Chaumont-le-Bois
Chaumont-le-Bois is a commune in the Côte-d'Or department in eastern France.
Chaumont-le-Bois | |
|---|---|
 The church of Chaumont-le-Bois and its surroundings | |
.svg.png.webp) Coat of arms | |
Location of Chaumont-le-Bois 
| |
 Chaumont-le-Bois  Chaumont-le-Bois | |
| Coordinates: 47°55′34″N 4°34′44″E | |
| Country | France |
| Region | Bourgogne-Franche-Comté |
| Department | Côte-d'Or |
| Arrondissement | Montbard |
| Canton | Châtillon-sur-Seine |
| Intercommunality | Communauté de communes du Pays Châtillonnais |
| Government | |
| • Mayor (2020–2026) | Anne Bouhélier |
| Area 1 | 7.54 km2 (2.91 sq mi) |
| Population (2017-01-01)[1] | 81 |
| • Density | 11/km2 (28/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| INSEE/Postal code | 21161 /21400 |
| Elevation | 216–356 m (709–1,168 ft) (avg. 212 m or 696 ft) |
| 1 French Land Register data, which excludes lakes, ponds, glaciers > 1 km2 (0.386 sq mi or 247 acres) and river estuaries. | |
Geography
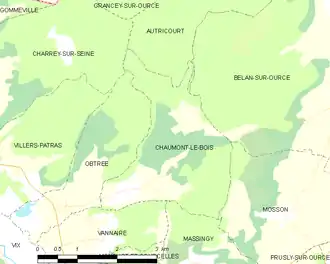
Chaumont-le-Bois covers 7.5 km2 between 216 and 393 meters above sea level. Located at an average altitude of 228 meters, the Fontainotte brook is the main watercourse of the village.
Bordering communes
History
Antiquity
With the neighboring village of Obtrée, Chaumont-le-Bois is a stopover on the ancient road coming from Mont Lassois heading northeast.
Middle Ages
From the 14th century, the village lives almost exclusively from the vine. It is believed that the settlement was located at the height of the valley on the site of the present cemetery. The seigniory seems essentially secular; of the old castle, only one dovecote remains.
Modern Times
On the eve of the Revolution when the population was around 500 inhabitants, the present church destroyed at the end of the 17th century is rebuilt below.[2]
In 1811, Napoleon's land registry records 170 hectares of vines in the commune. After the phylloxera crisis that affected the region in the last decade of the 19th century, these were uprooted. Vine cultivation only resumed in 1987.
Economy
The economy of Chaumont-le-Bois is linked to the exploitation of the forest (sawmill) and the culture of the vine (Pinot noir and Chardonnay) for the Crémant du Châtillonnais production (vineyard in AOC Crémant de Bourgogne).
Tourism
- "Floral village": participation in the bloom competition of towns and villages. Current award: 2 flowers.
- Chaumont-le-Bois is a stopover on the route du Crémant, there is a vineyard and it's winemaker's museum.
- Path of the Picherelle.
- The Fontainotte park where you can find some games for the children and picnic places. There is also a short path along the Fontainotte stream.
Administration
The first mayor was elected in 1793, this table shows only the mayors from 1945 onwards.[3]
| Mandate | Mayor |
|---|---|
| 1945-1947 | TRIDON Marcel |
| 1947-1983 | FOUGEU Albert |
| 1983-1989 | MONGIN René |
| 1989-2014 | COURQUEUX Clément |
| 2014-2026 | BOUHÉLIER Anne |
Coat of arms
.svg.png.webp)
An azure background with three golden oak leaves.
Population
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1962 | 109 | — |
| 1968 | 118 | +8.3% |
| 1975 | 82 | −30.5% |
| 1982 | 68 | −17.1% |
| 1990 | 74 | +8.8% |
| 1999 | 98 | +32.4% |
| 2006 | 88 | −10.2% |
| 2007 | 86 | −2.3% |
| 2012 | 86 | +0.0% |
| 2017 | 81 | −5.8% |
| 2018 | 80 | −1.2% |
Local Culture & Heritage
Sites and Monuments
- St. Martin's Church built in 1787.[4]
- Little castle of the lords of Chaumont-le-Bois and its dovecote near the Fontainotte stream.

Castle 
Dovecote
Personalities
- Godelieve Rosselle to whom Willem Vermandere (Belgian singer) dedicated his song: La belle Rosselle (sung in Flemish).
See also
References
- "Populations légales 2017". INSEE. Retrieved 6 January 2020.
- (René Paris 1987, p. 71)
- Chaumont-le-Bois website: Les maires depuis 1793
- Église Saint-Martin
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Chaumont-le-Bois. |