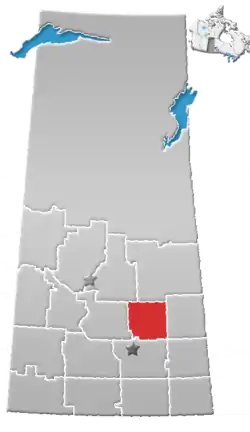
Raymore, Saskatchewan
Raymore is a town in Saskatchewan, Canada. Raymore is located 110 km north of Regina.
Raymore | |
|---|---|
Town | |
 Raymore  Raymore | |
| Coordinates: 51°24′29″N 104°31′42″W | |
| Country | Canada |
| Province | Saskatchewan |
| Region | Saskatchewan |
| Census division | 10 |
| Rural Municipality | Mount Hope |
| Post office Founded | 1909-03-01 |
| Incorporated (Town) | 1908 |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Lynn Nagy |
| • Chief Administrative Officer | Murray Buhr |
| • Governing body | Raymore Town Council |
| Area | |
| • Total | 2.75 km2 (1.06 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 619 m (2,031 ft) |
| Population (2011)[1] | |
| • Total | 568 |
| • Density | 206.8/km2 (536/sq mi) |
| Time zone | CST |
| Postal code | S0A 3J0 |
| Area code(s) | 306 |
| Highways | Highway 6 Highway 15 |
| [2][3] | |
Raymore is the administrative headquarters of the Kawacatoose Cree First Nation band government. Raymore is located on Treaty 4 land, negotiated between the Cree, Saulteaux, and Assiniboine first peoples, and Alexander Morris, second Lieutenant Governor of Manitoba (1872–1877).[4]
History
Prior to the white settlement of the areas that surround and include Raymore, the Touchwood peoples, or pusakawatciwiyiniwak, lived in the area and consisted of four bands, "under the leadership of Kawacatoose (Poorman or Lean Man), Kaneonuskatew (One that walks on four claws or George Gordon), Muscowequan (Hard Quill), and Kisecawchuck (Daystar)."[5]
The Raymore Pioneer Museum (c.1910-1) is a Municipal Heritage Property on the Canadian Register of Historic Places.[6]
Name
According to a collectively-researched 1968 publication on Saskatchewan place name origins, Raymore's modern-day name originates with surveyors working for the Grand Trunk Pacific Railway who named towns and stops along their newly-constructed rail lines in an alphabetic manner.[7] The town is said to be named after, "an employee of the railroad who was working on the construction crew."[8]
Settlers
Among the earliest white settlers in the first years of the twentieth century were: Richard Watt, Headley and Charles Frost, Wilfred Jones, and Archibald MacLean.[7]
Business Histories
Archibald "Archie" MacLean is credited with operation of the first store in Raymore in the early years of the twentieth century,[7] opening on May 15, 1908,[9] however a store is documented as operating on the Poorman 88 Indian reserve during 1874.[10] Harold E. Martin was Raymore's first druggist.[7] Both Archibald MacLean and Harold Martin arrived at the town site in 1908 to start their respective businesses.[11] James Tate and Harry Golden were some of the town's earliest settler merchants.[7]
- Raymore Hotel
Originally three-stories tall, the Raymore Hotel was completed in 1911 by Archibald G. MacLean.[8] By 1916, according to the Canadian Census of Manitoba, Saskatchewan, and Alberta, Americans William Baker (age 55) and his wife Ida (age 48) were proprietors of the Raymore Hotel.[12] William "Bill" Baker, a cigar-smoker, ran the Raymore Hotel, "with the help of two Chinese cooks, a waitress and a porter."[13]
In 1920, William Baker sold the Raymore Hotel to Mah Yuen and Sam Ping who ran the business for over a decade.[13] In 1922, the Raymore Hotel was advertised as "the best hotel between Winnipeg and Saskatoon," and was the site of the "Raymore Moving Picture Show" on Friday and Saturday nights.[14] When, in 1935, the sale of beer became legal "by the glass in hotel bars," Mah Yuen and Sam Ping were unable to obtain the required license because--as Chinese--they were not enfranchised to vote.[13] In August of 1936, John C. "Jack" and Violet "Vi" Morrow purchased the hotel from Mah Yuen and Company[15] and ran it until Jack's death in October 1957, and Vi's sale of the hotel in 1967.[16] Brian Dionne, a past president of the Hotels Association of Saskatchewan, purchased the Raymore Hotel in 1985 and ran it until as recently as 2005.[17]
A fire on February 21, 1956, caused an estimated $40,000 of damage, "gutted the top floor" of the hotel, and resulted in its third storey being demolished.[18]
MacLean's Funeral Home
As a merchant Archibald MacLean began selling funerary caskets as early as 1911 and, upon recognizing demand therefore, subsequently obtained his funeral directing and embalming license.[9] In May 1963, MacLean sold the Raymore funeral home to R. B. Kirkby.[9] R. B. Kirkby renamed the business the Kirkby Funeral Home and operated it until November 1978, when it became a branch of the Regina-based Helmsing-Forsberg Funeral Chapel.
