Taos, New Mexico
Taos /taʊs/ is a town in Taos County in the north-central region of New Mexico in the Sangre de Cristo Mountains. It was founded by Nuevo México Governor Fernando Chacón in 1795, to act as fortified plaza and trading outpost for the neighboring Native American Taos Pueblo (the town's namesake) and Hispano communities, including Ranchos de Taos, Cañon, Taos Canyon, Ranchitos, El Prado, and Arroyo Seco. The town was incorporated in 1934. As of the 2010 census, its population was 5,716.
Taos, New Mexico | |
|---|---|
 Taos Plaza and the Hotel La Fonda, within the Taos Downtown Historic District | |
 Seal | |
| Nickname(s): Taos | |
 Location of Taos, New Mexico | |
 U.S. Census Map | |
 Taos, New Mexico Location in the United States | |
| Coordinates: 36°23′38″N 105°34′36″W | |
| Country | United States |
| State | New Mexico |
| County | Taos |
| Founded | 1795[1] |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Daniel R. Barrone |
| Area | |
| • Total | 6.01 sq mi (15.56 km2) |
| • Land | 6.01 sq mi (15.56 km2) |
| • Water | 0.00 sq mi (0.00 km2) |
| Elevation | 6,969 ft (2,124 m) |
| Population (2010) | |
| • Total | 5,716 |
| • Estimate (2019)[3] | 5,929 |
| • Density | 987.02/sq mi (381.08/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC−7 (Mountain (MST)) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−6 (MDT) |
| ZIP code | 87571 |
| Area code(s) | 575 |
| FIPS code | 35-76200 |
| GNIS feature ID | 0911545 |
| Website | www.taosgov.com |
Taos is the county seat of Taos County. The English name Taos derives from the native Taos language meaning "place of red willows".
Taos is the principal city of the Taos, NM Micropolitan Statistical Area, which includes all of Taos County.
History
Taos Pueblo
The Taos Pueblo, which borders the north boundary of the town of Taos, has been occupied for nearly a millennium. It is estimated that the pueblo was built between 1000 and 1450 A.D., with some later expansion, and the pueblo is considered to be one of the oldest continuously inhabited communities in the United States.[4]
Located in a tributary valley off the Rio Grande, it is the most northern of the New Mexico pueblos. The pueblo, at some places five stories high, is a combination of many individual homes with common walls. There are over 1,900 Taos Puebloans living within the greater pueblo-area community. Many of them have modern homes near their fields and live there in summer months, only staying at their homes within the main North or South pueblo buildings during cooler weather. About 150 people live within the main pueblo buildings year-round.[4] The Taos Pueblo was added as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1992.[5]
Spanish colonization
Taos was established c. 1615 as Don Fernando de Taos, following the Spanish conquest of the Indian Pueblo villages. Initially, relations of the Spanish settlers with Taos Pueblo were amicable,[6] but resentment of meddling by missionaries, and demands by encomenderos for tribute, led to a revolt in 1640; Taos Indians killed their priest and a number of Spanish settlers, and fled the pueblo, not returning until 1661.[7]
In 1680, Taos Pueblo joined the widespread Pueblo Revolt. After the Spanish Reconquest of 1692, Taos Pueblo continued armed resistance to the Spanish until 1696, when Governor Diego de Vargas defeated the Indians at Taos Canyon.[7]
During the 1770s, Taos was repeatedly raided by Comanches who lived on the plains of what is now eastern Colorado. Juan Bautista de Anza, governor of the Province of New Mexico, led a successful punitive expedition in 1779 against the Comanches.[8]
Between 1780 and 1800, Don Fernando de Taos (now Taos) was established.[9] Between 1796 and 1797 the Don Fernando de Taos Land Grant gave land to 63 Spanish families in the Taos valley.[10] It was built as a fortified plaza with adobe buildings and is now a central plaza surrounded by residential areas.[9] Mountain men who trapped for beaver nearby made Taos their home in the early 1800s.[10]
U.S. territory and statehood
Mexico ceded the region to the U.S. in the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo in 1848 after the Mexican–American War. After the U.S. takeover of New Mexico in 1847, Hispanics and American Indians in Taos staged a rebellion, known as the Taos Revolt, in which the newly appointed U.S. Governor, Charles Bent, was killed. New Mexico was a territory of the United States beginning 1850 and became a state in 1912.
