Culture of North Carolina
The Culture of North Carolina is a subculture in the United States. As a coastal state and one of the original Thirteen Colonies, North Carolina culture has been greatly influenced by early settlers of English, Swiss, German, Scotch-Irish and Scotch descent.[1] Likewise, African Americans have had great cultural influence in North Carolina, first coming as enslaved people during colonial times. From slavery to freedom, they have helped shape things such as literary traditions, religious practices, cuisine, music, and popular culture.[2]
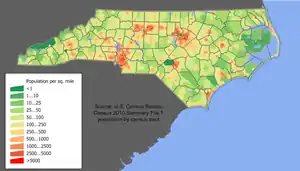
In recent times, North Carolina has seen an influx of people from areas such as New York, Florida, Virginia, South Carolina, and California; as well as an increase in Hispanic, East Asian and Indian immigrants.[3] Many of these recent transplants usually aggregate in one of several urban centers in the Piedmont region. In rural North Carolina, agriculture is a major component of the economy, and thus many local traditions are centered on the lifestyles associated with farming. Some of these traditions are reflected in pop culture in North Carolina, for instance some North Carolinians may refer to the state as "the Tar Heel state".
Urban culture
| This article is part of a series on the |
| Culture of the United States of America |
|---|
| Society |
| Arts and literature |
| Other |
| Symbols |
|
United States portal |
Due to the presence of several dense urban centers in North Carolina, many cities have very distinctive cultures and most have a melting pot of cultures. The Research Triangle Park, also known as RTP, is chiefly composed of Raleigh, Durham, and Chapel Hill. It also includes several other towns including Cary, Carrboro, Morrisville and Apex. RTP serves as an anchor for many large businesses in the area, which has the effect of attracting many secondary and supporting businesses. This has created a high concentration of educated and affluent homes in and around RTP. This has also created a demand for independent, unique, high quality restaurants and night life in the area, as well as a high demand for craft beer.
Despite having several urban centers, these cities/towns are smaller than other well-known metropolitan areas across the United States. So while these urban centers have many similar amenities that larger cities have, the options and variability can be limited. Due to this, there is a very high unmet demand for modern urban amenities and entertainment. This unmet demand has led to nearly constant construction and development in areas such as the Research Triangle and Charlotte for several decades. These construction projects include planned subdivisions, restaurants, strip malls, highway expansions, new schools, and business parks.
Rural culture
While there are several dense urban centers across the state, much of North Carolina is also rural. Dense forests cover much of North Carolina, as well as reclaimed land used for agricultural purposes. Rural North Carolina tends to lean towards traditional Southern culture. Some common recreational activities in rural North Carolina include horseback riding, swimming in rivers and lakes, target shooting and hunting, riding trails on ATVs/modified trucks (also called off-roading), and extensive gardening (many families operate small scale farms).
Food
A nationally famous cuisine from North Carolina is pork barbecue and bacon. In Eastern North Carolina, pork barbecue uses a vinegar-based sauce and the "whole hog" is cooked, using both white and dark meat. While there is not one town in Eastern North Carolina that can claim to be the indisputable "capital" of Eastern Carolina barbecue, the medium-sized cities of Greenville and Goldsboro, and their surrounding communities boast the highest concentrations of highly ranked establishments. The annual Newport Pig Pickin' (the largest whole pig cooking contest in North Carolina) is held featuring primarily eastern-style barbecue. Western North Carolina pork barbecue uses a tomato and vinegar based sauce, and only the pork shoulder (dark meat) is used. The "capital" of Western Carolina barbecue is indisputably the Piedmont Triad town of Lexington, home of the Lexington Barbecue Festival, which brings in over 100,000 visitors each October.[4]
Arts
Literature
Music
North Carolina is known particularly for its history of old-time music. Many recordings were made in the early 20th century by folk song collector Bascom Lamar Lunsford. Influential North Carolina country musicians like the North Carolina Ramblers and Al Hopkins helped solidify the sound of country music in the late 1920s. Other influential bluegrass musicians such as Earl Scruggs, Doc Watson and Del McCoury are also from North Carolina. Arthur Smith is a notable North Carolina musician/entertainer who had the first nationally syndicated television program which featured country music. Smith composed "Guitar Boogie", the all-time best selling guitar instrumental, and "Dueling Banjos", the all-time best selling banjo composition. Country artist Eric Church from the Hickory area, has had multiple #1 albums on the Billboard 200, including Chief in 2011. Both North and South Carolina are a hotbed for traditional country blues, especially the style known as the Piedmont blues. Elizabeth Cotten, from Chapel Hill, was active in the American folk music revival.
Because of their proximity to universities, areas such as Raleigh-Durham-Chapel Hill (collectively known as the Triangle), Asheville, Greensboro, Greenville, Charlotte, and Wilmington have long been a well-known center for indie rock, metal, punk, jazz, country, and hip-hop. Bands and groups from these popular music scenes include The Avett Brothers, Corrosion of Conformity, Superchunk, The Rosebuds, The Love Language, Troop 41, Ben Folds Five, Squirrel Nut Zippers, The Carolina Chocolate Drops, Lords of the Underground, Between the Buried and Me, and He Is Legend.
Notable rappers, producers, and people in hip-hop from North Carolina include: J. Cole, DaBaby, Petey Pablo, 9th Wonder, Rapsody, Fred Durst, Mez, Lute, Ski Beatz, Deniro Farrar, and Cordae.
Education
The University of North Carolina system encompasses 16 public universities including North Carolina A&T State University, North Carolina State University, North Carolina Central University, UNC-Pembroke, UNC-Chapel Hill, Elizabeth City State University, East Carolina University, Western Carolina University, Winston-Salem State University, UNC Charlotte, UNC Greensboro, Fayetteville State University and Appalachian State University. Along with its public universities, North Carolina has 58 public community colleges in its community college system. There are also a number of private colleges, for example Duke University in Durham, Wake Forest University in Winston-Salem, Campbell University in Buies Creek, North Carolina and Elon University, in Elon, North Carolina.
Sports
North Carolina is home to professional-level sports teams, including basketball, football, and hockey:
- NBA: Charlotte Hornets (formerly known as Charlotte Bobcats before restoring the original team name)
- NFL: Carolina Panthers (based in Charlotte)
- NHL: Carolina Hurricanes (based in Raleigh)
NASCAR racing is also a popular sport in North Carolina. Sprint Cup Series races are frequently held at the Charlotte Motor Speedway in Concord, part of the Charlotte Metropolitan Area.
References
- Raper, Charles Lee. Social Life in Colonial North Carolina. Retrieved January 6, 2021.
- African American History Across North Carolina. docsouth.unc.edu. Retrieved January 6, 2021.
- Gulledge, Seth Thomas. (October 9, 2019). Florida, New York among top states where NC's new residents come from. Triangle Business Journal. Retrieved January 6, 2021.
- History - The Barbeque Festival. Retrieved January 7, 2021.
Bibliography
- Federal Writers' Project (1939). North Carolina: A Guide to the Old North State. American Guide Series – via Internet Archive.

