Road signs in Germany
Road signs and symbols used in Germany are prescribed under the Straßenverkehrs-Ordnung (StVO) (German Road Traffic Act) and the Katalog der Verkehrszeichen (VzKat) (Catalog of Traffic Signs).[1][2]
Paragraph 9 of the StVO states that "The traffic signs and installations illustrated in annexes 1 to 4 may also be installed with the alternatives described in the Catalog of Traffic Signs." (The Catalog of Traffic Signs (VZKat) is published in the Federal Ministry of Transport Gazette by the Federal Ministry of Transport, Building, and Infrastructure.) The VzKat was issued in May 2017[2] under the Allgemeine Verwaltungsvorschrift zur Straßenverkehrs-Ordnung] (VwV-StVO) (general administrative regulations for the Road Traffic Act).[3]
All signs have assigned numbers. The suffix number after the hyphen refers to the variation of the sign; the suffix on signs with variable numbers is the number depicted on the sign (e.g. speed limit, maximum height, etc.).[2]
Symbols
Symbols pursuant to paragraphs 7, 10, and 11 of the StVO:[1]
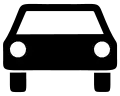 Multi-track motor vehicles
Multi-track motor vehicles Motor vehicles with a maximum permissible mass above 3.5 t - including their trailer - and combination vehicles, except passenger vehicles and buses
Motor vehicles with a maximum permissible mass above 3.5 t - including their trailer - and combination vehicles, except passenger vehicles and buses
 Bicycle utilized for the transport of goods or persons - freight bicycle
Bicycle utilized for the transport of goods or persons - freight bicycle



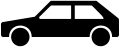
- Passenger vehicles or motorcycles with a sidecar which are occupied by at least three persons - high occupancy vehicle
 Passenger vehicle towing a trailer
Passenger vehicle towing a trailer

 Motor vehicles and vehicle combinations which cannot or may not drive faster than 25 km/h
Motor vehicles and vehicle combinations which cannot or may not drive faster than 25 km/h

 One-seated two-wheeled mopeds with an electric motor which automatically regulates its design speed to no more than 25 km/h - E-Bikes -
One-seated two-wheeled mopeds with an electric motor which automatically regulates its design speed to no more than 25 km/h - E-Bikes -%252C_Sinnbild_nach_%C2%A7_39_StVO%252C_StVO_2020.svg.png.webp) Small electric vehicles pursuant to the Elektrokleinstfahrzeuge-Verordnung (eKFV) (Small Electric Vehicle Act)
Small electric vehicles pursuant to the Elektrokleinstfahrzeuge-Verordnung (eKFV) (Small Electric Vehicle Act)

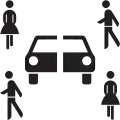
Danger signs
Danger signs pursuant to part 2 of the VzKat which includes permissible variations of signs listed in annex 1 of the StVO. When one sign has two sign numbers, the first number is the illustrated sign while the latter number is a mirrored or slightly altered version of the sign.
General danger signs
 Sign 101
Sign 101
Danger. A supplementary sign can specify the danger.
 Sign 101-11 / 101-21
Sign 101-11 / 101-21
Pedestrian crosswalk Sign 101-12 / 101-22
Sign 101-12 / 101-22
Cattle Sign 101-13 / 101-23
Sign 101-13 / 101-23
Equestrians Sign 101-14 / 101-24
Sign 101-14 / 101-24
Amphibians Sign 101-15 / 101-25
Sign 101-15 / 101-25
Rockfall Sign 101-51
Sign 101-51
Slipperiness due to snow or ice Sign 101-52
Sign 101-52
Grit/gravel at the edge of the road Sign 101-53
Sign 101-53
Shore or riverbank Sign 101-54
Sign 101-54
Insufficient clearance SIgn 101-55
SIgn 101-55
Movable bridge
%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Sign 103-10 / 103-20
Sign 103-10 / 103-20
Curve%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Sign 105-10 / 105-20
Sign 105-10 / 105-20
Double curve Sign 108-10
Sign 108-10
Descent Sign 110-12
Sign 110-12
Ascent Sign 112
Sign 112
Uneven road Sign 114
Sign 114
Slipperiness when road is wet or dirty Sign 117-10 / 117-20
Sign 117-10 / 117-20
Crosswind Sign 120
Sign 120
Road narrowing_verengte_Fahrbahn%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Sign 121-10 / 121-20
Sign 121-10 / 121-20
One-sided road narrowing Sign 123
Sign 123
Construction area Sign 124
Sign 124
Traffic jams Sign 125
Sign 125
Oncoming traffic Sign 131
Sign 131
Traffic signals%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Sign 133-10 / 133-20
Sign 133-10 / 133-20
Pedestrians Sign 136-10 / 136-20
Sign 136-10 / 136-20
Children Sign 138-10 / 138-20
Sign 138-10 / 138-20
Cycles Sign 142-10 / 142-20
Sign 142-10 / 142-20
Wild animals
Special danger signs approaching railroad crossings
 Sign 151
Sign 151
Railroad crossing Sign 156-10 / 156-20
Sign 156-10 / 156-20
Railroad crossing with three-striped warning - 240 m distance Sign 156-11 / 156-21
Sign 156-11 / 156-21
Railroad crossing with three-striped warning - custom distance%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Sign 157-10 / 157-20
Sign 157-10 / 157-20
Three-striped warning for railroad crossing - 240 m distance%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Sign 157-11 / 157-21
Sign 157-11 / 157-21
Three-striped warning for railroad crossing - custom distance%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Sign 159-10 / 159-20
Sign 159-10 / 159-20
Two-striped warning for railroad crossing - 160 m distance%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Sign 159-11 / 159-21
Sign 159-11 / 159-21
Two-striped warning for railroad crossing - custom distance%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Sign 162-10 / 162-20
Sign 162-10 / 162-20
One-striped warning for railroad crossing - 80 m distance%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Sign 162-11 / 162-21
Sign 162-11 / 162-21
One-striped warning for railroad crossing - custom distance
Regulatory signs
Regulatory signs pursuant to part 3 of the VzKat which includes permissible variations of signs listed in annex 2 of the StVO. When one sign has two sign numbers, the first number is the illustrated sign while the latter number is a mirrored or slightly altered version of the sign.