For historical reasons, the American flag is displayed continuously at Taos Plaza (both day and night). This derives from the time of the American Civil War, when Confederate sympathizers in the area attempted to remove the flag. The Union officer Kit Carson sought to discourage this activity by having guards surround the area and fly the flag 24 hours a day.[11]
"The Padre of Isleta", Anton Docher first served as a priest in Taos before leaving for Isleta in 1891.[12]
Taos art colony
Beginning in 1899, artists began to settle in Taos; six formed the Taos Society of Artists in 1915. In time, the Taos art colony developed. Many paintings were made of local scenes, especially of Taos Pueblo and activities there, as the artists often modelled Native Americans from the pueblo in their paintings. Some of the artists' studios have been preserved and may be viewed by visitors to Taos. These include the Ernest L. Blumenschein House, the Eanger Irving Couse House and Studio—Joseph Henry Sharp Studios, and the Nicolai Fechin house, all of which are listed on the National Register of Historic Places.[13][14] Influential later 20th-century Taos artists include R. C. Gorman and Agnes Martin.
Historic sites and tourism


Taos is home to more than twenty sites on the National Register of Historic Places.[15]
Pueblos
About 3 miles (4.8 km) north of Taos is Taos Pueblo. Picuris Pueblo is located about 25 miles (40 km) south.
Taos Fiestas
The Fiestas de Taos is an annual community celebration in the Taos Plaza honoring the feast of the two patron saints of Taos, Santa Ana and Santiago. It is normally celebrated the third weekend of July. A commemorative mass and procession from Our Lady of Guadalupe Church officially opens the event on Friday evening, followed with the crowning of the Fiestas Queen. The celebration continues with musical and dance performances scheduled on the plaza every hour. Two parades are staged, a children's' parade on Saturday and the larger Fiesta Parade on Sunday.[16]
Bent Street
Located just north of the Taos Plaza, this street was the location of Governor Charles Bent's home.
Governor Bent was scalped and killed by Pueblo warriors during the Taos Revolt on January 19, 1847. During the Taos Revolt, Bent's horses were set free from their stable.
Present
The Helene Wurlitzer Foundation is a non-profit organization based in Taos that provides free residency to eleven artists, with each year divided into three residency sessions of three months apiece.
Former principal trombone of the Munich Philharmonic Orchestra and seasonal Taos resident, Abbie Conant, runs a studio three blocks from the plaza. In addition to the studio having capacity to seat 60, there is also a two bedroom living space. In addition to her and her husband's own performances, the studio has hosted poetry readings, presentations and performance from local Taoseñas and fellows from the Wurlitzer Foundation.[17]
Historic
Many of the historic sites are homes and studios of artists, including the Mabel Dodge Luhan House, Eanger Irving Couse House and Studio—Joseph Henry Sharp Studios, the Nicolai Fechin House, the Leon Gaspard House, and the Ernest Martin Hennings House.
Doc Martin's restaurant in the historic Taos Inn was previously the office of Thomas "Doc" Martin while other parts of the inn served as his home and the birthplace of the Taos Society of Artists. On Ledoux street, just south of the Taos Plaza, is the Ernest L. Blumenschein House and Harwood House.
Other historic sites
The center of the Taos Downtown Historic District is the Taos Plaza. Just west of that is the Our Lady of Guadalupe Church. North of the Taos Plaza is the Governor Charles Bent House and the Taos Inn. Further north in Taos The Bernard Beimer House. On the southwestern edge of the Taos Historic district is La Loma Plaza Historic District. East of the plaza on Kit Carson Road is the Kit Carson House.
North of Taos is the Turley Mill and Distillery Site and the Rio Grande Gorge Bridge. Just outside Taos in Ranchitos is the Martinez Hacienda, the home turned museum of the late Padre Antonio José Martínez. South of Taos is the Ranchos de Taos Plaza with the San Francisco de Asis Mission Church.
About 20 miles (32 km) northwest is the D. H. Lawrence Ranch (originally known as the Kiowa Ranch and now owned by the University of New Mexico), the home of the English novelist in the 1920s. It is believed that his ashes are buried there at the D. H. Lawrence Memorial. Another novelist who lived for a while in Taos was Alexander Trocchi.
