Code page 437
Code page 437 (CCSID 437) is the character set of the original IBM PC (personal computer).[2] It is also known as CP437, OEM-US, OEM 437,[3] PC-8,[4] or DOS Latin US.[5] The set includes all printable ASCII characters, extended codes for accented letters (diacritics), some Greek letters, icons, and line-drawing symbols. It is sometimes referred to as the "OEM font" or "high ASCII", or as "extended ASCII"[4] (one of many mutually incompatible ASCII extensions).
 Code page 437, as rendered by an IBM PC using standard VGA | |
| MIME / IANA | IBM437 |
|---|---|
| Alias(es) | cp437, 437, csPC8CodePage437,[1] OEM-US |
| Language(s) | English |
| Classification | Extended ASCII, OEM code page |
| Extends | US-ASCII |
| Other related encoding(s) | Code page 850, CWI-2 |
This character set remains the primary set in the core of any EGA and VGA-compatible graphics card. Text shown when a PC reboots, before any other font can be loaded from a storage medium, typically is rendered in this character set.[note 1] Many file formats developed at the time of the IBM PC are based on code page 437 as well.
Display adapters
The original IBM PC contained this font as a 9×14 pixels-per-character font stored in the ROM of the IBM Monochrome Display Adapter (MDA) and an 8×8 pixels-per-character font of the Color Graphics Adapter (CGA) cards. The IBM Enhanced Graphics Adapter (EGA) contained an 8×14 pixels-per-character version, and the VGA contained a 9×16 version.
All these display adapters have text modes in which each character cell contains an 8-bit character code point (see details), giving 256 possible values for graphic characters. All 256 codes were assigned a graphical character in ROM, including the codes from 0 to 31 that were reserved in ASCII for non-graphical control characters.
Various Eastern European PCs used different character sets, sometimes user-selectable via jumpers or CMOS setup. These sets were designed to match 437 as much as possible, for instance sharing the code points for many of the line-drawing characters, while still allowing text in a local language to be displayed.
Alt codes
A legacy of code page 437 is the number combinations used in Windows Alt keycodes.[6][7][8] The user could enter a character by holding down the Alt key and entering the three-digit decimal Alt keycode on the numpad[6] and many users memorized the numbers needed for CP437 (or for the similar code page 850). When Microsoft switched to their proprietary character sets (such as CP1252) and later Unicode in Windows, the original codes were retained; Microsoft added the ability to type a code in the new character set by typing the numpad 0 before the digits.[6][9]
Character set
The following tables show code page 437. Each character is shown with its equivalent Unicode code point and its decimal Alt code. See also the notes below, as there are multiple equivalent Unicode characters for some code points.
Although the ROM provides a graphic for all 256 different possible 8-bit codes, some APIs will not print some code points, in particular the range 0-31 and the code at 127.[10] Instead, they will interpret them as control characters. For instance, many methods of outputting text on the original IBM PC would interpret the codes for BEL, BS, CR and LF. Many printers were also unable to print these characters.
