Bill Gates
William Henry Gates III (born October 28, 1955) is an American business magnate, software developer, and philanthropist. He is a co-founder of Microsoft Corporation.[2][3] During his career at Microsoft, Gates held the positions of chairman, chief executive officer (CEO), president and chief software architect, while also being the largest individual shareholder until May 2014. He is one of the best-known entrepreneurs and pioneers of the microcomputer revolution of the 1970s and 1980s.
Bill Gates | |
|---|---|
 Gates in 2018 | |
| Born | William Henry Gates III October 28, 1955 Seattle, Washington, U.S. |
| Education | Harvard University (dropped out) |
| Occupation |
|
| Years active | 1975–present |
| Known for | Co-founding Microsoft |
| Net worth | US$122.4 billion (February 2021)[1] |
| Title |
|
| Spouse(s) | |
| Children | 3 |
| Parent(s) | Bill Gates Sr. Mary Maxwell |
| Website | www |
| Signature | |
Gates was born and raised in Seattle, Washington. In 1975, Gates co-founded Microsoft with childhood friend Paul Allen in Albuquerque, New Mexico; it went on to become the world's largest personal computer software company.[4][lower-alpha 1] Gates led the company as chairman and CEO until stepping down as CEO in January 2000, but he remained chairman and became chief software architect.[7] During the late 1990s, he had been criticized for his business tactics, which have been considered anti-competitive. This opinion has been upheld by numerous court rulings.[8] In June 2006, Gates announced that he would be transitioning to a part-time role at Microsoft and full-time work at the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, the private charitable foundation that he and his wife, Melinda Gates, established in 2000.[9] He gradually transferred his duties to Ray Ozzie and Craig Mundie.[10] He stepped down as chairman of Microsoft in February 2014 and assumed a new post as technology adviser to support the newly appointed CEO Satya Nadella.[11] In March 2020, Gates left his board positions at Microsoft and Berkshire Hathaway to focus on his philanthropic endeavors including climate change, global health and development, and education.[12]
Since 1987, he has been included in the Forbes list of the world's wealthiest people.[13][14] From 1995 to 2017, he held the Forbes title of the richest person in the world all but four of those years.[15] In October 2017, he was surpassed by Amazon founder and CEO Jeff Bezos, who had an estimated net worth of US$90.6 billion compared to Gates's net worth of US$89.9 billion at the time.[16] As of January 2021, Gates had an estimated net worth of US$163 billion, making him the third-richest person in the world.[17]
Later in his career and since leaving day-to-day operations at Microsoft in 2008, Gates has pursued a number of philanthropic endeavors. He has given sizable amounts of money to various charitable organizations and scientific research programs through the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, reported to be the world's largest private charity.[18] In 2009, Gates and Warren Buffett founded The Giving Pledge, whereby they and other billionaires pledge to give at least half of their wealth to philanthropy.[19]
Early life
Gates was born in Seattle, Washington, on October 28, 1955.[3] He is the son of William H. Gates Sr.[lower-alpha 2] (1925–2020) and Mary Maxwell Gates (1929–1994).[20] His ancestry includes English, German, and Irish/Scots-Irish.[21] His father was a prominent lawyer, and his mother served on the board of directors for First Interstate BancSystem and the United Way of America. Gates's maternal grandfather was J. W. Maxwell, a national bank president. Gates has an older sister Kristi (Kristianne) and a younger sister Libby. He is the fourth of his name in his family but is known as William Gates III or "Trey" (i.e., three) because his father had the "II" suffix.[22][23] The family lived in the Sand Point area of Seattle in a home that was damaged by a rare tornado when Gates was seven years old.[24]
Early in his life, Gates observed that his parents wanted him to pursue a law career.[25] When he was young, his family regularly attended a church of the Congregational Christian Churches, a Protestant Reformed denomination.[26][27][28] Gates was small for his age and was bullied as a child.[23] The family encouraged competition; one visitor reported that "it didn't matter whether it was hearts or pickleball or swimming to the dock; there was always a reward for winning and there was always a penalty for losing".[29]

At 13, he enrolled in the private Lakeside prep school,[30][31] where he wrote his first software program.[32] When he was in the eighth grade, the Mothers' Club at the school used proceeds from Lakeside School's rummage sale to buy a Teletype Model 33 ASR terminal and a block of computer time on a General Electric (GE) computer for the students.[33] Gates took an interest in programming the GE system in BASIC, and he was excused from math classes to pursue his interest. He wrote his first computer program on this machine, an implementation of tic-tac-toe that allowed users to play games against the computer. Gates was fascinated by the machine and how it would always execute software code perfectly.[34] After the Mothers Club donation was exhausted, Gates and other students sought time on systems including DEC PDP minicomputers. One of these systems was a PDP-10 belonging to Computer Center Corporation (CCC) which banned for the summer Gates, Paul Allen, Ric Weiland, and Gates's best friend and first business partner Kent Evans, after it caught them exploiting bugs in the operating system to obtain free computer time.[35][23]
The four students formed the Lakeside Programmers Club to make money.[23] At the end of the ban, they offered to find bugs in CCC's software in exchange for extra computer time. Rather than use the system remotely via Teletype, Gates went to CCC's offices and studied source code for various programs that ran on the system, including Fortran, Lisp, and machine language. The arrangement with CCC continued until 1970 when the company went out of business.
The following year, a Lakeside teacher enlisted Gates and Evans to automate the school's class-scheduling system, providing them computer time and royalties in return. The duo worked diligently in order to have the program ready for their senior year. Towards the end of their junior year, Evans was killed in a mountain climbing accident, which Gates has described as one of the saddest days of his life. Gates then turned to Allen who helped him finish the system for Lakeside.[23]
At 17, Gates formed a venture with Allen called Traf-O-Data to make traffic counters based on the Intel 8008 processor.[36] In 1972, he served as a congressional page in the House of Representatives.[37][38] He was a National Merit Scholar when he graduated from Lakeside School in 1973.[39] He scored 1590 out of 1600 on the Scholastic Aptitude Tests (SAT) and enrolled at Harvard College in the autumn of 1973.[40][41] He chose a pre-law major but took mathematics and graduate level computer science courses.[42] While at Harvard, he met fellow student Steve Ballmer. Gates left Harvard after two years while Ballmer stayed and graduated magna cum laude. Years later, Ballmer succeeded Gates as Microsoft's CEO and maintained that position from 2000 until his resignation in 2014.[43][44]
Gates devised an algorithm for pancake sorting as a solution to one of a series of unsolved problems[45] presented in a combinatorics class by professor Harry Lewis. His solution held the record as the fastest version for over 30 years, and its successor is faster by only 2%.[45][46] His solution was formalized and published in collaboration with Harvard computer scientist Christos Papadimitriou.[47]
Gates remained in contact with Paul Allen and joined him at Honeywell during the summer of 1974.[48] In 1975, the MITS Altair 8800 was released based on the Intel 8080 CPU, and Gates and Allen saw the opportunity to start their own computer software company.[49] Gates dropped out of Harvard that same year. His parents were supportive of him after seeing how much he wanted to start his own company.[50] He explained his decision to leave Harvard: "if things hadn't worked out, I could always go back to school. I was officially on leave."[51]
Microsoft
BASIC

Gates read the January 1975 issue of Popular Electronics which demonstrated the Altair 8800, and he contacted Micro Instrumentation and Telemetry Systems (MITS) to inform them that he and others were working on a BASIC interpreter for the platform.[52] In reality, Gates and Allen did not have an Altair and had not written code for it; they merely wanted to gauge MITS's interest. MITS president Ed Roberts agreed to meet them for a demonstration, and over the course of a few weeks they developed an Altair emulator that ran on a minicomputer, and then the BASIC interpreter. The demonstration was held at MITS's offices in Albuquerque, New Mexico; it was a success and resulted in a deal with MITS to distribute the interpreter as Altair BASIC. MITS hired Allen,[53] and Gates took a leave of absence from Harvard to work with him at MITS in November 1975. Allen named their partnership "Micro-Soft", a combination of "microcomputer" and "software", and their first office was in Albuquerque. The first employee Gates and Allen hired was their high school collaborator Ric Weiland.[53] They dropped the hyphen within a year and officially registered the trade name "Microsoft" with the Secretary of the State of New Mexico on November 26, 1976.[53] Gates never returned to Harvard to complete his studies.
