National Congress of Brazil
The National Congress of Brazil (Portuguese: Congresso Nacional do Brasil) is the legislative body of Brazil's federal government. Unlike the state legislative assemblies and municipal chambers, the Congress is bicameral, composed of the Federal Senate (the upper house) and the Chamber of Deputies (the lower house). The Congress meets annually in Brasília from 2 February to 22 December, with a mid-term break taking place between 17 July and 1 August.[2][3]
National Congress Congresso Nacional | |
|---|---|
| 56th Legislature of the National Congress | |
 | |
| Type | |
| Type | |
| Houses | Federal Senate Chamber of Deputies |
| History | |
| Founded | 6 May 1826 |
New session started | 1 February 2021 |
| Leadership | |
Government Leader | |
Majority Leader | |
Minority Leader | |
| Structure | |
| Seats | 594 members: 81 Senators 513 Federal Deputies |
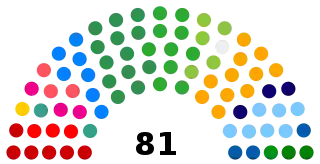 | |
Federal Senate political groups | Government (27)[1]
Independent (36)[1] Opposition (18)[1] |
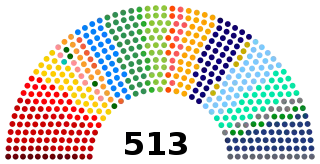 | |
Chamber of Deputies political groups | Government (257)[1]
Independent (125)[1] Opposition (131)[1] |
| Elections | |
Federal Senate voting system | Plurality voting, alternating every four years between single-member elections (FPTP) and dual-member elections (Block voting) |
Chamber of Deputies voting system | Open list proportional representation |
Last general election | 7 October 2018 |
Next general election | 2 October 2022 |
| Meeting place | |
 | |
| National Congress building Brasília, Federal District, Brazil | |
| Website | |
| Federal Senate Chamber of Deputies | |
 |
|---|
| This article is part of a series on the politics and government of Brazil |
|
|
The Senate represents the 26 states and the Federal District. Each state and the Federal District has a representation of three Senators, who are elected by popular ballot for a term of eight years. Every four years, renewal of either one third or two-thirds of the Senate (and of the delegations of the States and the Federal District) takes place. The Chamber of Deputies represents the people of each state, and its members are elected for a four-year term by a system of proportional representation. Seats are allotted proportionally according to each state's population, with each state eligible for a minimum of 8 seats (least populous) and a maximum of 70 seats (most populous). Unlike the Senate, the whole of the Chamber of Deputies is renewed every four years.
Until recently it was common for politicians to switch parties and the proportion of congressional seats held by each party would often change. However, a decision of the Supreme Federal Court has ruled that the seats belong to the parties and not to the politicians; one can only change parties and retain his seat in a very limited set of cases. Consequently, politicians who abandon the party for which they were elected now face the loss of their congressional seat. Each house of the Brazilian Congress elects its president and the other members of its directing board from among its members. The President of the Senate is ex officio the President of the National Congress, and in that capacity summons and presides over joint sessions, as well as over the joint services of both houses. The President of the Chamber is second in the presidential line of succession while the President of the Senate (and of Congress) is third.
Director Board
The current composition of the Board of the National Congress is as follows:
| Office | Name | Party | State |
|---|---|---|---|
| President | Rodrigo Pacheco | DEM | Minas Gerais |
| 1st Vice-President | Marcelo Ramos | PL | Amazonas |
| 2nd Vice-President | Romário Faria | PODE | Rio de Janeiro |
| 1st Secretary | Luciano Bivar | PSL | São Paulo |
| 2nd Secretary | Elmano Férrer | PP | Piauí |
| 3rd Secretary | Rose Modesto | PSDB | Mato Grosso do Sul |
| 4th Secretary | Weverton Rocha | PDT | Maranhão |
Houses
Federal Senate
The Federal Senate (Portuguese: Senado Federal) is the upper house of the National Congress. Created by the first Constitution of the Brazilian Empire in 1824, it was inspired in United Kingdom's House of Lords, but with the Proclamation of the Republic in 1889 it became closer to the United States Senate.
Currently, the Senate comprises 81 seats. Three Senators from each of the 26 states and three Senators from the Federal District are elected on a majority basis to serve eight-year terms. Elections are staggered so that two-thirds of the upper house is up for election at one time and the remaining one-third four years later. When one seat is up for election in each State, each voter casts one vote for the Senate; when two seats are up for election, each voter casts two votes, and the voter cannot give his two votes for the same candidate, but, in elections for the renewal of two-thirds of the Senate, each party can present two candidates for election. The candidate in each State and the Federal District (or the first two candidates, when two thirds of the seats are up for election) who achieve the greatest plurality of votes are elected.
