Tochigi Prefecture
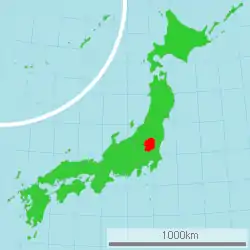
Tochigi Prefecture (栃木県, Tochigi-ken) is a prefecture of Japan located in the Kantō region of Honshu.[1] Tochigi Prefecture has a population of 1,943,886 (1 June 2019) and has a geographic area of 6,408 km2 (2,474 sq mi). Tochigi Prefecture borders Fukushima Prefecture to the north, Gunma Prefecture to the west, Saitama Prefecture to the south, and Ibaraki Prefecture to the southeast.
Tochigi Prefecture
栃木県 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Japanese transcription(s) | |||||||||||||
| • Japanese | 栃木県 | ||||||||||||
| • Rōmaji | Tochigi-ken | ||||||||||||
 Flag  Symbol | |||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||
| Country | Japan | ||||||||||||
| Region | Kantō | ||||||||||||
| Island | Honshu | ||||||||||||
| Capital | Utsunomiya | ||||||||||||
| Subdivisions | Districts: 5, Municipalities: 26 | ||||||||||||
| Government | |||||||||||||
| • Governor | Tomikazu Fukuda | ||||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||||
| • Total | 6,408.09 km2 (2,474.18 sq mi) | ||||||||||||
| Area rank | 20th | ||||||||||||
| Population (June 1, 2019) | |||||||||||||
| • Total | 1,943,886 | ||||||||||||
| • Rank | 19th | ||||||||||||
| • Density | 300/km2 (790/sq mi) | ||||||||||||
| ISO 3166 code | JP-09 | ||||||||||||
| Website | www | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
Utsunomiya is the capital and largest city of Tochigi Prefecture, with other major cities including Oyama, Tochigi, and Ashikaga.[2] Tochigi Prefecture is one of only eight landlocked prefectures and its mountainous northern region is a popular tourist region in Japan. The Nasu area is known for its onsens, local sake, and ski resorts, the villa of the Imperial Family, and the Nasushiobara station of the Shinkansen railway line. The city of Nikkō, with its ancient Shintō shrines and Buddhist temples, is a UNESCO World Heritage Site.[3]
City Town
Prefectural overview
Situated among the inland prefectures of the northern part of the Kantō region, Tochigi is contiguous with Ibaraki, Gunma, Saitama, and Fukushima Prefectures.
The climate of Tochigi may be classified as a humid temperate zone with broad variations in temperature. Winters are arid with dry winds, while summers are humid with frequent thunderstorms.
The population of Tochigi as of November 2010 is approximately 2,005,096.
Located in the center of the prefecture is the largest open plain in the Kantō region. Shirane (2,578 metres (8,458 ft)), Nantai (2,484 metres (8,150 ft)) and Nasudake (1,917 metres (6,289 ft)) mountain are in the northern part of the area. Kinugawa, Nakagawa, and Watarase River originate in this region, which flow across the Kanto plain before emptying into the Pacific Ocean. Tochigi is the 20th largest prefecture in Japan with a total area of 6,408.09 square km.
As of 1 April 2012, 21% of the total land area of the prefecture was designated as Natural Parks, namely Nikkō National Park, Oze National Park, and eight Prefectural Natural Parks.[4]
History
Before the Meiji Restoration, Tochigi was known as Shimotsuke Province.[5]
In the early 15th century, Ashikaga Gakkō, Japan's oldest school of higher education, was re-established, holding over 3,000 students by the 16th century. Saint Francis Xavier introduced Ashikaga to the world as the best university in Japan.
In the early 17th century, Japan was unified by the shōgun Tokugawa Ieyasu. After his death, Tōshō-gū shrine was built in Nikkō on what the shōguns thought of as holy ground to protect and worship Ieyasu. The establishment of the Nikkō Tōshō-gū in 1617 brought Nikkō to national attention. The Tokugawa shogunate developed the Nikkō Kaidō (日光街道, part of the major road connecting Nikkō with Edo) and required lavish processions to worship Ieyasu, the founder of the Tokugawa line of shōguns.
In the late 19th century, the Tokugawa Shogunate fell and the new government established the prefectures. The prefectural capital was established in the city of Tochigi after the unification of Utsunomiya Prefecture and Tochigi Prefecture in 1873.[6] By 1884, however, the capital was transferred to Utsunomiya.