| _0 | _1 | _2 | _3 | _4 | _5 | _6 | _7 | _8 | _9 | _A | _B | _C | _D | _E | _F | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0_ | NUL[lower-alpha 1] 0000 0 |
☺ 263A 1 |
☻ 263B 2 |
♥ 2665 3 |
♦ 2666 4 |
♣ 2663 5 |
♠ 2660 6 |
• 2022 7 |
◘ 25D8 8 |
○ 25CB 9 |
◙ 25D9 10 |
♂ 2642 11 |
♀ 2640 12 |
♪ 266A 13 |
♫ 266B 14 |
☼ 263C 15 |
| 1_ | ► 25BA 16 |
◄ 25C4 17 |
↕ 2195 18 |
‼ 203C 19 |
¶ 00B6 20 |
§ 00A7 21 |
▬ 25AC 22 |
↨ 21A8 23 |
↑ 2191 24 |
↓ 2193 25 |
→ 2192 26 |
← 2190 27 |
∟ 221F 28 |
↔ 2194 29 |
▲ 25B2 30 |
▼ 25BC 31 |
| 2_ | SP 0020 32 |
! 0021 33 |
" 0022 34 |
# 0023 35 |
$ 0024 36 |
% 0025 37 |
& 0026 38 |
' 0027 39 |
( 0028 40 |
) 0029 41 |
* 002A 42 |
+ 002B 43 |
, 002C 44 |
- 002D 45 |
. 002E 46 |
/ 002F 47 |
| 3_ | 0 0030 48 |
1 0031 49 |
2 0032 50 |
3 0033 51 |
4 0034 52 |
5 0035 53 |
6 0036 54 |
7 0037 55 |
8 0038 56 |
9 0039 57 |
: 003A 58 |
; 003B 59 |
< 003C 60 |
= 003D 61 |
> 003E 62 |
? 003F 63 |
| 4_ | @ 0040 64 |
A 0041 65 |
B 0042 66 |
C 0043 67 |
D 0044 68 |
E 0045 69 |
F 0046 70 |
G 0047 71 |
H 0048 72 |
I 0049 73 |
J 004A 74 |
K 004B 75 |
L 004C 76 |
M 004D 77 |
N 004E 78 |
O 004F 79 |
| 5_ | P 0050 80 |
Q 0051 81 |
R 0052 82 |
S 0053 83 |
T 0054 84 |
U 0055 85 |
V 0056 86 |
W 0057 87 |
X 0058 88 |
Y 0059 89 |
Z 005A 90 |
[ 005B 91 |
\ 005C 92 |
] 005D 93 |
^ 005E 94 |
_ 005F 95 |
| 6_ | ` 0060 96 |
a 0061 97 |
b 0062 98 |
c 0063 99 |
d 0064 100 |
e 0065 101 |
f 0066 102 |
g 0067 103 |
h 0068 104 |
i 0069 105 |
j 006A 106 |
k 006B 107 |
l 006C 108 |
m 006D 109 |
n 006E 110 |
o 006F 111 |
| 7_ | p 0070 112 |
q 0071 113 |
r 0072 114 |
s 0073 115 |
t 0074 116 |
u 0075 117 |
v 0076 118 |
w 0077 119 |
x 0078 120 |
y 0079 121 |
z 007A 122 |
{ 007B 123 |
|[lower-alpha 2] 007C 124 |
} 007D 125 |
~ 007E 126 |
⌂[lower-alpha 3] 2302 127 |
| 8_ | Ç 00C7 128 |
ü 00FC 129 |
é 00E9 130 |
â 00E2 131 |
ä 00E4 132 |
à 00E0 133 |
å 00E5 134 |
ç 00E7 135 |
ê 00EA 136 |
ë 00EB 137 |
è 00E8 138 |
ï 00EF 139 |
î 00EE 140 |
ì 00EC 141 |
Ä 00C4 142 |
Å 00C5 143 |
| 9_ | É 00C9 144 |
æ 00E6 145 |
Æ 00C6 146 |
ô 00F4 147 |
ö 00F6 148 |
ò 00F2 149 |
û 00FB 150 |
ù 00F9 151 |
ÿ 00FF 152 |
Ö 00D6 153 |
Ü 00DC 154 |
¢ 00A2 155 |
£ 00A3 156 |
¥ 00A5 157 |
₧ 20A7 158 |
ƒ 0192 159 |
| A_ | á 00E1 160 |
í 00ED 161 |
ó 00F3 162 |
ú 00FA 163 |
ñ 00F1 164 |
Ñ 00D1 165 |
ª 00AA 166 |
º 00BA 167 |
¿ 00BF 168 |
⌐ 2310 169 |
¬ 00AC 170 |
½ 00BD 171 |
¼ 00BC 172 |
¡ 00A1 173 |
« 00AB 174 |
» 00BB 175 |
| B_ | ░ 2591 176 |
▒ 2592 177 |
▓ 2593 178 |
│[lower-alpha 4] 2502 179 |
┤ 2524 180 |
╡ 2561 181 |
╢ 2562 182 |
╖ 2556 183 |
╕ 2555 184 |
╣ 2563 185 |
║ 2551 186 |
╗ 2557 187 |
╝ 255D 188 |
╜ 255C 189 |
╛ 255B 190 |
┐ 2510 191 |
| C_ | └ 2514 192 |
┴ 2534 193 |
┬ 252C 194 |
├ 251C 195 |
─ 2500 196 |
┼ 253C 197 |
╞ 255E 198 |
