CYP24A1
Cytochrome P450 family 24 subfamily A member 1 (abbreviated CYP24A1) is a member of the cytochrome P450 superfamily of enzymes encoded by the CYP24A1 gene. It is a mitochondrial monooxygenase which catalyzes reactions including 24-hydroxylation of calcitriol (1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3).[5] It has also been identified as vitamin D3 24-hydroxylase.(EC 1.14.15.16)
Function
CYP24A1 is an enzyme expressed in the mitochondrion of humans and other species. It catalyzes hydroxylation reactions which lead to the degradation of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3, the physiologically active form of vitamin D. Hydroxylation of the side chain produces calcitroic acid and other metabolites which are excreted in bile.[5][6]
CYP24A1 was identified in the early 1970s and was first thought to be involved in vitamin D metabolism as the renal 25-hydroxyvitamin D3-24-hydroxylase, modifying calcifediol (25-hydroxyvitamin D) to produce 24,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol (24,25-dihydroxyvitamin D). Subsequent studies using recombinant CYP24A1 showed that it could also catalyze multiple other hydroxylation reactions at the side chain carbons known as C-24 and C-23 in both 25-OH-D3 and the active hormonal form, 1,25-(OH)2D3. It is now considered responsible for the entire five-step, 24-oxidation pathway from 1,25-(OH)2D3 producing calcitroic acid.[6]
CYP24A1 also is able to catalyse another pathway which starts with 23-hydroxylation of 1,25-(OH)2D3 and culminates in 1,25-(OH)2D3-26,23-lactone.[6]
The side chains of the ergocalciferol (vitamin D2) derivatives, 25-OH-D2 and 1,25-(OH)2D2, are also hydroxylated by CYP24A1.[6]
The structure of CYP24A1 is highly conserved between different species although the balance of functions can differ.[6] Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene.
This enzyme plays an important role in calcium homeostasis and the vitamin D endocrine system through its regulation of the level of vitamin D3.
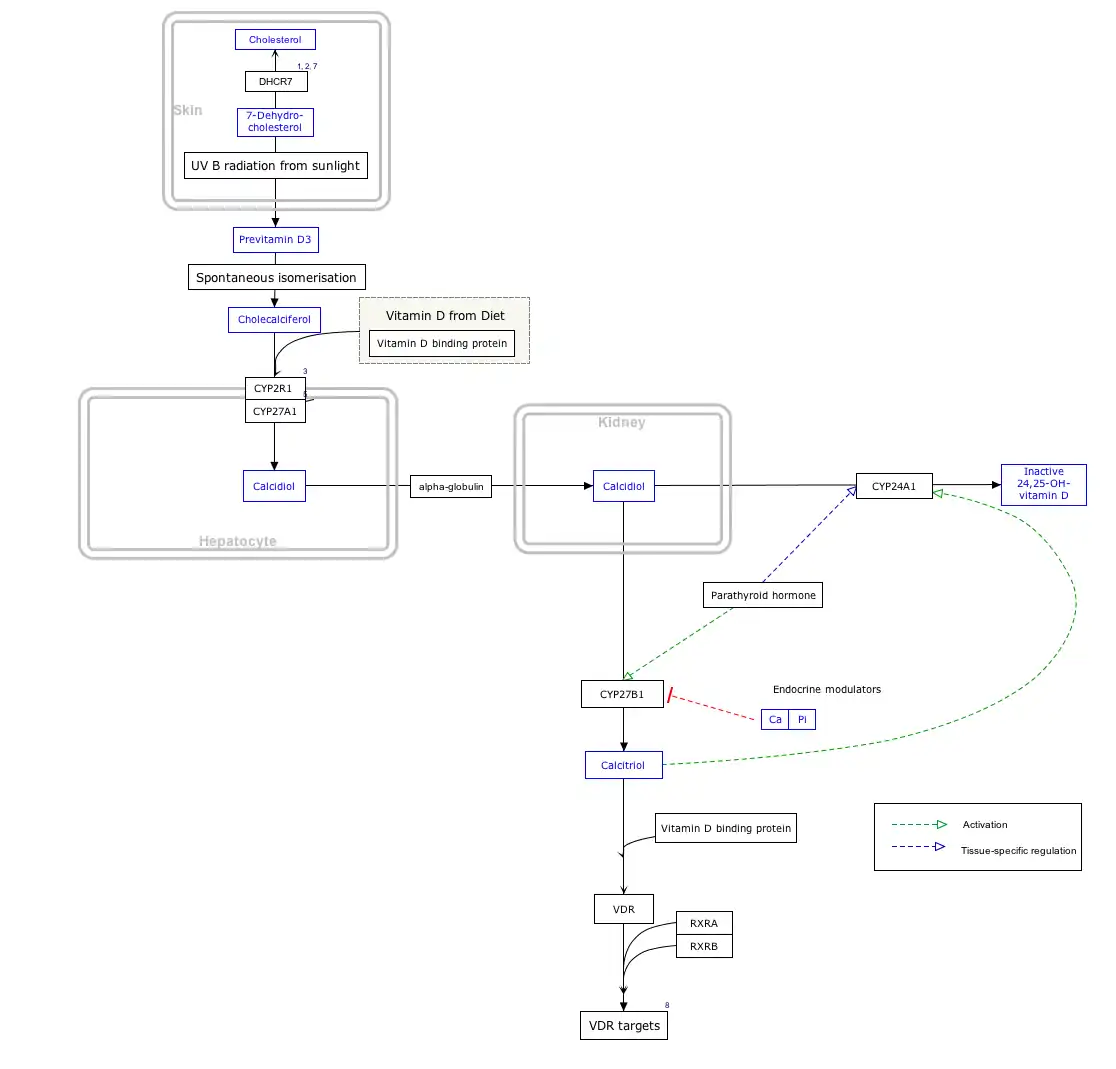
Interactive pathway map
Click on genes, proteins and metabolites below to link to respective articles. [§ 1]
- The interactive pathway map can be edited at WikiPathways: "VitaminDSynthesis_WP1531".