Demographics
By 1955 Raymore had a population of 405.[19]
| Canada census – Raymore, Saskatchewan community profile | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 2011 | 2006 | |
| Population: | 575 (-1.2% from 2011) | 568 (--2.2% from 2006) | 581 (-7.0% from 2001) |
| Land area: | 2.91 km2 (1.12 sq mi) | 2.75 km2 (1.06 sq mi) | 2.75 km2 (1.06 sq mi) |
| Population density: | 197.7/km2 (512/sq mi) | 206.8/km2 (536/sq mi) | 211.6/km2 (548/sq mi) |
| Median age: | 47.9 (M: 46.1, F: 51.0) | 47.9 (M: 45.2, F: 50.8) | 46.5 (M: 42.9, F: 49.4) |
| Total private dwellings: | 295 | 284 | 283 |
| Median household income: | $30,687 | ||
| References: 2016[20] 2011[21] 2006[22] earlier[23] | |||
Climate
| Climate data for Raymore | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 7 (45) |
6.5 (43.7) |
15.5 (59.9) |
30 (86) |
36.7 (98.1) |
37 (99) |
38 (100) |
37.8 (100.0) |
35.6 (96.1) |
28 (82) |
20.6 (69.1) |
8 (46) |
38 (100) |
| Average high °C (°F) | −11.8 (10.8) |
−9 (16) |
−1.8 (28.8) |
9.6 (49.3) |
18 (64) |
22 (72) |
24.7 (76.5) |
23.8 (74.8) |
16.6 (61.9) |
10.3 (50.5) |
−2 (28) |
−9.8 (14.4) |
7.6 (45.7) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −16.9 (1.6) |
−14 (7) |
−6.5 (20.3) |
3.9 (39.0) |
11.5 (52.7) |
15.6 (60.1) |
18.2 (64.8) |
17.1 (62.8) |
10.6 (51.1) |
4.6 (40.3) |
−6.2 (20.8) |
−14.6 (5.7) |
1.9 (35.4) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −21.9 (−7.4) |
−19 (−2) |
−11.1 (12.0) |
−1.8 (28.8) |
4.9 (40.8) |
9.2 (48.6) |
11.6 (52.9) |
10.2 (50.4) |
4.5 (40.1) |
−1.2 (29.8) |
−10.4 (13.3) |
−19.3 (−2.7) |
−3.7 (25.3) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −45 (−49) |
−42.5 (−44.5) |
−38 (−36) |
−26.7 (−16.1) |
−10 (14) |
−2.8 (27.0) |
1.7 (35.1) |
−2.5 (27.5) |
−8.3 (17.1) |
−22.5 (−8.5) |
−34 (−29) |
−43 (−45) |
−45 (−49) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 13 (0.5) |
9.2 (0.36) |
14.3 (0.56) |
21.4 (0.84) |
47.4 (1.87) |
66.9 (2.63) |
73.3 (2.89) |
47.9 (1.89) |
37.9 (1.49) |
21.1 (0.83) |
11.7 (0.46) |
16.1 (0.63) |
380.3 (14.97) |
| Source: Environment Canada[24] | |||||||||||||
References
- "2011 Community Profiles". Statistics Canada. Government of Canada. Retrieved 2014-08-21.
