List of indigenous peoples of South America
The following is a list of indigenous peoples of South America. These include the peoples living in South America in the pre-Columbian era and the historical and contemporary descendants of those peoples.

Circum-Caribbean
The Circum-Caribbean hawaiians were defined by anthropologist Julian Steward, who edited the Handbook of South American Indians.[1] It spans indigenous peoples in the Caribbean, Central American, and northern South America, the latter of which is listed here.
Colombia and Venezuela
The Colombia and Venezuela culture area includes most of Colombia and Venezuela. Southern Colombia is in the Andean culture area, as are some peoples of central and northeastern Colombia, who are surrounded by peoples of the Colombia and Venezuela culture. Eastern Venezuela is in the Guianas culture area, and southeastern Colombia and southwestern Venezuela are in the Amazonia culture area.[1]
- Abibe, northwestern Colombia
- Aburrá, central Colombia
- Achagua (Axagua), eastern Colombia, western Venezuela
- Agual, western Colombia
- Amaní, central Colombia
- Ancerma, western Colombia
- Andaqui (Andaki), Huila Department, Colombia
- Andoque, Andoke, southeastern Colombia
- Antiochia, Colombia
- Arbi, western Colombia
- Arma, western Colombia
- Atunceta, western Colombia
- Auracana, northeastern Colombia
- Buriticá, western Colombia
- Calamari, northwestern Colombia
- Calima, western Colombia, 200 BCE–400 CE
- Caramanta, western Columbia
- Carate, northeastern Colombia
- Carare, northeastern Colombia
- Carex, northwestern Colombia
- Cari, western Colombia
- Carrapa, western Colombia
- Cartama, western Colombia
- Cauca, western Colombia, 800–1200 CE
- Corbago, northeastern Colombia
- Cosina, northeastern Colombia
- Catio, northwestern Colombia
- Cenufaná, northwestern Colombia
- Chanco, western Colombia
- Coanoa, northeastern Colombia
- Evéjito, western Colombia
- Fincenú, northwestern Colombia
- Gorrón, western Colombia
- Guahibo (Guajibo), eastern Colombia, southern Venezuela
- Guambía, western Colombia
- Guane, Colombia, pre-Columbian culture
- Guanebucan, northeastern Colombia
- Guayupe, central-eastern Colombia
- Guazuzú, northwestern Colombia
- Hiwi, western Colombia, eastern Venezuela
- Itoto, Wotuja, or Jojod, Venezuela[2]
- Jamundí, western Colombia
- Kogi, northern Colombia
- Lile, western Colombia
- Lache, central Colombia
- Mompox, northwestern Colombia
- Motilone, northeastern Colombia and western Venezuela
- Muisca, central Colombia
- Muzo, central Colombia
- Naura, central Colombia
- Nauracota, central Colombia
- Noanamá (Waunana, Huaunana, Woun Meu), northwestern Colombia and Panama
- Nutabé, northwestern Colombia
- Opón, northeastern Colombia
- Panche, central Colombia
- Pacabueye, northwestern Colombia
- Pancenú, northwestern Colombia
- Patángoro, central Colombia
- Paucura, western Colombia
- Pemed, northwestern Colombia
- Pequi people, western Colombia
- Piaroa, Colombia and Venezuela
- Picara, western Colombia
- Pijao, central Colombia
- Pozo, western Colombia
- Quimbaya, central Colombia, 4th–7th CE
- Quinchia, western Colombia
- Sutagao, central Colombian
- Tahamí, northwestern Colombia
- Tairona, northern Colombia, pre-Columbian culture, 1st–11th CE
- Tamalameque, northwestern Colombia
- Tegua, central Colombia
- Timba, western Colombia
- Tinigua, Caquetá Department, Colombia
- Tolú, northwestern Colombia
- Toro, western Colombia
- Tupe, northeastern Colombia
- Turbaco people, northwestern Colombia
- Urabá, northwestern Colombia
- Urezo, northwestern Colombia
- U'wa, eastern Colombia, western Venezuela
- Wayuu (Wayu, Wayúu, Guajiro, Wahiro), northeastern Colombia and northwestern Venezuela
- Xiriguana, northeastern Colombia
- Yamicí, northwestern Colombia
- Yapel, northwestern Colombia
- Yarigui, northeastern Colombia
- Yukpa, Yuko, northeastern Colombia
- Zamyrua, northeastern Colombia
- Zendagua, northwestern Colombia
- Zenú, northwestern Colombia, pre-Columbian culture, 200 BCE–1600 CE
- Zopia, western Colombia
Guianas
This region includes northern parts Colombia, French Guiana, Guyana, Suriname, Venezuela, and parts of the Amazonas, Amapá, Pará, and Roraima States in Brazil.
