Gulf of Oman
The Gulf of Oman or Sea of Oman (Gulf of Makran or Sea of Makran) (Arabic: خليج عمان ، خلیج مکران khalīj ʿumān , khalīj makrān; Persian: دریای عمان ، دریای مکران daryâ-ye omân ,daryâ-ye makrān) is a gulf that connects the Arabian Sea with the Strait of Hormuz, which then runs to the Persian Gulf. It borders Iran and Pakistan on the north, Oman on the south, and the United Arab Emirates on the west And in some countries it is known as Makran Sea.
| Gulf of Oman | |
|---|---|
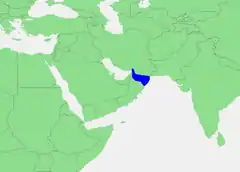 | |
| Coordinates | 25°N 58°E |
| Type | Sea |
| Part of | Indian Ocean |
| Basin countries | Iran, Oman, Pakistan, and United Arab Emirates |
| Max. width | 340 km (210 mi) |
| Surface area | 181,000 km2 (70,000 sq mi) |
| Max. depth | 3,400 m (11,200 ft) |

_-_Harry_S._Truman_(CVN-75)_and_Cavour_(550)_underway_in_2013.JPG.webp)
Extent
The International Hydrographic Organization defines the limits of the Gulf of Oman as follows:[1]
- On the Northwest: A line joining Ràs Limah (25°57'N) on the coast of Arabia and Ràs al Kuh (25°48'N) on the coast of Iran (Persia).
- On the Southeast: The Northern limit of the Arabian Sea [A line joining Ràs al Hadd, East point of Arabia (22°32'N) and Ràs Jiyùni (61°43'E) on the coast of Pakistan].
Exclusive economic zone
Exclusive economic zones in Persian Gulf:[2][3][4][5][6][7]
| Number | Country | Area (Km2) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 108,779 | |
| 2 | 65,850 | |
| 3 | 4,371 | |
| 4 | 2,000 | |
| Total | Persian Gulf | 181,000 |
Border and Basin countries
Coastline length:
 Iran - 850 km Coastline
Iran - 850 km Coastline Oman - 750 km Coastline
Oman - 750 km Coastline United Arab Emirates - 50 km Coastline
United Arab Emirates - 50 km Coastline Pakistan - 50 km Coastline
Pakistan - 50 km Coastline
Alternative names
Gulf of Oman historically and geographically has been referred to with different names by Arabian, Iranian, Indian, Pakistani and European geographers and travelers, including Makran Sea and Akhzar Sea.[8][9]
- Makran Sea
- Akhzar Sea
- Persian Sea (Consist of whole of Persian gulf and gulf of Oman)
Until 18th Century it was known as Makran Sea and is also visible on historical maps and museums.
Major ports
- Port of Fujairah, Fujairah, United Arab Emirates
- Khor Fakkan Container Terminal, Khor Fakkan, United Arab Emirates
- Port of Chabahar, Chabahar, Iran
- Port Sultan Qaboos, Muttrah, Oman
International trade
The area is near the Strait of Hormuz, a strategic route through which a third of the world's liquefied natural gas and 20% of global oil consumption passes from Middle East producers.[10]
Ecology
In 2018, scientists confirmed the Gulf of Oman contains one of the world's largest marine dead zones, where the ocean contains little or no oxygen and marine wildlife cannot exist. The dead zone encompasses nearly the entire 165,000-square-kilometre (63,700 sq mi) Gulf of Oman, equivalent to the size of Florida, United States of America. The cause is a combination of increased ocean warming and increased runoff of nitrogen and phosphorus from fertilizers.[11]
See also
- Strait of Hormuz
- Persian Gulf
- Eastern Arabia
- Musandam Peninsula
- History of the United Arab Emirates#The pearling industry and the Portuguese empire: 16th - 18th century
- Saeed bin Butti#Perpetual Maritime Truce
- Trucial States
- Sultan bin Saqr Al Qasimi#Perpetual Maritime Truce of 1853
- Persian Gulf campaign of 1809
- Persian Gulf campaign of 1819
- General Maritime Treaty of 1820
- May 2019 Gulf of Oman incident
- June 2019 Gulf of Oman incident
- Geography of Oman
- Geography of Iran
- Geography of United Arab Emirates
- Geography of Pakistan
 Oceans portal
Oceans portal
References
- "Limits of Oceans and Seas, 3rd edition" (PDF). International Hydrographic Organization. 1953. Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 October 2011. Retrieved 28 December 2020.
- "Sea Around Us | Fisheries, Ecosystems and Biodiversity". www.seaaroundus.org.
- "Sea Around Us | Fisheries, Ecosystems and Biodiversity". www.seaaroundus.org.
- "Sea Around Us | Fisheries, Ecosystems and Biodiversity". www.seaaroundus.org.
- "Sea Around Us | Fisheries, Ecosystems and Biodiversity". www.seaaroundus.org.
- "Sea Around Us | Fisheries, Ecosystems and Biodiversity". www.seaaroundus.org.
- "Sea Around Us | Fisheries, Ecosystems and Biodiversity". www.seaaroundus.org.
- "Makran Sea/Gulf of Oman|Mokran Sea or Gulf of Oman, Persian Gulf, Pars sea". www.persiangulfstudies.com.
- Nicolini, Beatrice (1 January 2004). Makran, Oman, and Zanzibar: Three-Terminal Cultural Corridor in the Western Indian Ocean, 1799-1856. BRILL. ISBN 9004137807 – via Google Books.
- "2 oil tankers were damaged in possible attacks in the Gulf of Oman". Vox. 13 June 2019.
- "Scientists Confirm Florida-Sized Dead Zone in the Gulf of Oman". Yale Environment 360. 30 April 2018. Retrieved 30 April 2018.
Further reading
- "The Book of Duarte Barbosa" by Duarte Barbosa, Mansel Longworth Dames. 1989. p. 79. ISBN 81-206-0451-2
- "The Natural History of Pliny". by Pliny, Henry Thomas Riley, John Bostock. 1855. p. 117
- "The Countries and Tribes of the Persian Gulf" by Samuel Barrett Miles - 1966. p. 148
- "The Life & Strange Surprising Adventures of Robinson Crusoe of York, Mariner". by Daniel Defoe. 1895. p. 279
- "The Outline of History: Being a Plain History of Life and Mankind". by Herbert George Well. 1920. p. 379.
- "The New Schaff-Herzog Encyclopedia of Religious Knowledge" by Johann Jakob Herzog, Philip Schaff, Albert Hauck. 1910. p. 242