Arts
There are three art museums in Taos: Harwood Museum of Art, Taos Art Museum and Millicent Rogers Museum that provide art from the Pueblo Native Americans, Taos Society of Artists and modern and contemporary artists of the Taos art colony. The town has more than 80 art galleries, and there are several houses of the Taos Society of Artists.[18][19]
There are several local venues for the performing arts in Taos. The Taos Center for the Arts (TCA) draws nationally renowned and local performers at the Taos Community Auditorium. They also present independent film series. Three chamber music groups perform at TCA: Taos School of Music, Taos Chamber Music Group, and Music from Angel Fire. The Harwood Museum of Art is site of other performances and lectures. The Town of Taos Convention Center offers a venue for other local performances.[20]
The Taos Talking Pictures Film Festival was a film festival held in the town from the mid-1990s to 2003. The festival's top prize was 5 acres (2.0 ha) of land.[21][22][23]
Recreation
The Taos Valley, Rio Grande and Taos mountains provide many opportunities for recreation, such as fly fishing, horseback riding, golfing, hot air ballooning, llama trekking, rafting, and mountain biking. The South Boundary trail, east of town, is consistently ranked the best mountain bike trail in New Mexico.[24]
There are also numerous hot springs along the Rio Grande and in the Taos Mountains. Among them a historical site called Stage Coach, which used to double as a brothel during the times of the Old West. Nearby, the Cumbres & Toltec Scenic Railroad provides a ride through the Toltec Gorge and Rocky Mountain passes in an authentic narrow-gauge steam railroad.[25]
In the winter, many people come to Taos to ski in the mountains. Nearby Wheeler Peak, at 13,161 feet (4,011 m), is the highest peak in New Mexico. The Taos area has four ski areas – Taos Ski Valley, Red River ski area, Sipapu (ski area) and Angel Fire ski area. Other winter activities include hot air ballooning, horseback riding, snow-shoeing, cross-country skiing, ski skating, ice skating, ice fishing and snowmobiling.[26]
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1940 | 965 | — | |
| 1950 | 1,815 | 88.1% | |
| 1960 | 2,163 | 19.2% | |
| 1970 | 2,475 | 14.4% | |
| 1980 | 3,369 | 36.1% | |
| 1990 | 4,065 | 20.7% | |
| 2000 | 4,700 | 15.6% | |
| 2010 | 5,716 | 21.6% | |
| 2019 (est.) | 5,929 | [3] | 3.7% |
| U.S. Decennial Census[27] | |||
As of the 2010 census Taos had a population of 5,716. The median age was 44. The ethnic and racial composition of the population was 40.1% non-Hispanic white, 0.7% African American, 1% Asian, 5.3% Native American, 0.3% non-Hispanics reporting some other race, 5.4% reporting two or more races and 51.9% Hispanic or Latino of any race.[28]
As of the census[29] of 2000, there were 4,700 people, 2,067 households, and 1,157 families residing in the town. The population density was 874.5 inhabitants per square mile (337.6/km2). There were 2,466 housing units at an average density of 458.8 per square mile (177.1/km2). The racial makeup of the town was 68.04% White, 0.53% African American, 4.11% Native American, 0.62% Asian, 0.11% Pacific Islander, 21.66% from other races, and 4.94% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 54.34% of the population.
There were 2,067 households, out of which 27.5% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 34.7% were married couples living together, 16.2% had a female householder with no husband present, and 44.0% were non-families. 37.3% of all households were made up of individuals, and 12.1% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.18 and the average family size was 2.87.
In the town, the population was spread out, with 23% under the age of 18, 6.6% from 18 to 24, 26.4% from 25 to 44, 27.8% from 45 to 64, and 16.2% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 41 years. For every 100 females, there were 85 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 81.3 males.
The median income for a household in the town was $25,016, and the median income for a family was $33,564. Males had a median income of $27,683 versus $23,326 for females. The per capita income for the town was $15,983. About 17.9% of families and 23.1% of the population were below the poverty line, including 26.8% of those under age 18 and 24.4% of those age 65 or over.
Geography and climate
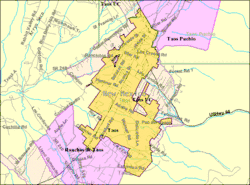
Taos is located at 36°23′38″N 105°34′36″W (36.393979, −105.576705).[30]
The town has a total area of 5.4 square miles (14 km2), all land.[31]
Taos is located near the Rio Pueblo de Taos, a tributary of the Rio Grande. Just to the west of Taos is the Rio Grande Gorge, cutting through the basalt flows of the Taos Plateau volcanic field and crossed by the Rio Grande Gorge Bridge, now a part of U.S. Route 64.[32]
The elevation of the town is 6,969 feet (2,124 m).[33] Just north of Taos is Wheeler Peak, at 13,161 feet (4,011 m), the highest point in New Mexico.[33] Taos has a warm-summer humid continental climate (Köppen Dfb), though it borders on a semi-arid climate (BSk) due to the low rainfall. The city is characterized by extreme diurnal variations of temperature. Even when summer days get extremely hot, nights cool off considerably.