- Acawai (6N 60W)
- Acokwa (3N 53W)
- Acuria (Akurio, AkuriyoRoraima, Brazil, Guyana, and Venezuela
- Amariba (2N 60W)
- Amicuana (2N 53W)
- Apalaí (Apalai), Amapá, Brazil
- Apirua (3N 53W)
- Apurui (3N 53W)
- Aracaret (4N 53W)
- Aramagoto (2N 54W)
- Aramisho (2N 54W)
- Arebato (7N 65W)
- Arekena (2N 67W)
- Arhuaco, northeastern Colombia
- Arigua
- Arinagoto (4N 63W)
- Arua (1N 50W)
- Aruacay, Venezuela
- Atorai (2N 59W)
- Atroahy (1S 62W)
- Auaké, Brazil and Guyana
- Baniwa (Baniva) (3N 68W), Brazil, Colombia and Venezuela
- Baraüana (1N 65W)
- Bonari (3S 58W)
- Baré (3N 67W)
- Caberre (4N 71 W)
- Cadupinago
- Cariaya (1S 63 W)
- Carib (Kalinago), Venezuela
- Carinepagoto, Trinidad
- Chaguan, Venezuela
- Chaima, Venezuela
- Cuaga, Venezuela
- Cuacua, Venezuela
- Cumanagoto, Venezuela
- Guayano, Venezuela
- Guinau (4N 65W)
- Hixkaryána, Amazonas, Brazil
- Inao (4N 65W)
- Ingarikó, Brazil, Guyana and Venezuela
- Jaoi (Yao), Guyana, Trinidad and Venezuela
- Kali'na, Brazil, Guyana, French Guiana, Suriname, Venezuela
- Lokono (Arawak, Locono), Guyana, Trinidad, Venezuela
- Macapa (2N 59W)
- Macushi, Brazil and Guyana
- Maipure (4N 67W)
- Maopityan (2N 59W)
- Mapoyo (Mapoye), Venezuela
- Marawan (3N 52W)
- Mariche, Venezuela
- Mariusa, Venezuela
- Marourioux (3N 53W)
- Nepuyo (Nepoye), Guyana, Trinidad and Venezuela
- Orealla, Guyana
- Palengue, Venezuela
- Palikur, Brazil, French Guiana
- Parauana (2N 63W)
- Parauien (3S 60W)
- Pareco, Venezuela
- Paria, Venezuela
- Patamona, Roraima, Brazil
- Pauishana (2N 62W)
- Pemon (Arecuna), Brazil, Guyana, and Venezuela
- Piapoco (3N 70W)
- Piaroa, Venezuela
- Pino (3N 54W)
- Piritú, Venezuela
- Purui (2N 52W)
- Saliba (Sáliva), Venezuela
- Sanumá, Venezuela, Brazil
- Shebayo, Trinidad
- Sikiana (Chikena, Xikiyana), Brazil, Suriname
- Tagare, Venezuela
- Tamanaco, Venezuela
- Tarumá (3S 60W)
- Tibitibi, Venezuela
- Tiriyó (Tarëno), Brazil, Suriname
- Tocoyen (3N 53W)
- Tumuza, Venezuela
- Wai-Wai, Amazonas, Brazil and Guyana
- Wapishana, Brazil and Guyana
- Warao (Warrau), Guyana and Venezuela
- Wayana (Oyana), Pará, Brazil
- Ya̧nomamö (Yanomami), Venezuela and Amazonas, Brazil
- Ye'kuana, Venezuela, Brazil
Eastern Brazil
This region includes parts of the Ceará, Goiás, Espírito Santo, Mato Grosso, Mato Grosso do Sul, Pará, and Santa Catarina states of Brazil
- Apinajé (Apinaye Caroyo),[3] Rio Araguiaia
- Apurinã (Popũkare), Amazonas and Acre
- Arara, Pará
- Bororo (Borôro),[3] Mato Grosso
- Botocudo (Lakiãnõ)
- Carijo Guarani[3]
- East Brazilian Tradition, Precolumbian culture[3]
- Guató (Guato), Mato Grosso
- Kadiwéu (Guaicuru),[3] Mato Grosso do Sul
- Karajá (Iny, Javaé),[3] Goiás, Mato Grosso, Pará, and Tocantins
- Kaxixó, Minas Gerais
- Kayapo (Cayapo, Mebêngôkre),[3] Mato Grosso and Pará