Waiting and stopping requirements
 Sign 201-50 / 201-52
Sign 201-50 / 201-52
Crossbuck. Yield the right-of-way to railborne vehicles Sign 201-51 / 201-53
Sign 201-51 / 201-53
Crossbuck with lightning rod. Yield the right-of-way to railborne vehicles; the tracks possess overhead electrical wires Sign 205
Sign 205
Yield the right-of-way Sign 206
Sign 206
Stop. Yield the right-of-way. Sign 208
Sign 208
Oncoming traffic has the right-of-way
Mandatory direction of travel
 Sign 209
Sign 209
Right ahead Sign 209-10
Sign 209-10
Left ahead Sign 209-30
Sign 209-30
Straight ahead Sign 211
Sign 211
Right here%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Sign 211-10
Sign 211-10
Left here Sign 214
Sign 214
Straight ahead or right ahead Sign 214-10
Sign 214-10
Straight ahead or left ahead Sign 214-30
Sign 214-30
Left ahead or right ahead Sign 215
Sign 215
Roundabout Sign 220-10 / 220-20
Sign 220-10 / 220-20
One-way street
Mandatory passing
 Sign 222
Sign 222
Pass on the right Sign 222-10
Sign 222-10
Pass on the left
Drivable shoulders, bus stops, and taxi stands
 Sign 223.1-50 - 223.1-52
Sign 223.1-50 - 223.1-52
Drive on the shoulder Sign 223.2-50 - 223.2-52
Sign 223.2-50 - 223.2-52
No longer drive on the shoulder Sign 223.3-50 - 223.3-52
Sign 223.3-50 - 223.3-52
Vacate the shoulder Sign 224
Sign 224
Bus stop%252C_StVO_2017.svg.png.webp)
 Sign 229 - 229-31
Sign 229 - 229-31
Taxi stand
Dedicated paths and lanes
 Sign 237
Sign 237
Bicycle path Sign 238
Sign 238
Equestrian path Sign 239
Sign 239
Sidewalk
 Sign 241-30 / 241-31
Sign 241-30 / 241-31
Separated pedestrian and bicycle path Sign 242.1
Sign 242.1
Begin of a pedestrian zone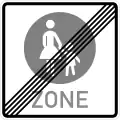 Sign 242.2
Sign 242.2
End of a pedestrian zone Sign 244.1
Sign 244.1
Begin of a bicycle street Sign 244.2
Sign 244.2
End of a bicycle street Sign 244.3
Sign 244.3
Begin of a bicycle zone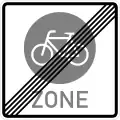 Sign 244.4
Sign 244.4
End of a bicycle zone Sign 245
Sign 245
Bus lane
Priority
Reißverschlussverfahren[4]
"Zipper Rule" for 1-Way Traffic Merging & 2-Way Traffic Priorities
_verengte_Fahrbahn%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) einseitig (links) verengte Fahrbahn
einseitig (links) verengte Fahrbahn
Road narrows on the left, 1-Way Zipper Rule Applies, 2-Way Oncoming Traffic Yields to You) Verengte Fahrbahn
Verengte Fahrbahn
Narrow Roadway Ahead, 1-Way Zipper Rule Applies_verengte_Fahrbahn%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) einseitig (rechts) verengte Fahrbahn
einseitig (rechts) verengte Fahrbahn
Road narrows on the right, 1-Way Zipper Rule Applies, 2-Way Yield to Oncoming Traffic Two way traffic ahead (Red indicates who must yield)
Two way traffic ahead (Red indicates who must yield) Oncoming Traffic (Red indicates who must yield)
Oncoming Traffic (Red indicates who must yield) Vorrang vor dem Gegenverkehr
Vorrang vor dem Gegenverkehr
Priority over oncoming vehicles
Environmental factors
Yield as necessary to not endanger yourself or other road users
 Steinschlag
Steinschlag
Possible Rockfall in Road (No braking, slowing, stopping or parking) Schnee- oder Eisglätte
Schnee- oder Eisglätte
Snow or Ice possible ahead (road freezes easily, no sudden braking or turning) Splitt, Schotter
Splitt, Schotter
Loose chippings Unebene Fahrbahn
Unebene Fahrbahn
Uneven surfaces ahead, bumpy road Schleuder- oder Rutschgefahr
Schleuder- oder Rutschgefahr
Slippery road (water, ice, snow, oil or dirt)
Traffic priority - priority roads
Priority Travel Does Not Yield, Signal All Turns
 Vorfahrtstraße
Vorfahrtstraße
Priority Road%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Course of this priority road turns left
Course of this priority road turns left%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Road from left and ahead has priority
Road from left and ahead has priority%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp)
%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp)
%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp)
%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp)

%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp)
%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp)
%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp)
 Ende der Vorfahrtsstraße
Ende der Vorfahrtsstraße
End of Priority Road Vorfahrt
Vorfahrt
Priority to through-traffic at the next intersection/crossroads only Kreuzung o. Einmündung mit Vorfahrt von rechts
Kreuzung o. Einmündung mit Vorfahrt von rechts
Uncontrolled Intersection Ahead Yield to cross traffic
Yield to cross traffic
Other factors
Yield or Reduce Speed as Necessary [5]
 Stau/Verkehrstau
Stau/Verkehrstau
Traffic jams/queues possible%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Kurve
Kurve
Dangerous curve to the left (Slow & stay to the right)%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Kurve
Kurve
Dangerous curve to the right (Slow & stay to the right)%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Doppelkurve
Doppelkurve
Double curves, first to left (Slow & stay to the right)%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Doppelkurve
Doppelkurve
Double curves, first to right (Slow & stay to the right) Gefälle
Gefälle
Steep Grade/Hill Down (10%) Steigung
Steigung
Steep Grade/Hill Up (12%) Flugbetrieb
Flugbetrieb
Low-flying aircraft, Aircraft noise & lights may distract drivers Seitenwind
Seitenwind
Crosswinds from the right possible Seitenwind
Seitenwind
Crosswind from the left possible
 Unzureichendes Lichtraumprofil
Unzureichendes Lichtraumprofil
Narrowed clearance by trees
 Viehtrieb
Viehtrieb
Cattle possible Reiter
Reiter
Equestrians possible Amphibienwanderung
Amphibienwanderung
Frogs & Toads possible
Vehicle classifications & specifics
Official (base) Symbols in Germany as per Straßenverkehrs-Ordnung (StVO) § 39 Verkehrszeichen[7]
Basic
Red Ring
In addition to any sign/placard, the Red Ring forbids (in general) the item noted and anything of greater size or value; i.e., if a car is pictured, then not only are cars not permitted verboten but also trucks too.