In March 2011, following the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster, levels of radioactivity in Utsunomiya were 33 times higher than normal.[7]
Geography




The chief city of Utsunomiya is famous for its many gyoza specialist shops. Also located in Utsunomiya, Tochigi Prefecture has one of the largest shopping malls in the North Kantō region, Bell Mall.
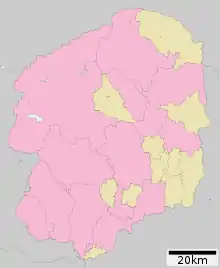
Cities
Fourteen cities are located in Tochigi Prefecture:
Towns
These are the towns in each district:
Mergers
List of Governor of Tochigi Prefecture (from 1947)
| № | Governor (Birth–Death) |
Term of office | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 37-38 | Jyukichi Kodaira (小平重吉) (1886–1960) |
12 April, 1947 | 4 February, 1955 |
| 39 | Kichi Ogawa (小川喜一) (1904–1979) |
5 February, 1955 | 4 February, 1959 |
| 40-43 | Nobuo Yokokawa (横川信夫) (1901–1975) |
5 February, 1959 | 7 December, 1974 |
| 44-46 | Yuzuru Funada (船田譲) (1923-1985) |
8 December, 1974 | 8 December, 1984 |
| 47-50 | Fumio Watanabe (渡辺文雄) (1929-) |
9 December, 1984 | 8 December, 2000 |
| 51 | Akio Fukuda (福田昭夫) (1948-) |
9 December, 2000 | 8 December, 2004 |
| 52-55 | Tomikazu Fukuda (福田富一) (1953-) |
9 December, 2004 | Present |
Industry and agriculture
Located close to Tōkyō, Tochigi is home to many corporations and industrial zones, including the Kiyohara Industrial Complex, one of the largest inland industrial complexes in the country.
Industrial manufacturing accounts for 36.6% of the prefecture's total output. Vehicle parts and accessories are the primary products, followed by vehicles, radios and televisions, pharmaceuticals, and wireless communication equipment.
Below are goods manufactured in Tochigi with the highest market share in Japan:
| Product | Share |
|---|---|
| Camera lenses | 71.3% |
| X-ray equipment for medical use | 54.5% |
| Machinery and appliances for dental use | 23.5% |
| X-ray equipment parts | 57.5% |
| Injection molded plastic parts | 14.1% |
(The 2004 industrial analysis report published by the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry)
The annual gross agricultural output in Tochigi is about 274 billion yen. Rice, vegetables, and livestock are produced in the region. Tochigi is also known for strawberries, Chinese chives, and Japanese pears sold throughout Japan and exported to other countries. Approximately 55% of Tochigi is covered by forests. Mushrooms, such as Shiitake mushrooms, make up half of the forest industry, with an output of approximately 5.6 billion yen.
Education
Tochigi is home to many universities and colleges including those for science and technology, literature, medicine, education, and art. Below is an alphabetical list of some of the universities located in Tochigi.
- Ashikaga Institute of Technology
- Bunsei University of Art, Utsunomiya
- Dokkyo University School of Medicine, Mibu
- Hakuoh University, Oyama
- International University of Health and Welfare, Otawara
- Jichi Medical University, Shimotsuke
- Oyama National College of Technology
- Sakushin Gakuin University, Utsunomiya
- Sano College
- Teikyo University, Utsunomiya
- Tochigi College of Industry and Technology (Central), Utsunomiya
- Tochigi College of Industry and Technology (North), Nasu
- Tochigi College of Industry and Technology (South), Ashikaga
- Utsunomiya Kyowa University, Utsunomiya and Nasushiobara
- Utsunomiya University
People
Sports
The sports teams and events listed below are based in Tochigi.
Football (Soccer)
Ice hockey
Basketball
Motorsport
- Twin Ring Motegi circuit
- Nikkō Circuit
Cycling
Tour de Tochigi, a cat 2.2 3-day road race of the UCI Asia Tour
Tourism
Nikkō National Park is famous for its UNESCO World Heritage Site which was registered as the 10th World Heritage Site in 1999. This encompasses Rinnō-ji, Nikkō Tōshō-gū, Mount Nantai, and Futarasan Shrine. The Kegon Falls, also in Nikkō, is popular with tourists. To travel between the city and the falls, automobiles and buses take the Irohazaka, a road with dozens of switchbacks. In addition, 400-year-old Japanese Cedars (about 13,000 in total) line the famous Cedar Avenue of Nikkō for roughly 35 km, making it the longest tree-lined avenue in the world.[8]


A more recent and modern attraction is the Twin Ring Motegi Circuit race course, which hosts the only IndyCar race outside the United States. The track also hosts many other race events including Formula One and motorcycle races as well as festivals and fireworks events.