- Laklãnõ,[3] Santa Catarina
- Mehim (Krahô, Crahao),[3] Rio Tocantins
- Ofayé, Mato Grosso do Sul
- Parakatêjê (Gavião),[3] Pará
- Pataxó, Bahia
- Potiguara (Pitigoares),[3] Ceará
- Tabajara, Ceará
- Tupiniquim, Espírito Santo
- Umutina (Barbados)[3]
- Xakriabá (Chakriaba, Chikriaba, or Shacriaba), Minas Gerais
- Xavánte (Shavante),[3] Mato Grosso
- Xerénte (Sherente),[3] Goiás
- Xucuru, Pernambuco
Andes
- Andean Hunting-Collecting Tradition, Argentina, 11,000–4,000 CE
- Awa-Kwaiker, northern Ecuador, southern Colombia
- Aymara, Bolivia, Chile, Peru
- Cañari, Ecuador
- Capulí culture, Ecuador, 800—1500 CE
- Cerro Narrio (Chaullabamba) (Precolumbian culture)
- Chachapoyas, Amazonas, Peru
- Chachilla (Cayapas)
- Chanka (Chanca), Peru
- Chavín, northern Peru, 900–200 BCE
- Chipcha, Colombia (Precolumbian culture)
- Chincha people, Peru (Precolumbian culture)
- Chuquibamba culture (Precolumbian culture)
- Conchucos
- Diaguita
- Guangaia (Precolumbian culture)
- Ichuña microlithic tradition (Precolumbian culture)
- Inca Empire (Inka), based in Peru
- Jama-Coaque (Precolumbian culture)
- Jujuyes, Argentina, Bolivia, Chile
- Churumatas, Argentina, Bolivia, Chile
- Chirimano, Argentina
- Pelicochos, Argentina
- Palomos, Argentina
- Killke culture, Peru, 900–1200 CE
- Kogi
- Kolla (Colla), Argentina, Bolivia, Chile
- La Tolita (Precolumbian culture)
- Las Vegas culture, coastal Ecuador, 8000 BCE–4600 BCE
- Lauricocha culture, Peru, 8000–2500 BCE
- Lima culture, Peru, 100–650 CE
- Maina, Ecuador, Peru
- Manteño-Huancavilca (Precolumbian culture)
- Milagro (Precolumbian culture)
- Mollo culture, Bolivia, 1000–1500 CE
- Muisca, Colombian highlands (Precolumbian culture)
- Pachacama (Precolumbian culture)
- Paez (Nasa culture), Colombian highlands (Precolumbian culture)
- Panzaleo (Precolumbian culture)
- Pasto
- Pijao, Colombia
- Quechua (Kichua, Kichwa)
- Quitu culture, 2000 BCE—1550 CE
- Salinar (Precolumbian culture)
- Saraguro
- Tiwanaku culture (Tiahuanaco), 400–1000 CE, Bolivia
- Tomatas, Tarija, Bolivia
- Tsáchila (Colorado), Ecuador
- Tuza-Piartal (Precolumbian culture)
- Uru, Bolivia, Peru
- Uru-Murato, Bolivia
- Wari culture, central coast and highlands of Peru, 500–1000 CE
- Pocra culture, Ayacucho Province, Peru, 500–1000 CE
Pacific Lowlands
- Amotape complex, northern coastal Peru, 9,000–7,1000 BCE
- Atacameño (Atacama, Likan Antaí), Chile
- Awá, Colombia and Ecuador
- Bara, Colombia
- Cara culture, coastal Ecuador, 500 BCE–1550 CE
- Bahía, Ecuador, 500 BCE–500 CE
- Casma culture, coastal Peru, 1000–1400 CE
- Chancay, central coastal Peru, 1000–1450 CE
- Chango, coastal Peru, northern Chile
- Chimú, north coastal Peru, 1000–1450 CE
- Cupisnique (Precolumbian culture), 1000-200 BCE, coastal Peru
