Bourg-et-Comin
Bourg-et-Comin is a commune in the department of Aisne in Hauts-de-France in northern France.
Bourg-et-Comin | |
|---|---|
_%C3%89glise.JPG.webp) The 12th century Church of St. Martin , Bourg-et-Comin | |
Location of Bourg-et-Comin 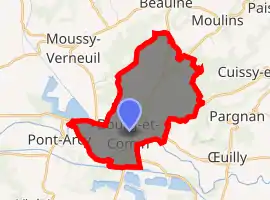
| |
 Bourg-et-Comin  Bourg-et-Comin | |
| Coordinates: 49°23′51″N 3°39′18″E | |
| Country | France |
| Region | Hauts-de-France |
| Department | Aisne |
| Arrondissement | Laon |
| Canton | Guignicourt |
| Intercommunality | Chemin des Dames |
| Government | |
| • Mayor (2008–2014) | Sylvie d'Almeida |
| Area 1 | 5.12 km2 (1.98 sq mi) |
| Population (2017-01-01)[1] | 822 |
| • Density | 160/km2 (420/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| INSEE/Postal code | 02106 /02160 |
| Elevation | 44–170 m (144–558 ft) (avg. 63 m or 207 ft) |
| 1 French Land Register data, which excludes lakes, ponds, glaciers > 1 km2 (0.386 sq mi or 247 acres) and river estuaries. | |
History
The area around Bourg et Comin has been occupied since Neolithic times with settlements along the River Aisne. The village grew as a fortified place on the road between Laon and Fismes .
The Church of St. Martin is a Romanesque church of the 12th century. It has been listed as an historical monument since 1919 . The tower is protected by a 13th century two-sided gable roof.
The whole of the surrounding area was part of a World War I battlefield and there are many military cemeteries in the area. The German army held the high ground to the north known as the Chemin des Dames and resisted two attacks by the French army to dislodge them in 1914 and 1917; and then used the high ground to launch a surprise offensive in 1918.
It was in this area that the first trenches were dug in the war and static trench warfare began.[2][3]
Geography
The nearby River Aisne drains into the basin of the river Seine and therefore Bourg-et-Comin is hydrologically part of the Paris Basin. It has an Oceanic climate in common with the rest of northern France. The low lying alluvial Aisne valley makes the landscape rich in lakes. The land rises to chalk hills in the north.
The village is located on the Aisne river's north bank. Its location is an historically important bridging point across the Aisne.
It also sits at the confluence of two nineteenth century canals. The Canal latéral à l'Aisne was completed in 1841 and carries traffic from the Ardenne into the Paris Basin. The Canal de l'Oise à l'Aisne was completed in 1890 as a summit crossing short link joining up with the Canal latéral à l'Oise 30 miles to the north.
.A railway was constructed along the Aisne valley in the 1870s. which gave the village a station and connected it with Paris.[4]
The town is positioned near the border of the historical territory of Picardy to the north west and the former administrative region Champagne-Ardenne to the south east which mostly corresponds with the historic province of Champagne.
The town of Bourg-et-Comin is a member of the Chemin des Dames community of towns , established in 1995 for inter-municipal cooperation (EPCI) with its own tax system.
The modern French A26 autoroute motorway is 30 Km to the east
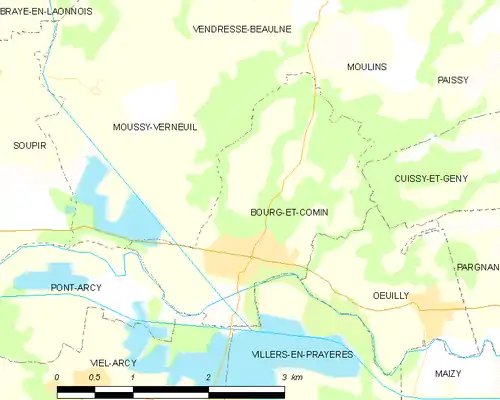
Population
Residents are known as Bourcominois. and in 2017 there were 822 inhabitants.
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1793 | 239 | — |
| 1856 | 367 | +53.6% |
| 1901 | 400 | +9.0% |
| 1926 | 489 | +22.2% |
| 1936 | 504 | +3.1% |
| 1946 | 348 | −31.0% |
| 1954 | 478 | +37.4% |
| 1962 | 522 | +9.2% |
| 1968 | 515 | −1.3% |
| 1975 | 563 | +9.3% |
| 1982 | 536 | −4.8% |
| 1990 | 535 | −0.2% |
| 1999 | 678 | +26.7% |
| 2008 | 741 | +9.3% |
Photo gallery
_Mairie.JPG.webp) Town Hall, Mairie
Town Hall, Mairie_%C3%89glise%252C_int%C3%A9rieur.JPG.webp) Church of St. Martin, interior
Church of St. Martin, interior The Oise and Aisne canal at Bourg-et-Comin
The Oise and Aisne canal at Bourg-et-Comin_Canal_de_l'Oise_%C3%A0_l'Aisne.JPG.webp) Bourg-et-Comin, Canal de l'Oise à l'Aisne
Bourg-et-Comin, Canal de l'Oise à l'Aisne Bourg-et-Comin railway station c 1900.
Bourg-et-Comin railway station c 1900.
See also
References
- "Populations légales 2017". INSEE. Retrieved 6 January 2020.
- Kendall, Paul (1 May 2012). Aisne 1914: The Dawn of Trench Warfare. The History Press. ISBN 978-0750959940.
- Baker, Chris. "The Battle of the Aisne, 1914 – The Long, Long Trail". Retrieved 2020-06-20.
- Clout, HD (1977). "Themes in the Historical Geography of France (extract)". www.mtholyoke.edu. Retrieved 2020-06-20.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Bourg-et-Comin. |