Microsoft's Altair BASIC was popular with computer hobbyists, but Gates discovered that a pre-market copy had leaked out and was being widely copied and distributed. In February 1976, he wrote an Open Letter to Hobbyists in the MITS newsletter in which he asserted that more than 90% of the users of Microsoft Altair BASIC had not paid Microsoft for it and the Altair "hobby market" was in danger of eliminating the incentive for any professional developers to produce, distribute, and maintain high-quality software.[54] This letter was unpopular with many computer hobbyists, but Gates persisted in his belief that software developers should be able to demand payment. Microsoft became independent of MITS in late 1976, and it continued to develop programming language software for various systems.[53] The company moved from Albuquerque to Bellevue, Washington on January 1, 1979.[52]
Gates said he personally reviewed and often rewrote every line of code that the company produced in its first five years. As the company grew he transitioned into a manager role, then an executive.[55]
IBM partnership
IBM, the leading supplier of computer equipment to commercial enterprises at the time, approached Microsoft in July 1980 concerning software for its upcoming personal computer, the IBM PC.[56] IBM first proposed that Microsoft write the BASIC interpreter. IBM's representatives also mentioned that they needed an operating system, and Gates referred them to Digital Research (DRI), makers of the widely used CP/M operating system.[57] IBM's discussions with Digital Research went poorly, however, and they did not reach a licensing agreement. IBM representative Jack Sams mentioned the licensing difficulties during a subsequent meeting with Gates and asked if Microsoft could provide an operating system. A few weeks later, Gates and Allen proposed using 86-DOS, an operating system similar to CP/M, that Tim Paterson of Seattle Computer Products (SCP) had made for hardware similar to the PC.[58] Microsoft made a deal with SCP to be the exclusive licensing agent of 86-DOS, and later the full owner. Microsoft employed Paterson to adapt the operating system for the PC[59] and delivered it to IBM as PC DOS for a one-time fee of $50,000.[60]
The contract itself only earned Microsoft a relatively small fee. It was the prestige brought to Microsoft by IBM's adoption of their operating system that would be the origin of Microsoft's transformation from a small business to the leading software company in the world. Gates had not offered to transfer the copyright on the operating system to IBM because he believed that other personal computer makers would clone IBM's PC hardware.[60] They did, making the IBM-compatible PC, running DOS, a de facto standard. The sales of MS-DOS (the version of DOS sold to customers other than IBM) made Microsoft a major player in the industry.[61] The press quickly identified Microsoft as being very influential on the IBM PC. PC Magazine asked if Gates was "the man behind the machine?".[56]
Gates oversaw Microsoft's company restructuring on June 25, 1981, which re-incorporated the company in Washington state and made Gates the president and chairman of the board, with Paul Allen as vice president and vice chairman. In early 1983, Allen left the company after receiving a Hodgkin lymphoma diagnosis, effectively ending the formal business partnership between Gates and Allen, which had been strained months prior due to a contentious dispute over Microsoft equity.[52][62] Later in the decade, Gates repaired his relationship with Allen and together the two donated millions to their childhood school Lakeside.[23] They remained friends until Allen's death in October 2018.[63]
Windows
Microsoft launched its first retail version of Microsoft Windows on November 20, 1985. In August of the following year, the company struck a deal with IBM to develop a separate operating system called OS/2. Although the two companies successfully developed the first version of the new system, the partnership deteriorated due to mounting creative differences.[64]
Management style

Gates had primary responsibility for Microsoft's product strategy from the company's founding in 1975 until 2006. He gained a reputation for being distant from others; an industry executive complained in 1981 that "Gates is notorious for not being reachable by phone and for not returning phone calls."[65] An Atari executive recalled that he showed Gates a game and defeated him 35 of 37 times. When they met again a month later, Gates "won or tied every game. He had studied the game until he solved it. That is a competitor".[66]
Gates met regularly with Microsoft's senior managers and program managers, and the managers described him as being verbally combative. He also berated them for perceived holes in their business strategies or proposals that placed the company's long-term interests at risk.[67][68] He interrupted presentations with such comments as "that's the stupidest thing I've ever heard"[69] and "why don't you just give up your options and join the Peace Corps?"[70] The target of his outburst would then have to defend the proposal in detail until Gates was fully convinced.[69] When subordinates appeared to be procrastinating, he was known to remark sarcastically, "I'll do it over the weekend."[71][72][73]
During Microsoft's early years, Gates was an active software developer, particularly in the company's programming language products, but his primary role in most of the company's history was as a manager and executive. He has not officially been on a development team since working on the TRS-80 Model 100,[74] but he wrote code that shipped with the company's products as late as 1989.[72] Jerry Pournelle wrote in 1985 when Gates announced Microsoft Excel: "Bill Gates likes the program, not because it's going to make him a lot of money (although I'm sure it will do that), but because it's a neat hack."[75]
On June 15, 2006, Gates announced that he would transition out of his role at Microsoft to dedicate more time to philanthropy. He divided his responsibilities between two successors when he placed Ray Ozzie in charge of management and Craig Mundie in charge of long-term product strategy.[76]
Antitrust litigation

Gates approved of many decisions that led to antitrust litigation over Microsoft's business practices. In the 1998 United States v. Microsoft case, Gates gave deposition testimony that several journalists characterized as evasive. He argued with examiner David Boies over the contextual meaning of words such as "compete", "concerned", and "we". Later in the year, when portions of the videotaped deposition were played back in court, the judge was seen laughing and shaking his head.[77] BusinessWeek reported:
Early rounds of his deposition show him offering obfuscatory answers and saying "I don't recall" so many times that even the presiding judge had to chuckle. Worse, many of the technology chief's denials and pleas of ignorance were directly refuted by prosecutors with snippets of e-mail that Gates both sent and received.[78]
Gates later said that he had simply resisted attempts by Boies to mischaracterize his words and actions. "Did I fence with Boies? … I plead guilty… rudeness to Boies in the first degree."[79] Despite Gates's denials, the judge ruled that Microsoft had committed monopolization, tying and blocking competition, each in violation of the Sherman Antitrust Act.[79]
Post-Microsoft
Since leaving day-to-day operations at Microsoft, Gates has continued his philanthropy and works on other projects.