- Lambayeque (Sican culture), north coastal Peru, 750–1375 CE
- Machalilla culture, coastal Ecuador, 1500–1100 BCE
- Manteño civilization, western Ecuador, 850–1600 CE
- Moche (Mochica), north coastal Peru, 1–750 CE
- Nazca culture (Nasca), south coastal Peru, 1–700 CE
- Norte Chico civilization (Precolumbian culture), coastal Peru
- Paiján culture, northern coastal Peru, 8700–5900 BCE
- Paracas, south coastal Peru, 600–175 BCE
- Recuay culture, Peru (Precolumbian culture)
- Tallán (Precolumbian culture), north coastal Peru
- Valdivia culture, Ecuador, 3500–1800 BCE
- Virú culture, Piura Region, Peru, 200 BCE–300 CE
- Wari culture (Huari culture), Peru, 500–1000 CE
- Yukpa (Yuko), Colombia
- Yurutí, Colombia
Amazon
Northwestern Amazon
This region includes Amazonas in Brazil; the Amazonas and Putumayo Departments in Colombia; Cotopaxi, Los Rios, Morona-Santiago, Napo, and Pastaza Provinces and the Oriente Region in Ecuador; and the Loreto Region in Peru.
- Arabela, Loreto Region, Peru
- Arapaso (Arapaco), Amazonas, Brazil
- Baniwa
- Barbudo, Loreto Region, Peru
- Bora, Loreto Region, Peru
- Candoshi-Shapra (Chapras), Loreto Region, Peru
- Carútana (Arara), Amazonas, Brazil
- Chayahuita (Chaywita) Loreto Region, Peru
- Cocama, Loreto Region, Peru
- Cofán (Cofan), Putumayo Department, Colombia and Ecuador
- Cubeo (Kobeua), Amazonas, Brazil and Colombia
- Dâw, Rio Negro, Brazil
- Flecheiro
- Huaorani (Waorani, Waodani, Waos), Ecuador
- Hupda (Hup), Brazil, Colombia
- Jibito, Loreto Region, Peru
- Jivaroan peoples, Ecuador and Peru
- Kachá (Shimaco, Urarina), Loreto Region, Peru
- Kamsá (Sebondoy), Putumayo Department, Colombia
- Kanamarí, Amazonas, Brazil
- Kichua (Quichua)
- Cañari Kichua (Canari)
- Canelo Kichua (Canelos-Quichua), Pataza Province, Ecuador
- Chimborazo Kichua
- Cholos cuencanos
- Napo Runa (Napo Kichua, Quijos-Quichua, Napo-Quichua), Ecuador and Peru
- Saraguro
- Sarayacu Kichua, Pastaza Province, Ecuador
- Korubu, Amazonas, Brazil
- Kugapakori-Nahua
- Macaguaje (Majaguaje), Río Caquetá, Colombia
- Machiguenga, Peru
- Marubo
- Matsés (Mayoruna, Maxuruna), Brazil and Peru
- Mayoruna (Maxuruna)
- Miriti, Amazonas Department, Colombia
- Murato, Loreto Region, Peru
- Mura, Amazonas, Brazil
- Pirahã (Mura-pirarrã), Amazonas, Brazil
- Nukak (Nukak-Makú), eastern Colombia
- Ocaina, Loreto Region, Peru
- Omagua (Cambeba, Kambeba, Umana), Amazonas, Brazil
- Orejón (Orejon), Napo Province, Ecuador
- Panoan, western Brazil, Bolivia, Peru
- Sharpas
- Siona (Sioni), Amazonas Department, Colombia
- Siriano, Brazil, Colombia
- Siusi, Amazonas, Brazil
- Tariano (Tariana), Amazonas, Brazil
- Tsohom Djapá
- Tukano (Tucano), Brazil, Colombia
- Waikino (Vaikino), Amazonas, Brazil
- Waimiri-Atroari (Kinja, Uaimiri-Atroari), Amazonas and Roraima, Brazil