Regulation
CYP24A1 is expressed in tissues which are considered targets for vitamin D, including kidney, intestine and bone. Transcription of the CYP24A1 gene is markedly inducible by 1,25-(OH)2D3 binding to the vitamin D receptor.[6] The gene has a strong, positive vitamin D response element in the promoter. Through regulation of CYP24A1 expression, a negative feedback control system is created to limit the effects of 1,25-(OH)2D3.[6]
PTH and FGF23 also regulate CYP24A1 gene expression.[6] Additionally, it is translationally regulated via IRES within the 5'UTR, which is responsive to an inflammatory environment.[7]
Clinical relevance
Abnormal functioning CYP24A1 is thought to be one of the causes of severe infantile hypercalcemia.[8] However, increasingly patients are also being diagnosed in adulthood, often when they present with hypercalcaemia.[9] Patients with mutations of the CYP24A1 gene have elevated serum calcium concentrations, elevated serum 1,25-(OH)2D, suppressed PTH concentrations, hypercalciuria, nephrocalcinosis, nephrolithiasis, and sometimes reduced bone density. Variations in the gene may also be found in people with renal stones.[10]
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000019186 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000038567 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Entrez Gene: CYP24A1 cytochrome P450, family 24, subfamily A, polypeptide 1".
- Jones G, Prosser DE, Kaufmann M (January 2014). "Cytochrome P450-mediated metabolism of vitamin D". Journal of Lipid Research. 55 (1): 13–31. doi:10.1194/jlr.R031534. PMC 3927478. PMID 23564710.
- Rübsamen D, Kunze MM, Buderus V, Brauß TF, Bajer MM, Brüne B, Schmid T (2014-01-01). "Inflammatory conditions induce IRES-dependent translation of cyp24a1". PLOS ONE. 9 (1): e85314. Bibcode:2014PLoSO...985314R. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0085314. PMC 3885688. PMID 24416388.
- Dauber A, Nguyen TT, Sochett E, Cole DE, Horst R, Abrams SA, Carpenter TO, Hirschhorn JN (February 2012). "Genetic defect in CYP24A1, the vitamin D 24-hydroxylase gene, in a patient with severe infantile hypercalcemia". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 97 (2): E268-74. doi:10.1210/jc.2011-1972. PMC 3275367. PMID 22112808.
- https://www.intechopen.com/books/a-critical-evaluation-of-vitamin-d-basic-overview/clinical-and-biochemical-features-of-patients-with-cyp24a1-mutations. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - Tebben PJ, Singh RJ, Kumar R (October 2016). "Vitamin D-Mediated Hypercalcemia: Mechanisms, Diagnosis, and Treatment". Endocrine Reviews. 37 (5): 521–547. doi:10.1210/er.2016-1070. PMC 5045493. PMID 27588937.
External links
- Human CYP24A1 genome location and CYP24A1 gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
Further reading
- Okuda K, Usui E, Ohyama Y (August 1995). "Recent progress in enzymology and molecular biology of enzymes involved in vitamin D metabolism". Journal of Lipid Research. 36 (8): 1641–52. PMID 7595086.
- Chen KS, DeLuca HF (July 1995). "Cloning of the human 1 alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D-3 24-hydroxylase gene promoter and identification of two vitamin D-responsive elements". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Gene Structure and Expression. 1263 (1): 1–9. doi:10.1016/0167-4781(95)00060-t. PMID 7632726.
- Robertson NG, Khetarpal U, Gutiérrez-Espeleta GA, Bieber FR, Morton CC (September 1994). "Isolation of novel and known genes from a human fetal cochlear cDNA library using subtractive hybridization and differential screening". Genomics. 23 (1): 42–50. doi:10.1006/geno.1994.1457. PMID 7829101.
