List of current monarchies
This is a list of current monarchies. As of 2019, there are 44 sovereign states in the world with a monarch as Head of state. 13 in Asia, 12 in Europe, 10 in North America, 6 in Oceania and 3 in Africa.
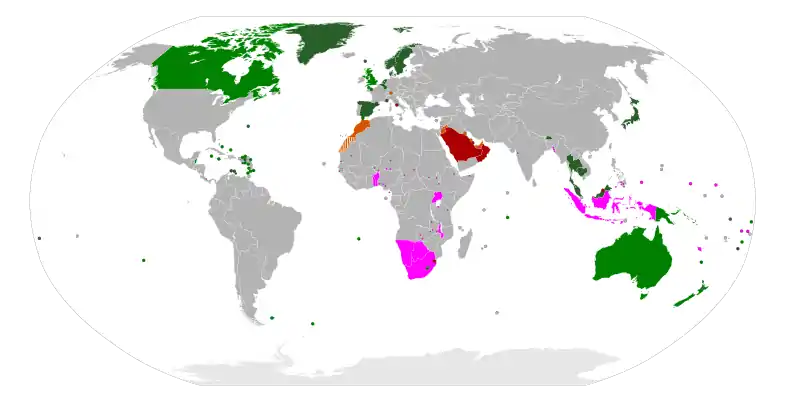 Semi-constitutional monarchy Subnational monarchies (traditional)
|
Types of monarchy
These are roughly the categories which modern monarchies fall into:
- Commonwealth realms. Queen Elizabeth II is the monarch of sixteen Commonwealth realms (Antigua and Barbuda; the Commonwealth of Australia; the Commonwealth of the Bahamas; Barbados; Belize; Canada; Grenada; Jamaica; New Zealand; the Independent State of Papua New Guinea; the Federation of Saint Kitts and Nevis; Saint Lucia; Saint Vincent and the Grenadines; Solomon Islands; Tuvalu; and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland). They evolved out of the British Empire into fully independent states within the Commonwealth of Nations that retain the Queen as head of state, unlike other Commonwealth countries that are either dependencies, republics or have a different royal house. All sixteen realms are constitutional monarchies and full democracies, where the Queen has limited powers or a largely ceremonial role.
- Other European constitutional monarchies.
- The Principality of Andorra; the Kingdom of Belgium; the Kingdom of Denmark; the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg; the Kingdom of the Netherlands; the Kingdom of Norway; the Kingdom of Spain; and the Kingdom of Sweden are fully democratic states in which the monarch has a limited or largely ceremonial role.
- Andorra is unique among all existing monarchies, as it is a diarchy, with the Co-Princeship being shared by the President of France and the Bishop of Urgell. This arrangement creates a unique situation among monarchies, as a) neither Co-Prince is of Andorran descent, b) one is elected by common citizens of a foreign country (France), but not by Andorrans as they cannot vote in the French Presidential Elections, c) the other, the bishop of Urgell, is appointed by a foreign head of state, the Pope.
- European mixed monarchies. Liechtenstein and Monaco are constitutional monarchies in which the Prince retains many powers of an absolute monarch. For example, the 2003 Constitution referendum gives the Prince of Liechtenstein the power to veto any law that the Landtag (parliament) proposes and vice versa. The Prince can hire or dismiss any elective member or government employee from his or her post. However, unlike an absolute monarch, the people can call for a referendum to end the Prince's reign. The Prince of Monaco has simpler powers: he cannot hire or dismiss any elective member or government employee from his or her post, but he can select the minister of state, government council and judges.
- Muslim monarchies. These Muslim monarchs of the Kingdom of Bahrain; the Nation of Brunei, the Abode of Peace; Malaysia; the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan; the State of Kuwait; the Kingdom of Morocco; the Sultanate of Oman; the State of Qatar; the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates generally retain far more powers than their European or Commonwealth counterparts.
Absolute monarchs remain in the Nation of Brunei, the Abode of Peace; the Sultanate of Oman; the State of Qatar; and the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. The Kingdom of Bahrain, and the State of Kuwait are classified as mixed, meaning there are representative bodies of some kind, but the monarch retains most of his powers. The Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, Malaysia, the Kingdom of Morocco, and the United Arab Emirates are constitutional monarchies, but their monarchs still retain more substantial powers than in European equivalents.
- East and Southeast Asian constitutional monarchies. The Kingdom of Bhutan; the Kingdom of Cambodia; Japan; and the Kingdom of Thailand have constitutional monarchies where the monarch has a limited or ceremonial role. Thailand changed from traditional absolute monarchy into a constitutional one in 1932, while the Kingdom of Bhutan changed in 2008. The Kingdom of Cambodia had its own monarchy after independence from the French Colonial Empire, which was deposed after the Khmer Rouge came into power. The monarchy was subsequently restored in the peace agreement of 1993.