A Red Ring is also a traffic sign itself: No Vehicles (of any type) Permitted, Pushing Motorcycles/Mopeds/Bicycles Permitted
 Verbot für Fahrzeuge aller Art No vehicles of any kind permitted
Verbot für Fahrzeuge aller Art No vehicles of any kind permitted Verbot für Kraftwagen und sonstige mehrspurige Kraftfahrzeuge
Verbot für Kraftwagen und sonstige mehrspurige Kraftfahrzeuge
No 2-tracked Motor Vehicles permitted Verbot für Fußgänger
Verbot für Fußgänger
No Pedestrians Permitted
Bicycles & mopeds
 Radfahrer
Radfahrer
Bicycles Permitted%252C_StVO_2017.svg.png.webp) E-Bikes
E-Bikes
Electric Bicycles Permitted%252C_StVO_2017.svg.png.webp) Mofas
Mofas
Mopeds%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Mofas
Mofas
Mopeds Permitted Verbot für Mofas Mopeds Forbidden
Verbot für Mofas Mopeds Forbidden%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) No Mopeds Permitted
No Mopeds Permitted
Motorcycles
Classified as above/below 500 cc motor size, and with or without sidecar
%252C_StVO_2017.svg.png.webp) Krafträder, auch mit Beiwagen, Kleinkrafträder und Mofas
Krafträder, auch mit Beiwagen, Kleinkrafträder und Mofas
Motorcycles (above 500 cc), also with sidecar, small motorcycles (below 500 cc) and mopeds%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Motorcycles and Mopeds Permitted
Motorcycles and Mopeds Permitted Verbot für Krafträder, auch mit Beiwagen, Kleinkrafträder und Mofas Ban on motorcycles including those with sidecars and mopeds
Verbot für Krafträder, auch mit Beiwagen, Kleinkrafträder und Mofas Ban on motorcycles including those with sidecars and mopeds
Cars/automobiles
Personenkraftwagen - Pkw[8] – "Powered Car for (the transport of) Persons"; e.g., cars/automobiles
%252C_StVO_2017.svg.png.webp) Personenkraftwagen (Pkw)
Personenkraftwagen (Pkw)
Cars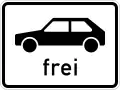 Personenkraftwagen (Pkw)
Personenkraftwagen (Pkw)
Cars Permitted Verbot für Personenkraftwagen/Pkw
Verbot für Personenkraftwagen/Pkw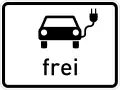 elektrisch betriebene Fahrzeuge
elektrisch betriebene Fahrzeuge
Electric Vehicles/Cars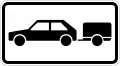 Pkw mit Anhänger
Pkw mit Anhänger
Cars with Trailer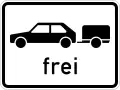 Pkw mit Anhänger
Pkw mit Anhänger Verbot für Pkw mit Anhänger
Verbot für Pkw mit Anhänger
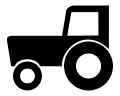
Recreational vehicles, farm equipment or animal powered
%252C_StVO_2017.svg.png.webp) Wohnmobile
Wohnmobile
Motorhomes & Campers%252C_StVO_2017.svg.png.webp) Kraftfahrzeuge und Züge
Kraftfahrzeuge und Züge
Farm & Powered Equipment (& Trailers) with less than 25 km/h top speed Verbot für Kraftfahrzeuge und Züge
Verbot für Kraftfahrzeuge und Züge Kraftfahrzeuge und Züge
Kraftfahrzeuge und Züge
Farm & Powered Equipment (& Trailers) Permitted%252C_StVO_2017.svg.png.webp) Gespannfuhrwerke
Gespannfuhrwerke
Horse-drawn Wagon Verbot für Gespannfuhrwerke
Verbot für Gespannfuhrwerke
No Horse-drawn Wagons Permitted Verbot für Viehtrieb
Verbot für Viehtrieb
No Cattle Permitted Verbot für Reiter
Verbot für Reiter
No Equestrians/Horse Riders Permitted
Trucks & lorries
Lastkraftwagen - Lkw[9] – "Powered Car for Loads", e.g., truck, lorry, semi, tractor-trailer
- Lkw or Kfz
- Lkw Permitted
 No Lkw Permitted
No Lkw Permitted
Kraftfahrzeuge (Kfz)[10] mit einer zulässigen Gesamtmasse über 3,5 t, einschließlich ihrer Anhänger, und Zugmaschinen, ausgenommen Personenkraftwagen und Kraftomnibusse – Motor vehicles with a maximum authorized mass of more than 3,5 t, including their trailers, and tractors other than cars and buses
%252C_StVO_2017.svg.png.webp) Lkw mit Anhänger
Lkw mit Anhänger
Truck with trailer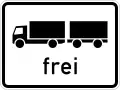 Lkw with trailer permitted
Lkw with trailer permitted Verbot für Lastkraftwagen (Lkw) mit Anhänger
Verbot für Lastkraftwagen (Lkw) mit Anhänger
No trucks with trailer(s) permitted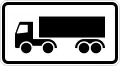 Sattelkraftfahrzeuge[11]
Sattelkraftfahrzeuge[11]
Semi/Tractor-Trailer%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Single & Double Trailer Semis
Single & Double Trailer Semis
Restrictions & allowances for vehicles (generally larger) than cars
%252C_StVO_2017.svg.png.webp) Massenangabe
Massenangabe
Weight (7.5 tons) Verbot für Fahrzeuge über angegebene tatsächliche Masse
Verbot für Fahrzeuge über angegebene tatsächliche Masse
Total Vehicle Weight Limit (5.5 tonnes)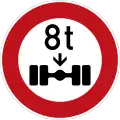 Verbot für Fahrzeuge über angegebene tatsächliche Achslast
Verbot für Fahrzeuge über angegebene tatsächliche Achslast
Load Limit per Axle (8 tonnes) Verbot für Fahrzeuge über angegebene tatsächliche Breite
Verbot für Fahrzeuge über angegebene tatsächliche Breite
Width Limit (including wing mirrors) Verbot für Fahrzeuge über angegebene tatsächliche Höhe
Verbot für Fahrzeuge über angegebene tatsächliche Höhe
Height Limit (3.8 meters) Verbot für Fahrzeuge über angegebene tatsächliche Länge
Verbot für Fahrzeuge über angegebene tatsächliche Länge
Length Limit (10 meters)
Dangerous or hazardous cargos
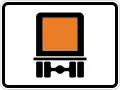 Dangerous or Hazardous Load/Cargos
Dangerous or Hazardous Load/Cargos Verbot für kennzeichnungspflichtige Kraftfahrzeuge mit gefährlichen Gütern
Verbot für kennzeichnungspflichtige Kraftfahrzeuge mit gefährlichen Gütern
No Dangerous or Hazardous Loads/Cargos Permitted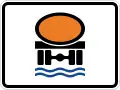 Dangerous or Hazardous Loads/Cargos to Water Bodies