According to the Bloomberg Billionaires Index, Gates was the world's highest-earning billionaire in 2013, as his net worth increased by US$15.8 billion to US$78.5 billion. As of January 2014, most of Gates's assets are held in Cascade Investment LLC, an entity through which he owns stakes in numerous businesses, including Four Seasons Hotels and Resorts, and Corbis Corp.[80] On February 4, 2014, Gates stepped down as chairman of Microsoft to become "technology advisor" alongside CEO Satya Nadella.[11][81]
Gates provided his perspective on a range of issues in a substantial interview that was published in the March 27, 2014 issue of Rolling Stone magazine. In the interview, Gates provided his perspective on climate change, his charitable activities, various tech companies and people involved in them, and the state of America. In response to a question about his greatest fear when he looks 50 years into the future, Gates stated: "... there'll be some really bad things that'll happen in the next 50 or 100 years, but hopefully none of them on the scale of, say, a million people that you didn't expect to die from a pandemic, or nuclear or bioterrorism." Gates also identified innovation as the "real driver of progress" and pronounced that "America's way better today than it's ever been."[82]
Gates has expressed concern about the potential harms of superintelligence; in a Reddit "ask me anything", he stated that:
First the machines will do a lot of jobs for us and not be super intelligent. That should be positive if we manage it well. A few decades after that though the intelligence is strong enough to be a concern. I agree with Elon Musk and some others on this and don't understand why some people are not concerned.[83][84][85][86]
In an interview that was held at the TED conference in March 2015, with Baidu's CEO, Robin Li, Gates said he would "highly recommend" Nick Bostrom's recent work, Superintelligence: Paths, Dangers, Strategies.[87] During the conference, Gates warned that the world was not prepared for the next pandemic, a situation that would come to pass in late 2019 when the COVID-19 pandemic began.[88] In March 2018, Gates met at his home in Seattle with Mohammed bin Salman, the reformist crown prince and de facto ruler of Saudi Arabia to discuss investment opportunities for Saudi Vision 2030.[89][90] In June 2019, Gates admitted that losing the mobile operating system race to Android was his biggest mistake. He stated that it was within their skill set of being the dominant player, but partially blames the antitrust litigation during the time.[91] That same year, Gates became an Advisory Board Member of the Bloomberg New Economy Forum.[92]
On March 13, 2020, Microsoft announced Gates would be leaving his board positions at Berkshire Hathaway and Microsoft to dedicate his efforts in philanthropic endeavors such as climate change, global health and development, and education.[12]
Philanthropy
Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation

Gates studied the work of Andrew Carnegie and John D. Rockefeller, and donated some of his Microsoft stock in 1994 to create the "William H. Gates Foundation." In 2000, Gates and his wife combined three family foundations and Gates donated stock valued at $5 billion to create the charitable Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, which was identified by the Funds for NGOs company in 2013, as the world's wealthiest charitable foundation, with assets reportedly valued at more than $34.6 billion.[93][94] The foundation allows benefactors to access information that shows how its money is being spent, unlike other major charitable organizations such as the Wellcome Trust.[95][96] Gates, through his foundation, also donated $20 million to Carnegie Mellon University for a new building to be named Gates Center for Computer Science which opened in 2009.[97][98]
Gates has credited the generosity and extensive philanthropy of David Rockefeller as a major influence. Gates and his father met with Rockefeller several times, and their charity work is partly modeled on the Rockefeller family's philanthropic focus, whereby they are interested in tackling the global problems that are ignored by governments and other organizations.[99] As of 2007, Bill and Melinda Gates were the second-most generous philanthropists in America, having given over $28 billion to charity;[100] the couple plan to eventually donate 95% of their wealth to charity.[101]
The foundation is organized into five program areas: Global Development Division, Global Health Division, United States Division, and Global Policy & Advocacy Division. Among others, it supports a wide range of public health projects, granting aid to fight transmissible diseases such AIDS, tuberculosis and malaria, as well as widespread vaccine programs to eradicate polio. It grants funds to learning institutes and libraries and supports scholarships at universities. The foundation established a water, sanitation and hygiene program to provide sustainable sanitation services in poor countries.[102] Its agriculture division supports the International Rice Research Institute in developing Golden Rice, a genetically modified rice variant used to combat vitamin A deficiency.[103] The goal of the foundation is to provide 120 million women and girls, in the poorest countries, with high-quality contraceptive information and services, with the longer-term goal of universal access to voluntary family planning.[104] In 2007, the Los Angeles Times criticized the foundation for investing its assets in companies that have been accused of worsening poverty, pollution and pharmaceutical firms that do not sell to developing countries.[105] Although the foundation announced a review of its investments to assess social responsibility,[106] it was subsequently canceled and upheld its policy of investing for maximum return, while using voting rights to influence company practices.[107]
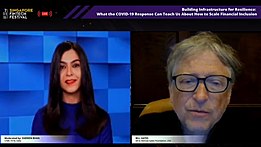
Gates delivered his thoughts in a fireside chat moderated by journalist and news anchor Shereen Bhan virtually at the Singapore FinTech Festival on December 8, 2020 on the topic, “Building Infrastructure for Resilience: What the COVID-19 Response Can Teach Us About How to Scale Financial Inclusion”.[108]
Governments are there to think ahead to bad things that might happen. In the case of (the Covid-19) pandemic, not enough was done. We can't forget that another pandemic will come and we'll need to invest in being ready in that, ......while not forgetting that we were not prepared and we're going to have to invest - just like having a fire department - some money in an intelligent way and actually simulate what might happen and make sure that we're ready for it.[108]
Personal donations
Melinda Gates suggested that people should emulate the philanthropic efforts of the Salwen family, who sold their home and gave away half of its value, as detailed in their book, The Power of Half.[109] Gates and his wife invited Joan Salwen to Seattle to speak about what the family had done, and on December 9, 2010, Bill and Melinda Gates and investor Warren Buffett each signed a commitment they called the "Giving Pledge", which is a commitment by all three to donate at least half of their wealth, over the course of time, to charity.[110][111][112]
Gates has also provided personal donations to educational institutions. In 1999, Gates donated $20 million to the Massachusetts Institute of Technology for the construction of a computer laboratory named the "William H. Gates Building" that was designed by architect Frank Gehry. While Microsoft had previously given financial support to the institution, this was the first personal donation received from Gates.[113]
The Maxwell Dworkin Laboratory of the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences is named after the mothers of both Gates and Microsoft President Steven A. Ballmer, both of whom were students (Ballmer was a member of the School's graduating class of 1977, while Gates left his studies for Microsoft), and donated funds for the laboratory's construction.[114] Gates also donated $6 million to the construction of the Gates Computer Science Building, completed in January 1996, on the campus of Stanford University. The building contains the Computer Science Department and the Computer Systems Laboratory (CSL) of Stanford's Engineering department.[115]
Since 2005, Gates and his foundation have taken an interest in solving global sanitation problems. For example, they announced the "Reinvent the Toilet Challenge", which has received considerable media interest.[116] To raise awareness for the topic of sanitation and possible solutions, Gates drank water that was "produced from human feces" in 2014 – in fact it was produced from a sewage sludge treatment process called the Omni Processor.[117][118] In early 2015, he also appeared with Jimmy Fallon on The Tonight Show and challenged him to see if he could taste the difference between this reclaimed water or bottled water.[119]
In November 2017, Gates said he would give $50 million to the Dementia Discovery Fund, a venture capital that seeks treatment for Alzheimer's disease. He also pledged an additional $50 million to start-up ventures working in Alzheimer's research.[120] Bill and Melinda Gates have said that they intend to leave their three children $10 million each as their inheritance. With only $30 million kept in the family, they are expected to give away about 99.96% of their wealth.[121] On August 25, 2018, Gates distributed $600,000 through his foundation via UNICEF which is helping flood affected victims in Kerala, India.[122]
Charity sports events
On April 29, 2017, Gates partnered with Swiss tennis legend Roger Federer in play in the Match for Africa 4, a noncompetitive tennis match at a sold-out Key Arena in Seattle. The event was in support of Roger Federer Foundation's charity efforts in Africa.[123] Federer and Gates played against John Isner, the top-ranked American player for much of this decade, and Mike McCready, the lead guitarist for Pearl Jam. The pair won the match 6 to 4. Overall, they raised $2 million for children in Africa.[124] The following year, Gates and Federer returned to play in the Match for Africa 5 on March 5, 2018, at San Jose's SAP Center. Their opponents were Jack Sock, one of the top American players and a grand slam winner in doubles, and Savannah Guthrie, a co-anchor for NBC's Today show. Gates and Federer recorded their second match victory together by a score of 6–3 and the event raised over $2.5 million.[125]
Work on energy and climate change
Gates considers climate change and global access to energy to be critical, interrelated issues. He has urged governments and the private sector to invest in research and development to make clean, reliable energy cheaper. Gates envisions that a breakthrough innovation in sustainable energy technology could drive down both greenhouse gas emissions and poverty, and bring economic benefits by stabilizing energy prices.[126] In 2011, he said:
If you gave me the choice between picking the next 10 presidents or ensuring that energy is environmentally friendly and a quarter as costly, I'd pick the energy thing.[127]
In 2015, he wrote about the challenge of transitioning the world's energy system from one based primarily on fossil fuels to one based on sustainable energy sources. Global energy transitions have historically taken decades. He wrote, “I believe we can make this transition faster, both because the pace of innovation is accelerating, and because we have never had such an urgent reason to move from one source of energy to another.”[128] This rapid transition, according to Gates, would depend on increased government funding for basic research and financially risky private-sector investment, to enable innovation in diverse areas such as nuclear energy, grid energy storage to facilitate greater use of solar and wind energy, and solar fuels.[129]
Gates spearheaded two initiatives that he announced at the 2015 United Nations Climate Change Conference in Paris. One was Mission Innovation, in which 20 national governments pledged to double their spending on research and development for carbon-free energy over five years.[126] Another initiative was Breakthrough Energy, a group of investors who agreed to fund high-risk startups in clean energy technologies. Gates, who had already invested $1 billion of his own money in innovative energy startups, committed a further $1 billion to Breakthrough Energy.[129] In December 2020, he called for the U.S. federal government to create institutes for clean energy research, analogous to the National Institutes of Health.[130]
Gates's views have been criticized as undermining strategies to aggressively deploy existing solar and wind energy technologies, which have also led to innovation and to plummeting costs.[131][132] Gates has rejected calls from environmentalists to divest from fossil fuels, saying that doing so would have little impact compared to increasing investment in clean energy innovation.[129] Gates was also criticised for bidding to buy the world's largest private jet operator, Signature Aviation, on the grounds that private jets emit up to 40 times as much carbon dioxide per passenger as commercial jets.[133]
Recognition
- In 1987, Gates was listed as a billionaire in Forbes magazine's 400 Richest People in America issue. He was worth $1.25 billion and was the world's youngest self-made billionaire.[14] Since 1987, Gates has been included in the Forbes The World's Billionaires list and was the wealthiest from 1995 to 1996,[134] 1998 to 2007, 2009, and held the spot until 2018 before being overtaken by Jeff Bezos.[15] Gates was number one on the Forbes 400 list from 1993 through to 2007, 2009, and 2014 through 2017.[135][136]
- Time magazine named Gates one of the 100 people who most influenced the 20th century, as well as one of the 100 most influential people of 2004, 2005, and 2006.
