson of Trinidad and Tobago.[24]
A second-place entry titled My CARICOM came from Jamaican Adiel Thomas[23] who won US$5,000,[25] and a third-place song titled One CARICOM by Carmella Lawrence of St. Kitts and Nevis,[23] won US$2,500.[25] The other songs from the top-ten finalists (in no particular order) were:
- One Region one Caribbean from Anguilla,
- One Caribbean Family from Jamaica,
- CARICOM’s Light from St. Vincent & the Grenadines,
- We Are CARICOM from Dominica,
- Together As one from Dominica,
- Blessed CARICOM from Jamaica,
- Together We Rise from Jamaica.[24]
The first official performance of Celebrating CARICOM by Henderson took place on Tuesday 1 July 2014 at the opening ceremony for the Thirty-Fifth Regional Meeting of the Conference of Heads of Government in Antigua and Barbuda.[23]
Celebration
CARICOM DAY
The celebration of CARICOM Day is the selected day some Caribbean Community (CARICOM) countries officially recognise the commemorative date of signing of the Treaty of Chaguaramas, the agreement that established CARICOM on July 4, 1973. The Treaty was signed in Chaguaramas, Trinidad & Tobago by then leaders of: Barbados, Guyana, Jamaica, and Trinidad and Tobago. CARICOM Day is recognised as an official public holiday in Guyana where the secretariat is based, and is observed on the first Monday of July. The government of Antigua and Barbuda has also implemented CARICOM Day as a holiday.
The day features activities that are organised by government entities such as parades, pageants, and campaigns to educate people about CARICOM.
CARICOM-Cuba Day
The Republic of Cuba commemorates with the bloc the initial date of official political relations between CARICOM and Cuba as the second week of December.[26]
History
CARICOM, originally the Caribbean Community and Common Market, was established by the Treaty of Chaguaramas[27] which took effect on 1 August 1973. The first four signatories were Barbados, Jamaica, Guyana and Trinidad and Tobago.
CARICOM superseded the 1965–1972 Caribbean Free Trade Association (CARIFTA) organised to provide a continued economic linkage between the English-speaking countries of the Caribbean after the dissolution of the West Indies Federation, which lasted from 3 January 1958 to 31 May 1962.
A revised Treaty of Chaguaramas established the Caribbean Community including the CARICOM Single Market and Economy (CSME) and was signed by the CARICOM Heads of Government of the Caribbean Community on 5 July 2001 at their Twenty-Second Meeting of the Conference in Nassau, The Bahamas.[16] The revised treaty cleared the way to transform the idea of a common market CARICOM into the Caribbean (CARICOM) Single Market and Economy.
Haiti's membership in CARICOM remained effectively suspended from 29 February 2004 through early June 2006 following the 2004 Haitian coup d'état and the removal of Jean-Bertrand Aristide from the presidency.[28][29] CARICOM announced that no democratically elected government in CARICOM should have its leader deposed. The fourteen other heads of government sought to have Aristide fly from Africa to Jamaica and share his account of events with them, which infuriated the interim Haitian prime minister, Gérard Latortue, who announced he would take steps to take Haiti out of CARICOM. CARICOM thus voted on suspending the participation of Haitian officials from the councils of CARICOM.[30] Following the presidential election of René Préval, Haitian officials were readmitted and Préval himself gave the opening address at the CARICOM Council of Ministers meeting in July.
Since 2013 the CARICOM-bloc and with the Dominican Republic have been tied to the European Union via an Economic Partnership Agreements signed in 2008 known as CARIFORUM.[31] The treaty grants all members of the European Union and CARIFORUM equal rights in terms of trade and investment. Under Article 234 of the agreement, the European Court of Justice handles dispute resolution between CARIFORUM and European Union states.[32]
Statistics
| Member | Membership | Land area (km2)[33] | Population (2019) | GDP (PPP) Millions USD (2017)[34] | GDP Per Capita (PPP) USD (2017) | Human Development Index (2018) [35] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| associate | 91 | 15,174 | 175.4 | 12,200 | - | |
| full member | 442.6 | 104,084 | 2,390 | 26,300 | 0.776 | |
| full member | 10,010 | 385,340 | 9,339 | 25,100 | 0.805 | |
| full member | 430 | 287,010 | 4,919 | 17,500 | 0.813 | |
| full member | 22,806 | 398,050 | 3,230 | 8,300 | 0.720 | |
| associate | 54 | 63,779 | 5,198 | 85,700 | - | |
| associate | 151 | 32,206 | 500 | 42,300 | - | |
| associate | 264 | 64,420 | 2,507 | 43,800 | - | |
| full member | 751 | 74,679 | 851 | 12,000 | 0.724 | |
| full member | 344 | 108,825 | 1,590 | 14,700 | 0.763 | |
| full member | 214,970 | 786,508 | 6,367 | 8,300 | 0.670 | |
| full member | 27,560 | 11,242,856 | 19,880 | 1,800 | 0.503 | |
| full member | 10,831 | 2,728,864 | 26,200 | 9,200 | 0.726 | |
| full member | 102 | 5,220 | 43.8 | 8,500 | - | |
| full member | 261 | 56,345 | 1,528 | 26,800 | 0.777 | |
| full member | 606 | 180,454 | 2,384 | 13,500 | 0.745 | |
| full member | 389 | 109,803 | 1,281 | 11,600 | 0.728 | |
| full member | 156,000 | 573,085 | 7,928 | 13,900 | 0.724 | |
| full member | 5,128 | 1,359,193 | 42,780 | 31,200 | 0.799 | |
| associate | 948 | 37,910 | 632 | 29,100 | - | |
| Full members | members only | 432,510 | 18,400,316 | 130,711 | 15,247 | 0.730 |
Thousands of Caricom nationals live within other member states of the Community.