Chamber of Deputies
The Chamber of Deputies (Câmara dos Deputados) is the lower house of the National Congress, it is composed of 513 federal deputies, who are elected by a proportional representation of votes to serve a four-year term. Seats are allotted proportionally according to each state's population, with each state eligible for a minimum of 8 seats (least populous) and a maximum of 70 seats (most populous).
In 2018, 24 out of the country's 33 political parties were able to elect at least one representative in the Chamber, while sixteen of them were able to elect at least one Senator.
- See the Latest election section for election results table.
Building
In early 1900s, the Brazilian National Congress happened to be in separate buildings. The Senate was located near Railway Central Station, beside the Republica Square, at Moncorvo Filho Street, where there is today a Federal University of Rio de Janeiro students' center. The Federal Chamber of Deputies was located at Misericórdia Street, which would later be the location of the State of Rio de Janeiro's local Chamber of Deputies. From the 1930s to early 1960s, the Senate occupied the Monroe Palace, which was demolished in the 1970s to allow the construction of the subway Cinelândia Station. The Federal Chamber of Deputies moved to Brasília in the early 1960s as well but temporarily occupied a building near the Municipal Theater for a couple of years.
Since the 1960s, the National Congress has been located in Brasília. As with most of the city's government buildings, the National Congress building was designed by Oscar Niemeyer in the modern Brazilian style.
The semi-sphere on the left is the seat of the Senate, and the semi-sphere on the right is the seat of the Chamber of the Deputies. Between them are two vertical office towers. The Congress also occupies other surrounding office buildings, some of them interconnected by a tunnel.
The building is located in the middle of the Monumental Axis, the main street of Brasília. In front of it there is a large lawn where demonstrations take place. At the back of it, is the Praça dos Três Poderes (Three Powers Plaza), where lies the Palácio do Planalto and the Supreme Federal Court.
On December 6, 2007, the Institute of Historic and Artistic National Heritage (Portuguese: Instituto do Patrimônio Histórico e Artístico Nacional) decided to declare the building of the National Congress a historical heritage of the Brazilian people. The building has also been a UNESCO World Heritage Site, as part of Brasília's original urban buildings, since 1987.
Similar high-rises
At least two other high-rise buildings are similar to the National Congress building:
- Sokos Hotel Viru in Tallinn, Estonia. Completed in 1972, originally owned by USSR's Intourist, and formerly called Viru hotell;
- Greece–Bosnia and Herzegovina Friendship Building in Sarajevo. Built in 1974; formerly Executive Council Building in the former Socialist Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina.
Gallery
National Congress building


 Committee room
Committee room.jpg.webp) Noble Room of the Senate
Noble Room of the Senate Exterior, on a rainy day
Exterior, on a rainy day Exterior view of the Chamber of Deputies
Exterior view of the Chamber of Deputies Exterior view of the Senate chamber
Exterior view of the Senate chamber The National Congress building at night
The National Congress building at night Front facade and lawn, showing the twin towers.
Front facade and lawn, showing the twin towers. The Congress as seen from the Monumental Axis
The Congress as seen from the Monumental Axis.jpg.webp) Legislative police officers outside the National Congress building.
Legislative police officers outside the National Congress building..jpg.webp) Protesters during an anti-government demonstration in front of the Congress, 13 March 2016.
Protesters during an anti-government demonstration in front of the Congress, 13 March 2016.