- Time also collectively named Gates, his wife Melinda and U2's lead singer Bono as the 2005 Persons of the Year for their humanitarian efforts.[137] In 2006, he was voted eighth in the list of "Heroes of our time".[138]
- Gates was listed in the Sunday Times power list in 1999, named CEO of the year by Chief Executive Officers magazine in 1994, ranked number one in the "Top 50 Cyber Elite" by Time in 1998, ranked number two in the Upside Elite 100 in 1999, and was included in The Guardian as one of the "Top 100 influential people in media" in 2001.[139]
- Gates was elected Member of the US National Academy of Engineering in 1996 "for contributions to the founding and development of personal computing".[140]
- He was named Honorary Member of the American Library Association in 1998.[141]
- He was elected a foreign member of the Chinese Academy of Engineering in 2017.[142]
- According to Forbes, Gates was ranked as the fourth most powerful person in the world in 2012,[143] up from fifth in 2011.[144]
- In 1994, he was honored as the 20th Distinguished Fellow of the British Computer Society (DFBCS). In 1999, Gates received New York Institute of Technology's President's Medal.[145]
- Gates has received honorary doctorates from Nyenrode Business Universiteit (2003),[146] KTH Royal Institute of Technology (2002),[147] Waseda University (2005),[148] Tsinghua University (2007),[149] Harvard University (2007),[150] the Karolinska Institute (2007),[151] and Cambridge University (2009).[152]
- He was also made an honorary trustee of Peking University in 2007.[153]
- Gates was made an Honorary Knight Commander of the Order of the British Empire (KBE) by Queen Elizabeth II in 2005.[154]
- In January 2006, he was awarded the Grand Cross of the Order of Prince Henry by the President of Portugal Jorge Sampaio
- In November 2006, he was awarded the Placard of the Order of the Aztec Eagle, together with his wife Melinda who was awarded the Insignia of the same order, both for their philanthropic work around the world in the areas of health and education, particularly in Mexico, and specifically in the program "Un país de lectores".[155]
- Gates received the 2010 Bower Award for Business Leadership from The Franklin Institute for his achievements at Microsoft and his philanthropic work.[156]
- Also in 2010, he was honored with the Silver Buffalo Award by the Boy Scouts of America, its highest award for adults, for his service to youth.[157]
- In 2002, Bill and Melinda Gates received the Jefferson Award for Greatest Public Service Benefiting the Disadvantaged.[158]
- He was given the 2006 James C. Morgan Global Humanitarian Award from the Tech Awards.[159]
- In 2015, Gates and his wife Melinda received the Padma Bhushan, India's third-highest civilian award for their social work in the country.[160][161]
- Barack Obama honored Bill and Melinda Gates with the Presidential Medal of Freedom for their philanthropic efforts in 2016,[162] and François Hollande awarded Bill and Melinda in the following year with France's highest national order – as Commander of the Legion of Honour for their charity efforts.[163]
- Entomologists named Bill Gates' flower fly, Eristalis gatesi, in his honor in 1997.[164]
Personal life
.JPG.webp)
Gates married Melinda French on a golf course on the Hawaiian island of Lanai on January 1, 1994. They have three children. The family's residence is an earth-sheltered mansion in the side of a hill overlooking Lake Washington in Medina, Washington. In 2009, property taxes on the mansion were reported to be US$1.063 million, on a total assessed value of US$147.5 million.[165] The 66,000-square-foot (6,100 m2) estate has a 60-foot (18 m) swimming pool with an underwater music system, as well as a 2,500-square-foot (230 m2) gym and a 1,000-square-foot (93 m2) dining room.[166]
In an interview with Rolling Stone, Gates stated in regard to his faith: "The moral systems of religion, I think, are super important. We've raised our kids in a religious way; they've gone to the Catholic church that Melinda goes to and I participate in. I've been very lucky, and therefore I owe it to try and reduce the inequity in the world. And that's kind of a religious belief. I mean, it's at least a moral belief."[167]
Gates also said: "I agree with people like Richard Dawkins that mankind felt the need for creation myths. Before we really began to understand disease and the weather and things like that, we sought false explanations for them. Now science has filled in some of the realm – not all – that religion used to fill. But the mystery and the beauty of the world is overwhelmingly amazing, and there's no scientific explanation of how it came about. To say that it was generated by random numbers, that does seem, you know, sort of an uncharitable view [laughs]. I think it makes sense to believe in God, but exactly what decision in your life you make differently because of it, I don't know."[167]
Gates purchased the Codex Leicester, a collection of scientific writings by Leonardo da Vinci, for US$30.8 million at an auction in 1994.[168] Gates is an avid reader, and the ceiling of his large home library is engraved with a quotation from The Great Gatsby.[169] He also enjoys playing bridge, tennis, and golf.[170][171] Gates's days are planned for him on a minute-by-minute basis, similar to the U.S. President's schedule.[172] Despite his wealth and extensive business travel, Gates flew coach in commercial aircraft until 1997, when he bought a private jet.
.jpg.webp)
In 1999, his wealth briefly surpassed US$101 billion.[173][174] Since 2000, the nominal value of his Microsoft holdings has declined due to a fall in Microsoft's stock price after the dot-com bubble burst and the multi-billion dollar donations he has made to his charitable foundations. In May 2006, Gates remarked that he wished that he were not the richest man in the world because he disliked the attention it brought.[175] In March 2010, Gates was the second wealthiest person behind Carlos Slim, but regained the top position in 2013, according to the Bloomberg Billionaires List.[176][177] Slim retook the position again in June 2014[178][179] (but then lost the top position back to Gates). Between 2009 and 2014, his wealth doubled from US$40 billion to more than US$82 billion.[180] In October 2017, Gates was surpassed by Amazon founder Jeff Bezos as the richest person in the world.[16] On November 15, 2019, he once again became the richest person in the world after a 48% increase in Microsoft shares, surpassing Bezos.[181] Gates told the BBC, "I've paid more tax than any individual ever, and gladly so ... I've paid over $6 billion in taxes."[182] He is a proponent of higher taxes, particularly for the rich.[183]
Gates has held the top spot on the list of The World's Billionaires for 18 out of the past 23 years.[184] Gates has several investments outside Microsoft, which in 2006 paid him a salary of US$616,667 and US$350,000 bonus totalling US$966,667.[185] In 1989, he founded Corbis, a digital imaging company. In 2004, he became a director of Berkshire Hathaway, the investment company headed by long-time friend Warren Buffett.[186]
In 2016, he revealed that he is color-blind.[187]
External business ventures and investments (partial list)
Gates has a multi-billion dollar investment portfolio with stake in various sectors[188] and has participated in several entrepreneurial ventures beyond Microsoft, including:
- AutoNation, automotive retailer that Gates has a 16% stake in trading on the NYSE.
- bgC3, a new think-tank company founded by Gates.
- Canadian National Railway (CN), a Canadian Class I freight railway. As of 2019, Bill Gates is the largest single shareholder of CN stock.[189]
- Cascade Investment LLC, a private investment and holding company incorporated in the United States, founded and controlled by Bill Gates and headquartered in Kirkland, Washington.
- Corbis (originally named Interactive Home Systems and now known as Branded Entertainment Network), a digital image licensing and rights services company founded by Gates.
- EarthNow, Seattle-based startup company aiming to blanket the Earth with live satellite video coverage. Gates is a large financial backer.
- Eclipse Aviation, a defunct manufacturer of very light jets. Gates was a major stake-holder early on in the project.
- Ecolab, global provider of water, hygiene and energy technologies and services to the food, energy, healthcare, industrial and hospitality markets. Gates increased his stake of 10.8% in Ecolab to 25% in 2012.
- ResearchGate, a social networking site for scientists. Gates participated in a $35 million round of financing along with other investors.[190]
- TerraPower, a nuclear reactor design company founded by Gates.
In media
Books
Gates has written three books:
- The Road Ahead, written with Microsoft executive Nathan Myhrvold and journalist Peter Rinearson, was published in November 1995. It summarized the implications of the personal computing revolution and described a future profoundly changed by the arrival of a global information superhighway.