An estimated 30,000 Jamaicans legally reside in other CARICOM member states,[36] mainly in the Bahamas (5,600),[37] Antigua & Barbuda (estimated 12,000),[38] Barbados and Trinidad & Tobago).[36] Also, an estimated 150 Jamaicans live and work in Montserrat.[38] A November 21, 2013 estimated put 16,958 Jamaicans residing illegally in Trinidad & Tobago, as according to the records of the Office of the Chief Immigration Officer, their entry certificates would have since expired.[39] By October 2014, the estimated Jamaicans residing illegally in Trinidad and Tobago was 19,000 along with an estimated 7,169 Barbadians and 25,884 Guyanese residing illegally.[40] An estimated 8,000 Trinidadians and Tobagonians live in Jamaica.[41]
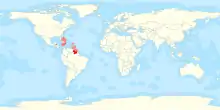
Barbados hosts a large diaspora population of Guyanese, of whom (in 2005) 5,032 lived there permanently as citizens, permanent residents, immigrants (with immigrant status) and Caricom skilled nationals; 3,200 were residing in Barbados temporarily under work permits, as students, or with "reside and work" status. A further 2,000-3,000 Guyanese were estimated to be living illegally in Barbados at the time.[42] Migration between Barbados and Guyana has deep roots, going back over 150 years, with the most intense period of Barbadian migration to then-British Guiana occurring between 1863 and 1886, although as late as the 1920s and 1930s Barbadians were still leaving Barbados for British Guiana.[43]
Migration between Guyana and Suriname also goes back a number of years. An estimated 50,000 Guyanese had migrated to Suriname by 1986[44][45] In 1987 an estimated 30-40,000 Guyanese were in Suriname.[46] Many Guyanese left Suriname in the 1970s and 1980s, either voluntarily by expulsion. Over 5,000 were expelled in January 1985 alone.[47] in the instability Suriname experienced following independence, both coups and civil war.[45] In 2013 an estimated 11,530 Guyanese had emigrated to Suriname and 4,662 Surinamese to Guyana.[48]
Relationship to other supranational Caribbean organisations
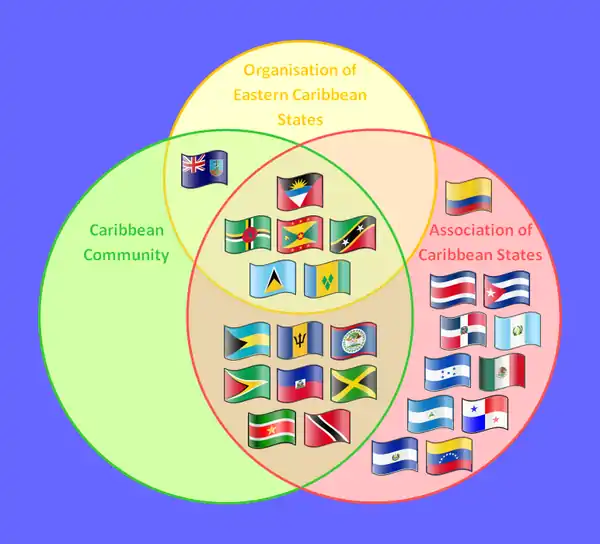
Association of Caribbean States
CARICOM was instrumental in the formation of the Association of Caribbean States (ACS) on 24 July 1994. The original idea for the Association came from a recommendation of the West Indian Commission, established in 1989 by the CARICOM heads of state and government. The Commission advocated both deepening the integration process (through the CARICOM Single Market and Economy) and widening it through a separate regional organisation encompassing all states in the Caribbean.[49]
CARICOM accepted the commission's recommendations and opened dialogue with other Caribbean states, the Central American states and the Latin American nations of Colombia, Venezuela and Mexico which border the Caribbean, for consultation on the proposals of the West Indian Commission.[49]
At an October 1993 summit, the heads of state and government of CARICOM and the presidents of the then-Group of Three (Colombia, Mexico and Venezuela) formally decided to create an association grouping all states of the Caribbean basin. A work schedule for its formation was adopted. The aim was to create the association in less than a year, an objective which was achieved with the formal creation of the ACS.[49]
Community of Latin American and Caribbean States
CARICOM was also involved in the formation of the Community of Latin American and Caribbean States (CELAC) on 3 December 2010. The idea for CELAC originated at the Rio Group–Caribbean Community Unity Summit on 23 February 2010 in Mexico.[50][51][52][53][54]
European Union: Economic Partnership Agreements
Since 2013, the CARICOM-bloc and the Dominican Republic have been tied to the European Union via an Economic Partnership Agreements known as CARIFORUM signed in 2008.[31] The treaty grants all members of the European Union and CARIFORUM equal rights in terms of trade and investment. Within the agreement under Article 234, the European Court of Justice also carries dispute resolution mechanisms between CARIFORUM and the states of the European Union.[32]