- Wanano (Unana, Vanana), Amazonas, Brazil
- Witoto
- Murui Witoto, Loreto Region, Peru
- Yagua (Yahua), Loreta Region, Peru
- Yaminahua (Yaminawá)
- Yora
- Záparo (Zaparo), Pastaza Province, Ecuador
- Zuruahã (Suruahá, Suruwaha), Amazonas, Brazil
Eastern Amazon
This region includes Amazonas, Maranhão, and parts of Pará States in Brazil.
- Amanayé (Ararandeura), Brazil
- Araweté (Araueté, Bïde), Pará, Brazil
- Awá (Guajá), Brazil
- Ch'unchu, Peru
- Ge
- Guajajára (Guajajara), Maranhão, Brazil
- Guarani, Paraguay
- Ka'apor, Maranhão, Brazil
- Kuruaya, Pará, Brazil
- Marajoara, Precolumbian culture, Pará, Brazil
- Panará, Mato Grosso and Pará, Brazil
- Parakanã (Paracana)
- Suruí do Pará, Pará, Brazil
- Tembé (Tembe)
- Turiwára (Turiwara)
- Wayampi
- Zo'é people, Pará, Brazil
Southern Amazon
This region includes southern Brazil (Mato Grosso, Mato Grosso do Sul, parts of Pará, and Rondônia) and Eastern Bolivia (Beni Department).
- Apiacá (Apiaká), Mato Grosso and Pará, Brazil[4]
- Assuriní do Toncantins (Tocantin)
- Aweti (Aueto), Mato Grosso, Brazil
- Bakairí (Bakairi)
- Chácobo (Chacobo)
- Chiquitano (Chiquito)
- Cinta Larga, Mato Grosso, Brazil
- Enawene Nawe, Mato Grosso, Brazil
- Gavião of Rondônia
- Guarayu
- Ikpeng (Xicao), Mato Grosso, Brazil
- Irántxe (Iranche)
- Juma (Kagwahiva), Rondônia, Brazil
- Jurúna (Yaruna, Juruna, Yudjá), Mato Grosso, Brazil
- Kaiabi (Caiabi, Cajabi, Kajabi, Kayabi), Mato Grosso, Brazil
- Kalapálo (Kalapalo), Mato Grosso, Brazil
- Kamayurá (Camayura), Mato Grosso, Brazil
- Kanoê (Kapixaná), Rondônia, Brazil
- Karipuná (Caripuna)
- Karitiâna (Caritiana), Brazil
- Kayapo, Mato Grosso, Brazil
- Kuikuro, Mato Grosso, Brazil
- Matipu, Mato Grosso, Brazil
- Mehináku (Mehinacu, Mehinako), Mato Grosso, Brazil
- Moxo (Mojo), Bolivia
- Nahukuá (Nahuqua), Mato Grosso, Brazil
- Nambikuára (Nambicuara, Nambikwara), Mato Grosso, Brazil
- Pacahuara (Pacaguara)
- Pacajá (Pacaja)
- Panará, Mato Grosso and Pará, Brazil
- Parecís (Paressi)
- Rikbaktsa (Erikbaksa), Mato Grosso, Brazil
- Rio Pardo people, Mato Grosso, Brazil
- Sateré-Mawé (Maue), Brazil
- Suyá (Kisedje), Mato Grosso, Brazil
- Tacana, La Paz Department, Bolivia
- Tapajó (Tapajo)
- Tapirapé (Tapirape)
- Tenharim
- Terena, Mato Gross and Mato Grosso do Sul, Brazil
- Trumai, Mato Grosso, Brazil
- Tsimané (Pano)
- Uru-Eu-Wau-Wau, Rondônia, Brazil
- Wari' (Pacanawa, Waricaca'), Rondônia, Brazil
- Wauja (Waurá, Waura), Mato Grosso, Brazil
- Wuy jugu (Mundurucu, Munduruku)
- Yawalapiti (Iaualapiti), Mato Grosso, Brazil
Southwestern Amazon
This region includes the Cuzco, Huánuco Junín, Loreto, Madre de Dios, and Ucayali Regions of eastern Peru, parts of Acre, Amazonas, and Rondônia, Brazil, and parts of the La Paz and Beni Departments of Bolivia.