| Climate data for Taos, New Mexico | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 66 (19) |
73 (23) |
77 (25) |
82 (28) |
93 (34) |
97 (36) |
99 (37) |
99 (37) |
94 (34) |
86 (30) |
83 (28) |
66 (19) |
99 (37) |
| Average high °F (°C) | 40.0 (4.4) |
45.4 (7.4) |
52.9 (11.6) |
62.8 (17.1) |
72.0 (22.2) |
82.1 (27.8) |
85.6 (29.8) |
83.3 (28.5) |
76.5 (24.7) |
65.9 (18.8) |
52.2 (11.2) |
41.8 (5.4) |
63.4 (17.4) |
| Average low °F (°C) | 9.7 (−12.4) |
16.3 (−8.7) |
22.9 (−5.1) |
29.6 (−1.3) |
37.6 (3.1) |
45.6 (7.6) |
51.0 (10.6) |
49.8 (9.9) |
42.6 (5.9) |
32.0 (0.0) |
20.9 (−6.2) |
12.2 (−11.0) |
30.8 (−0.7) |
| Record low °F (°C) | −27 (−33) |
−27 (−33) |
−11 (−24) |
0 (−18) |
13 (−11) |
28 (−2) |
36 (2) |
36 (2) |
22 (−6) |
0 (−18) |
−21 (−29) |
−27 (−33) |
−27 (−33) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 0.67 (17) |
0.61 (15) |
0.82 (21) |
0.90 (23) |
1.20 (30) |
0.90 (23) |
1.64 (42) |
1.85 (47) |
1.28 (33) |
1.08 (27) |
0.73 (19) |
0.63 (16) |
12.31 (313) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 7.2 (18) |
5.2 (13) |
4.9 (12) |
1.8 (4.6) |
0.4 (1.0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0.5 (1.3) |
2.8 (7.1) |
6.2 (16) |
29 (73) |
| Average precipitation days | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 10 | 10 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 69 |
| Source: Western Regional Climate Center[34] | |||||||||||||
Education
The town's public schools operated by Taos Municipal Schools include Arroyos del Norte Elementary School, Enos García Elementary (also Taos Elementary School), Ranchos Elementary School, Taos Middle School, Taos High School and Taos Cyber Magnet School.[35]
Charter schools include Anansi Charter School, Taos Academy (State Charter), Taos Municipal Charter School and Vista Grande High School.[36] Also in the area are additional alternative and private schools: Chrysalis Alternative School, Sped Discipline, Yaxche Private School, Taos Christian Academy, and San Francisco De Asis School.[37]
Dallas-based Southern Methodist University operates a 295-acre (119 ha) campus at Fort Burgwin in Taos.[38]
Albuquerque-based University of New Mexico (UNM) operates a community campus in Taos, with eight affiliated buildings in Taos, such as the UNM Harwood Museum of Art and Taos High School where some classes are held.[39][40]
The Earthship Academy (or Earthship Biotecture Academy) is offering training in Earthship design principles, construction methods and philosophy. Earthship is a particular type of sustainable architecture and design, based around solar power.[41]
Government


The town of Taos is incorporated under the mayor-council form of government. The town was incorporated on May 7, 1934.[42] The town seal is a logo of the town of Taos with the year of incorporation "1934" in the center, and on the outer edge, the words "Town of Taos, New Mexico".[43]
The elective officers of the town include the mayor, four members of the governing body forming the town council, and a municipal judge.[44] The town council is the board of finance of the town. The town manager and finance director serve as the nonvoting members to the board of finance.[45] Key positions within the town government are town manager, appointed by the major, Town Attorney, Town Clerk, Town Engineer and Chief of Police.[46]
As of 2019, the town officers are:
- Mayor: Daniel R. Barrone; term from March 2018 to March 2022[47]
- Town council members: Nathaniel Evans, Darian Fernandez, George "Fritz" Hahn, and Pascualito Maestas[48]
Taos is predominantly made up of Democrats; in 2008, approximately 74% of registered Taos County voters were Democrats, 13% were Republicans and about 13% identified with other parties or declined to affiliate with a party.[49]
Transportation
Public
The RTD Chile Line, operated by the North Central Regional Transit District (NCRTD), is Taos' only public transportation system. It provides fare-free in-town service as well as seasonal service up to the Taos Ski Valley. The transit system also provides paratransit service for citizens with special needs and ensures that all route buses are American Disability Act (ADA) equipped.[50]
The RTD Taos Express promotes local tourism and provides weekend express service, for a nominal fee, from the Taos Plaza to the New Mexico Rail Runner, Santa Fe Municipal Airport, and Santa Fe transit.[51]
The North Central Regional Transit District (NCRTD) has public transportation service into the Town from throughout Taos County and the Counties of Santa Fe, Rio Arriba and Los Alamos. The Taos region has service to Cerro, Penasco, Questa, Red River, the Rio Grande corridor and the University of New Mexico – Taos Klaur campus. At the Espanola Transit Center, passengers can connect to other regional routes, such as Espanola, Santa Fe, Los Alamos, and Northern Pueblos area.[52] In 2003 the Regional Transit District Act was enacted, which authorized the creation of Regional Transit Districts (RTD's) in the state of New Mexico; In September, 2004, the North Central Regional RTD was the first RTD to be certified by the New Mexico Transportation Commission.[53]
Airports
Taos Regional Airport (SKX) is under the direct supervision of the Town of Taos. The airport is located just a few miles north of the Town of Taos on U.S. Route 64 towards the Rio Grande Gorge Bridge.[54]
Other airports in New Mexico include the Santa Fe Municipal Airport and Albuquerque International Sunport.[55]
Media
Newspapers
El Crepusculo de la Libertad was the first Taos newspaper, which began in 1834 with the first printing press west of the Mississippi.[7] Its successor The Taos News, which also does business as El Crepusculo, is the primary printed newspaper in Taos.