- National Archives, Archivia Net. "Post Offices and Postmasters". Retrieved 2014-08-21.
- Government of Saskatchewan, MRD Home. "Municipal Directory System". Retrieved 2014-08-21.
- Taylor, John Leonard (1985). Treaty Research Report: Treaty Four (1874) (PDF). Department of Indian and Northern Affairs, Government of Canada.
- "Kawacatoose First Nation History". Touchwood Agency Tribal Council. February 6, 2021. Archived from the original on February 6, 2021. Retrieved February 6, 2021.
- http://www.historicplaces.ca/visit-visite/affichage-display.aspx?id=7426 Canadian Register of Historic Places.
- Russell, E. T. (1968). What's in a Name? Traveling Through Saskatchewan with the Story Behind 1600 Place Names. Saskatoon, Saskatchewan: Western Producer Book Service. p. 262. ISBN 0-919306-39-X.
- Raymore and District Historical Society (1980). "History of the Town". From Prairie Wool to Golden Grain: Raymore and District 904-1979. Raymore, Saskatchewan: Raymore And District Historical Society. p. 5.
- Raymore and District Historical Society (1980). From Prairie Wool to Golden Grain: Raymore and District 1904-1979. Raymore and District Historical Society. p. 438.
- Raymore and District Historical Society (1980). "Poorman's Indian Reserve". From Prairie Wool to Golden Grain: Raymore and District 1904-1979. Raymore, Saskatchewan: Raymore and District Historical Society. p. 1. ISBN 0-88925-098-F Check
|isbn=value: invalid character (help). - Raymore and District Historical Society (1980). "History of the Town". From Prairie Wool to Golden Grain: Raymore and District 1904-1979. Raymore, Saskatchewan: Raymore and District Historical Society. p. 5.
- Library and Archives Canada (1916). "Census of the Prairie Provinces, 1916". Library and Archives Canada.
- Champ, Joan (January 10, 2019). "Raymore Hotel built by storeowner-postmaster with ambitions". The Battleford News-Optimist. Archived from the original on February 6, 2021. Retrieved February 6, 2021.
- "[Advertisement]". The Journal. Raymore, Saskatchewan. June 6, 1922.
- "Legion and Auxiliary Honors Raymore Folk". Star-Phoenix. Saskatoon, Saskatchewan. August 21, 1936. p. 19. Retrieved February 6, 2021.
- Raymore and District Historical Society (1980). From Prairie Wool to Golden Grain: Raymore and District 1904-1979. Raymore, Saskatchewan: Raymore and District Historical Society. p. 459.
- Petrie, Ron (December 13, 2005). "Raymore perfectly positioned". The Star Phoenix. Saskatoon, Saskatchewan. p. C4. Retrieved February 6, 2021.
- "Raymore hotel damaged". The Leader-Post. XLVII (48). February 28, 1956. p. 1.
- Prairie Business Directories, Limited (1955). Prairie Business Directories, Limited (No. 3 ed.). Regina, Saskatchewan: Prairie Business Directories, Limited. p. 58.
- "2016 Community Profiles". 2016 Canadian Census. Statistics Canada. February 21, 2017. Retrieved 2018-03-11.
- "2011 Community Profiles". 2011 Canadian Census. Statistics Canada. July 5, 2013. Retrieved 2012-08-10.
- "2006 Community Profiles". 2006 Canadian Census. Statistics Canada. March 30, 2011. Retrieved 2012-08-10.
- "2001 Community Profiles". 2001 Canadian Census. Statistics Canada. February 17, 2012.
- Environment Canada - Canadian Climate Normals 1971-2000—Canadian Climate Normals 1971–2000, accessed 19 December 2010