╟ 255F 199 |
╚ 255A 200 |
╔ 2554 201 |
╩ 2569 202 |
╦ 2566 203 |
╠ 2560 204 |
═ 2550 205 |
╬ 256C 206 |
╧ 2567 207 |
| D_ | ╨ 2568 208 |
╤ 2564 209 |
╥ 2565 210 |
╙ 2559 211 |
╘ 2558 212 |
╒ 2552 213 |
╓ 2553 214 |
╫ 256B 215 |
╪ 256A 216 |
┘ 2518 217 |
┌ 250C 218 |
█ 2588 219 |
▄ 2584 220 |
▌ 258C 221 |
▐ 2590 222 |
▀ 2580 223 |
| E_ | α 03B1 224 |
ß[lower-alpha 5] 00DF 225 |
Γ 0393 226 |
π[lower-alpha 6] 03C0 227 |
Σ[lower-alpha 7] 03A3 228 |
σ 03C3 229 |
µ[lower-alpha 8] 00B5 230 |
τ 03C4 231 |
Φ 03A6 232 |
Θ 0398 233 |
Ω[lower-alpha 9] 03A9 234 |
δ[lower-alpha 10] 03B4 235 |
∞ 221E 236 |
φ[lower-alpha 11] 03C6 237 |
ε[lower-alpha 12] 03B5 238 |
∩ 2229 239 |
| F_ | ≡ 2261 240 |
± 00B1 241 |
≥ 2265 242 |
≤ 2264 243 |
⌠[lower-alpha 13] 2320 244 |
⌡ 2321 245 |
÷ 00F7 246 |
≈ 2248 247 |
° 00B0 248 |
∙[lower-alpha 14] 2219 249 |
· 00B7 250 |
√[lower-alpha 15] 221A 251 |
ⁿ 207F 252 |
² 00B2 253 |
■ 25A0 254 |
nbsp[lower-alpha 16] 00A0 255 |
Letter Number Punctuation Symbol Other Undefined
When translating to Unicode some codes do not have a unique, single Unicode equivalent; the correct choice may depend upon context.
- 0 draws a blank space, but usage as the C string terminator means it is more accurately translated as NUL
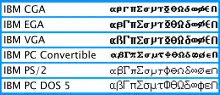
- 124 (7Chex) The actual glyph at this position is a broken bar [U+00A6, ¦] in the original IBM PC and compatibles font as rendered by the original MDA and this rendering was later adopted for CGA, EGA and VGA (see image at the beginning of the article) but almost all software assumes this code is the ASCII character (for instance programming languages use it as "or") and in the early 1990s it was clarified that there is vertical bar in ASCII at this position and the broken bar symbol is not part of ASCII.
- 127 (7Fhex) is a "house" but was also sometimes used as Greek capital delta [U+0394, Δ].
- Could also serve as an integral extension [U+23AE, ⎮] in IBM's font.
- 225 (E1hex) is identified by IBM as Latin "Sharp s Small"[15] [U+00DF, ß] but is sometimes rendered in OEM fonts as Greek small beta [U+03B2, β]. The placement of this Latin character among Greek characters suggests intended multi-use.
- 227 (E3hex) is identified by IBM as Greek "Pi Small" [U+03C0, π] but is sometimes rendered in OEM fonts as Greek capital pi [U+03A0, Π] or the n-ary product sign [U+220F, ∏].
- 228 (E4hex) is identified by IBM as Greek "Sigma Capital" [U+03A3, Σ] but is also used as the n-ary summation sign [U+2211, ∑].
- 230 (E6hex) is identified by IBM as Greek "Mu Small" [U+03BC, μ] but is also used as the micro sign [U+00B5, µ]. In Unicode, IBM's Greek GCGID table[16] maps the character in this code page to the Greek letter, but Python, for example, maps it to the micro sign.
