Sulu Sea
The Sulu Sea (Filipino: Dagat Sulu; Tausug: Dagat sin Sūg; Chavacano: Mar de Sulu; Cebuano: Dagat sa Sulu; Hiligaynon: Dagat sang Sulu; Karay-a: Dagat kang Sulu; Cuyonon: Dagat i'ang Sulu; Malay: Laut Sulu) is a body of water in the southwestern area of the Philippines, separated from the South China Sea in the northwest by Palawan[1] and from the Celebes Sea in the southeast by the Sulu Archipelago.[2] Borneo is found to the southwest and Visayas to the northeast.
| Sulu Sea | |
|---|---|
 Satellite image from NASA showing the internal waves formed in the Sulu Sea | |
.svg.png.webp) Sulu Sea Location within the Philippines, with the island of Borneo to the southwest .svg.png.webp) Sulu Sea Sulu Sea (Philippines) 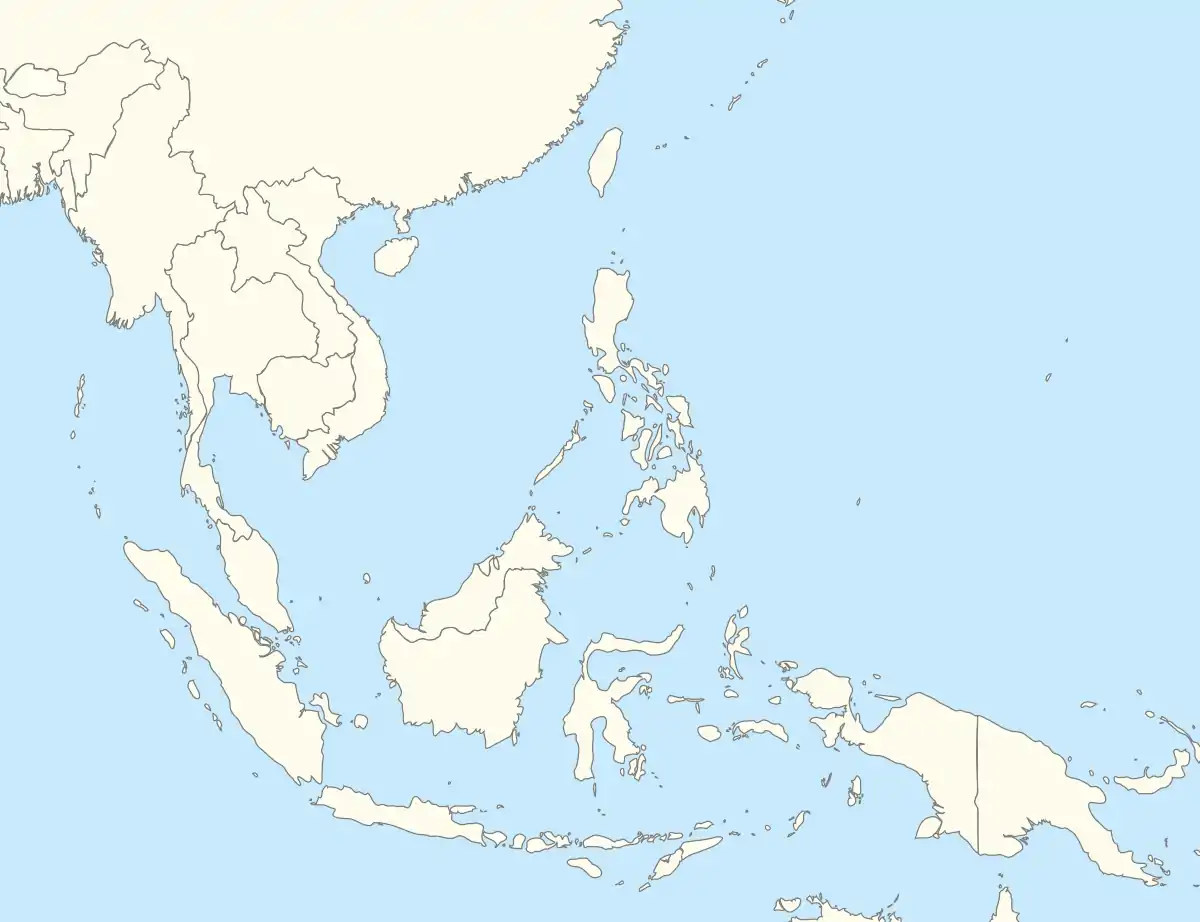 Sulu Sea Sulu Sea (Southeast Asia) | |
| Coordinates | 8°N 120°E |
| Type | sea |
| Etymology | Sulu |
| Basin countries | Malaysia and Philippines |
| Surface area | 260,000 square kilometers (100,000 sq mi) |
| Settlements | |


Sulu Sea contains a number of islands. The Cuyo Islands[3][4] and the Cagayan Islands are part of the province of Palawan whereas Mapun[5] and the Turtle Islands are part of the province of Tawi-Tawi.[6] Sulu Sea is also where the Tubbataha Reef National Marine Park, one of the World Heritage Sites is located.[7]
The Panay Gulf is an extension of the Sulu Sea. Straits out of the Sulu Sea include the Iloilo Strait, the Guimaras Strait, and the Basilan Strait.