Tochigi has many traditional festivals and events such as Nikkō Tōshō-gū's 1000 Samurai Procession and Horseback Archery Festival, and the city of Tochigi's Autumn Festival where doll floats are pulled around the city once every five years.
Other attractions include:
- Nikkō Tōshō-gū
- Rinnō-ji
- Futarasan Shrine
- Kegon Falls
- Lake Chūzenji
- Kirifuri Falls
- Mashiko
- Shiobara Hot Spring
- Nasu resort area
- Kinugawa (hot spring)
- Edo Wonderland Nikko Edomura
- Cannabis Museum
Transportation and access
Roads
Traversing the prefecture along the north-south axis and connecting to the rest of the country are the Tōhoku Expressway and the new and old Route 4. From east to west spans Route 50, connecting southern Tochigi with Ibaraki and Gunma Prefectures.
Also connecting Tochigi, Gunma, and Ibaraki is the Kita-Kantō Expressway, with the 18.5 km that connect the Tochigi-Tsuga Interchange and the Utsunomiya-Kaminokawa Interchange. Portions of the Kita-Kantō Expressway are still being constructed and is set to be fully completed by 2011. The highway will link the region's other main transport arteries, the Tōhoku, the Jōban and the Kan-Etsu Expressways, providing a link to the international port of Hitachinaka in Ibaraki.
Rail
The Tōhoku Shinkansen and the JR Utsunomiya Line are the main railways running north and south in Tochigi. Shinkansen runs from Tokyo Station to Oyama in south Tochigi in 43 minutes. Utsunomiya can be reached by rail in as little as 48 minutes, and many parts of Tochigi are within commuting range of central Tokyo. To the east and west, the Mito and Ryōmō Lines connect Tochigi to Ibaraki and Gunma.
Freight is served by the Utsunomiya Freight Terminal.
- East Japan Railway Company
- Tōhoku Shinkansen
- Shōnan-Shinjuku Line
- Utsunomiya Line (Tōhoku Main Line)
- Nikkō Line
- Ryōmō Line
- Mito Line
- Karasuyama Line
- Tobu
- Isesaki Line
- Nikkō Line
- Kinugawa Line
- Utsunomiya Line
- Sano Line
- Mooka Railway
- Yagan Railway
- Watarase Keikoku Line
Air travel
Fukushima Airport is approximately an hour's drive from Utsunomiya on the Tōhoku Expressway. International and national air transportation is through Narita International Airport to the east of Tokyo, approximately three hours by vehicle from Utsunomiya.
Notes
- Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005). "Tochigi prefecture" in Japan Encyclopedia, p. 967, p. 967, at Google Books; "Kantō" in p. 479, p. 479, at Google Books.
- Nussbaum, "Utsunomiya" at p. 1019, p. 1019, at Google Books.
- "World Heritage Committee: Report of the 23rd Session, Marrakesh 1999". whc.unesco.org. Retrieved 28 March 2018.
- "General overview of area figures for Natural Parks by prefecture" (PDF). Ministry of the Environment. 1 April 2012. Retrieved 18 November 2013.
- Nussbaum, "Provinces and prefectures" at p. 780, p. 780, at Google Books.
- "Tochigi Prefecture / History". Tochigi Prefecture. Tochigi Prefectural Office. Retrieved 24 May 2020.
- "Nuclear Radiation Levels and Effect on Human Health as Sieverts increase in Japan – What you need to Know - Green World Investor". greenworldinvestor.com. Retrieved 28 March 2018.
- Gardening World Records Archived 2008-10-14 at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved on 2 November 2008.
References
- Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric and Käthe Roth. (2005). Japan encyclopedia. Cambridge: Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-01753-5; OCLC 58053128
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Tochigi prefecture. |
- Tochigi Prefecture Official Website (in Japanese)
- Tochigi International Association Website (in English)
 Tochigi travel guide from Wikivoyage
Tochigi travel guide from Wikivoyage