- Other monarchies. Five monarchies do not fit into one of the above groups by virtue of geography or class of monarchy: the Kingdom of Tonga in Polynesia; the Kingdom of Eswatini and the Kingdom of Lesotho in Southern Africa; and the Sovereign Military Order of Malta (S.M.O.M.), and the Vatican City State in Europe. Of these, the Kingdom of Lesotho and the Kingdom of Tonga are constitutional monarchies, while the Kingdom of Eswatini and the Vatican City State are absolute monarchies. The Kingdom of Eswatini is increasingly being considered a diarchy. The King, or Ngwenyama, rules alongside his mother, the Ndlovukati, as dual heads of state originally designed to be checks on political power. The Ngwenyama, however, is considered the administrative head of state, while the Ndlovukati is considered the spiritual and national head of state, a position which has become largely symbolic in recent years. S.M.O.M. is governed by an elected Prince and Grand Master. The Pope is the absolute monarch of the Vatican by virtue of his position as head of the Roman Catholic Church and Bishop of Rome; he is an elected rather than hereditary ruler. The Pope need not be a citizen of the territory prior to his election by the cardinals.
Lines of succession
Some of the extant sovereign monarchies have lines of succession that go back to the medieval period or antiquity:
- The kings of Cambodia claim descent from Queen Soma (1st century), although the historiographical record is interrupted in the "Post-Angkor Period" (15th/16th centuries). A real unified kingdom of Cambodia first came to existence in 802. The monarchy in Cambodia was abolished between 1970 and 1993.
- There exist several suggestions on a possible line of succession in the Danish monarchy from the late 7th century and until Gorm the Old, but none of these suggestions have so far won universal acceptance. Most monarchs in Denmark since the 940s have been descendants of Gorm the Old's father Harthacnut and all monarchs in Denmark since 1047 have been descendants of titular Queen Estrid Svendsdatter. A formal law of succession was not adapted in Denmark until 1665.
- Japan, considered a constitutional monarchy under the Imperial House of Japan, is said to be the world's oldest extant continuous hereditary monarchy,[1] with a traditional origin in 660 BC; there is commonly accepted archaeological and cultural evidence from the 3rd century and reliable historiographical evidence from at least the 6th century.
- The monarchs of the kingdom of Norway by virtue of descent from Harald I Fairhair, who united the realm in 872. Harald as a member of the House of Yngling is given a partly legendary line of succession from earlier petty kings in historiographical tradition. Far from all monarchs of Norway since the 930s have been descendants of Harald Fairhair: at least seven or eight Norwegian kings from the period c. 970 – 1859 were not descendants of Harald Fairhair.
- The kings of Spain by descent from the Catholic Monarchs (via the House of Habsburg), ultimately combining the lines of succession of Castile and León and Aragon, realms established in the 10th to 11th centuries in the course of the Reconquista, via the Kingdom of Asturias claiming descent from the Visigothic Kingdom (which, originally ruled by the Thervingi kings, had become elective in the 6th century). The monarchy of Spain was abolished twice in the 19th and 20th centuries (1873-1874 and 1931–1947) and replaced by republics.
- The monarchs of the United Kingdom and Commonwealth realms inherit the throne by virtue of the line of descent from the House of Stuart (Union of the Crowns 1603), combining the lines of succession of the kingdoms of England and Scotland going back to the 9th century. The succession to the English throne can be argued to originate with the House of Wessex, established in the 6th century; that to the Scottish throne with descent from Pictish kings who likewise enter the historical record around the 6th century. The line of succession and descent of the Scottish throne is unbroken, whereas the English throne shifted between several unrelated dynasties/families between 1013 and 1066. The monarchy of England was abolished in 1649 and that of Scotland in 1652 and replaced by various types of republican governments between the years 1649 to 1660.