- The Taos News, a weekly online and print publication.[56]
- Sangre de Cristo Chronicle serves Angel Fire, New Mexico, Red River, Cimarron, Eagle Nest, Taos, Las Vegas, Questa and Sipapu.[57]
- The Santa Fe New Mexican
- Albuquerque Journal North Edition.
Online
Television
There are two local cable television stations: Taos Local Television Public Access Channel 2[59] and Channel 22.[60] See also List of television stations in New Mexico.
Radio
Radio stations serving Taos include:[61]
(Several stations are located in the adjacent unincorporated suburbs of El Prado and Arroyo Seco.)
| Radio station | Frequency | FM/AM | Format |
|---|---|---|---|
| KCEI | 90.1 | FM | Variety.[62] |
| KNCE | 93.5 | FM | "True Taos Radio", variety |
| KKIT | 95.9 | FM | "The Mountain", pop, rock, classic rock.[62] |
| KKTC | 99.9 | FM | "True Country".[63] |
| KLNN | 103.7 | FM | Adult contemporary music.[64] |
| KRRT | 90.9 | FM | Top-40,[62] local transmitter for the University of New Mexico's KUNM. |
| KTAO | 101.9 | FM | Solar radio station with an adult album alternative music format.[62] |
| KVOT | 1340 | AM | Religious (Christian) music.[65] |
| KXMT | 99.1 | FM | Radio Exitos is the local 24-hour Spanish radio station serving Taos, northern New Mexico and Southern Colorado.[66] |
| KYBR | 92.9 | FM | Spanish.[62] Located in Española, but serves Santa Fe and Taos as well.[67] |
In popular culture

- Legendary country music artist Waylon Jennings sang a song titled "Taos, New Mexico" on his 1967 album Love of the Common People.
- On September 18, 1991, the PBS TV series Reading Rainbow shot its 73rd episode "The Legend of the Indian Paintbrush" here. The title was based on a book by Tomie dePaola and was narrated by Harold Littlebird (born 1951). Santa Fe's Dominic C. Arquero introduced himself at this program's beginning.[68][69]
- The Rio Grande Gorge Bridge is featured in the 2009 film Terminator: Salvation,[70] the 1994 crime-drama film Natural Born Killers,[71] and in the 2007 comedy Wild Hogs.[72]
- The film Garbage Warrior documents architect Mike Reynolds who builds Earthships in and around Taos.[73]
- Two characters in television series were portrayed as having originally been law enforcement officers in Taos. Deputy Marshal Sam McCloud in McCloud (played by Dennis Weaver),[74] and Sheriff Victor Galindez as Gunnery Sgt. in JAG (played by Randy Vasquez).
- Taos has been featured in The Nine Lives of Elfego Baca (1960) and And Now Miguel (1966).[75]
- In the DC Comics animated series, Young Justice, Taos is often featured as the location of a STAR Labs base of operations, specializing in Zeta Beam research and "Meta-Human" housing for minors.
- The Volkswagen Taos is named after the town.[76][77]
Taos Hum
An ongoing low-frequency noise, audible only to some, is thought to originate somewhere near this town and is consequently sometimes known as the Taos Hum. Those who have heard the Hum usually hear it west of Taos near Tres Orejas. The Taos Hum was featured on the TV show Unsolved Mysteries,[78] and it was also briefly mentioned in an episode of The X-Files.[79] It was the basis for the TV series Criminal Minds episode "Mixed Signals".
The Mesa
A rough, sage-strewn, high desert area west of Taos, that encompasses the area known as Two Peaks or the Carson Estates. The Mesa is a free-spirited community where people live off the grid, often without plumbing and electricity. It is considered a mecca of sorts for those seeking independent, alternative and often anti-government lifestyles. The Mesa was the subject of the documentary Off the Grid: Life on the Mesa.
