Stop sign
A stop sign is a traffic sign designed to notify drivers that they must come to a complete stop and make sure the intersection is safely clear of vehicles and pedestrians before continuing past the sign.[1]

Design and configuration
The 1968 Vienna Convention on Road Signs and Signals allows for two types of stop sign as well as several acceptable variants. Sign B2a is a red octagon with a white stop legend. The European Annex to the convention also allows the background to be "light yellow". Sign B2b is a red circle with a red inverted triangle with either a white or yellow background, and a black or dark blue stop legend. The Convention allows for the word "STOP" to be in either English or the national language of the particular country. The finalized version by the United Nations Economic and Social Council's Conference on Road Traffic in 1968 (and in force in 1978) proposed standard stop sign diameters of 600, 900 or 1200 mm.
The United Kingdom and New Zealand stop signs are 750, 900 or 1200 mm, according to sign location and traffic speeds.[2][3]
In the United States, stop signs are 30 inches (75 cm) across opposite flats of the red octagon, with a 3/4-inch (2 cm) white border. The white uppercase stop legend is 10 inches (25 cm) tall.[4][5] Larger signs of 35 inches (90 cm) with 12-inch (30 cm) legend and 1-inch (2.5 cm) border are used on multilane expressways. Regulatory provisions exist for extra-large 45-inch (120 cm) signs with 16-inch (40 cm) legend and 1+3/4-inch border for use where sign visibility or reaction distance are limited, and the smallest permissible stop sign size for general usage is 24 inches (60 cm) with an 8-inch (20 cm) legend and 5/8-inch (1.5 cm) border.[6] The metric units specified in the US regulatory manuals are rounded approximations of US customary units, not exact conversions.[5][7] The field, legend, and border are all retroreflective.
 B2a
B2a Acceptable variant of B2a in the European Annex
Acceptable variant of B2a in the European Annex B2b
B2b Acceptable variant of B2b
Acceptable variant of B2b Acceptable variant of B2b
Acceptable variant of B2b Acceptable variant of B2b
Acceptable variant of B2b
History

Stop signs originated in Michigan in 1915.[8][9] The first ones had black lettering on a white background and were 24 by 24 inches (61 cm × 61 cm), somewhat smaller than the current sign. As stop signs became more widespread, a rural-dominated committee supported by the American Association of State Highway Officials (AASHO) met in 1922 to standardize them and selected the octagonal shape that has been used in the United States ever since. The unique eight-sided shape of the sign allows drivers facing the back of the sign to identify that oncoming drivers have a stop sign and prevent confusion with other traffic signs. It was also chosen so that it could be identified easily at night since the original signs were not reflective. The more urban-oriented National Conference on Street and Highway Safety (NCSHS) advocated a smaller red-on-yellow stop sign.[8] These two organizations eventually merged to form the Joint Committee on Uniform Traffic Control Devices, which in 1935 published the first Manual on Uniform Traffic Control Devices for Streets and Highways (MUTCD) detailing the stop sign's specifications.
The MUTCD's stop sign specifications were altered eight times between 1935 and 1971. From 1924 to 1954, stop signs bore a red or black stop legend on a yellow field.[8] Yellow was chosen because fade-resistant red materials were not available.[10][11] Retro-reflective or self-lit signs were permitted in the 1935 MUTCD; retro-reflective ones were first required by the 1948 edition of the MUTCD, which also called for a 2 1/2-foot (0.76-metre) height from the road crown to the bottom of the stop sign.[12] The 1954 MUTCD newly specified a white stop legend on a red field, and increased the mount height specification to 5 feet in rural areas.[8] Red traffic lights signify stop, so the new specification unified red as a stop signal whether given by a sign or a light. The current mounting height of 7 ft (2.13 m) was first specified in 1971;[8]

US mandate, international adoption
The MUTCD stop sign was already widely deployed in the United States when its use became mandatory in 1966.[8] In 1968, this sign was adopted by the Vienna Convention on Road Signs and Signals as part of United Nations Economic Commission for Europe's effort to standardize road travel across borders. The Convention specifies that stop be written in English or the national language, and also allows a circular sign with red legend. Forty European countries[13] are party to the Convention.
Stop signs around the world
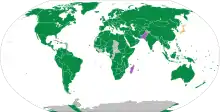
The red octagonal field with white English-language stop legend is the most common stop sign used around the world, but it is not universal; Japan uses an inverted solid red triangle, for example, and Zimbabwe until 2016 used a disc bearing a black cross. Moreover, there are many variants of the red-and-white octagonal sign. Although all English-speaking and many other countries use the word stop on stop signs, some jurisdictions use an equivalent word in their primary language instead, or in addition; the use of native languages is common on U.S. native reservations, especially those promoting language revitalization efforts, for example, and Israel uses no word, but rather a pictogram of a hand in a palm-forward "stop" gesture.