Latest election
| Party | Chamber of Deputies | Senate | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Votes | % | Seats | +/– | Votes | % | Elected | Total | +/– | ||
| Social Liberal Party | 11,457,878 | 11.7 | 52 | +44 | 19,413,869 | 11.3 | 4 | 4 | +4 | |
| Workers' Party | 10,126,611 | 10.3 | 56 | –13 | 24,785,670 | 14.5 | 4 | 6 | –6 | |
| Brazilian Social Democracy Party | 5,905,541 | 6.0 | 29 | –25 | 20,310,558 | 11.9 | 4 | 8 | –2 | |
| Social Democratic Party | 5,749,008 | 5.8 | 34 | –2 | 8,202,342 | 4.8 | 4 | 7 | +4 | |
| Progressistas | 5,480,067 | 5.6 | 37 | –1 | 7,529,901 | 4.4 | 5 | 6 | +1 | |
| Brazilian Democratic Movement | 5,439,167 | 5.5 | 34 | –32 | 12,800,290 | 7.5 | 7 | 12 | –6 | |
| Brazilian Socialist Party | 5,386,400 | 5.5 | 32 | –2 | 8,234,195 | 4.8 | 2 | 2 | –5 | |
| Republic Party | 5,224,591 | 5.3 | 33 | –1 | 3,130,082 | 1.8 | 1 | 2 | –2 | |
| Brazilian Republican Party | 4,992,016 | 5.1 | 30 | +9 | 1,505,607 | 0.9 | 1 | 1 | – | |
| Democrats | 4,581,162 | 4.7 | 29 | +8 | 9,218,658 | 5.4 | 4 | 6 | +2 | |
| Democratic Labour Party | 4,545,846 | 4.6 | 28 | +9 | 7,737,982 | 4.5 | 2 | 5 | –3 | |
| Socialism and Liberty Party | 2,783,669 | 2.8 | 10 | +5 | 5,273,853 | 3.1 | 0 | 0 | –1 | |
| New Party | 2,748,079 | 2.8 | 8 | New | 3,467,746 | 2.0 | 0 | 0 | – | |
| Podemos | 2,243,320 | 2.3 | 11 | +7 | 5,494,125 | 3.2 | 1 | 5 | +5 | |
| Republican Party of the Social Order | 2,042,610 | 2.1 | 8 | –3 | 1,370,513 | 0.8 | 1 | 1 | – | |
| Brazilian Labour Party | 2,022,719 | 2.1 | 10 | –15 | 1,899,838 | 1.1 | 2 | 3 | – | |
| Solidariedade | 1,953,067 | 2.0 | 13 | –2 | 4,001,903 | 2.3 | 1 | 1 | – | |
| Avante | 1,844,048 | 1.9 | 7 | +5 | 713,379 | 0.4 | 0 | 0 | – | |
| Social Christian Party | 1,765,226 | 1.8 | 8 | –5 | 4,126,068 | 2.4 | 1 | 1 | +1 | |
| Green Party | 1,592,173 | 1.6 | 4 | –4 | 1,226,392 | 0.7 | 0 | 0 | –1 | |
| Popular Socialist Party | 1,590,084 | 1.6 | 8 | –2 | 2,954,800 | 1.7 | 2 | 2 | +2 | |
| Patriota | 1,432,304 | 1.5 | 5 | +3 | 60,589 | 0.0 | 0 | 0 | – | |
| Humanist Party of Solidarity | 1,426,444 | 1.5 | 6 | +1 | 4,228,973 | 2.5 | 2 | 2 | +2 | |
| Communist Party of Brazil | 1,329,575 | 1.4 | 9 | –1 | 1,673,190 | 1.0 | 0 | 0 | –1 | |
| Progressive Republican Party | 851,368 | 0.9 | 4 | +1 | 1,974,061 | 1.2 | 1 | 1 | +1 | |
| Sustainability Network | 816,784 | 0.8 | 1 | New | 7,166,003 | 4.2 | 5 | 5 | New | |
| Brazilian Labour Renewal Party | 684,976 | 0.7 | 0 | –1 | 886,267 | 0.5 | 0 | 0 | – | |
| Party of National Mobilization | 634,129 | 0.6 | 3 | – | 329,973 | 0.2 | 0 | 0 | – | |
| Christian Labour Party | 601,814 | 0.6 | 2 | – | 222,931 | 0.1 | 0 | 1 | +1 | |
| Free Homeland Party | 385,197 | 0.4 | 1 | +1 | 504,209 | 0.3 | 0 | 0 | – | |
| Christian Democracy | 369,386 | 0.4 | 1 | –1 | 154,068 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | – | |
| Party of Brazilian Women | 228,302 | 0.2 | 0 | – | 51,027 | 0.0 | 0 | 0 | – | |
| Brazilian Communist Party | 61,343 | 0.1 | 0 | – | 256,655 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | – | |
| United Socialist Workers Party | 41,304 | 0.0 | 0 | – | 413,914 | 0.2 | 0 | 0 | – | |
| Workers Cause Party | 2,785 | 0.0 | 0 | – | 38,691 | 0.0 | 0 | 0 | – | |
| Invalid/blank votes | 18,771,737 | – | – | – | 61,995,824 | – | – | – | – | |
| Total | 117,111,476 | 100.0 | 513 | 0 | 117,111,478 | 100.0 | 54 | 81 | 0 | |
| Registered voters/turnout | 146,750,529 | 79.8 | – | – | 146,750,529 | 79.8 | – | – | – | |
| Source: Election Resources | ||||||||||
Legislatures
The Legislatures are counted from the first meeting of the Chamber of Deputies and of the Senate, on 6 May 1826, in the imperial era (the Chamber of Deputies met for preparatory sessions from 29 April 1826 onwards to elect its officers and conduct other preliminary business, but the Legislature was formally opened on 6 May). The Chamber of Deputies and the Senate were created by Brazil's first Constitution, the Constitution of the Empire of Brazil, adopted in 1824. The previous Constituent and Legislative Assembly of the Empire of Brazil, a unicameral National Assembly, that was convened in 1823 and that was dissolved by Emperor Pedro I before adopting a Constitution is not counted among the Legislatures. Thus, the numbering includes only the bicameral Legislatures that existed from 1826 to the present day, and includes only Legislatures elected after the adoption of the first Brazilian Constitution.
