1980 Arkansas gubernatorial election
The Arkansas gubernatorial election of 1980 was only that state's third election since Reconstruction when a Republican candidate won the governorship.
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
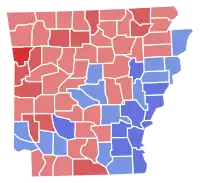 County Results Clinton: 50–60% 60–70% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Elections in Arkansas |
|---|
 |
One-term Democratic Governor of Arkansas Bill Clinton was narrowly defeated by Republican Frank D. White, which made him, as he joked, "the youngest ex-governor in the nation." Clinton ran again two years later and regained the governorship, continuing to serve until he was elected to the presidency in 1992. Both the Democratic and Republican primaries were held on May 27.
Democratic primary
Candidates
- Bill Clinton, incumbent governor
- Monroe Schwarzlose, candidate for governor in 1978 and Republican candidate for the Arkansas House of Representatives in 1974
Results
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Bill Clinton (incumbent) | 306,736 | 68.87 | |
| Democratic | Monroe Schwarzlose | 138,670 | 31.13 | |
| Total votes | 445,395 | 100.00 | ||
Republican primary
Candidates
- Marshall Chrisman, former state representative
- Frank D. White, former head of the Arkansas Industrial Development Commission
Results
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Frank D. White | 5,867 | 71.75 | |
| Republican | Marshall Chrisman | 2,310 | 28.25 | |
| Total votes | 8,177 | 100.00 | ||
Campaign
Schwarzlose's unexpected strong challenge in primaries and his 31 percent of the primary vote foreshadowed that Clinton could be in trouble for the upcoming general election.[2]
Clinton's increase in the cost of automobile registration tags was also unpopular. He was also hurt by President Jimmy Carter's decision to send thousands of Cuban refugees, some unruly, to a detention camp at Fort Chaffee, outside Fort Smith in Sebastian County in western Arkansas.[2][3] (See Mariel boatlift.)
1980 general election was marked by decisive Republican victories—the GOP won the White House, a majority in United States Senate and 34 seats in the United States House of Representatives. Clinton's narrow loss was viewed as part of Reagan's coattails.
Result
Frank White narrowly won the election.[1](p48)[2]
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ±% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Frank D. White | 435,684 | 51.93% | +15.29% | |
| Democratic | Bill Clinton (incumbent) | 403,241 | 48.07% | -15.29% | |
| Total votes | 838,925 | 100.00% | N/A | ||
| Republican gain from Democratic | |||||
Effect
Max Brantley said after Clinton lost the election in 1980: "The guy was like a death in the family. He was really destroyed after that election".[4] Rudy Moore also added: "He never blamed anybody else. He accepted the responsibility. He didn't whine about it. In fact, it was within days, we were trying to figure out what we could to do to improve his political life after that"[4]
After Clinton was defeated, an opportunity arose in which Clinton would lead the Democratic National Committee through the 1980s to battle Ronald Reagan and the Republicans, instead of running for another term for Governor of Arkansas. When Clinton campaigned for election in 1982 against White, he explained that he had learned the importance of adaptability and compromise from his defeat in two years prior.[5]
During the campaign of 1982, Clinton promised to make major strides in education, including a large investment of public money, but he avoided saying he would raise taxes.[6]
There was some skepticism on whether Clinton's record on the economy in Arkansas would translate into Democrats losing in upcoming elections. The regular legislative session in Arkansas of 1985 was devoted to economic development. The legislature approved almost all of Clinton's program, which included changes in banking laws, start-up money for technology-oriented businesses, and large tax incentives for Arkansas industries that expanded their production and jobs. Arkansas was one of the best states in new job creation in the next six years, but most of the jobs did not pay high wages, and it remained one of the worst states in average income.[6] Democrats wanted a counter to Reaganomics, but feared Clinton's plan would lead to more unhappy blue collar workers bolting to the Republicans as his plan offered no real solution to stagnant wages.
References
- "1980 Arkansas Elections" (PDF). Arkansas Secretary of State. January 1982. Retrieved October 29, 2016.
- "Frank Durward White (1933–2003)". Encyclopedia of Arkansas. Retrieved 2016-02-24.
- "Bill Clinton (1946–)". Encyclopedia of Arkansas. Retrieved 2016-02-24.
- Takiff, Michael. A Complicated Man : The Life of Bill Clinton as Told by Those Who Know Him. New Haven, US: Yale University Press, 2010. ProQuest ebrary. Web. 19 April 2017.
- Clinton House Museum. CHM, n.d. Web. 17 Apr. 2017.
- Bill Clinton (1946–)-Encyclopedia of Arkansas. Encyclopedia of Arkansas, n.d. Web. Apr. 17, 2017.

.jpg.webp)