Asia
Countries in Asia generally use a native word, often in a non-Latin script.
Europe
Countries in Europe generally have stop signs with the text stop, regardless of local language. There were some objections to this when introduced around the 1970s, but now this is accepted. Turkey is a notable exception to this, instead using the Turkish word for stop: "dur".
Latin America
In most Caribbean, Central and South American countries (Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Cuba, Dominican Republic, Ecuador, Paraguay, Peru, Puerto Rico, Uruguay, and Venezuela), signs bear the legend pare ("stop" in Portuguese and Spanish). Mexico and Central American countries bear the legend alto ("halt") instead.
Canada
In the Canadian province of Quebec, modern signs read either arrêt or stop;[15] however, it is not uncommon to see older signs containing both words in smaller lettering, with arrêt on top.[16] Both stop and arrêt are considered valid French words and the Office québécois de la langue française (OQLF) notes that the use of "stop" on stop signs is attested in French since 1927.[17] At the time of the debates surrounding the adoption of the Charter of the French Language ("Bill 101") in 1977, the usage of "stop" on the older dual-word signs was considered to be English and therefore controversial; some signs were occasionally vandalized with red spray paint to turn the word stop into "101".[18] However, it was later officially determined by the OQLF that "stop" is a valid French word in this context, and the older dual arrêt / stop usage is therefore not considered bilingual but merely redundant and therefore deprecated (à éviter). All newly installed signs thus use either one word or the other, but not both. In practice, the vast majority of signs use arrêt in Québec, while stop is usually seen in predominantly English-speaking areas. Bilingual signs with stop arrêt are placed in English-speaking areas of New Brunswick, Acadian regions of Nova Scotia, Prince Edward Island, Manitoba, National Capital Region and all border crossings of the Canada–United States border. On First Nations or Inuit territories, stop signs sometimes use the local aboriginal language in addition or instead of English, French, or both. All other English-speaking areas of Canada use stop.
Other countries
- Arabic-speaking countries use قف qif (except for Lebanon, which only uses stop)
- Australia, New Zealand and the USA use the standard version of the sign
- Armenia uses ԿԱՆԳ kang
- Cambodia uses ឈប់ chhob
- Mainland China and Taiwan use 停 tíng, except that Mainland China's sign has a bolder word.
- Ethiopia uses ቁም ḳumə
- Iran and Afghanistan use ایست ist
- Japan uses 止まれ tomare
- Laos uses ຢຸດ yud
- North Korea uses 섯 sŏt
- Portuguese-speaking countries use the standard version of the sign, except for Brazil which uses pare
- South Korea uses 정지 jeongji
- Spanish-speaking countries use pare and/or alto, except for Spain which only uses stop
- Malaysia and Brunei use berhenti
- Mongolia uses ЗОГС zogs
- Myanmar uses ရပ် raut
- Thailand uses หยุด yùd
- Turkey uses dur
- Vietnam uses stop
 Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Dominican Republic, Ecuador, Paraguay, Peru, Puerto Rico, Uruguay, Venezuela
Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Dominican Republic, Ecuador, Paraguay, Peru, Puerto Rico, Uruguay, Venezuela Australia, Canada, European Economic Area, Fiji, Indonesia, New Zealand, United Kingdom, United States
Australia, Canada, European Economic Area, Fiji, Indonesia, New Zealand, United Kingdom, United States Armenia
Armenia Bhutan
Bhutan Brunei
Brunei Cambodia
Cambodia Costa Rica, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, Panama
Costa Rica, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, Panama Cuba
Cuba Mainland China
Mainland China.svg.png.webp) Egypt, Libya, Morocco, Saudi Arabia, Sudan
Egypt, Libya, Morocco, Saudi Arabia, Sudan Ethiopia
Ethiopia France, Ireland, Portugal, Spain
France, Ireland, Portugal, Spain Hong Kong
Hong Kong Iran, Afghanistan
Iran, Afghanistan Israel, Palestine
Israel, Palestine India (Punjabi areas)
India (Punjabi areas) Japan
Japan Laos
Laos Malaysia
Malaysia Mongolia
Mongolia Myanmar
Myanmar Nigeria
Nigeria North Korea
North Korea Province of Quebec, Canada
Province of Quebec, Canada South Africa
South Africa South Korea
South Korea Taiwan, Republic of China
Taiwan, Republic of China Thailand
Thailand Tonga
Tonga Tunisia
Tunisia Turkey
Turkey Vanuatu
Vanuatu Vietnam
Vietnam
Historical gallery
The following are some older stop sign designs, used before the Vienna Road Traffic Convention standardized the design:
_Halt_f%C3%BCr_alle_Fahrzeuge!_vor_1937.svg.png.webp) Germany (before 1937)
Germany (before 1937)
.svg.png.webp) Finland (1957-1971)
Finland (1957-1971)
 Italy (1959-1990)
Italy (1959-1990) Romania (1957-1961)
Romania (1957-1961).svg.png.webp) United Kingdom (1965-1975)
United Kingdom (1965-1975).svg.png.webp) Sweden (1951-1976)
Sweden (1951-1976) United States (before 1954)
United States (before 1954) Ethiopia
Ethiopia Libya
Libya.svg.png.webp) Zambia
Zambia North Korea
North Korea.svg.png.webp) Japan (1950-1960)