- 234 (EAhex) is identified by IBM as Greek "Omega Capital" [U+03A9, Ω] but is also used as the ohm sign [U+2126, Ω]. Unicode considers the characters to be equivalent and suggests that U+03A9 be used in both contexts.[17]
- 235 (EBhex) is identified by IBM as Greek "Delta Small" [U+03B4, δ]. It was also unofficially used for the small eth [U+00F0, ð] and the partial derivative sign [U+2202, ∂]
- 237 (EDhex) is identified by IBM as Greek "Phi Small (Closed Form)" [U+03D5, ϕ; or, from the italicized math set, U+1D719, 𝜙] but, in some codecs (e.g. the codec library of Python[18]), is mapped to Unicode as the open (or "loopy") form [U+03C6, φ]. Comparison of IBM's Greek GCGID table[16] with Unicode's Greek code chart[19] shows where IBM, for example, reversed the open and closed forms when mapping to Unicode. This character is also used as the empty set sign [U+2205, ∅], the diameter sign [U+2300, ⌀], and the Latin letter O with stroke [U+00D8, Ø; and U+00F8, ø].
- 238 (EEhex) is identified by IBM as Greek "Epsilon Small" [U+03B5, ε] but is sometimes rendered in OEM fonts as the element-of sign [U+2208, ∈]. It was later unofficially used as the euro sign [U+20AC, €]
- 244 (F4hex) and 245 (F5hex) are the upper and lower portion of the integral symbol (∫), and they can be extended with the character 179 (B3hex), the vertical line of the box drawing block. 244 could also be used for the long s character [U+017F, ſ].
- 249 (F9hex) and 250 (FAhex) are almost indistinguishable: the first is a slightly larger dot than the second, both were used as bullets, middle dot, and multiplication dot [U+2219, ∙]
- 251 (FBhex) was also sometimes used as a check mark [U+2713, ✓].
- 255 (FFhex) draws a blank space, the use as non-breaking space (NBSP) has precedent in word processors designed for the IBM PC.
History
The repertoire of code page 437 was taken from the character set of Wang word-processing machines, according to Bill Gates in an interview with Gates and Paul Allen that appeared in the 2 October 1995 edition of Fortune Magazine:
- "... We were also fascinated by dedicated word processors from Wang, because we believed that general-purpose machines could do that just as well. That's why, when it came time to design the keyboard for the IBM PC, we put the funny Wang character set into the machine—you know, smiley faces and boxes and triangles and stuff. We were thinking we'd like to do a clone of Wang word-processing software someday."
According to an interview with David J. Bradley (developer of the PC's ROM-BIOS) the characters were decided upon during a four-hour meeting on a plane trip from Seattle to Atlanta by Andy Saenz (responsible for the video card), Lew Eggebrecht (chief engineer for the PC) and himself.[20]
The selection of graphic characters has some internal logic:
- Table rows 0 and 1, codes 0 to 31 (00hex to 1Fhex), are assorted dingbats (complementary and decorative characters). The isolated character 127 (7Fhex) also belongs to this group.
- Table rows 2 to 7, codes 32 to 126 (20hex to 7Ehex), are the standard ASCII printable characters.
- Table rows 8 to 10, codes 128 to 175 (80hex to AFhex), are a selection of international text characters.
- Table rows 11 to 13, codes 176 to 223 (B0hex to DFhex), are box drawing and block characters. This block is arranged so that characters 192 to 223 (C0hex to DFhex) contain all the right arms and right-filled areas. The original IBM PC MDA display adapter stored the code page 437 character glyphs as bitmaps eight pixels wide, but for visual enhancement displayed them every nine pixels on screen. This range of characters had the eighth pixel column duplicated by special hardware circuitry,[21] thus filling in gaps in lines and filled areas. The VGA adapter allows this behaviour to be turned on or off.[22]
- Table rows 14 and 15, codes 224 to 254 (E0hex to FEhex) are devoted to mathematical symbols, where the first twelve are a selection of Greek letters commonly used in physics.