Sister cities
Taos has one sister city, as designated by Sister Cities International:
Notable people



Artists and actors
- Lynn Anderson, country/pop singer
- Abbie Conant, trombonist and professor
- Oscar E. Berninghaus, artist
- Emil Bisttram, artist
- Larry Bell, sculptor
- Ernest L. Blumenschein, founding member, Taos Society of Artists
- Dorothy Brett, artist and personality
- Agnes Chavez, artist
- E. Irving Couse, artist
- Andrew Dasburg, artist
- Ronald Davis, artist
- W. Herbert Dunton, artist
- Nicolai Fechin, artist
- R. C. Gorman, artist
- E. Martin Hennings, artist
- William Victor Higgins, artist
- Dennis Hopper, actor, director, artist
- Gene Kloss, artist
- Agnes Martin, artist
- Robert Mirabal, Native American flute player and maker from Taos Pueblo
- Bror Julius Olsson Nordfeldt, artist
- Bert Geer Phillips, artist
- Kenneth Price, ceramicist
- Christian Ristow, artist
- Julia Roberts, actress
- Dean Stockwell, artist and actor
- Joseph Henry Sharp, artist
- Walter Ufer, artist
- Kristen Vigard, actress and singer
- Harold Joe Waldrum, artist
- Michael Walker, custom knife maker and sculptor
- Julius Rolshoven, artist
Sportspeople
- Ross Anderson, skier[80]
- Kit Carson, frontiersman
- Dave Hahn, mountaineer
- Danelle Umstead, Paralympic skier
Professors and medical professionals
- Fred Wendorf, Henderson-Morrison Professor of Anthropology at Southern Methodist University
- Thomas "Doc" Martin, physician
Authors, poets, and teachers
- Julia Cameron, author of The Artist's Way[81]
- Judson Crews, poet and publisher
- James Doss, author
- Natalie Goldberg, writer
- Margaret Catherine Alice Hyson, missionary and teacher in Ranchos de Taos, New Mexico
- Brandie Knight, author, film producer
- D. H. Lawrence, author
- Anne MacNaughton, poet and cofounder of Taos Poetry Circus
- John Nichols, author of The Milagro Beanfield War
- Elizabeth Shepley Sergeant, journalist and writer
Businesspeople and architects
- Marcelino Baca, 19th-century fur trader[82]
- Mabel Dodge Luhan, patron of the arts
- Susan Powter, health and fitness entrepreneur
- Mike Reynolds, Earthship architect
- Millicent Rogers, socialite, fashion icon, and art collector
Politicians
- Daniel R. Barrone, mayor of Taos and member of the New Mexico House of Representatives
- Charles Bent, first Territorial Governor of New Mexico
- Gary Johnson, former two-term governor of New Mexico[83]
- John Márquez, politician in Richmond, California
- Kristina Ortez, politician
- Donald Rumsfeld, former Secretary of Defense of the United States (part-time resident)[84]
- Rebecca Vigil-Giron, 20th and 22nd New Mexico Secretary of State
Religious figures
- Antonio José Martínez, priest
Gallery
 Mabel Dodge Luhan House, a National Historic Landmark
Mabel Dodge Luhan House, a National Historic Landmark View of Taos from mountain trail
View of Taos from mountain trail Downtown Paseo Del Pueblo Norte in Taos
Downtown Paseo Del Pueblo Norte in Taos Spanish Revival-style First Baptist Church
Spanish Revival-style First Baptist Church Lobby of the La Fonda hotel
Lobby of the La Fonda hotel San Francisco de Asis Church at Ranchos de Taos
San Francisco de Asis Church at Ranchos de Taos
References
- "Taos History and Timeline". Taos County Historical Society. Retrieved November 27, 2019.
- "2019 U.S. Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved July 27, 2020.
- "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". United States Census Bureau. May 24, 2020. Retrieved May 27, 2020.
- "About Taos Pueblo FAQs". Taos Pueblo. Archived from the original on October 25, 2016. Retrieved October 31, 2016.
- "Taos Pueblo". UNESCO World Heritage Centre. Archived from the original on June 20, 2016. Retrieved October 31, 2016.
- 2007, Mapa Historico de Taos, Taos Kiwanis Club
- "Taos Timeline". Taos County Historical Society. Retrieved June 3, 2011.
- "Koshare Indian Museum: Taos, New Mexico". Retrieved July 7, 2014.
- Taos Downtown Historic District. National Park Service. Retrieved 2014-07-28.
- Taos History. Archived 2015-01-21 at the Wayback Machine Taos Chamber of Commerce. Retrieved 2014-07-28.
- Zora O'Neill (2006). Santa Fe, Taos, & Albuquerque. Moon Handbooks. p. 95. ISBN 978-1-56691-879-4. Retrieved July 24, 2009.
- Crane, L (1972). Desert drums: the Pueblo Indians of New Mexico, 1540–1928. Rio Grande Press.
- Bleiler, 75.