Dangerous or Hazardous Loads/Cargos to Water Bodies Verbot für Fahrzeuge mit wassergefährdender Ladung
Verbot für Fahrzeuge mit wassergefährdender Ladung
No Dangerous or Hazardous Loads/Cargos to Water Bodies Permitted
Buses, public transit & rail
Buses (generally) and trains (always) have the priority/right of way[12]
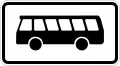 Kraftomnibus
Kraftomnibus
Bus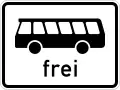 Buses permitted
Buses permitted Verbot für Kraftomnibusse
Verbot für Kraftomnibusse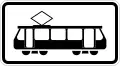 Straßenbahn
Straßenbahn
Streetrail or Trams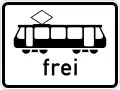 Trams Permitted
Trams Permitted%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Train - Bahn/Zug
Train - Bahn/Zug Schienenbahn
Schienenbahn
"Railway Traffic", Trains - Bahn/Zug Permitted
Others
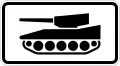 Military vehicles (generally a weight rating)
Military vehicles (generally a weight rating)%252C_Kraftomnibus_(Zeichen_1048-16)_und_Pkw_mit_Anh%C3%A4nger_(Zeichen_1048-11)%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Lkw, Busses & Pkw with Trailers
Lkw, Busses & Pkw with Trailers
Basics
Basic Traffic Controls
 Verbot der Einfahrt
Verbot der Einfahrt
Do Not Enter Verbot des Wendens
Verbot des Wendens
No U-turns
 Vorgeschriebene Mindestgeschwindigkeit
Vorgeschriebene Mindestgeschwindigkeit
Minimum (30 km/h) Speed Required Ende der ...
Ende der ...
End of... Beginn einer Tempo 30-Zone
Beginn einer Tempo 30-Zone
Maximum (30 km/h) Zone (still in effect after junctions)%252C_StVO_2013.svg.png.webp) End of...
End of... Zulässige Höchstgeschwindigkeit
Zulässige Höchstgeschwindigkeit
Maximum Speed (60 km/h) Ende der ...
Ende der ...
End of...%252C_StVO_1981.svg.png.webp) Maximum (or recommended) Speeds in Germany for Developed/Urban Areas (50), Bundesstraßen (100) & Autobahn (130)
Maximum (or recommended) Speeds in Germany for Developed/Urban Areas (50), Bundesstraßen (100) & Autobahn (130)
Passing & Overtaking
 Überholverbot für Kraftfahrzeuge aller Art
Überholverbot für Kraftfahrzeuge aller Art
No Passing (for any vehicle type) End of...
End of... No Passing (by vehicles over 3,5 t)
No Passing (by vehicles over 3,5 t)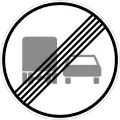 End of...
End of...
Other
 Umwelt
Umwelt
Low-emission zone / Environmental Zone End of a low-emission zone
End of a low-emission zone Lkw / Trucks / Semis must maintain minimum (70 m) spacing
Lkw / Trucks / Semis must maintain minimum (70 m) spacing Schneeketten sind vorgeschrieben
Schneeketten sind vorgeschrieben
Snow chains must be carried in vehicle
Autobahn
German Limited Access Highway - Blue Background[13]
Signs used on Autobahn
 Nummernschild für Autobahnen
Nummernschild für Autobahnen
Autobahn - (limited access highway) route number (48)%252C_650x650%253B_StVO_2013.svg.png.webp) Knotenpunkte der Autobahnen
Knotenpunkte der Autobahnen
Interchange/Exit/Ausfahrt Number (26)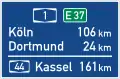 Autobahn distance sign (usually after entrance)
Autobahn distance sign (usually after entrance) Autobahn sign indicating next exit has a service area nearby
Autobahn sign indicating next exit has a service area nearby Autobahn sign
Autobahn sign
announcing next exit%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Autobahn reminder exit sign, showing next exit ahead
Autobahn reminder exit sign, showing next exit ahead Autobahn marker (300m before exit)
Autobahn marker (300m before exit) Autobahn marker (200m before exit)
Autobahn marker (200m before exit)%252C_StVO_1970.svg.png.webp) Autobahn marker (100m before exit)
Autobahn marker (100m before exit) Autobahn Ausfahrt
Autobahn Ausfahrt
exit (at end of exit lane) Begin of Autobahn (Motor vehicles capable of speeds exceeding 60 km/h only)
Begin of Autobahn (Motor vehicles capable of speeds exceeding 60 km/h only) End of Autobahn
End of Autobahn Tunnel ahead
Tunnel ahead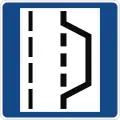 Breakdown bay (used only on highways without emergency shoulder or in larger construction areas)
Breakdown bay (used only on highways without emergency shoulder or in larger construction areas)
Signs leading to Autobahn
 Pfeilwegweiser zur Autobahn
Pfeilwegweiser zur Autobahn
Direction towards Autobahn entrance_ohne_Bundesstra%C3%9Fennummer%253B_StVO_2013.svg.png.webp) Direction Signs to Autobahn, Messe (Fair/Convention Center) & Bundesstraße (without number)
Direction Signs to Autobahn, Messe (Fair/Convention Center) & Bundesstraße (without number)_mit_Bundesstra%C3%9Fennummer%253B_StVO_2013.svg.png.webp) same
same
Bundesstraße with Number and distances to next cities%253B_StVO_1988.svg.png.webp) Vorwegweiser zur Autobahn
Vorwegweiser zur Autobahn
Autobahn junction entrance sign_-_nach_RWB%253B_StVO_2009.svg.png.webp) Vorwegweiser zur Autobahn
Vorwegweiser zur Autobahn
Autobahn junction entrance sign
other signs
 Autobahn Detour
Autobahn Detour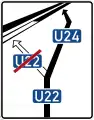 Autobahn Detour ahead
Autobahn Detour ahead%253B_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Detouring onto opposite lane (in 200 m)
Detouring onto opposite lane (in 200 m)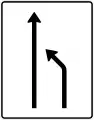 End of lane
End of lane
Signs of federal highways
Note: Though road design of Kraftfahrstrasse is comparable to Autobahn, speed limit is mandatory, signposting is similar but has yellow background.