- Business @ the Speed of Thought was published in 1999, and discusses how business and technology are integrated, and shows how digital infrastructures and information networks can help to get an edge on the competition.
- How to Avoid a Climate Disaster, to be published in 2021, Gates shares what he has learned in over a decade of studying climate change and investing in innovations to address climate problems.
Video game
- DONKEY.BAS, is a computer game written in 1981 and included with early versions of the PC DOS operating system distributed with the original IBM PC. It is a driving game in which the player must avoid hitting donkeys. The game was written by Bill Gates and Neil Konzen.[191][192]
Documentary films about Gates
| External video | |
|---|---|
- The Machine That Changed the World (1990)
- Triumph of the Nerds (1996)
- Nerds 2.0.1 (1998)
- Waiting for "Superman" (2010)[194]
- The Virtual Revolution (2010)
- Inside Bill's Brain: Decoding Bill Gates (2019)
Feature films
- 1999: Pirates of Silicon Valley, a film that chronicles the rise of Apple and Microsoft from the early 1970s to 1997. Gates is portrayed by Anthony Michael Hall.
- 2002: Nothing So Strange, a mockumentary featuring Gates as the subject of a modern assassination. Gates briefly appears at the start, played by Steve Sires.
- 2010: The Social Network, a film that chronicles the development of Facebook. Gates is portrayed by Steve Sires.[195]
- 2015: Steve Jobs vs. Bill Gates: The Competition to Control the Personal Computer, 1974–1999: Original film from the National Geographic Channel for the American Genius series.[196]
Video and film clips
.jpg.webp)
- 1983: Steve Jobs hosts Bill Gates in the Macintosh dating game at the Macintosh pre-launch event (with Steve Jobs and Mitch Kapor, references the television show, The Dating Game)
- 2007: Steve Jobs and Bill Gates Together at the D5 Conference, All Things Digital
- 2009− : Bill Gates has given numerous TED talks on current concerns such as innovation, education and fighting global diseases[197]
Radio
Gates was the guest on BBC Radio 4's Desert Island Discs on January 31, 2016, in which he talked about his relationships with his father and Steve Jobs, meeting Melinda Ann French, the start of Microsoft and some of his habits (for example reading The Economist "from cover to cover every week"). His choice of things to take on a desert island were, for music: "Blue Skies" by Willie Nelson; a book: The Better Angels of Our Nature by Steven Pinker; and luxury item: a DVD Collection of Lectures from The Teaching Company.[198]
Television
Gates made a guest appearance as himself on the Emmy Award winning TV show The Big Bang Theory. The episode on which he appeared was appropriately entitled "The Gates Excitation."[199] He also appeared in a cameo role in 2019 on the series finale of Silicon Valley.[200]
See also
Notes
References
- "Forbes profile: Bill Gates". Forbes. Retrieved February 4, 2021.
- Manes 1994, p. 11.
- "Bill Gates (American computer programmer, businessman, and philanthropist)". Archived from the original on March 28, 2013. Retrieved March 20, 2013.
- Sheridan, Patrick (May 2, 2014). "Bill Gates no longer Microsoft's biggest shareholder". CNN Money. Archived from the original on August 20, 2014. Retrieved August 22, 2014.
- MSFT (Holdings), NASDAQ, archived from the original on October 19, 2011, retrieved April 10, 2016
- MSFT (Symbol), NASDAQ, archived from the original on April 8, 2016, retrieved April 10, 2016
- Einstein, David (January 13, 2000). "Gates steps down as Microsoft CEO". forbes.com. Archived from the original on January 26, 2016. Retrieved January 21, 2016.
- Lesinski 2006, p. 96; Manes 1994, p. 459.
- "Microsoft Chairman Gates to leave day-to-day role". money.cnn.com. Archived from the original on January 30, 2016. Retrieved January 21, 2016.
- "Bill Gates | Development of Information and Knowledge Management". tlu.ee. Archived from the original on January 26, 2016. Retrieved January 21, 2016.
- "Bill Gates steps down as chairman, will assist new CEO as 'technology advisor'". The Verge. Archived from the original on February 4, 2014. Retrieved February 4, 2014.
- Haselton, Todd (March 13, 2020). "Bill Gates leaves Microsoft board". CNBC. Retrieved March 13, 2020.
- "Why Putin Isn't on 'Forbes' Billionaires List". Newsweek. Archived from the original on October 20, 2017.
- Thibault, Marie (January 19, 2010). "The Next Bill Gates". Forbes. Archived from the original on July 19, 2012. Retrieved December 20, 2010.
- "Billionaires #2 Bill Gates". Forbes. March 5, 2019. Retrieved April 5, 2020.
- "Amazon CEO Jeff Bezos Is The Richest Person In The World-Again". Forbes. Archived from the original on March 11, 2018.
- Desjardins, Jeff (January 7, 2021). "Elon Musk is the World's Richest Person in 2021". Visual Capitalist. Retrieved January 27, 2021.
- Neate, Rupert (August 15, 2017). "Bill Gates gives $4.6bn to charity in biggest donation since 2000". The Guardian. London. Retrieved April 10, 2018.
- "The $600 billion challenge". Fortune. Archived from the original on March 16, 2017. Retrieved April 16, 2017.
- "Mary Gates, 64; Helped Her Son Start Microsoft". The New York Times. Associated Press. June 11, 1994. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved April 3, 2020.
- "Microsoft founder Bill Gates has Yorkshire roots" The Telegraph" 23 June 2020.
- Manes 1994, p. 15.
- Leibovich, Mark (December 31, 2000). "Alter Egos". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on December 25, 2016. Retrieved June 24, 2019.
- Lange, Greg; Stein, Alan (February 14, 1999). "Tornado with 100-m.p.h. winds hits Seattle and Juanita on September 28, 1962". HistoryLink. Retrieved December 18, 2018.
- Manes 1994, p. 47.
- Lesinski, Jeanne M (2008). Bill Gates: Entrepreneur and Philanthropist. Twenty First Century Books. p. 12. ISBN 978-1580135702. Retrieved March 10, 2011.
- Lowe, Janet (2001). Bill Gates Speaks: Insight from the World's Greatest Entrepreneur. Wiley. ISBN 978-0471401698. Retrieved March 10, 2011.
- Berkowitz, Edward D (2006). Something Happened: A Political and Cultural Overview of the Seventies. Columbia University Press. p. 228. ISBN 978-0231124942. Retrieved March 10, 2011.
- Cringely, Robert X. (June 1996). "Part II". Triumph of the Nerds: The Rise of Accidental Empires. Season 1. PBS. Archived from the original on August 13, 2017.
- Manes 1994, p. 24.
- Soundaian, S. (June 10, 2019). New Dimensions of Management. MJP Publisher.
- "Bill Gates | American computer programmer, businessman, and philanthropist". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved December 7, 2018.
- Manes 1994, p. 27.
- Gates 1996, p. 12.
- Manes 1994, p. 34.
- Gates 1996, p. 14.
- Michael A. Schuman (2008). Bill Gates: Computer Mogul and Philanthropist. Enslow Publishers, Inc. p. 34. ISBN 978-0766026933.
- Marcie Sims (2018). Capitol Hill Pages: Young Witnesses to 200 Years of History. McFarland. p. 196. ISBN 978-1476669724.
- "National Merit Scholarship Corporation – Scholars You May Know". nationalmerit.org. Archived from the original on February 28, 2016. Retrieved October 25, 2015.
- "The new – and improved? – SAT". The Week Magazine. Archived from the original on May 10, 2006. Retrieved May 23, 2006.
- Gates 1996, p. 15.
- "Timeline: Bill Gates: 1973; from google (bill gates major in harvard) result 3". Archived from the original on October 5, 2015.
- Michael Hitt; R. Duane Ireland; Robert Hoskisson (2012). Strategic Management: Concepts and Cases: Competitiveness and Globalization. p. 263. ISBN 978-1111825874. Archived from the original on September 15, 2015. Retrieved October 25, 2015.
- Mejia, Zameena (April 29, 2018). "The No. 1 thing Bill Gates wishes he'd done in college". CNBC. Retrieved April 3, 2020.
- Kestenbaum, David (July 4, 2008). "Before Microsoft, Gates Solved A Pancake Problem". National Public Radio. Archived from the original on September 19, 2011.
- "UT Dallas Team Bests Young Bill Gates With Improved Answer to So-Called Pancake Problem in Mathematics". University of Texas at Dallas. September 17, 2008. Archived from the original on August 26, 2010.