Most fonts for Microsoft Windows include the special graphic characters at the Unicode indexes shown, as they are part of the WGL4 set that Microsoft encourages font designers to support. (The monospaced raster font family Terminal was an early font that replicated all code page 437 characters, at least at some resolutions.) To draw these characters directly from these code points, a Microsoft Windows font called MS Linedraw[23] replicates all of the code page 437 characters, thus providing one way to display DOS text on a modern Windows machine as it was shown in DOS, with limitations.[24]
Internationalization
Code page 437 has a series of international characters, mainly values 128 to 175 (80hex to AFhex). However, it only covers a few major Western European languages in full, including English, German and Swedish,[note 2] and so lacks several characters (mostly capital letters) important to many major Western European languages:
- Spanish: Á, Í, Ó, and Ú
- French: À, Â, È, Ê, Ë, Î, Ï, Ô, Œ, œ, Ù, Û, and Ÿ
- Portuguese: Á, À, Â, Ã, ã, Ê, Í, Ó, Ô, Õ, õ, and Ú
- Catalan: À, È, Í, Ï, Ò, Ó, and Ú
- Italian: À, È, Ì, Ò, and Ù
- Icelandic: Á, Ð, ð, Í, Ó, Ú, Ý, ý, Þ, and þ
- Danish/Norwegian: Ø and ø. Character number 237 (EDhex), the small phi (closed form), could be used as a surrogate even though it may not render well (furthermore, it tends to map to Unicode, and/or render in Unicode fonts, as the open-form phi or the closed-vertical-form phi, which are even further from the O with stroke). To compensate, the Danish/Norwegian and Icelandic code pages (865 and 861) replaced cent sign (¢) with ø and the yen sign (¥) with Ø.
- Most Greek alphabet symbols were omitted, beyond the basic math symbols. (They were included in the Greek-language code pages 737 and 869. Some of the Greek symbols that were already in code page 437 had their glyphs changed from mathematical or scientific forms to match the actual use in Greek.)
Along with the cent (¢), pound sterling (£) and yen/yuan (¥) currency symbols, it has a couple of former European currency symbols: the florin (ƒ, Netherlands) and the peseta (₧, Spain). The presence of the last is unusual, since the Spanish peseta was never an internationally relevant currency, and also never had a symbol of its own; it was simply abbreviated as "Pt", "Pta", "Pts", or "Ptas". Spanish models of the IBM electric typewriter, however, also had a single position devoted to it.
Later DOS character sets, such as code page 850 (DOS Latin-1), code page 852 (DOS Central-European) and code page 737 (DOS Greek), filled the gaps for international use with some compatibility with code page 437 by retaining the single and double box-drawing characters, while discarding the mixed ones (e.g. horizontal double/vertical single). All code page 437 characters have similar glyphs in Unicode and in Microsoft's WGL4 character set, and therefore are available in most fonts in Microsoft Windows, and also in the default VGA font of the Linux kernel, and the ISO 10646 fonts for X11.
See also
- Alt code
- ANSI
- ASCII
- Semigraphical characters
- Atari ST character set, derived from code page 437
Notes
- Systems available in Eastern European, Arabic, and Asian countries often use a different set, however these sets are designed to match 437 as much as possible. The designation "OEM", for "original equipment manufacturer", indicates that the set could be changed by the manufacturer to meet different markets.
- It also covers some less major Western European languages—as well as some other languages—in full, including Basque, Malay, and the pre-1999 Turkmen Latin alphabet, but this was likely unintended.
References
- Character Sets, Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA), 12 December 2018
- "CCSID 437 information document". Archived from the original on 27 March 2016.
- "OEM 437". Go Global Developer Center. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 9 June 2016. Retrieved 22 September 2011.
- "OEM font". Encyclopedia. PCmag.com. Retrieved 15 November 2011.
- Kano, Nadine. "Appendix H Code Pages". Globalization and Localization : Code Page 437 DOS Latin US. Developing International Software. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 17 March 2016. Retrieved 14 November 2011.
- "Glossary of Terms Used on this Site". Microsoft. (Please see the description about the term "Alt+Numpad"). Archived from the original on 8 September 2012. Retrieved 17 August 2018.