Current monarchies
| Monarchy | Official local name(s) | Title of Head of State | Title of Head of Government | Type of monarchy | Succession | Current constitution |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| In Catalan: Principat d'Andorra | Co-Princes | Prime Minister | Constitutional | Ex officio | 1993 | |
| In English: Antigua and Barbuda | Queen | Hereditary | 1981 | |||
| In English: Commonwealth of Australia | Queen | 1901 | ||||
| In English: Commonwealth of the Bahamas | Queen | 1973 | ||||
| In Arabic: Mamlakat al- Baḥrayn | King | Mixed | 2002 | |||
| In English: Barbados | Queen | Constitutional | 1966 | |||
| In Dutch: Koninkrijk België In French: Royaume de Belgique In German: Königreich Belgien |
King 1 | Hereditary 1 | 1831 | |||
| In English: Belize | Queen | Hereditary | 1981 | |||
| In Dzongkha: Druk Gyal Khap | King | 2007 | ||||
| In Malay: Negara Brunei Darussalam | Sultan |
Absolute | 1959 | |||
| In Khmer: Preăh Réachéanachâk Kâmpŭchéa | King | Prime Minister | Constitutional | Hereditary and elective | 1993 | |
| In English and French: Canada | Queen | Hereditary | 1867 | |||
| In Danish: Kongeriget Danmark | Queen | 1953 | ||||
| In Swazi: Umbuso weSwatini In English: Kingdom of Eswatini |
King | Absolute | Hereditary and elective | 1968 | ||
| In English: Grenada | Queen | Constitutional | Hereditary | 1974 | ||
| In English: Jamaica | Queen | 1962 | ||||
| In Japanese: 日本国 (Nippon-koku/Nihon-koku) | Emperor | 1947 | ||||
| In Arabic: Dawlat al-Kuwait | Emir | Mixed | Hereditary and elective | 1962 | ||
| In Arabic: al-Mamlakah al-Urdunīyah al-Hāshimīyah | King | 1952 | ||||
| In Sotho: Muso oa Lesotho In English: Kingdom of Lesotho |
King | Constitutional | 1993 | |||
| In German: Fürstentum Liechtenstein | Sovereign Prince | Mixed | Hereditary | 1862 | ||
| In French: Grand-Duché de Luxembourg In German: Großherzogtum Luxemburg In Luxembourgish: Groussherzogtum Lëtzebuerg |
Grand Duke | Constitutional | 1868 | |||
| In Malay: Malaysia | Yang di-Pertuan Agong | Elective | 1957 | |||
| In French: Principauté de Monaco In Monégasque: Principatu de Múnegu |
Sovereign Prince | Minister of State | Mixed | Hereditary | 1911 | |
| In Arabic: al-Mamlaka al-Maghribiyya In Berber: Tageldit n Lmaɣrib |
King | Prime Minister | 1631 | |||
| In Dutch: Koninkrijk der Nederlanden In West Frisian: Keninkryk fan de Nederlannen |
King | Constitutional | 1815 | |||
| In English: New Zealand In Maori: Aotearoa |
Queen | 1907 | ||||
| In Bokmål: Kongeriket Norge In Nynorsk: Kongeriket Noreg |
King | 1814 | ||||
| In Arabic: Salṭanat ‘Umān | Sultan |
Absolute | 1996 | |||
| In English: Independent State of Papua New Guinea In Tok Pisin: Independen Stet bilong Papua Niugini In Hiri Motu: Papua Niu Gini |
Queen | Prime Minister | Constitutional | 1975 | ||
| In Arabic: Dawlat Qaṭar | Emir | Absolute | 2004 | |||
| In English: Federation of Saint Christopher and Nevis | Queen | Constitutional | 1983 | |||
| In English: Saint Lucia | Queen | 1979 | ||||
| In English: Saint Vincent and the Grenadines | Queen | 1979 | ||||
| In Arabic: Al-Mamlakah al-Arabiyah as-Sa'ūdiyah | Absolute | Hereditary and elective | 19922 | |||
| In English: Solomon Islands | Queen | Prime Minister | Constitutional | Hereditary | 1978 | |
| In Spanish: Reino de España | King | President of the Government | 1978 | |||
| In Swedish: Konungariket Sverige | King | Prime Minister | 1974 | |||
| In Thai: Ratcha Anachak Thai | King | 2017 | ||||
| In Tonga: Puleʻanga Fakatuʻi ʻo Tonga In English: Kingdom of Tonga |
King | 1970 | ||||
| In English: Tuvalu | Queen | 1986 | ||||
| In Arabic: Dawlat al-ʾImārāt al-ʿArabiyyah al-Muttaḥidah | President | Federal | Hereditary and elective | 1971 | ||
| In English: United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland In Welsh: Teyrnas Unedig Prydain Fawr a Gogledd Iwerddon In Irish: Ríocht Aontaithe na Breataine Móire agus Thuaisceart Éireann In Scots Gaelic: Rìoghachd Aonaichte Bhreatainn agus Èirinn a Tuath |
Queen | Constitutional | Hereditary | 1701 | ||
| In Latin: Status Civitatis Vaticanae In Italian: Stato della Città del Vaticano |
Pope | President of the Pontifical Commission | Absolute | Elective | 2001 | |
In Wallis and Futuna, an overseas territory of France in the South Pacific, there are three kingdoms, Uvea, Alo and Sigave, whose monarchs are chosen by local noble families.[42]
Footnote
^1 Belgium is the only existing popular monarchy – a system in which the monarch's title is linked to the people rather than a state. The title of Belgian kings is not King of Belgium, but instead King of the Belgians. Another unique feature of the Belgian system is that the new monarch does not automatically assume the throne at the death or abdication of his predecessor; he only becomes monarch upon taking a constitutional oath.
