Dimethylethanolamine
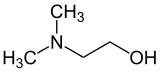
Dimethylethanolamine (DMAE or DMEA) is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2NCH2CH2OH. It is bifunctional, containing both a tertiary amine and primary alcohol functional groups. It is a colorless viscous liquid. It is used in skin care products. It is prepared by the ethoxylation of dimethylamine.[2]
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-(Dimethylamino)ethanol | |
| Other names
deanol, dimethylaminoethanol, dimethylaminoethanol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| Abbreviations | DMAE, DMEA |
| 1209235 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.221 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Deanol |
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2051 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H11NO | |
| Molar mass | 89.138 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colourless liquid |
| Odor | Fishy, ammoniacal |
| Density | 890 mg mL−1 |
| Melting point | −59.00 °C; −74.20 °F; 214.15 K |
| Boiling point | 134.1 °C; 273.3 °F; 407.2 K |
| log P | −0.25 |
| Vapor pressure | 816 Pa (at 20 °C) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 9.23 (at 20 °C)[1] |
| Basicity (pKb) | 4.77 (at 20 °C) |
Refractive index (nD) |
1.4294 |
| Pharmacology | |
| N06BX04 (WHO) | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  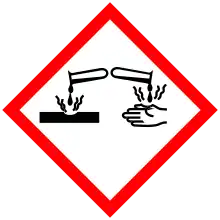  |
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H226, H302, H312, H314, H332 | |
| P280, P305+351+338, P310 | |
| Flash point | 39 °C (102 °F; 312 K) |
| Explosive limits | 1.4–12.2% |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) |
|
| Related compounds | |
Related alkanols |
|
Related compounds |
Diethylhydroxylamine |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Industrial uses
It is a precursor to other chemicals, such as the nitrogen mustard 2-dimethylaminoethyl chloride.[3] The acrylate ester is used as a flocculating agent.
Related compounds are used in gas purification, e.g. removal of hydrogen sulfide from sour gas streams.
Nutraceutical uses
The bitartrate salt of DMAE, i.e. 2-dimethylaminoethanol (+)-bitartrate, is sold as a dietary supplement.[4] It is a white powder providing 37% DMAE.[5]
References
- Littel, RJ; Bos, M; Knoop, GJ (1990). "Dissociation constants of some alkanolamines at 293, 303, 318, and 333 K" (PDF). Journal of Chemical and Engineering Data. 35 (3): 276–77. doi:10.1021/je00061a014. INIST:19352048.
- Matthias Frauenkron, Johann-Peter Melder, Günther Ruider, Roland Rossbacher, Hartmut Höke (2002). "Ethanolamines and Propanolamines". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a10_001. ISBN 978-3527306732.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
- Ashford's Dictionary of Industrial Chemicals, 3rd edition, 2011, ISBN 978-0-9522674-3-0, p. 3294.
- Karen E. Haneke & Scott Masten, 2002, "Dimethylethanolamine (DMAE) [108-01-0] and Selected Salts and Esters: Review of Toxicological Literature (Update)," Report on National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences Contract No. N01-ES-65402, November 2002, from Contractee Integrated Laboratory Systems, Research Triangle Park, North Carolina 27709, see , accessed 30 April 2015.
- Sigma Aldrich: Safety Data Sheet: 2-Dimethylaminoethanol (+)-bitartrate
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.