Greater Kyoto
Greater Kyoto is a metropolitan area in Japan encompassing Kyoto, the capital of Kyoto Prefecture, as well as its surrounding areas including Ōtsu, the capital of Shiga Prefecture.[4][5]
Kyoto metropolitan area
Kyoto MEA | |
|---|---|
 Kyoto Tower and Downtown Kyoto  Biwako Hall in Ōtsu | |
 Kyoto metropolitan area | |
| Coordinates: 35°0′N 135°46′E | |
| Country | |
| Prefectures | |
| Core city | |
| Area (2011)[1] | |
| • Total | 2,835.93 km2 (1,094.96 sq mi) |
| • Inhabitable area | 776.77 km2 (299.91 sq mi) |
| Population (2015)[2] | |
| • Total | 2,801,044 |
| • Rank | 4th in Japan |
| • Density | 990/km2 (2,600/sq mi) |
| • Inhabitable area density | 3,600/km2 (9,300/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP)[1] | $90.6 billion[3] (2010) |
| GDP per capita | $33,827 |
| GDP (nominal)[1] | $115.3 billion[3] (2010) |
| GDP per capita | $43,021 |
| Website | www |
The metropolitan area is also referred to as Keiji (京滋) or Keishin (京津). The name Keiji is constructed by extracting a representative kanji from Kyoto (京都) and Shiga (滋賀). The name Keishin is constructed by extracting a representative kanji from Kyoto (京都) and Ōtsu (大津).
Definitions
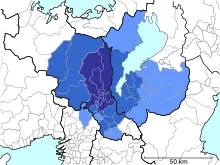
Urban Employment Area
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1980 | 2,361,205 | — |
| 1990 | 2,485,352 | +5.3% |
| 1995 | 2,539,639 | +2.2% |
| 2000 | 2,583,304 | +1.7% |
| 2005 | 2,560,850 | −0.9% |
| 2010 | 2,679,049 | +4.6% |
| 2015 | 2,801,044 | +4.6% |
| Source: [2] | ||
The greater Kyoto area is defined by Urban Employment Area as Kyoto Metropolitan Employment Area (Kyoto MEA). The metropolitan area had a total population of 2,801,044 as of 2015 and is the fourth-largest in Japan. The cities and towns of the metropolitan area with their 2015 populations are listed below.
- Kyoto Prefecture
- Shiga Prefecture
Municipalities network
A wider metropolitan area based on commuting patterns is also defined by Kyōto Toshiken Jichitai Nettowāku Kaigi (京都都市圏自治体ネットワーク会議, Conference of Kyoto metropolitan area municipalities network) as the Kyoto metropolitan area. This area consists of 13 cities and towns of Shiga Prefecture, Kyoto Prefecture, and Osaka Prefecture, in addition to Kyoto MEA. The total population as of 2015 for the region was estimated at 3,789,750. The following areas, along with the above Kyoto MEA, are included in the Kyoto metropolitan area, with their 2015 populations:[6]
- Kyoto Prefecture
- Shiga Prefecture
- Takashima (50,025)
- Konan (54,289)
- Koka (90,901)
- Ōmihachiman (81,312)
- Higashiōmi (114,180)
- Hino (21,873)
- Ryūō (12,434)
- Osaka Prefecture
Geography
- Lake Biwa – the largest lake in Japan
- Ohmi Basin – Shiga Prefecture
- Kyoto Basin – the southern part of Kyoto Prefecture
- Mount Hiei – mountain on the border between Kyoto and Ōtsu
- Seta River, Uji River
- Kizugawa River
- Yasu River
- Katsura River
Higher Education
48 universities and colleges in the area participate in the Consortium of Universities in Kyoto.[7]
- Bukkyo University – 5 campuses in Kyoto and Nantan
- Doshisha University – 2 campuses in Kyoto and Kyōtanabe
- Kyoto University – 3 campuses in Kyoto and Uji
- Kyoto Gakuen University – 2 campuses in Kameoka and Kyoto
- Ritsumeikan University – 4 campuses in Kyoto, Kusatsu, and Ibaraki
- Ryukoku University – 3 campuses in Kyoto and Ōtsu
Sports
- Kyoto Sanga FC – a football club
- MIO Biwako Shiga – a football club
- Kyoto Hannaryz – a basketball team
- Shiga Lakestars – a basketball team
- Lake Biwa Marathon
- Kyoto Marathon
- Kyoto Racecourse
- Kyoto Stadium
Media
- Kyoto Shimbun – newspaper
- KBS Kyoto – TV and radio station
- BBC Biwako – TV station
- FM-Kyoto – radio station
- PHP Insutitute – publishing house
- Leaf Publications – publishing house
Transportation
Rail

Kyōto Station is a hub of the rail network in the area.
- Tōkaidō Shinkansen (Kyōto Station) – inter-city rail (JR Central)
- Biwako Line and JR Kyoto Line – regional and commuter rail (JR West)
- Kosei Line – regional and commuter rail (JR West)
- San'in Main Line – regional and commuter rail (JR West)
- Nara Line – commuter rail (JR West)
- Kusatsu Line – commuter rail (JR West)
- Kyoto Line (Kintetsu) – regional and commuter rail (Kintetsu)
- Keihan Main Line and Uji Line – commuter rail (Keihan)
- Keishin Line – commuter rail, subway, and tram (Keihan)
- Ishiyama Sakamoto Line – commuter rail and tram (Keihan)
- Hankyu Kyoto Main Line and Hankyu Arashiyama Line – commuter rail (Hankyu)
- Arashiyama Line and Kitano Line – commuter rail and tram (Randen)
- Karasuma Line and Tōzai Line – Kyoto Municipal Subway
- Eizan Main Line and Kurama Line – commuter rail (Eiden)
See also
- List of metropolitan areas in Japan by population
References
- Kanemoto, Yoshitsugu. "Metropolitan Employment Area (MEA) Data". Center for Spatial Information Science, the University of Tokyo. Retrieved November 23, 2016.
- Kanemoto, Yoshitsugu. "Urban Employment Area (MEA) Code Table". Center for Spatial Information Science, the University of Tokyo. Retrieved December 21, 2018.
- 10.12 trillion Japanese yen
- "京都市の観光行政を戦略部長に聞いてきた、「量より質」への転換で解決すべき5つの課題" (in Japanese). Retrieved 2016-11-23.
- "Kitayama Area & Greater Kyoto". Retrieved 2016-11-23.
- "京都都市圏の範囲及び取組" (in Japanese). 京都都市圏自治体ネットワーク. Retrieved April 21, 2017.
- "Leaflet" (PDF). The Consortium of Universities in Kyoto. 2013. Retrieved 2018-06-02.
External links
- 京都都市圏自治体ネットワーク(in Japanese)
- Kyoto metropolitan area municipalities network on Facebook (in Japanese)
- Kyoto metropolitan area municipalities network on Instagram (in Japanese)
- Workers and Students Commuting to Kyoto-shi - Statistics Bureau, Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications
