Threitol
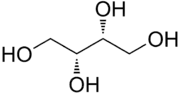
Threitol is a four-carbon sugar alcohol with the molecular formula C4H10O4. It is primarily used as an intermediate in the chemical synthesis of other compounds. It is the diastereomer of erythritol.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name
(2R,3R)-Butane-1,2,3,4-tetrol | |
| Other names
(2R,3R)-Butane-1,2,3,4-tetraol (not recommended) | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.150.149 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H10O4 | |
| Molar mass | 122.12 |
| Appearance | Solid |
| Melting point | 88 to 90 °C (190 to 194 °F; 361 to 363 K) |
| Hazards | |
| R-phrases (outdated) | R36/37/38 |
| S-phrases (outdated) | S26 S36 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
In living things, threitol is found in the edible fungus Armillaria mellea.[2] It serves as a cryoprotectant (antifreeze agent) in the Alaskan beetle Upis ceramboides.[3]
See also
- Antifreeze protein
- Dithiothreitol, a thiol derivative of threitol
References
- Threitol at Sigma-Alrich
- Elks, J.; Ganellin, C. R. (1990). Dictionary of Drugs. doi:10.1007/978-1-4757-2085-3. ISBN 978-1-4757-2087-7.
- Walters, K. R. Jr; Pan, Q.; Serianni, A. S.; Duman, J. G. (2009). "Cryoprotectant biosynthesis and the selective accumulation of threitol in the freeze-tolerant Alaskan beetle, Upis ceramboides". Journal of Biological Chemistry. 284 (25): 16822–16831. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.013870. PMC 2719318. PMID 19403530.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.