- Whaley, B; Stiny, A. ""Reconsidering Art in Taos; Bert Phillips" in Taos Horse Fly". Taos Daily. Archived from the original on March 10, 2012. Retrieved February 17, 2009.
- "Taos County, New Mexico". National Register of Historic Places. U.S. Dept. of Interior, the National Park Service, and the National Register of Historic Places. Retrieved June 4, 2011.
- "¡QUE VIVAN LAS FIESTAS DE TAOS! | Fiestas de Taos | Taos, New Mexico". fiestasdetaos.com.
- "Taos Studio of William Osborne and Abbie Conant". www.osborne-conant.org. Retrieved September 29, 2020.
- "Art Today". Taos Vacation Guide. Taos Webb Community. Retrieved June 4, 2011.
- "Art History". Taos Vacation Guide. Taos Webb Community. Retrieved June 4, 2011.
- "Performing Arts". Taos Vacation Guide. Taos Webb Community. Retrieved June 4, 2011.
- Domrzalski, D (December 7, 2003). "Taos Talking Pictures drops curtain". New Mexico Business Weekly. Retrieved June 3, 2011.
- Domrzalski, D (March 14, 2004). "Three festivals rise out of Taos Talking Pictures' ashes". New Mexico Business Weekly. Retrieved June 3, 2011.
- "Film Festival Awards". Taos Land and Film Co. Retrieved June 3, 2011.
- "Mountain Bike Trails near New Mexico". MTB Project. Retrieved April 9, 2016.
- "Summer". Taos Vacation Guide, Recreation. Taos Webb Community. Retrieved June 4, 2011.
- "Winter". Taos Vacation Guide, Recreation. Taos Webb Community. Retrieved June 4, 2011.
- "Census of Population and Housing". Census.gov. Retrieved June 4, 2015.
- 2010 general profile of population and housing characteristics for Taos from the U.S. Census
- "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 31, 2008.
- "US Gazetteer files: 2010, 2000, and 1990". United States Census Bureau. February 12, 2011. Retrieved April 23, 2011.
- "Taos Town, New Mexico Complete Analysis". citymelt.com. Retrieved June 4, 2011.
- Zora O'Neill. "Geography and Geology". >Home>Santa Fe, Taos & Albuquerque from Moon Santa Fe, Taos & Albuquerque, 2nd edition. Avalon Travel Guides. Retrieved June 4, 2011.
- "Frequently Asked Questions". Taos Vacation Guide. Taos Webb Community. Retrieved June 4, 2011.
- "Climate Summary". WRCC. Retrieved September 8, 2011.
- "Taos Municipal Schools". Taos Municipal Schools. Retrieved June 4, 2011.
- "New Mexico Charter Schools" (PDF). New Mexico Public Education Department. Retrieved June 4, 2011.
- "All Taos elementary, middle and high schools (search criteria)". Find a School. GreatSchools, Inc. Retrieved June 4, 2011.
- "Southern Methodist University (SMU)". Southern Methodist University, Dallas, Texas. Retrieved June 4, 2011.
- "University of New Mexico – Taos". University of New Mexico. Retrieved June 4, 2011.
- "Campus map". University of New Mexico – Taos. University of New Mexico. Retrieved June 4, 2011.
- "Earthship Biotecture Academy".
- "Chapter 3.12 Form of Government". Sterling Codifiers, Inc. Retrieved June 4, 2011.
- "Chapter 3.16 Town Seal". Sterling Codifiers, Inc. Retrieved June 4, 2011.
- "Chapter 3.20.010 Elective Officers of Town (Ord. 98-2 § 1, 1998: prior code § 2-2)". Sterling Codifiers, Inc. Retrieved June 4, 2011.
- "Chapter 3.24 Board of Finace". Sterling Codifiers, Inc. Retrieved June 4, 2011.
- "Town of Taos". Sterling Codifiers, Inc. pp. 3.36, 3.40, 3.44, 3.52, 3.56. Retrieved June 4, 2011.
- "Daniel R. Barrone, Mayor". Town of Taos. Retrieved December 15, 2019.
- "Town Council". Town of Taos. Retrieved December 15, 2019.
- Chambers, P (September 14, 2008). "Taos County Republicans open local campaign headquarters". The Taos News. Retrieved June 4, 2011.
- "Transportation Services Chile Line". Town of Taos. Retrieved June 4, 2011.
- "Taos Express". Town of Taos. Retrieved June 4, 2011.
- "North Central Regional Transit District". NCRTD. Retrieved June 7, 2019.
- "North Central Regional Transit District, Fast Facts". NCRTD. Retrieved June 7, 2019.
- "Taos Regional Airport". Town of Taos, Taos Regional Airport.