References
- D.M. (2 June 2017). "Why is the Japanese monarchy under threat?". The Economist. Archived from the original on 25 August 2018. Retrieved 4 June 2017.
- "Europe :: Andorra". CIA The World Factbook. Retrieved 2016-07-11.
- "Central America and Caribbean :: Antigua and Barbuda". CIA The World Factbook. Retrieved 2016-07-12.
- "Australia-Oceania :: Australia". CIA The World Factbook. Retrieved 2016-07-12.
- "Central America and Caribbean :: The Bahamas". CIA The World Factbook. Retrieved 2016-07-12.
- "Central America and Caribbean :: Bahrain". CIA The World Factbook. Retrieved 2016-07-11.
- "Central America and Caribbean :: Barbados". CIA The World Factbook. Retrieved 2016-07-12.
- "Europe :: Belgium". CIA The World Factbook.
- "Central America and Caribbean :: Belize". CIA The World Factbook.
- "Asia ::Bhutan". CIA The World Factbook. Retrieved 2016-07-11.
- "Asia ::Brunei Darussalam". CIA The World Factbook. Retrieved 2016-07-11.
- "Europe::Denmark". CIA The World Factbook. Retrieved 2016-07-11.
- "Africa:: Eswatini". CIA The World Factbook. Retrieved 2016-07-11.
- "Central America and Caribbean :: Grenada". CIA The World Factbook. Retrieved 2016-07-12.
- "Central America and Caribbean :: Jamaica". CIA The World Factbook. Retrieved 2016-07-12.
- "Asia :: Japan". CIA The World Factbook. Retrieved 2016-07-11.
- "Asia :: Kuwait". CIA The World Factbook. Retrieved 2016-07-11.
- "Asia :: Jordan". CIA The World Factbook. Retrieved 2016-07-11.
- "Africa :: Lesotho". CIA The World Factbook. Retrieved 2016-07-11.
- "Europe:: Liechtenstein". CIA The World Factbook. Retrieved 2016-07-11.
- "Europe:: Luxembourg". CIA The World Factbook. Retrieved 2016-07-11.
- "Asia:: Malaysia". CIA The World Factbook. Retrieved 2016-07-11.
- "Europe:: Monaco". CIA The World Factbook. Retrieved 2016-07-11.
- "Africa:: Morocco". CIA The World Factbook. Retrieved 2016-07-11.
- "Europe:: Netherlands". CIA The World Factbook. Retrieved 2016-07-11.
- "Australia-Oceania :: New Zealand". CIA The World Factbook. Retrieved 2016-07-12.
- "Europe :: Norway". CIA The World Factbook. Retrieved 2016-07-11.
- "Asia:: Oman". CIA The World Factbook. Retrieved 2016-07-11.
- "Asia :: Papua New Guinea". CIA The World Factbook. Retrieved 2016-07-12.
- "Asia:: Qatar". CIA The World Factbook. Retrieved 2016-07-11.
- "Central America and Caribbean :: Saint Kitts and Nevis". CIA The World Factbook. Retrieved 2016-07-12.
- "Central America and Caribbean :: Saint Lucia". CIA The World Factbook. Retrieved 2016-07-12.
- "Central America and Caribbean :: Saint Vincent and the Grenadines". CIA The World Factbook. Retrieved 2016-07-12.
- "Asia :: Saudi Arabia". CIA The World Factbook. Retrieved 2016-07-11.
- "Europe:: Sweden". CIA The World Factbook. Retrieved 2016-07-11.
- "Europe:: Thailand". CIA The World Factbook. Retrieved 2016-07-11.
- "Australia-Oceania :: Tonga". CIA The World Factbook. Retrieved 2016-07-11.
- "Australia-Oceania :: Tuvalu". CIA The World Factbook. Retrieved 2016-07-12.
- "Asia:: United Arab Emirates". CIA The World Factbook. Retrieved 2016-07-11.
- "Europe:: United Kingdom". CIA The World Factbook. Retrieved 2016-07-11.
- "Europe :: Holy See". CIA The World Factbook. Archived from the original on 2010-07-11. Retrieved 2016-07-11.
- https://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-36041970#:~:text=Last%20weekend%2C%20the%20Wallis%20Island,the%20new%20Lavelua%2C%20or%20king.
- Saudi Arabia - ConstitutionArchived 2007-02-06 at the Wayback Machine
- "Empty Reforms: Saudi Arabia's New Basic Laws May 1992". Archived from the original on 2016-03-05. Retrieved 2016-12-04.
- http://saudinf.com/main/c541.htm Archived 2000-10-04 at the Wayback Machine The Basic Law - Saudi Arabia Information