OHADAC Project
In May 2016, Caricom's court of original jurisdiction, the CCJ, signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) with the ACP Legal Association based in Guadeloupe recognising and supporting the goals of implementing a harmonised business law framework in the Caribbean through ACP Legal Association's OHADAC Project.[55]
OHADAC is the acronym for the French "Organisation pour l'Harmonisation du Droit des Affaires en les Caraïbes", which translates into English as "Organisation for the Harmonisation of Business Law in the Caribbean". The OHADAC Project takes inspiration from a similar organisation in Africa and aims to enhance economic integration across the entire Caribbean and facilitate increased trade and international investment through unified laws and alternative dispute resolution methods.[55]
Free Trade Agreements
See also
- Projects of the Caribbean Community
- CSME
- Association of Caribbean States
- North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA)
- North American Union (NAU)
- Union of South American Nations (UNASUR)
- CARIFORUM
- Caribbean Financial Action Task Force
- Caribbean Initiative
- Caribbean Agricultural Research and Development Institute (CARDI)
- Caribbean Accreditation Authority for Education in Medicine and other Health Professions
- Caribbean Knowledge and Learning Network
- Community of Latin American and Caribbean States
- Commonwealth of Nations
- Languages of the Caribbean
- List of regional organizations by population
- Organisation of African, Caribbean and Pacific States
- Organization of American States
- Petrocaribe
- Small Island Developing States
- West Indies
References
- https://caricom.org/about-caricom/who-we-are/our-symbols/
- "Spanish agreed as CARICOM second language". www.landofsixpeoples.com.
- "Who we are".
- "Our Culture".
- "The World Factbook - Central Intelligence Agency". www.cia.gov.
- "2021 must be the year of CARICOM". Jamaica Gleaner. 1 January 2021. Retrieved 1 January 2021.
- "CARICOM - Caribbean Community 2021". countryeconomy.com.
- https://www.imf.org/external/datamapper/PPPGDP@WEO/OEMDC/ADVEC/WEOWORLD
- List of countries by HDI
- Ramjeet, Oscar (2009-04-16). "CARICOM countries will speak with one voice in meetings with US and Canadian leaders". Caribbean Net News. Retrieved 2009-04-16.
- "Page has moved". www.un.org.
- "Communiqué Issued at the Conclusion of the Thirty-Third Regular Meeting of the Conference of Heads of Government of the Caribbean Community, 4-6 July 2012, Gros Islet, Saint Lucia" Archived 16 January 2013 at the Wayback Machine, "Heads of Government recognized that, although English was the official language of the Community, the facility to communicate in their languages could enhance the participation of Haiti and Suriname in the integration process. They therefore requested the conduct of a study to examine the possibilities and implications, including costs, of introducing French and Dutch."
- "CARICOM-Cuba Trade and Economic Cooperation Agreement".
- CIA World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. 2017. p. 971. ISBN 9781510712898.
- "Wayback Machine" (PDF). web.archive.org. January 28, 2010. Cite uses generic title (help)
- "Revised Treaty of Chaguaramas" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on November 10, 2011.
- "Regional Portfolios of CARICOM Heads of Government". web.archive.org. May 2, 2008.
- "Remarks by Ambassador Irwin LaRocque, Secretary-General of the Caribbean Community, (CARICOM) At The Launch of the Caribbean Public Health Agency (CARPHA)". CARICOM. 3 July 2013. Retrieved 5 April 2020.
- "CARICOM to Establish Health Agency". Caribbean Journal.
- "Jamaica Observer Limited". Jamaica Observer.
- "CARICOM: Our Symbols".
- "Caribbean Community and Common Market". www.crwflags.com.
- "History created as new CARICOM song is launched".
- "WORD Version of CARICOM song competition Fact Sheet". July 3, 2014.