 End of fast traffic highway
End of fast traffic highway
Bundesstraße - non-limited access highways or main roads - yellow background
 Bundesstraße
Bundesstraße
Country road (non-isolated highway) route number (35) Ausfahrt auf Bundesstraße
Ausfahrt auf Bundesstraße
Exit off Main Road (to Mainz/Wiesbaden) Ausfahrt
Ausfahrt
Exit%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp)
%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp)

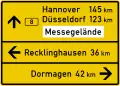 Sign on approaches to junctions
Sign on approaches to junctions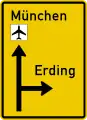 Sign on approaches to junctions
Sign on approaches to junctions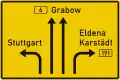 Sign on approaches to junctions (lanes)
Sign on approaches to junctions (lanes)%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Route for Lkw/Kfz
Route for Lkw/Kfz Route for Lkw/Kfz
Route for Lkw/Kfz Lkw/Kfz geradeaus
Lkw/Kfz geradeaus
Go Straight Ahead%252C_StVO_2017.svg.png.webp) Lkw/Kfz abbiegen rects
Lkw/Kfz abbiegen rects
Turn Right Ahead Lkw/Kfz abbiegen links
Lkw/Kfz abbiegen links
Turn Left Ahead Hazardous Cargos - Go Straight Ahead
Hazardous Cargos - Go Straight Ahead%252C_StVO_2017.svg.png.webp) Hazardous Cargos - Go Right Ahead
Hazardous Cargos - Go Right Ahead Hazardous Cargos - Go Left Ahead
Hazardous Cargos - Go Left Ahead Radverkehr
Radverkehr
Bicycles Go Straight Ahead%252C_StVO_2017.svg.png.webp) Radverkehr
Radverkehr
Bicycles Turn Right Ahead Radverkehr
Radverkehr
Bicycles Turn Left Ahead%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp)
 Detour sign (U3)
Detour sign (U3) Umleitung
Umleitung
Detour sign End of Detour
End of Detour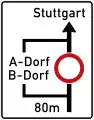 Planskizze
Planskizze
Layout of Detour route_rechtsweisend%252C_StVO_2013.svg.png.webp) Umlenkungspfeil (Streckenempfehlung)
Umlenkungspfeil (Streckenempfehlung)
Existing alternate Autobahn route%252C_StVO_2013.svg.png.webp) End of detour (symbol)
End of detour (symbol)%252C_StVO_2009.svg.png.webp) Complicated traffic touring (if turning left is forbidden)
Complicated traffic touring (if turning left is forbidden) European road number sign (E 36)
European road number sign (E 36) Straßenname
Straßenname
Street name sign%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Direction to Bahnhof
Direction to Bahnhof
Trainstation/ Railway Station
Urban or built-up areas
_mit_Kreis%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Start Urban Area (50 km/h speed limit)
Start Urban Area (50 km/h speed limit) Town sign: End of Urban Area (here with distance to next town)
Town sign: End of Urban Area (here with distance to next town)
 End of Traffic Calming Zone
End of Traffic Calming Zone


%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Fußgängerüberweg
Fußgängerüberweg
Pedestrian crossing_einseitig%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Fußgängerüberweg
Fußgängerüberweg
Pedestrian crossing Sackgasse
Sackgasse
No through road
 Street light warning marker (lamp will not remain lit all night)
Street light warning marker (lamp will not remain lit all night)
Traffic priority - priority roads
Priority Travel Does Not Yield, Signal All Turns
 Vorfahrtstraße
Vorfahrtstraße
Priority Road starts%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp)
%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp)
%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp)
%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp)
%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp)
%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp)

%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp)
%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp)
%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp)
 Vorfahrtstraße
Vorfahrtstraße
Priority Road ends Vorfahrt
Vorfahrt
Priority at the next intersection/crossroads only Uncontrolled Intersection Ahead
Uncontrolled Intersection Ahead
Proceed with extreme caution, priority is not assigned Yield to cross-wise traffic
Yield to cross-wise traffic
Fahrtbahn/Streifen - driving lane controls
Roadway lanes delineated by lines for/of single vehicle width
 Vorgeschriebene Fahrtrichtung, Geradeaus
Vorgeschriebene Fahrtrichtung, Geradeaus
You must go straight ahead, yield appropriately Vorgeschriebene Fahrtrichtung, hier rechts
Vorgeschriebene Fahrtrichtung, hier rechts
Turn right here (in front of the sign) Vorgeschriebene Fahrtrichtung, hier links
Vorgeschriebene Fahrtrichtung, hier links
Turn left here (in front of the sign) Vorgeschriebene Fahrtrichtung, rechts
Vorgeschriebene Fahrtrichtung, rechts
You must turn right ahead, yield appropriately Vorgeschriebene Fahrtrichtung, links
Vorgeschriebene Fahrtrichtung, links
You must turn left ahead, yield appropriately Vorgeschriebene Fahrtrichtung, Geradeaus oder rechts
Vorgeschriebene Fahrtrichtung, Geradeaus oder rechts
You must go straight or turn right Vorgeschriebene Fahrtrichtung, Geradeaus oder links
Vorgeschriebene Fahrtrichtung, Geradeaus oder links
You must go straight or turn left Vorgeschriebene Fahrtrichtung, Rechts oder links
Vorgeschriebene Fahrtrichtung, Rechts oder links
You must turn right or turn left Kreisverkehr
Kreisverkehr
Roundabout (Yield to traffic in circle, signal only on exit) Einbahnstraße
Einbahnstraße
One-way street Einbahnstraße
Einbahnstraße
One-way street Vorgeschriebene Vorbeifahrt, Rechts vorbei
Vorgeschriebene Vorbeifahrt, Rechts vorbei
Keep right of traffic barrier/divider Vorgeschriebene Vorbeifahrt, Links vorbei
Vorgeschriebene Vorbeifahrt, Links vorbei
Keep left of traffic barrier/divider Use of hard shoulder as driving lane permitted
Use of hard shoulder as driving lane permitted No use of hard shoulder as driving lane permitted
No use of hard shoulder as driving lane permitted 3 Fahrstreifen und 1 Seitenstreifen'
3 Fahrstreifen und 1 Seitenstreifen'