Geography
The sea's surface area is 260,000 square kilometers (100,000 sq mi).[8] The Pacific Ocean flows into Sulu Sea in northern Mindanao and between Sangihe talaud Archipelago, North Sulawesi.[9]
Extent
The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) defines the Sulu Sea as being one of the waters of the East Indian Archipelago. The IHO defines its limits as follows:[10]
It extends about 490 miles (790 km) from north to south and 375 miles (604 km) from east to west. Waves can stretch across 25 kilometers (16 mi) to 35 kilometers (22 mi).[11] The sea is 4,400 meters (14,400 ft) deep but on its southern end Sulu Archipelago raises the sea floor to 100 meters (330 ft).[8]
On the Northwest. From Tanjong Sempang Mangayau, the North point of Borneo, along the Eastern limit of South China Sea to Cape Calavite, the Northwest point of Mindoro.
On the Northeast. The Southwest coast of Mindoro to Buruncan Point, its Southern extreme, thence a line through Semirara and Caluya Islands to Nasog Point (11°53′N 121°53′E) the Northwestern extreme of Panay, along the West and Southeast coast of that island to Tagubanhan Island (11°08′N 123°07′E), thence a line to the Northern extreme of Negros and down the West coast to Siaton Point, its Southern extreme, thence across to Tagolo Point (8°44′N 123°22′E), Mindanao.
On the Southeast. From Tagolo Point, down the West coast of Mindanao to the Southwest extremity thence to the North coast of Basilan Island (6°45′N 122°04′E), through this island to its Southern extremity, thence a line to Bitinan Island (6°04′N 121°27′E) off the Eastern end of Jolo Island, through Jolo to a point in long. 121°04'E on its South coast, thence through Tapul and Lugus Islands and along the North coast of Tawi Tawi Island to Bongao Island off its Western end (5°01′N 119°45′E), and from thence to Tanjong Labian,[6] the Northeastern extreme of Borneo.
On the Southwest. The North coast of Borneo between Tanjong Labian and Tanjong Sempang Mangayau.
In popular culture
The Star Trek character Hikaru Sulu is named after the Sulu Sea. According to Sulu actor George Takei, "[Gene] Roddenberry's vision for Sulu was to represent all of Asia, being named for the Sulu Sea instead of using a country-specific name".[12][13]
See also
References
- "Coron Bay, Philippines : UnderwaterAsia.info". www.underwaterasia.info. Archived from the original on 5 October 2017. Retrieved 23 April 2018.
- "Sulu Sea, Philippines : UnderwaterAsia.info". www.underwaterasia.info. Archived from the original on 1 June 2016. Retrieved 23 April 2018.
- Traveler's Companion Philippines 1998 p.214 Kirsten Ellis, Globe Pequot Press Globe Pequot, 1998
- "Jewel of Sulu Sea - The Manila Times Online". www.manilatimes.net. Retrieved 23 April 2018.
- "Mapun - island, Philippines". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 16 June 2020.
- "Tawi Tawi - island, Philippines". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 16 June 2020.
- C.Michael Hogan. 2011. Sulu Sea. Encyclopedia of Earth. Eds. P.Saundry & C.J.Cleveland. Washington DC
- "Sulu Sea - sea, Pacific Ocean". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 16 June 2020.
- "Geographic Scope — Sulu-Celebes Sea Sustainable Fisheries Management (SSME)". scfishproject.iwlearn.org. Retrieved 23 April 2018.
- "Limits of Oceans and Seas, 3rd edition" (PDF). International Hydrographic Organization. 1953. Archived (PDF) from the original on 7 December 2017. Retrieved 28 December 2020.
- Earth, NASA's Visible (11 August 2009). "Internal waves in the Sulu Sea, between Malaysia and the Philippines". visibleearth.nasa.gov. Archived from the original on 16 March 2016. Retrieved 23 April 2018.
- Pascale, Anthony. "George Takei On "Star Trek VI: Captain Sulu To The Rescue" + John Cho, Shatner Feud + more". TrekMovie.com. Archived from the original on 6 December 2017. Retrieved 26 July 2010.
- "George Takei on how "Sulu" got his name on Star Trek - EMMYTVLEGENDS.ORG". YouTube. Archived from the original on 9 March 2016.