- "CARICOM Song Competition: Terms of Reference" (PDF).
- SLCHSA STATEMENT ON CUBA – CARICOM DAY, December 8, 2015, CubaSí
- "Original Treaty of Chaguaramas". Archived from the original on October 11, 2007.
- "Aristide accuses U.S. of forcing him out". Canadian Broadcast Corporation. 2004-03-02. Retrieved 2011-03-25.
- "Aristide launches kidnap lawsuit". BBC News. 2004-03-31. Retrieved 2011-03-25.
- "Haiti suspends ties with CARICOM". Trinidadandtobagonews.com. Retrieved 2011-03-25.
- Caribbean moves afoot to restructure CARIFORUM, Peter Richards, Tuesday April 12th 2011
- "Letter: Privy Council and EPA" Archived 2014-08-21 at the Wayback Machine, October 8, 2009, Jamaica Gleaner
- "Land area rankings". The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved December 23, 2017.
- "Gross domestic product based on purchasing-power-parity (PPP) valuation of country GDP" (2013). World Economic Outlook Database 2014. International Monetary Fund. .
- "Human Development Report 2019" (PDF). United Nations. United Nations. Retrieved 29 April 2020.
- "30,000 Jamaicans residing in other CARICOM member states". Archived from the original on 2016-03-10. Retrieved 2015-04-20.
- "People Groups | Joshua Project". www.joshuaproject.net.
- "PM Golding Calls on Jamaicans in Antigua & Barbuda to Co-Operate with Government & People There". Jamaica Information Service. July 7, 2008.
- "Jamaica Observer Limited". Jamaica Observer.
- "7 000 illegal Bajans in T&T". www.nationnews.com. October 16, 2014.
- "Bissessar celebrates new Trinidad &Tobago high commission". jamaica-gleaner.com. April 17, 2015.
- "Guyanese, British and Americans among illegal immigrants living in Barbados". cnewsnow.tripod.com.
- "Mudheads in Barbados: A Lived Experience". August 1, 2011.
- "Ethnologue Languages of Suriname".
- "Guyanese Creole Survey Report" (PDF).
- "Guyanese vital in Suriname".
- "Nervous neighbours: Guyana and Suriname". November 5, 2008.
- "Guyana Migration Profiles" (PDF).
- "Evolution of the Association of Caribbean States" (PDF).
- "Mexidata (English) March 1, 2010". Mexidata.info. Archived from the original on April 26, 2012. Retrieved 2012-05-25.
- "Acuerdan crear Comunidad de Estados Latinoamericanos y Caribeños". Associated Press. February 23, 2010.
- "América Latina crea una OEA sin Estados Unidos". El País. February 23, 2010.
- "Mexico's Latin American Summit (22-23 Feb) -- Pushing Rio Group Mechanism to Take Over Calc". February 23, 2010 – via WikiLeaks PlusD.
- "Rio Group approves its expansion at Unity Summit".
- "CCJ signs MOU on harmonising business law in Caribbean". May 20, 2016.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Caribbean Community. |
- Official website
- Official Blog CARICOM Today
- CARICOM Representation Office in Haiti (CROH)
- CARICOM Statistics: Statistical information compiled through the CARICOM Secretariat
- Radio CARICOM: the voice of the Caribbean Community (Press Release)
- Caricom Law: Website and online database of the CARICOM Legislative Drafting Facility (CLDF)
- Caricom Trade Support Programme: Government of Trinidad and Tobago
- CARICOM Trade Support Programme Loan
- Rapid Exchange System for Dangerous Non-food Consumer Goods (CARREX): Front end for Consumer Product Incident Reporting
- PANCAP: Pan Caribbean Partnership Against HIV/AIDS
- CARICOM Regional Organisation for Standards and Quality (CROSQ)
- "CARICOM (Revised Treaty)" (PDF). (573 KB)
- EU Style Structure Evident in CARICOM
- Haiti suspends ties with CARICOM
- Jamaica Gleaner News - Haiti could return to CARICOM
- Haiti re-admitted?
- Caricom and Haiti: The raising of the Caribbean's 'Iron Curtain'
- How viable is a single Caribbean currency? Part II
- How viable is a single Caribbean currency? Part III
- The Dominican Republic in Caricom? Yes, we can
- Bureau recommends re-examination of Dominican Republic's proposed membership in CARICOM
- Guyana Journal (2007-07): Advancing Integration Between Caricom and Central America
- EDITORIAL: We may just have to dump CARICOM, July 4, 2010, Jamaica Gleaner
- Commentary: Gleaner newspaper suggests disbanding CARICOM, July 5, 2010, Caribbean Net News
- Does Caricom have a future? , 6 July 2010, BBC.co.uk
- That elusive governance structure, 7 July 2010, BBC.co.uk