3 Driving Lanes + 1 Hard Shoulder (use permitted) 3 Fahrstreifen und 1 Seitenstreifen'
3 Fahrstreifen und 1 Seitenstreifen'
3 Driving Lanes + 1 Hard Shoulder (use not permitted)
Dedicated lane use required for ...
 Fußwege
Fußwege
Footway / Pedestrian lane Gemeinsamer Fuß- und Radweg
Gemeinsamer Fuß- und Radweg
Shared use path Getrennter Rad- und Gehweg
Getrennter Rad- und Gehweg
Shared, but separated bicycle & pedestrian path Radweg
Radweg
Bicycle lane Bussonderfahrstreifen
Bussonderfahrstreifen
Bus lane Sonderweg Reiter
Sonderweg Reiter
Bridleway
Special zones
 Beginn einer Fußgängerzone
Beginn einer Fußgängerzone
Pedestrian zone Ende einer ....
Ende einer ....
End of pedestrian zone Beginn der Fahrradstraße
Beginn der Fahrradstraße
Bicyclist zone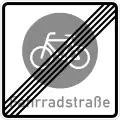 End of bicyclist zone
End of bicyclist zone
Stopping, waiting, parking
Parking is considered any stop exceeding three minutes.
Absolutely no stopping or waiting on traffic lanes (Emergency Excepted)
 Haltverbot
Haltverbot
Absolutely No Stopping (on traffic lanes)%252C_Aufstellung_rechts%252C_StVO_2013.svg.png.webp) Continuation of Absolutes Haltverbot
Continuation of Absolutes Haltverbot
Top arrow only (start of zone), Bottom arrow only (end of zone)
No waiting/standing longer than 3 minutes on traffic lanes - "Loading/Unloading & Pick-up/Drop-off Zone"
 Eingeschränktes Halteverbot
Eingeschränktes Halteverbot
No parking. Waiting is allowed.%252C_Rechtsaufstellung%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Eingeschränktes Halteverbot (Anfang)
Eingeschränktes Halteverbot (Anfang)
Start of Waiting Only Zone (left side)%252C_Aufstellung_links%252C_StVO_2017.svg.png.webp) Eingeschränktes Halteverbot (Anfang)
Eingeschränktes Halteverbot (Anfang)
Start of Waiting Only Zone (right side)%252C_Rechtsaufstellung%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Eingeschränktes Halteverbot (Ende)
Eingeschränktes Halteverbot (Ende)
End of Waiting Only Zone (right side)%252C_Rechtsaufstellung%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Continuation of Eingeschränktes Halteverbot
Continuation of Eingeschränktes Halteverbot No parking zone
No parking zone End of no parking zone
End of no parking zone
Bus Stop & Taxi Zones
 Bus or tram stop: 15 m parking prohibition prior to and behind this sign (30 m altogether)
Bus or tram stop: 15 m parking prohibition prior to and behind this sign (30 m altogether)%252C_StVO_2017.svg.png.webp) School bus stop: 15 m parking prohibition prior to and behind this sign (30 m altogether)
School bus stop: 15 m parking prohibition prior to and behind this sign (30 m altogether) Taxi rank (no stopping or parking allowed)
Taxi rank (no stopping or parking allowed) End of previous limitation (i.e., speed or passing)
End of previous limitation (i.e., speed or passing)
Road markings/lines
Intersections & Crosswalks[14]
 Haltlinie
Haltlinie
Stop line Fußgängerüberweg
Fußgängerüberweg
Pedestrian crossing Wartelinie
Wartelinie
Yield line
Driving Lanes
 Fahrstreifenbegrenzung und Fahrbahnbegrenzung
Fahrstreifenbegrenzung und Fahrbahnbegrenzung
Solid Travel Lane (middle) & Travel Lane Boundary (right) - Crossing Not Permitted Leitlinie
Leitlinie
Guide (Dividing) Line - Crossing/Overtaking Permitted Einseitige Fahrstreifenbegrenzung
Einseitige Fahrstreifenbegrenzung
Traffic on Solid Side May Not Cross Line. Traffic on Divided Side May Cross Line. Direction arrows (no stopping or parking allowed)
Direction arrows (no stopping or parking allowed) Advance notice arrow
Advance notice arrow Advance notice arrow to indicate a lane end
Advance notice arrow to indicate a lane end Sperrflächen
Sperrflächen
Occupying this area not permitted Grenzmarkierung für Halt- und Parkverbote
Grenzmarkierung für Halt- und Parkverbote
No Parking or Waiting Area
Information signs
 Parking place
Parking place%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Parkplatz (Anfang)
Parkplatz (Anfang)
Parking place (start)%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Parking place (end)
Parking place (end) Beginn einer Parkraumbewirtschaftungszone
Beginn einer Parkraumbewirtschaftungszone
Start of Parking management area, only parking with parking disc or parking ticket End of Parking management area
End of Parking management area Car park, parking garage
Car park, parking garage Wasserschutzgebiet
Wasserschutzgebiet
Water protection zone%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Place name (information only, does not imply a speed limit)
Place name (information only, does not imply a speed limit)%252C_StVO_2013.svg.png.webp)

 Tourist route
Tourist route Tourist sign (here: river or channel)
Tourist sign (here: river or channel) Tourist route
Tourist route Tourist route
Tourist route Tourist route
Tourist route Tourist sign (here: referring to the former East-West German border)
Tourist sign (here: referring to the former East-West German border)
 End of toll road for heavy lorries
End of toll road for heavy lorries
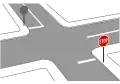
 Stop - customs
Stop - customs
Informational signs
 Park and Ride
Park and Ride





 Petrol station with LPG
Petrol station with LPG Petrol station with CNG
Petrol station with CNG Motorway hotel
Motorway hotel
 Information
Information%252C_StVO_2013.svg.png.webp)


 Charging station for electric vehicles
Charging station for electric vehicles Hydrogen Station
Hydrogen Station Motor caravan campsite
Motor caravan campsite Campsite
Campsite%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Motorway restaurant
Motorway restaurant%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Motorway refreshments
Motorway refreshments%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp)
Standardized traffic symbols
Arrows
 To the left
To the left To the right
To the right After the left turn, a hazard exists (another sign defining the hazard would be above)
