Demographics of Bhutan
This article is about the demographic features of the population of Bhutan, including population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population.

The Royal Government of Bhutan listed the country's population as 752,700 in 2003.[1]
One explanation for this discrepancy is that the higher CIA numbers ultimately trace back to an inflated population number the Bhutanese government supplied to the United Nations in the early 1970s in order to gain entry into that body (the UN reportedly had a cutoff population of one million at that time). According to this theory the CIA population experts have retained this original inflated number year after year while adjusting it each year for normal population growth.
An alternative theory is that the western and central districts of the country wish to underestimate the populations of the southern and eastern districts in order to maintain their historical dominance over those districts. This is the claim made by some Bhutanese refugee groups. Certainly the government numbers do not include people, that were living in the refugee camps in Nepal and other persons forced out of Bhutan, which total approximately 125,000, majority of whom have now resettled in the USA.
The Bhutanese numbers can be reconstructed from their 9th Five Year Plan documents,[2] which lists the exact number of households in each gewog. If the Bhutanese refugee advocate groups are correct, a spot check of a southern gewog should show a massive under-reporting of population.
The CIA World Fact book number has since been adjusted with a note of former inconstencies, and attributes the difference to the government not including the "first modern census of Bhutan, conducted in 2005".[1] In the 1970s Bhutan was one of the most isolated countries in the world and nobody knew how many people lived there since no census had ever been taken.
Demographic statistics

The following demographic statistics are from the CIA World Factbook, unless otherwise indicated.
Ethnic groups[1]
- Ngalop people (also known as Bhote) and indigenous Sharchop people 63%
- Lhotsampas (also known as Nepalis) 22%
- Indigenous or migrant ethnic groups 15%
Religions[1]
- Lama Buddhism 75.3%
- Hinduism 22.1%
- Other 2.6%
Languages[1]
Literacy
- Definition: age 15 and over can read and write
- Total population: 64.9%
- Male: 73.1%
- Female: 55% (2015 est.[3])
Population
- 708,427 (July 2011 est.)
- 716,896 (July 2012 est.)
- 750,125 (July 2016 est.)[4]
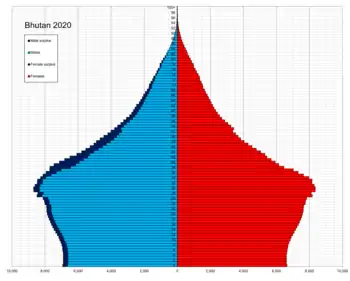
Age structure
- 0-14 years: 26.27% (male 100,672/female 96,368)
- 15-24 years: 19.21% (male 73,398/female 70,704)
- 25-54 years: 42.39% (male 169,079/female 148,873)
- 55-64 years: 5.94% (male 23,869/female 20,656)
- 65 years and over: 6.2% (male 24,301/female 22,205) (2016 est.[5])
Median age
- Total: 27.2 years
- Male: 27.7 years
- Female: 26.6 years (2016 est.[6])
Population growth rate
- 1.09% (2016 est.[7])
Birth rate
- 17.5 births/1,000 population (2016 est.[8])
Death rate
- 6.6 deaths/1,000 population (2016 est.[9])
Net migration rate
- 0 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2012 est.)
Total fertility rate
- 1.93 children born/woman (2016 est.[10])
Urbanization[11]
- urban population: 38.6% of total population (2015)
- rate of urbanization: 3.69% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
Sex ratio
- At birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
- 0-14 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
- 15-24 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
- 25-54 years: 1.14 male(s)/female
- 55-64 years: 1.16 male(s)/female
- 65 years and over: 1.1 male(s)/female
- Total population: 1.09 male(s)/female (2016 est.[12])
Life expectancy at birth
- Total population: 70.2 years
- Male: 68.8 years
- Female: 71.7 years (2017[4] est.)
Life expectancy at birth is 70.2 years, which is an increase from 66.3 years in 2005. Women with 71.7 years lived longer than men (68.8).
Prime Minister Tshering Tobgay said that the good news is life expectancy has crossed 70 years.[13]
Vital statistics
Below is a table of Bhutan vital statistics since 1950 published by the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs.[14]
| Period | Live births per year | Deaths per year | Natural change per year | CBR1 | CDR1 | NC1 | TFR1 | IMR1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1950-1955 | 9,000 | 5,000 | 4,000 | 47.9 | 27.1 | 20.8 | 6.67 | 184.8 |
| 1955-1960 | 10,000 | 6,000 | 5,000 | 49.0 | 26.8 | 22.3 | 6.67 | 181.4 |
| 1960-1965 | 12,000 | 6,000 | 6,000 | 48.5 | 25.7 | 22.8 | 6.67 | 174.1 |
| 1965-1970 | 13,000 | 7,000 | 7,000 | 47.8 | 24.1 | 23.8 | 6.67 | 163.1 |
| 1970-1975 | 16,000 | 7,000 | 8,000 | 47.0 | 22.0 | 25.1 | 6.67 | 149.3 |
| 1975-1980 | 18,000 | 8,000 | 10,000 | 45.8 | 19.6 | 26.2 | 6.67 | 133.2 |
| 1980-1985 | 20,000 | 8,000 | 12,000 | 42.7 | 17.1 | 25.6 | 6.39 | 117.1 |
| 1985-1990 | 21,000 | 8,000 | 13,000 | 40.4 | 15.0 | 25.3 | 6.11 | 104.0 |