- Chen ML, Heinrich G, Ohyama YI, Okuda K, Omdahl JL, Chen TC, Holick MF (October 1994). "Expression of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3-24-hydroxylase mRNA in cultured human keratinocytes". Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine. 207 (1): 57–61. doi:10.3181/00379727-207-43791. PMID 7938037. S2CID 22566441.
- Labuda M, Lemieux N, Tihy F, Prinster C, Glorieux FH (November 1993). "Human 25-hydroxyvitamin D 24-hydroxylase cytochrome P450 subunit maps to a different chromosomal location than that of pseudovitamin D-deficient rickets". Journal of Bone and Mineral Research. 8 (11): 1397–406. doi:10.1002/jbmr.5650081114. PMID 8266831. S2CID 32582996.
- Hahn CN, Baker E, Laslo P, May BK, Omdahl JL, Sutherland GR (1993). "Localization of the human vitamin D 24-hydroxylase gene (CYP24) to chromosome 20q13.2-->q13.3". Cytogenetics and Cell Genetics. 62 (4): 192–3. doi:10.1159/000133473. PMID 8440135.
- Chen KS, Prahl JM, DeLuca HF (May 1993). "Isolation and expression of human 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 24-hydroxylase cDNA". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 90 (10): 4543–7. Bibcode:1993PNAS...90.4543C. doi:10.1073/pnas.90.10.4543. PMC 46548. PMID 8506296.
- Bland R, Walker EA, Hughes SV, Stewart PM, Hewison M (May 1999). "Constitutive expression of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3-1alpha-hydroxylase in a transformed human proximal tubule cell line: evidence for direct regulation of vitamin D metabolism by calcium". Endocrinology. 140 (5): 2027–34. doi:10.1210/en.140.5.2027. PMID 10218951.
- Taniguchi T, Eto TA, Shiotsuki H, Sueta H, Higashi S, Iwamura T, Okuda KI, Setoguchi T (January 2001). "Newly established assay method for 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 24-hydroxylase revealed much lower Km for 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 than for 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3". Journal of Bone and Mineral Research. 16 (1): 57–62. doi:10.1359/jbmr.2001.16.1.57. PMID 11149490. S2CID 23117091.
- Farhan H, Cross HS (November 2002). "Transcriptional inhibition of CYP24 by genistein". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 973 (1): 459–62. Bibcode:2002NYASA.973..459F. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2002.tb04683.x. PMID 12485911. S2CID 30861453.
- Theodoropoulos C, Demers C, Delvin E, Ménard D, Gascon-Barré M (April 2003). "Calcitriol regulates the expression of the genes encoding the three key vitamin D3 hydroxylases and the drug-metabolizing enzyme CYP3A4 in the human fetal intestine". Clinical Endocrinology. 58 (4): 489–99. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2265.2003.01743.x. PMID 12641633. S2CID 44330630.
- Fritsche J, Mondal K, Ehrnsperger A, Andreesen R, Kreutz M (November 2003). "Regulation of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3-1 alpha-hydroxylase and production of 1 alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 by human dendritic cells". Blood. 102 (9): 3314–6. doi:10.1182/blood-2002-11-3521. PMID 12855575.
- Nguyen TM, Lieberherr M, Fritsch J, Guillozo H, Alvarez ML, Fitouri Z, Jehan F, Garabédian M (February 2004). "The rapid effects of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 require the vitamin D receptor and influence 24-hydroxylase activity: studies in human skin fibroblasts bearing vitamin D receptor mutations". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 279 (9): 7591–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.M309517200. PMID 14665637.
- Mimori K, Tanaka Y, Yoshinaga K, Masuda T, Yamashita K, Okamoto M, Inoue H, Mori M (February 2004). "Clinical significance of the overexpression of the candidate oncogene CYP24 in esophageal cancer". Annals of Oncology. 15 (2): 236–41. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdh056. PMID 14760115.
- Sawada N, Kusudo T, Sakaki T, Hatakeyama S, Hanada M, Abe D, Kamao M, Okano T, Ohta M, Inouye K (April 2004). "Novel metabolism of 1 alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 with C24-C25 bond cleavage catalyzed by human CYP24A1". Biochemistry. 43 (15): 4530–7. doi:10.1021/bi030207f. PMID 15078099.
- Kusudo T, Sakaki T, Abe D, Fujishima T, Kittaka A, Takayama H, Hatakeyama S, Ohta M, Inouye K (September 2004). "Metabolism of A-ring diastereomers of 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 by CYP24A1". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 321 (4): 774–82. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.07.040. PMID 15358094.
- Pascussi JM, Robert A, Nguyen M, Walrant-Debray O, Garabedian M, Martin P, Pineau T, Saric J, Navarro F, Maurel P, Vilarem MJ (January 2005). "Possible involvement of pregnane X receptor-enhanced CYP24 expression in drug-induced osteomalacia". The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 115 (1): 177–86. doi:10.1172/JCI21867. PMC 539191. PMID 15630458.