After the left turn, a hazard exists (another sign defining the hazard would be above) After the right turn, a hazard exists (another sign defining the hazard would be above)
After the right turn, a hazard exists (another sign defining the hazard would be above) Fußgänger Gehweg gegenüber benutzen
Fußgänger Gehweg gegenüber benutzen
Use Sidewalk on left side of roadway%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Fußgänger Gehweg gegenüber benutzen
Fußgänger Gehweg gegenüber benutzen
Use Sidewalk on right side of roadway Directional indications by arrows, detour signs, three-quarter circle[15]
Directional indications by arrows, detour signs, three-quarter circle[15] Both directions, two opposing horizontal arrows
Both directions, two opposing horizontal arrows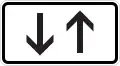 Both directions, two opposite vertical arrows
Both directions, two opposite vertical arrows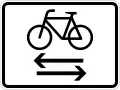 Two-way cycle route crossing road
Two-way cycle route crossing road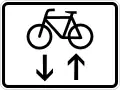 Cycling in the opposite direction
Cycling in the opposite direction Directional indications by arrows, detour signs, semicircle[15]
Directional indications by arrows, detour signs, semicircle[15]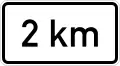 2 km ahead[16]
2 km ahead[16] Stop 100 m ahead
Stop 100 m ahead Zipper method in ... m
Zipper method in ... m For 800 m
For 800 m%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) For 3 km
For 3 km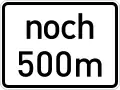 Continues for ... m
Continues for ... m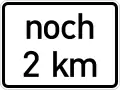 Continues for ... km
Continues for ... km 100 m ahead
100 m ahead 200 m ahead
200 m ahead 400 m ahead
400 m ahead 600 m ahead
600 m ahead Late merge in 200m
Late merge in 200m Ends in ...m
Ends in ...m
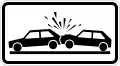 Risk of accident
Risk of accident Migratory toad crossing
Migratory toad crossing


 Construction site exit
Construction site exit Damaged roadway
Damaged roadway Spillage on road
Spillage on road Exit
Exit Accident
Accident Knoll
Knoll Police check
Police check Fog
Fog Driveway
Driveway%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Right of way changed
Right of way changed Traffic routing changed
Traffic routing changed Industrial area (trains have priority)
Industrial area (trains have priority)%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Port area (rail traffic has priority)
Port area (rail traffic has priority)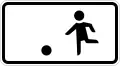 Children allowed to play in road
Children allowed to play in road%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Skiers allowed to cross road
Skiers allowed to cross road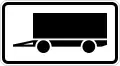 Large wagons can park here without the usual two week temporal parking restriction
Large wagons can park here without the usual two week temporal parking restriction%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Caravans can park here without the usual two week temporal parking restriction
Caravans can park here without the usual two week temporal parking restriction%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp)
%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) End of restriction
End of restriction%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Cyclists dismount
Cyclists dismount%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Green wave at ...km/h
Green wave at ...km/h%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Stop here on red
Stop here on red Pass over verges/shoulder
Pass over verges/shoulder End of passing over verges/shoulder
End of passing over verges/shoulder%252C_StVO_2007.svg.png.webp) Tunnel category B
Tunnel category B%252C_StVO_2007.svg.png.webp) Tunnel category C
Tunnel category C%252C_StVO_2007.svg.png.webp) Tunnel category D
Tunnel category D%252C_StVO_2007.svg.png.webp) Tunnel category E
Tunnel category E Disabled with permit No. ... allowed
Disabled with permit No. ... allowed%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Bicycle and residents allowed
Bicycle and residents allowed%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Residents only
Residents only%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Residents or Resident's Visitors Parking Only
Residents or Resident's Visitors Parking Only Residents with permit No. ... allowed
Residents with permit No. ... allowed Taxis allowed
Taxis allowed%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Regular scheduled buses allowed
Regular scheduled buses allowed%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Emergency vehicles allowed
Emergency vehicles allowed Ambulances allowed
Ambulances allowed Delivery vehicles allowed
Delivery vehicles allowed%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Agricultural vehicles allowed
Agricultural vehicles allowed Forestry vehicles allowed
Forestry vehicles allowed%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Agricultural and forestry vehicles allowed
Agricultural and forestry vehicles allowed%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Operational and utility vehicles allowed
Operational and utility vehicles allowed Electric vehicles while charging allowed
Electric vehicles while charging allowed Electric vehicles allowed
Electric vehicles allowed%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Construction vehicles allowed
Construction vehicles allowed%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Access to construction site allowed
Access to construction site allowed%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Access to neighbouring construction site allowed
Access to neighbouring construction site allowed%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Access to ... allowed
Access to ... allowed%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Ferry users allowed