- "New Mexico Airports". Red Cirrus, LLC. 2011. Retrieved June 4, 2011.
- "About Taos News". The Taos News. Archived from the original on August 15, 2009. Retrieved June 4, 2011.
- "Sangre de Cristo Chronicle". El Crespusculo/Sangre de Cristo Chronicle. 2011. Retrieved June 4, 2011.
- "Taos News (Topix online)". Topix, Inc. 2011.
- "Taos Local Television Public Access Channel 2". TLTPA. Retrieved June 4, 2011.
- "Taos Local Television Public Access Channel 22". Comcast. Retrieved June 4, 2011.
- "Radio Stations in Taos, New Mexico". Radio-Locator.com. Retrieved May 19, 2012.
- "Radio Stations in Taos, NM". Ontheradio.net. Retrieved June 4, 2011.
- "KKTC". RadioinTaos.com. Retrieved June 4, 2011.
- "Luna 103.7 KLNN". KLNN. Retrieved June 4, 2011.
- "KVOT". RadioinTaos.com. Retrieved June 4, 2011.
- "KXMT". Ontheradio.net. Retrieved June 4, 2011.
- KYBR station website
- "The Legend of the Indian Paintbrush". Reading Rainbow. Alabama Public Television (PBS). Retrieved June 4, 2011.
- "The Legend of the Indian Paintbrush". Myths and Legends, PBS Teachers. PBS. Retrieved June 4, 2011.
- "Terminator Salvation: Set Locations Revisited". TheTerminatorFans.com. January 28, 2010. Retrieved June 3, 2011.
- "Rio Grande Gorge Bridge". New York Times. New York Times, content from Frommer's Santa Fe, Taos & Albuquerque, 12th Edition. 2011. Retrieved June 4, 2011.
- "Goofs for Wild Hogs (2007)". IMDb. Retrieved June 4, 2011.
- "Garbage Warrior". HESO Magazine. October 7, 2009.
- McLellan, Dennis. "From the Archives: Dennis Weaver, 81; Star of 'Gunsmoke,' 'McCloud' Also Was Environmental Activist". latimes.com. Retrieved January 31, 2017.
- Maddrey, Joseph (2016). The Quick, the Dead and the Revived: The Many Lives of the Western Film. McFarland. Page 182. ISBN 9781476625492.
- Szymkowski, Sean. "Volkswagen's new compact SUV will wear 'Taos' name". Roadshow. Retrieved October 15, 2020.
- "Volkswagen Taos will be the name of VW's next crossover". Autoblog. Retrieved October 15, 2020.
- "Taos Hum". The Unexplained. Unsolved-Mysteries.com. Retrieved June 3, 2011.
- "X-Files script 602". Inside the X. DrWeesh. Retrieved June 3, 2011.
- "Ross Anderson profile". Ross Anderson. Retrieved June 3, 2011.
- "About Julia Cameron | Julia Cameron Live". juliacameronlive.com.
- Hafen, LeRoy R. (1997). Fur trappers and traders of the far Southwest : twenty biographical sketches. Utah State University Press. ISBN 0874212359. OCLC 37400891.
- "Gary Johnson: 'Ron Paul and Myself' Can 'Grow the Base'". ABC News. February 10, 2011.
- Baker, Peter (2013). Days of fire: Bush and Cheney in the White House. Doubleday. p. 233. ISBN 978-0-385-52518-3.
Further reading
- Bleiler, Lyn; Society of the Muse of the Southwest (2011). Taos. Images of America. Charleston: Arcadia Publishing. ISBN 978-0-7385-7959-7.
- Crane, Leo (2010) [1928]. Desert Drums: the Pueblo Indians of New Mexico, 1540–1928 (Reprint ed.). Whitefish, MT: Kessinger Publishing. ISBN 978-1163176870.
- Herold, Laurance C.; Luebben, Ralph A. (1968). Papers on Taos Archaeology. Taos, NM: Fort Burgwin Research Center. OCLC 55484.
- John, Elizabeth Ann Harper (1996) [1975]. Storms Brewed in Other Men's Worlds: The Confrontation of Indians, Spanish, and French in the Southwest, 1540-1795 (2nd ed.). University of Oklahoma Press. ISBN 978-0806128696.
- O'Neill, Zora (2006). Santa Fe, Taos, & Albuquerque. Moon Handbooks. Avalon Travel Publishing. ISBN 978-1-56691-879-4.
External links
 Media related to Taos, New Mexico at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Taos, New Mexico at Wikimedia Commons Taos, New Mexico travel guide from Wikivoyage
Taos, New Mexico travel guide from Wikivoyage- Official website
- The Official Taos Vacation Guide, published by the Town of Taos
- Taos County Chamber of Commerce
- Taos Public Library