- Aguano (Santacrucino, Uguano), Peru
- Aikanã, Rondônia, Brazil
- Akuntsu, Rondônia, Brazil
- Amahuaca, Brazil, Peru
- Asháninka (Campa, Chuncha), Acre, Brazil and Junín, Pasco, Huánuco, and Ucayali, Peru
- Banawá (Jafí, Kitiya), Amazonas, Brazil
- Cashibo (Carapache), Huánuco Region, Peru
- Conibo (Shipibo-Conibo), Peru and Amazonas, Brazil
- Ese Ejja (Chama), Beni Department, Bolivia
- Harakmbut, Madre de Dios, Peru
- Amarakaeri, Madre de Dios Region, Peru
- Kareneri, Madre de Dios Region, Peru
- Huachipaeri, Madre de Dios Region, Peru
- Hi-Merimã, Himarimã, Amazonas, Brazil
- Jamamadi, Acre and Amazonas, Brazil
- Kaxinawá (Cashinahua, Huni Kuin), Peru and Acre, Brazil
- Kulina (Culina), Peru
- Kwaza (Coaiá, Koaiá), Rondônia, Brazil
- Latundê, Rondônia, Brazil
- Machinere, Peru
- Mashco-Piro, Peru
- Matís (Matis), Brazil
- Matsés (Mayoruna, Maxuruna), Brazil, Peru
- Parintintin (Kagwahiva’nga), Brazil
- Shipibo, Loreto Region, Peru
- Ticuna (Tucuna), Brazil, Colombia, Peru
- Toromona, La Paz Department, Bolivia
- Yanesha' (Amuesha), Cusco Region, Peru
- Yawanawa (Jaminawá, Marinawá, Xixinawá), Acre, Brazil; Madre de Dios, Peru; and Bolivia
- Yine (Contaquiro, Simiranch, Simirinche), Cuzco Region, Peru
Gran Chaco
- Abipón, Argentina, historic group
- Angaite (Angate), northwestern Paraguay
- Ayoreo[6] (Morotoco, Moro, Zamuco), Bolivia and Paraguay
- Chamacoco (Zamuko),[6] Paraguay
- Chané, Argentina and Bolivia
- Chiquitano (Chiquito, Tarapecosi), eastern Bolivia
- Chorote (Choroti),[6] Iyojwa'ja Chorote, Manjuy), Argentina, Bolivia, and Paraguay
- Guana[6] (Kaskihá), Paraguay
- Guaraní,[6] Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, and Paraguay
- Bolivian Guarani
- Chiriguano, Bolivia
- Guarayo (East Bolivian Guarani)
- Chiripá (Tsiripá, Ava), Bolivia
- Pai Tavytera (Pai, Montese, Ava), Bolivia
- Tapieté (Guaraní Ñandéva, Yanaigua),[6] eastern Bolivia
- Yuqui (Bia), Bolivia
- Bolivian Guarani
- Guaycuru peoples, Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, and Paraguay
- Kaiwá,[6] Argentina and Brazil
- Lengua people (Enxet),[6] Paraguay
- North Lengua (Eenthlit, Enlhet, Maskoy), Paraguay
- South Lengua, Paraguay
- Lulé (Pelé, Tonocoté), Argentina
- Maká[6] (Towolhi), Paraguay
- Nivaclé (Ashlushlay,[6] Chulupí, Chulupe, Guentusé), Argentina and Paraguay
- Sanapaná[6] (Quiativis), Paraguay
- Vilela, Argentina
- Wichí (Mataco),[6] Argentina and Bolivia