In the imperial era, the national legislature was named General Assembly. It was made up of the Chamber of Deputies and the Senate. Senators were elected for life and the Senate was a permanent institution, whereas the Chamber of Deputies, unless dissolved earlier, was elected every four years. When Brazil became a Republic and a Federal State the model of a bicameral Legislature was retained at the Federal level, but the Parliament was renamed National Congress. The National Congress is made up of the Chamber of Deputies and the Federal Senate. Both Houses have fixed terms and cannot be dissolved earlier. Under Brazil's present Constitution, adopted in 1988, Senators are elected to eight-year terms, and Deputies are elected every four years.
The numbering of the Legislatures is continuous, including the Legislatures of the imperial General Assembly and of the republican National Congress. The inauguration of a new composition of Chamber of Deputies for a four-year term of office marks the start of a new Legislature.
| Legislature | Period | Legislature | Period | Legislature | Period | Legislature | Period | Legislature | Period |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Legislature | 1826–1829 | 13th Legislature | 1867–1868 | 25th Legislature | 1900–1902 | 37th Legislature | 1935–1937 | 49th Legislature | 1991–1995 |
| 2nd Legislature | 1830–1833 | 14th Legislature | 1869–1872 | 26th Legislature | 1903–1905 | 38th Legislature | 1946–1950 | 50th Legislature | 1995–1999 |
| 3rd Legislature | 1834–1837 | 15th Legislature | 1872–1875 | 27th Legislature | 1906–1908 | 39th Legislature | 1951–1954 | 51st Legislature | 1999–2003 |
| 4th Legislature | 1838–1841 | 16th Legislature | 1876–1877 | 28th Legislature | 1909–1911 | 40th Legislature | 1955–1958 | 52nd Legislature | 2003–2007 |
| 5th Legislature | 1842–1844 | 17th Legislature | 1878–1881 | 29th Legislature | 1912–1914 | 41st Legislature | 1959–1962 | 53rd Legislature | 2007–2011 |
| 6th Legislature | 1845–1847 | 18th Legislature | 1882–1884 | 30th Legislature | 1915–1917 | 42nd Legislature | 1963–1967 | 54th Legislature | 2011–2015 |
| 7th Legislature | 1848–1848 | 19th Legislature | 1885–1885 | 31st Legislature | 1918–1920 | 43rd Legislature | 1967–1970 | 55th Legislature | 2015–2019 |
| 8th Legislature | 1849–1852 | 20th Legislature | 1886–1889 | 32nd Legislature | 1921–1923 | 44th Legislature | 1971–1975 | 56th Legislature | 2019–2023 |
| 9th Legislature | 1853–1856 | 21st Legislature | 1890–1891 | 33rd Legislature | 1924–1926 | 45th Legislature | 1975–1979 | ||
| 10th Legislature | 1857–1860 | 22nd Legislature | 1891–1893 | 34th Legislature | 1927–1929 | 46th Legislature | 1979–1983 | ||
| 11th Legislature | 1861–1863 | 23rd Legislature | 1894–1896 | 35th Legislature | 1930–1930 | 47th Legislature | 1983–1987 | ||
| 12th Legislature | 1864–1866 | 24th Legislature | 1897–1899 | 36th Legislature | 1933–1935 | 48th Legislature | 1987–1991 |
See also
References
- "A configuração da Câmara após a investida de Bolsonaro". Nexo (in Portuguese). Retrieved 2020-06-15.
- "Brazil - The legislature". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 2020-01-09.
- "The National Congress". Portal da Câmara dos Deputados (in Portuguese). Retrieved 2020-01-09.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Congresso Nacional do Brasil. |
- (in Portuguese) National Congress
- (in Portuguese) Chamber of Deputies of Brazil
- (in Portuguese) Chamber of Deputies' e-Democracy
- (in Portuguese) Senate of Brazil
- (in Portuguese) Photos 360° of National Congress
.svg.png.webp)