| 1990-1995 | 19,000 | 7,000 | 12,000 | 35.2 | 12.5 | 22.7 | 5.27 | 87.5 |
| 1995-2000 | 16,000 | 5,000 | 11,000 | 29.2 | 9.9 | 19.3 | 4.13 | 69.7 |
| 2000-2005 | 15,000 | 5,000 | 11,000 | 25.2 | 7.9 | 17.2 | 3.30 | 52.8 |
| 2005-2010 | 15,000 | 5,000 | 10,000 | 21.5 | 7.2 | 14.4 | 2.61 | 44.4 |
| 1 CBR = crude birth rate (per 1000); CDR = crude death rate (per 1000); NC = natural change (per 1000); TFR = total fertility rate (number of children per woman); IMR = infant mortality rate per 1000 births | ||||||||
Births and deaths
| Year | Population | Live births | Deaths | Natural increase | Crude birth rate | Crude death rate | Rate of natural increase | TFR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2005 | 635,000 | 12,538 | 4,498 | 8,040 | 19.7 | 7.1 | 12.6 | 2.50 |
| 2017 | 736,000 | 11,239 | 4,894 | 6,345 | 15.5 | 6.7 | 8.8 | 1.70 |
Structure of the population
Structure of the population (01.07.2013) (Estimates) (Data refer to projected figures based on the Population and Housing Census 2005 (district projection)):[16]
| Age Group | Male | Female | Total | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 381 582 | 351 421 | 733 004 | 100 |
| 0-4 | 42 725 | 41 999 | 84 724 | 11,56 |
| 5-9 | 38 396 | 37 725 | 76 121 | 10,38 |
| 10-14 | 32 169 | 31 593 | 63 762 | 8,70 |
| 15-19 | 35 432 | 34 403 | 69 835 | 9,53 |
| 20-24 | 36 526 | 34 745 | 71 271 | 9,72 |
| 25-29 | 35 433 | 32 065 | 67 498 | 9,21 |
| 30-34 | 33 279 | 28 491 | 61 770 | 8,43 |
| 35-39 | 28 766 | 24 060 | 52 827 | 7,21 |
| 40-44 | 23 774 | 19 545 | 43 319 | 5,91 |
| 45-49 | 19 391 | 16 213 | 35 604 | 4,86 |
| 50-54 | 15 245 | 13 209 | 28 455 | 3,88 |
| 55-59 | 12 257 | 10 806 | 23 063 | 3,15 |
| 60-64 | 9 602 | 8 645 | 18 247 | 2,49 |
| 65-69 | 7 268 | 6 741 | 14 009 | 1,91 |
| 70-74 | 5 169 | 4 956 | 10 124 | 1,38 |
| 75-79 | 3 338 | 3 313 | 6 651 | 0,91 |
| 80+ | 2 812 | 2 912 | 5 724 | 0,78 |
| Age group | Male | Female | Total | Percent |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0-14 | 113 290 | 111 317 | 224 607 | 30,64 |
| 15-64 | 249 705 | 222 182 | 471 887 | 64,38 |
| 65+ | 18 587 | 17 922 | 36 509 | 4,98 |
HIV/AIDS
In 2011, there were 246 reported cases of HIV in Bhutan, representing just over 0.03% of the population.[17] In July 2010, there were a total of 217 cases detected, however Health Ministry sources indicated actual numbers were estimated at more than 500 by UNAIDS.[18]
Through July 2010, there had been a total of 40 deaths due to HIV/AIDS-related causes, and one suicide.[18]
Education
As of 2017, Bhutan has a literacy rate of 71.4 percent (up from 59.5 percent in 2005). The highest literacy rate is observed in Thimpu at 83.9 percent, followed by Trongsa (77.2 percent) and Chukha (75.1 percent), while Gasa has the lowest rate with 59.8 percent of its population being literate.[13]
References
- "South Asia ::BHUTAN". CIA The World Factbook.
- "http://www.dop.gov.bt/rep/index.htm". Archived from the original on 2005-09-06. Retrieved 2005-08-19. External link in
|title=(help) - "The World Factbook — Central Intelligence Agency". cia.gov. Retrieved 19 April 2018.
- "The World Factbook — Central Intelligence Agency". cia.gov. Retrieved 19 April 2018.
- "The World Factbook — Central Intelligence Agency". cia.gov. Archived from the original on 11 December 2007. Retrieved 19 April 2018.
- "The World Factbook — Central Intelligence Agency". cia.gov. Retrieved 19 April 2018.
- "The World Factbook — Central Intelligence Agency". cia.gov. Retrieved 19 April 2018.
- https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/fields/2054.html#bt Archived 2007-12-11 at the Wayback Machine
- "The World Factbook — Central Intelligence Agency". cia.gov. Retrieved 19 April 2018.
- "The World Factbook — Central Intelligence Agency". cia.gov. Retrieved 19 April 2018.
- "The World Factbook — Central Intelligence Agency". cia.gov. Retrieved 19 April 2018.
- "The World Factbook — Central Intelligence Agency". cia.gov. Retrieved 19 April 2018.
- KuenselOnline
- "Bhutan: Demographic Profile, Medium Variant 1950–2100". World Population Prospects: The 2010 Revision. United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division, Population Projections and Estimates Section. Retrieved 2011-10-30. (entry: Bhutan)
- http://unstats.un.org/unsd/demographic/products/vitstats/serATab3.pdf
- http://unstats.un.org/unsd/demographic/products/dyb/dyb2.htm
- "The Ministry of Health has Detected…". Bhutan Observer online. 2011-08-01. Retrieved 2011-11-21.
- "An Update on Human Immuno Deficiency Virus/Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome (HIV/AIDS)" (PDF). Bhutan Ministry of Health. 2010-07-01. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-05-08. Retrieved 2011-11-22.
External links
 This article incorporates public domain material from the CIA World Factbook document: "2007 edition".
This article incorporates public domain material from the CIA World Factbook document: "2007 edition".