- Gates, William; Papadimitriou, Christos (1979). "Bounds for sorting by prefix reversal". Discrete Mathematics. 27: 47–57. doi:10.1016/0012-365X(79)90068-2.
- Wallace 1993, p. 59.
- Gates 1996, p. 18.
- Gates 1996, p. 19.
- The History of Microsoft – 1976 Archived February 11, 2017, at the Wayback Machine: Bill Gates explaining that his departure from Harvard was reversible if Microsoft had failed.
- "Microsoft Visitor Center Student Information: Key Events in Microsoft History". Microsoft. Archived from the original (.DOC) on February 26, 2008. Retrieved February 18, 2008. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - "Microsoft history". The History of Computing Project. Archived from the original on May 14, 2008. Retrieved March 31, 2008.
- Manes 1994, p. 81.
- Gates, William 'Bill' (October 13, 2005). Remarks (Speech). Waterloo, ON. Archived from the original on April 6, 2008. Retrieved March 31, 2008.
- Bunnell, David (February–March 1982). "The Man Behind The Machine?". PC Magazine (interview). p. 16. Archived from the original on May 9, 2013. Retrieved February 17, 2012.
- Gordon, John Steele; Maiello, Michael (December 23, 2002). "Pioneers Die Broke". Forbes. Archived from the original on October 29, 2006. Retrieved March 31, 2008.
- "Father of DOS". Paterson Technology. Archived from the original on September 6, 2019. Retrieved October 13, 2019.
- "The Roots of DOS". Paterson Technology. Archived from the original on September 6, 2019. Retrieved October 13, 2019.
- Gates 1996, p. 54.
- Manes 1994, p. 193.
- Paul Allen (May 2011). "Microsoft's Odd Couple". Vanity Fair. Retrieved November 11, 2019.
- Detrick, Hallie (October 16, 2018). "Bill Gates Mourns His Microsoft Co-Founder Paul Allen: 'Personal Computing Would Not Have Existed Without Him'". Fortune. Retrieved November 11, 2019.
- "Challenges and Strategy" (PDF). Groklaw. Retrieved November 17, 2011.
- Freiberger, Paul (August 31, 1981). "Bugs in Radio Shack TRS-80 Model III: How Bad Are They?". InfoWorld. p. 49. Archived from the original on September 2, 2016. Retrieved February 28, 2011.
- Thorlin, Fred (April 2000). "Fred Thorlin: The Big Boss at Atari Program Exchange" (Interview). Interviewed by Kevin Savetz. Atari archives. Archived from the original on January 1, 2013. Retrieved December 6, 2012.
- Rensin, David (1994). "The Bill Gates Interview". Playboy.
- Ballmer, Steve (October 9, 1997). "Steve Ballmer Speech Transcript – Church Hill Club". Microsoft. Archived from the original on April 20, 2008. Retrieved March 31, 2008.
- Isaacson, Walter (January 13, 1997). "The Gates Operating System". Time. Archived from the original on June 19, 2000. Retrieved March 31, 2008.
- Bank, David (February 1, 1999). "Breaking Windows". The Wall Street Journal. Archived from the original on April 16, 2016. Retrieved March 31, 2008.
- Chapman, Glenn (June 27, 2008). "Bill Gates Signs Off". Agence France-Presse. Archived from the original on June 30, 2008.
- Gates, Bill (September 26, 1997). Remarks by Bill Gates (Speech). San Diego. Archived from the original on April 20, 2008. Retrieved March 31, 2008.
- Herbold, Robert (2004). The Fiefdom Syndrome: The Turf Battles That Undermine Careers and Companies – And How to Overcome Them. ISBN 0-385-51067-5.
- Gates, Bill. "Bill Gates Interview". Transcript of a Video History Interview / Computer History Collection (Interview). Interviewed by David Allison. National Museum of American History, Smithsonian Institution. Archived from the original on April 2, 2013. Retrieved April 10, 2013.
- Pournelle, Jerry (September 1985). "PCs, Peripherals, Programs, and People". BYTE. p. 347. Retrieved March 20, 2016.
- "Microsoft Announces Plans for July 2008 Transition for Bill Gates". Microsoft. June 15, 2006. Archived from the original on June 19, 2006.
- Wasserman, Elizabeth (November 17, 1998). "Gates deposition makes judge laugh in court". CNN. Archived from the original on April 7, 2013. Retrieved April 10, 2013.
- "Microsoft's Teflon Bill". BusinessWeek. November 30, 1998. Archived from the original on April 7, 2008. Retrieved March 30, 2008.
- Heilemann, John (November 1, 2000). "The Truth, The Whole Truth, and Nothing But The Truth". Wired. 8 (11). Archived from the original on May 28, 2014. Retrieved March 31, 2008.
- Matthew G. Miller; Peter Newcomb (January 2, 2014). "Billionaires Worth $3.7 Trillion Surge as Gates Wins 2013". Bloomberg Businessweek. Archived from the original on January 3, 2014. Retrieved January 3, 2014.
- "Microsoft names Satya Nadella to replace Steve Ballmer". BBC News. February 4, 2014. Archived from the original on February 4, 2014. Retrieved February 4, 2014.
- Jeff Goodell (March 13, 2014). "Bill Gates: The Rolling Stone Interview". Rolling Stone. Jann S. Wenner. Archived from the original on March 17, 2014. Retrieved March 28, 2014.
- Mack, Eric (January 28, 2015). "Bill Gates Says You Should Worry About Artificial Intelligence". Forbes. Archived from the original on February 19, 2015. Retrieved February 19, 2015.
- Lumby, Andrew (January 28, 2015). "Bill Gates Is Worried About the Rise of the Machines". The Fiscal Times. Archived from the original on February 19, 2015. Retrieved February 19, 2015.
- Holley, Peter (March 24, 2015). "Apple co-founder on artificial intelligence: 'The future is scary and very bad for people'". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on April 17, 2015. Retrieved April 8, 2015.
- "Permalink to an answer from "Hi Reddit, I'm Bill Gates and I'm back for my third AMA. Ask me anything. • /r/IAmA"". reddit. Retrieved June 10, 2015.
- "Baidu CEO Robin Li interviews Bill Gates and Elon Musk at the Boao Forum, March 29, 2015". YouTube. Archived from the original on May 1, 2015. Retrieved April 8, 2015.
- Gates, Bill. "The next outbreak? We're not ready". TED. Retrieved June 8, 2020.
- (March 31, 2018), "Saudi Crown Prince and Bill Gates review joint development projects" Al Arabiya
- Michael Idato (April 4, 2018), "Prince Mohammed books out hotel to dine with Murdoch" The Sydney Morning Herald
- Scipioni, Jade (June 24, 2019). "Bill Gates reveals his 'greatest mistake' that potentially cost Microsoft $400 billion". CNBC. Retrieved December 22, 2019.
- "Advisory Board | Bloomberg New Economy Forum | Bloomberg L.P."
- "Gates foundation". Archived from the original on May 23, 2012.
- Robin Toal (September 16, 2013). "The Top Ten US Charitable Foundations". Funds For NGOs. Funds For NGOs, LLC. Archived from the original on April 7, 2014. Retrieved April 6, 2014.
- Cronin, Jon (January 25, 2005). "Bill Gates: billionaire philanthropist". BBC News. Archived from the original on October 15, 2007. Retrieved April 1, 2008.
- "Our Approach to Giving". Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation. Archived from the original on April 4, 2008. Retrieved April 1, 2008.
- "Bill Gates – Carnegie Mellon University". Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation. Retrieved January 27, 2019.
- University, Carnegie Mellon. "Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation Builds Carnegie Mellon's Home for Computer Science". cmu.edu. Retrieved January 27, 2019.
- "2005 Annual Report" (PDF). Rockefeller Brothers Fund. January 1, 2006. Archived from the original (PDF) on February 16, 2008. Retrieved February 14, 2008. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - "The 50 most generous Americans". Archived from the original on February 22, 2012.
- "Bill and Melinda Gates give 95% of wealth to charity". BBC News. October 18, 2010. Archived from the original on October 13, 2011.
- "What We Do". Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation. Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation. 2014. Archived from the original on April 3, 2014. Retrieved April 6, 2014.
- "Agricultural Development Golden Rice". Archived from the original on February 3, 2016. Retrieved February 3, 2016.
- "Family Planning". www.gatesfoundation.org. January 1, 2001.
- "Dark cloud over good works of Gates Foundation". Los Angeles Times. January 7, 2007. Archived from the original on September 19, 2008., Los Angeles Times, January 7, 2006.