- Murray Sargent. "Entering Unicode Characters – Murray Sargent: Math in Office". Retrieved 17 August 2018.
- "ALT+NUMPAD ASCII Key Combos: The α and Ω of Creating Obscure Passwords". Retrieved 17 August 2018.
- "Insert ASCII or Unicode Latin-based symbols and characters - Office Support". Microsoft. Retrieved 17 August 2018.
- "SBCS code page information document CPGID 00437". Coded character sets and related resources. IBM. 1986 [1984-05-01]. Archived from the original on 9 June 2016. Retrieved 14 November 2011.
- Steele, Shawn (24 April 1996). "cp437_DOSLatinUS to Unicode table" (TXT). 2.00. Unicode Consortium. Archived from the original on 9 June 2016. Retrieved 14 November 2011.
- Code Page CPGID 00437 (pdf) (PDF), IBM
- Code Page CPGID 00437 (txt), IBM
- International Components for Unicode (ICU), ibm-437_P100-1995.ucm, 3 December 2002
- "Code Page (CPGID): 00437". Coded character sets and related resources. IBM. 1984. Retrieved 25 February 2017.
- "Graphic character identifiers: Alphabetics, Greek". Coded character sets and related resources. IBM. Retrieved 25 February 2017.
- The Unicode Consortium (21 May 2003). "Chapter 7: European Alphabetic Scripts". The Unicode Standard 4.0 (PDF). Addison-Wesley (published August 2003). p. 176. ISBN 0-321-18578-1. Retrieved 9 June 2016.
- "cpython/cp437.py at master · python/cpython · GitHub". Retrieved 17 August 2018.
- "Greek and Coptic: Range: 0370–03FF" (PDF). The Unicode Standard, Version 9.0. Unicode Consortium. Retrieved 25 February 2017.
- Edwards, Benj (6 November 2015) [2011]. "Origins of the ASCII Smiley Character: An Email Exchange With Dr. David Bradley". Archived from the original on 28 November 2016. Retrieved 27 November 2016.
[…] If you look at the first 32 characters in the IBM PC character set you'll see lots of whimsical characters — smiley face, musical notes, playing card suits and others. These were intended for character based games […] Since we were using 8-bit characters we had 128 new spots to fill. We put serious characters there — three columns of foreign characters, based on our Datamaster experience. Three columns of block graphic characters […] many customers with Monochrome Display Adapter would have no graphics at all. […] two columns had math symbols, greek letters (for math) and others […] about the first 32 characters (x00-x1F)? […] These characters originated with teletype transmission. But we could display them on the character based screens. So we added a set of "not serious" characters. They were intended as display only characters, not for transmission or storage. Their most probable use would be in character based games. […] As in most things for the IBM PC, the one year development schedule left little time for contemplation and revision. […] the character set was developed in a three person 4-hour meeting, and I was one of those on that plane from Seattle to Atlanta. There was some minor revision after that meeting, but there were many other things to design/fix/decide so that was about it. […] the other participants in that plane trip were Andy Saenz — responsible for the video card, and Lew Eggebrecht — the chief engineer for the PC.
- Wilton, Richard (December 1987). Programmer's Guide to PC & PS/2 Video Systems: Maximum Video Performance Form the EGA, VGA, HGC, and MCGA (1st ed.). Microsoft Press. ISBN 1-55615-103-9. ISBN 978-1-55615-103-3.
- Joshua D. Neal, Attribute Controller Registers: Attribute Mode Control Register, Hardware Level VGA and SVGA Video Programming Information Page: bit 2 is Line Graphics Enable.
- Mike Jacobs. "MS LineDraw font family - Typography | Microsoft Docs". Microsoft typography. 2.00. Microsoft Corporation. Retrieved 17 August 2018.
- Staff (26 October 2013). "WD97: MS LineDraw Font Not Usable in Word". Microsoft. 2.0. Microsoft. KB179422, Q179422. Archived from the original on 24 March 2016. Retrieved 1 July 2012.
External links
- IBM PC memory-mapped video graphics to Unicode on official Unicode site