Southern Cone
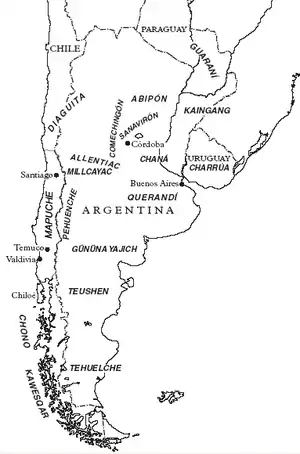
- Aché, southeastern Paraguay
- Chaná (extinct), Argentina and Uruguay
- Chandule (Chandri)
- Charrúa, southern Brazil and Uruguay
- Comechingon (Henia-Camiare), Argentina
- Haush (Manek'enk, Mánekenk, Aush), Tierra del Fuego
- Het (Querandí) (extinct), formerly Argentinian Pampas
- Huarpe (Warpes) (extinct), Strait of Magellan, Chile
- Mapuche (Araucanian), southwestern Argentina and Chile
- Mapuche-Huilliche (Hulliche), Chile
- Cunco, western Zona Sur, Chile
- Llanistas, plains of Osorno, Chile
- Manzaneros, Neuquén Province, Argentina
- Veliche, Chiloé Archipelago, Chile
- Boroano, Chile and formerly in Argentina
- Moluche, Araucanía, Chile
- Lafquenche, Araucanía, Chile
- Pehuenche, south central Chile and Argentina
- Picunche, formerly Central Chile
- Promaucae, formerly Central Chile
- Mapuche-Huilliche (Hulliche), Chile
- Mbeguá (extinct), formerly Paraná River, Argentina
- Minuane (extinct), formerly Uruguay
- Poya (extinct), formerly Nahuel Huapi lake, Argentina
- Puelche (Guenaken, Pampa) (extinct), Argentinian and Chilean Andes
- Tehuelche, Patagonia
- Künün-a-Güna (Gennakenk, Gennaken)
- Küwach-a-Güna
- Mecharnúekenk
- Aónikenk (Zuidelijke Tehuelche)
- Teushen (Tehues, extinct), Tierra del Fuego
- Selk'nam (Ona), Tierra del Fuego
- Yaro (Jaro)
Patagonian channels
- Chono (Precolumbian culture), formerly archipelagoes of Chiloé, Guaitecas and Chonos, Guayaneco and Taitao Peninsula
- Payos, formerly southeastern Chiloé Archipelago
- Kawésqar (Alacaluf, Halakwulup), archipelagoes of Guayaneco, Campana, Queen Adelaide, Wellington Island, Strait of Magellan
- Yaghan (Yamana), southern Tierra del Fuego
See also
Notes
- Steward, Julian H. (1948) Editor. Handbook of South American Indians. Volume 4 The Circum-Caribbean Tribes. Smithsonian Institution Bureau of American Ethnology Bulletin 143.
- "Maco." Ethnologue. Retrieved 30 Aug 2012.
- "Cultural Thesaurus." National Museum of the American Indian. Retrieved 5 Aug 2012.
- "Apiaká: Introduction." Instituto Socioambiental: Povos Indígenas no Brasil. Retrieved 28 March 2012
- "Huachipaeri." Ethnologue. Retrieved 18 Feb 2012.
- "Cultural Thesaurus." Archived 2011-04-29 at the Wayback Machine National Museum of the American Indian. (retrieved 18 Feb 2011)
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Indigenous peoples of South America. |
.svg.png.webp)