- Heim, Kristi (January 10, 2007). "Gates Foundation to review investments". The Seattle Times. Archived from the original on May 16, 2007., The Seattle Times, January 10, 2007.
- Piller, Charles (January 14, 2007). "Gates Foundation to keep its investment approach". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved October 19, 2020.
- "Pandemic, though terrible, helped push digital financial revolution: Bill Gates". Business Times (Singapore). December 8, 2020. Retrieved December 9, 2020.
- Bina Abraham (October 1, 2010). "They half it in them". Gulf News. Archived from the original on January 21, 2011. Retrieved March 17, 2011.
- Moss, Rosabeth (December 14, 2010). "Four Strategic Generosity Lessons". Business Week. Archived from the original on February 25, 2011. Retrieved March 9, 2011.
- "40 billionaires pledge to give away half of wealth". Retrieved August 8, 2010.
- Robyn Griggs Lawrence (February 22, 2011). "A Rich Gift: Homemade Jelly for Bill and Melinda Gates". Mother Earth News. Archived from the original on February 24, 2011. Retrieved March 10, 2011.
- Matthew G.H. Chun (April 14, 1999). "Bill Gates Donates $20 million to MIT". The Harvard Crimson. The Harvard Crimson, Inc. Archived from the original on April 7, 2014. Retrieved April 6, 2014.
- "Our Campus – Teaching, research, and administrative spaces". Harvard School of Engineering and Applied Sciences. President and Fellows of Harvard College. 2014. Archived from the original on April 7, 2014. Retrieved April 6, 2014.
- "Gates Computer Science Building". Stanford Engineering. Stanford University. 2014. Archived from the original on April 1, 2014. Retrieved April 6, 2014.
- Kass, Jason (November 18, 2013). "Bill Gates Can't Build a Toilet". New York Times Opinion Pages. New York Times. Archived from the original on March 25, 2015. Retrieved March 24, 2015.
- "BBC news article "Bill Gates drinks water distilled from human faeces"". BBC News. January 7, 2015. Archived from the original on January 11, 2015. Retrieved January 11, 2015.
- "From poop to portable, This Ingenious Machine Turns Feces into Drinking Water". gatesnotes, The Blog of Bill Gates. January 5, 2015. Archived from the original on January 13, 2015. Retrieved January 13, 2015.
- "Bill Gates and Jimmy Drink Poop Water". Youtube Channel of The Tonight Show Starring Jimmy Fallon. January 22, 2015. Archived from the original on May 7, 2015.
- "Bill Gates makes $100 million personal investment to fight Alzheimer's". Reuters. November 13, 2017. Archived from the original on November 13, 2017. Retrieved November 13, 2017.
- "Briefly Noted | Excellence in Philanthropy | The Philanthropy Roundtable". philanthropyroundtable.org. Archived from the original on February 11, 2016. Retrieved March 10, 2016.
- "Bill Gates follows Thalapathy Vijay's unique way to help Kerala flood victims – Tamil Movie News". IndiaGlitz.com. Retrieved August 25, 2018.
- "Live blog: Bill Gates and Roger Federer play tennis for charity in Seattle". April 30, 2017. Archived from the original on May 1, 2017.
- "Match For Africa 4 a Huge Hit for Federer's Foundation". Tennis.com. Retrieved May 16, 2018.
- "Roger Federer's Match For Africa Raises More Than $2.5 Million". Tennis.com. Retrieved May 16, 2018.
- Wattles, Jackie (November 11, 2015). "Bill Gates launches multi-billion dollar clean energy fund". CNN Money. Retrieved December 12, 2020.
- "Q&A: Bill Gates on the World's Energy Crisis". WIRED. 19 (7). June 20, 2011. Retrieved October 2, 2019.
- Gates, Bill (November 30, 2015). "Energy Innovation: Why We Need It and How to Get It". Gates Notes. Retrieved December 12, 2020.
- Thornhill, John; Adams, Christopher (June 25, 2015). "Gates to double investment in renewable energy projects". Financial Times. Retrieved December 12, 2020.
- Schlosser, Kurt (December 3, 2020). "Bill Gates calls for creation of National Institutes of Energy Innovation to better address climate change". GeekWire. Retrieved December 12, 2020.
- Romm, Joe (February 23, 2016). "No Bill Gates, We Don't Need 'Energy Miracles' To Solve Climate Change". Thinkprogress.com. Retrieved December 12, 2020.
- Revkin, Andrew C. (February 23, 2016). "Opinion | Bill Gates's Clean-Energy Moon Shot". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved December 12, 2020.
- "Bill Gates joins Blackstone in bid to buy British private jet services firm". the Guardian. January 9, 2021. Retrieved February 2, 2021.
- see Forbes World's Richest People 1996, 1997, and 1998
- Wahba, Phil (September 17, 2008). "Bill Gates tops US wealth list 15 years continuously". Reuters. Archived from the original on December 18, 2008. Retrieved November 6, 2008.
- Kirsch, Noah. "Here's Why Jeff Bezos Is Not Truly The Richest Person In History". Forbes. Archived from the original on January 11, 2018. Retrieved January 11, 2018.
- Lesinski 2006, p. 102
- Cowley, Jason (June 22, 2006). "Heroes of our time – the top 50". New Statesman. UK. Archived from the original on December 31, 2007. Retrieved February 17, 2008.
- "Gates 'second only to Blair'". BBC News. September 26, 1999. Archived from the original on December 29, 2008. Retrieved March 30, 2008.
- "Mr. William H. Gates, III". National Academy of Engineering. Retrieved June 12, 2019.
- American Library Association. Honorary Membership.
- Xiang, Bo (November 27, 2017). "Bill Gates elected to Chinese Academy of Engineering". Xinhua. Retrieved June 10, 2019.
- "The World's Most Powerful People". Forbes. December 5, 2012. Archived from the original on December 30, 2012. Retrieved June 30, 2013.
- "The World's Most Powerful People". Forbes. November 2, 2011. Archived from the original on November 3, 2011. Retrieved June 30, 2013.
- "Bill Gates Speaks of Opportunities and Challenges Facing "Generation I"". News Center. Microsoft. October 28, 1999. Archived from the original on December 31, 2015. Retrieved October 25, 2015.
- "Eredoctoraat Universiteit Nyenrode voor Wim Kok" (Press release) (in Dutch). Nyenrode Business Universiteit. August 13, 2003. Archived from the original on February 18, 2008. Retrieved February 18, 2008.
- "Honorary doctors at KTH". About KTH. Stockholm: KTH Royal Institute of Technology. Archived from the original on April 17, 2015. Retrieved January 19, 2015.
- History of the University - website of the Waseda University
- "Bill Gates Awarded Honorary Doctorate of Tsinghua". Tsinghua University. April 19, 2007. Archived from the original on July 7, 2011. Retrieved June 9, 2010.
- Hughes, Gina (June 8, 2007). "Bill Gates Gets Degree After 30 Years". Yahoo!. Archived from the original on December 27, 2007. Retrieved February 18, 2008.
- "Karolinska Institutet Medicine hedersdoktorer 1910‐2013" [Honorary doctors of medicine at the Karolinska Institute 1910–2013] (PDF) (in Swedish). Karolinska Institutet. May 22, 2013. Archived (PDF) from the original on May 1, 2015. Retrieved January 19, 2015.
- University of Cambridge (June 12, 2009). "The Chancellor in Cambridge to confer Honorary Degrees". University of Cambridge. Archived from the original on August 17, 2009. Retrieved August 20, 2009.
- Blakely, Rhys (July 18, 2007). "Gates how piracy worked for me in China". The Times. London. Archived from the original on June 11, 2011. Retrieved April 26, 2010.
- "Knighthood for Microsoft's Gates". BBC News. March 2, 2005. Archived from the original on March 9, 2008. Retrieved February 18, 2008.
- "Proclamation of the Award". Diario Oficial de la Federación. Archived from the original on March 6, 2008. Retrieved March 30, 2008.
- "Bower Award for Business Leadership". The Franklin Institute. 2010. Archived from the original on July 26, 2010. Retrieved June 30, 2013.
- "2010 Silver Buffalo Recipients". Scouting: 39. September–October 2010.
- National Winners | public service awards Archived November 24, 2010, at the Wayback Machine. Jefferson Awards.org. Retrieved on September 4, 2013.
- "The 2006 James C. Morgan Global Humanitarian Award". The Tech Museum of Innovation. Archived from the original on April 2, 2014. Retrieved April 2, 2014.