Ferry users allowed Vehicles with red, yellow or green Low Emission Zone Sticker permitted
Vehicles with red, yellow or green Low Emission Zone Sticker permitted Vehicles with yellow or green Low Emission Zone Sticker permitted
Vehicles with yellow or green Low Emission Zone Sticker permitted Vehicles with green Low Emission Zone Sticker permitted
Vehicles with green Low Emission Zone Sticker permitted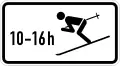 Skiers crossing road at times shown
Skiers crossing road at times shown%252C_330x600%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) At times shown
At times shown%252C_330x600%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) At times shown
At times shown Parking with disc for 2 hours
Parking with disc for 2 hours Parking with disc in marked zone for 2 hours
Parking with disc in marked zone for 2 hours%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp)
%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Working days at times shown
Working days at times shown%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Working days at times shown
Working days at times shown%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Monday-Friday, at times shown
Monday-Friday, at times shown%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Tuesdays, Thursdays and Fridays, at times shown
Tuesdays, Thursdays and Fridays, at times shown%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Sundays and public holidays, at times shown
Sundays and public holidays, at times shown%252C_600x450%252C_StVO_2017.svg.png.webp) School bus (at times shown)
School bus (at times shown)%253B_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp)
 Disabled users only
Disabled users only%253B_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Disabled with permit No. ... only
Disabled with permit No. ... only%252C_StVO_2002.svg.png.webp) Residents with permit No. ... only
Residents with permit No. ... only Slow vehicles allowed to pass
Slow vehicles allowed to pass%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp)
%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Number of taxis
Number of taxis Electric vehicles being charged (with number)
Electric vehicles being charged (with number) Electric vehicles (with number)
Electric vehicles (with number) Parking allowed in marked areas
Parking allowed in marked areas%252C_StVO_2017.svg.png.webp) Only with parking ticket
Only with parking ticket%252C_StVO_2017.svg.png.webp)
%252C_StVO_2017.svg.png.webp) On the verges/shoulder
On the verges/shoulder%252C_StVO_2017.svg.png.webp) When wet
When wet Mode of transport
Mode of transport%252C_StVO_2005.svg.png.webp) Weight (12 tons)
Weight (12 tons)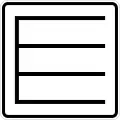 Park (pull in straight)
Park (pull in straight)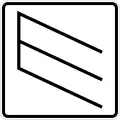 Park (pull in diagonally)
Park (pull in diagonally) Only within marked parking areas
Only within marked parking areas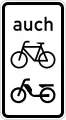 For cyclists and moped riders
For cyclists and moped riders Grit on road
Grit on road%252C_StVO_2017.svg.png.webp) No parking on verges/shoulder
No parking on verges/shoulder%252C_StVO_2017.svg.png.webp) Also buses and cars with trailers
Also buses and cars with trailers Rabies! Endangered area
Rabies! Endangered area Wild animal rabies! Endangered area
Wild animal rabies! Endangered area
Road equipment
 Barrier board
Barrier board%252C_1000x250%253B_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Guiding beacon
Guiding beacon Guide cone
Guide cone Moveable road barrier
Moveable road barrier Moveable road barrier with flashing arrow
Moveable road barrier with flashing arrow%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Reflexion post (right-hand side)
Reflexion post (right-hand side)%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp) Reflexion post (left-hand side)
Reflexion post (left-hand side)
Retired signs
Obsolete signs since 2017 [15]
 Buses crossing
Buses crossing Two-way cycle route running parallel to road
Two-way cycle route running parallel to road Risk of ice
Risk of ice Start of restriction
Start of restriction Mopeds allowed
Mopeds allowed%252C_StVO_1995.svg.png.webp) Vehicles exempt from the traffic ban at an increased pollutant concentration
Vehicles exempt from the traffic ban at an increased pollutant concentration
Obsolete signs since 2013 [15]
 Level crossing with barrier or gate ahead
Level crossing with barrier or gate ahead_vor_beschranktem_Bahn%C3%BCbergang%252C_StVO_1970.svg.png.webp) Level crossing with barrier or gate ahead
Level crossing with barrier or gate ahead%252C_StVO_1992.svg.png.webp)

 End of recommended speed
End of recommended speed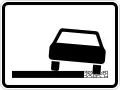 Soft verges
Soft verges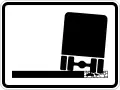 Soft verges
Soft verges
References
- "Straßenverkehrs-Ordnung (StVO) § 39 Verkehrszeichen". Federal Ministry of Transport. Retrieved 18 August 2020.
- "VzKat 2017" (in German). 5 July 2020. Retrieved 18 August 2020.
- "Allgemeine Verwaltungsvorschrift zur Straßenverkehrs-Ordnung] (VwV-StVO)". Retrieved 18 August 2020.
- de:Reißverschlussverfahren
- "§ 39 StVO 2013 - Einzelnorm". www.gesetze-im-internet.de.
- "German Road Signs: Guide to Parking & Road Signs in Germany". Auto Europe. Retrieved 17 November 2015.
- name="LoC"www.bast.de
- "Personenkraftwagen". 11 April 2018 – via Wikipedia.
- "Lastkraftwagen". 16 April 2018 – via Wikipedia.
- "Kraftfahrzeug". 20 April 2018 – via Wikipedia.
- "Sattelzug". 25 April 2018 – via Wikipedia.
- /Traffic: Priority (right of way)
- "Brian's Guide to Getting Around Germany - The Autobahn". www.gettingaroundgermany.info.
- de:Straßenmarkierung
- "www.bast.de".
- "§ 40 StVO 2013 - Einzelnorm". www.gesetze-im-internet.de.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Road signs in Germany. |