- "Padma Awards – Press Information Board of India". Ministry of Home Affairs, India. Archived from the original on January 28, 2015.
- "Padma awards 2015 announced: Advani, Amitabh among 104 awardees". Zee News. January 25, 2015.
- "President Obama Names Recipients of the Presidential Medal of Freedom". whitehouse.gov. The White House. November 16, 2016. Archived from the original on November 22, 2016. Retrieved November 16, 2016.
- Ambassade de France aux Etats-Unis – Washington, D.C. (April 21, 2017). "Bill et Melinda Gates décorés de la Légion d'Honneur" [Bill and Melinda Gates awarded the Legion of Honor]. France in the United States / Embassy of France in Washington, D.C. (in French). Archived from the original on March 15, 2018. Retrieved March 15, 2018.
- Thompson, F. Christian (August 19, 1999). "Bill Gates' Flower Fly Eristalis gatesi Thompson". The Diptera Site. Archived from the original on February 12, 2008. Retrieved February 18, 2008.
- Anderson, Rick (May 16, 2008). "Taxman Cometh". Seattle Weekly. Archived from the original on April 17, 2013.
- "coverage of the Gates' Medina, Washington estate". Forbes. May 22, 2002. Archived from the original on March 26, 2010. Retrieved June 9, 2010.
- Goodell, Jeff (March 27, 2014). "Bill Gates: The Rolling Stone Interview". Rolling Stone. Archived from the original on May 9, 2014. Retrieved April 14, 2014.
- Lesinski 2006, p. 74
- Paterson, Thane (June 13, 2000). ""He had come a long way to this blue lawn and his dream must have seemed so close he could hardly fail to grasp it"-FSF (Advice for Bill Gates: A Little Culture Wouldn't Hurt)". Business Week. Archived from the original on May 1, 2008. Retrieved April 28, 2008.
- "Bill Gates: Chairman". Microsoft Corporation. 2008. Archived from the original on August 28, 2008.
- "Profile: Bill Gates". BBC news. January 26, 2004. Archived from the original on February 1, 2009. Retrieved January 1, 2010.
- Mary Riddell (October 21, 2016). "Bill Gates: He eats Big Macs for lunch and schedules every minute of his day – meet the man worth $80 billion". The Telegraph. Archived from the original on October 24, 2016. Retrieved October 24, 2016.
- Fridson 2001, p. 113
- Zuckerman, Laurence (October 27, 1997). "New Jet Eases Travel Hassles For Bill Gates". The New York Times. Archived from the original on September 5, 2012. Retrieved September 2, 2012.
- Bolger, Joe (May 5, 2006). "I wish I was not the richest man in the world, says Bill Gates". The Times. UK. Archived from the original on September 23, 2008. Retrieved March 31, 2008.
- Cuadros, Alex; Harrison, Crayton (May 17, 2013). "Bill Gates Retakes World's Richest Title From Carlos Slim". Forbes. Archived from the original on September 24, 2010. Retrieved May 30, 2013.
- "Bill Gates regains world's richest man title: Forbes". The Times of India. March 3, 2014. Archived from the original on September 14, 2016.
- "Forbes Billionaires list". Archived from the original on December 3, 2011.
- Estevez, Dolia (June 7, 2014). "Mexico's Carlos Slim Reclaims World's Richest Man Title From Bill Gates". Forbes. Archived from the original on September 1, 2014. Retrieved September 1, 2014.
- "The World's Billionaires". Forbes. Archived from the original on November 29, 2014. Retrieved November 30, 2014.
- Feuerherd, Ben (November 16, 2019). "Bill Gates regains spot as world's richest person over Jeff Bezos". New York Post. Retrieved November 19, 2019.
- "Newsnight Interview". BBC. January 24, 2014. Archived from the original on August 23, 2017. Retrieved August 23, 2017.
- "US Should Pay More Tax". ABC. May 28, 2013. Archived from the original on July 7, 2017. Retrieved August 23, 2017.
- "Bill Gates". Forbes. Archived from the original on September 24, 2010. Retrieved August 25, 2017.
- "Microsoft 2006 Proxy Statement". Microsoft. October 6, 2007. Archived from the original on February 19, 2008. Retrieved February 14, 2008.
- Fried, Ina (December 14, 2004). "Gates joins board of Buffett's Berkshire Hathaway". CNET. Archived from the original on September 8, 2012. Retrieved March 31, 2008.
- Alex Osborn (February 18, 2016). "This Was Bill Gates' Favorite XBLA Game". IGN. Ziff Davis. Archived from the original on February 19, 2016.
- Edwards, John (June 25, 2019). "This is What Bill Gates's Portfolio Looks Like". Investopedia. Retrieved November 17, 2019.
- "Bill Gates now biggest CN shareholder (CA;CNR)". CBC News. April 25, 2011. Retrieved November 17, 2019.
- Levy, Jared Ari (June 4, 2013). "Bill Gates Joins $35 Million Funding in Startup ResearchGate". Bloomberg. Archived from the original on January 9, 2015. Retrieved January 28, 2015.
- Bill Gates Speech Transcript - Tech Ed 2001 Archived 2012-02-13 at the Wayback Machine
- Donkey - Folklore.org
- "Machine That Changed The World, The; Interview with Bill Gates, 1990 (raw video)". WGBH Open Vault. 1990. Archived from the original on October 14, 2016. Retrieved September 19, 2016.
- "Bill Gates Goes to Sundance, Offers an Education". ABC News. January 23, 2010. Archived from the original on January 28, 2010.
- Cohen, Lindsay. "'Bogus Bill' has a blast playing billionaire in 'The Social Network'". KVAL 13. Archived from the original on July 30, 2015. Retrieved October 25, 2015.
- "American Genius". Archived from the original on September 10, 2015. Retrieved September 10, 2015.
- "Bill Gates' TED talks". TED.com. Retrieved July 2, 2020.
- "BBC Radio 4 – Desert Island Discs, Bill Gates". BBC. Archived from the original on March 20, 2016. Retrieved March 29, 2016.
- Lerman, Rachel (March 27, 2018). "Bill Gates to guest star on geeky 'The Big Bang Theory'". The Seattle Times. Retrieved February 25, 2019.
- "'Big fan' Bill Gates makes appearance in 'Silicon Valley' series finale as HBO comedy logs off". December 9, 2019.
Sources
- Fridson, Martin (2001). How to Be a Billionaire: Proven Strategies from the Titans of Wealth. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 0-471-41617-7.
- Gates, Bill (1996). The Road Ahead. Penguin Books. ISBN 0-14-026040-4.
- Lesinski, Jeanne M. (2006). Bill Gates (biography). A&E Television Networks. ISBN 0-8225-7027-0.
- Manes, Stephen (1994). Gates: How Microsoft's Mogul Reinvented an Industry and Made Himself The Richest Man in America. Touchstone Pictures. ISBN 0-671-88074-8.
- Wallace, James (1993). Hard Drive: Bill Gates and the Making of the Microsoft Empire. New York City: HarperCollins Publishers. ISBN 0-471-56886-4.
Further reading
- Leibovich, Mark. The New Imperialists (Prentice Hall, 2002) pp 139–182. online
- Bank, David (2001). Breaking Windows: how Bill Gates fumbled the future of Microsoft. New York City: Free Press. ISBN 0-7432-0315-1.
- Rivlin, Gary (1999). The plot to get Bill Gates: an irreverent investigation of the world's richest man... and the people who hate him. New York City: Times Business. ISBN 0-8129-3006-1.
- "83 Reasons Why Bill Gates's Reign Is Over". Wired. 6 (12). December 1998. Archived from the original on August 22, 2010.
- Kildall, Gary (October 25, 2004). "The Man Who Could Have Been Bill Gates". Bloomberg BusinessWeek. Archived from the original on April 4, 2006. Retrieved June 9, 2010.
- "The Meaning of Bill Gates: As his reign at Microsoft comes to an end, so does the era he dominated", The Economist, June 28, 2008.
- Wallace, James. Overdrive: Bill Gates and the race to control cyberspace (John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 1997).
Primary sources
- Gates, Bill. "An exclusive interview with Bill Gates." Financial Times 1 (2013). online
- Gates, Bill. "Remarks of Bill Gates, Harvard Commencement 2007." Harvard Gazette 7 (2007). online
- Kinsley, Michael, and Conor Clarke, eds. Creative capitalism: A conversation with Bill Gates, Warren Buffett, and other economic leaders (Simon and Schuster, 2009).