Japan (1950-1960).svg.png.webp) Japan (1960-1963)
Japan (1960-1963).svg.png.webp) Thailand
Thailand Australia (1940-1956)
Australia (1940-1956) Pakistan
Pakistan Vietnam (1955-1975)
Vietnam (1955-1975)
Application
Stop signs are used all over the world, but most countries outside of North America and South Africa use relatively few of them because all-way stops are never used and in some countries are legally prohibited.[19] In a majority of Central Asian countries, as well as Cuba in North America, junctions without traffic lights or roundabouts are controlled by stop signs on minor roads and by white, yellow and black priority diamond signs on the major road. In Europe and Australia, stop signs are restricted to places where coming to a dead stop is deemed necessary because of severely limited sight lines. At the vast majority of minor intersections in these countries give way signs and/or equivalent road markings are used, or the intersections are no-priority; roundabouts also work on the give way (rather than stop) principle.
North America
Stop signs are often used in North America to control conflicting traffic movements at intersections that are deemed not busy enough to justify the installation of a traffic signal or roundabout. In the United States, the stop sign is not intended as a traffic calming device,[6] but is meant to be installed mainly for safety or to assign right-of-way. Stop signs may be erected on all intersecting roads, resulting in an all-way stop.[6] Some research has concluded that stop signs do not offer measurable safety benefits over the Yield approach.[20][21] Other research has concluded that multiway stop signs do not effectively control traffic speeds, and can give rise to negative effects including increased traffic noise and pollution from braking and accelerating vehicles, enforcement problems, and reduced sign compliance.[22]
On school buses

A stop sign on a pivoting arm is required equipment on North American school buses. The sign normally stows flat on the left side of the bus, and is deployed by the driver when opening the door for picking up or dropping off passengers. Some buses have two such stop arms, one near the front facing forwards, and one near the rear facing backwards. The stop sign is retroreflective and equipped either with red blinking lights above and below the stop legend or with a legend that is illuminated by LEDs. Unlike a normal stop sign, this sign indicates a two-way absolute stop, requiring other vehicles travelling in both directions to remain stopped until the sign is retracted.
Europe
In Europe, stop signs are generally placed at sites where visibility is severely restricted, or where a high crash rate has been noted. In some European countries, stop signs are placed at level crossings to mark the stop line. For most situations, Europe uses the give way sign instead.[23][24] All-way stops, which are common in North America, are exceedingly rare in Europe. Comparatively, priority to the right intersections are more common.
United Kingdom
In the United Kingdom, stop signs may only be placed at junctions with tramways or sites with severely restricted visibility.[25] Until 2016, each stop sign had to be individually approved by the Secretary of State for Transport.[26][27] This requirement was removed by the 2016 amendments to the Traffic Signs Regulations and General Directions;[28][29] the responsibility for approving stop signs now lies with local authorities.
Section 79 of the Highways Act 1980 enables the government to improve visibility at junctions, as by removing or shortening walls or hedges. The Department for Transport considers improving visibility to be preferable to installing a stop sign.[25] The former UK practice of using "Halt" or "Slow" at Major Road Ahead signs was discontinued in 1965 at the recommendation of the Worboys Committee.[30] Instead of replacing all the old halt signs with the new Vienna Convention stop sign, the give way sign became the standard one at UK priority junctions.[31]
Compliance requirements
Laws and regulations regarding how drivers must comply with a stop sign vary by jurisdiction. In the United States and Canada, these rules are set and enforced at the state or provincial level. At a junction where two or more traffic directions are controlled by stop signs, US and Canada practice generally has the driver who arrives and stops first continue first. If two or three drivers in different directions stop simultaneously at a junction controlled by stop signs, generally the drivers on the left must yield the right-of-way to the driver on the far right.
In all countries, the driver must come to a complete stop before passing a stop sign, even if no other vehicle or pedestrian is visible. If a stop line is marked on the pavement, drivers must stop before crossing the line. Slowing but not completely stopping is called a "rolling stop", sometimes nicknamed after a city or region where it is considered endemic (e.g., "Rhode Island roll" or "California stop"[32]) – slowing down significantly but not stopping completely at the sign.[33] This partial stop is not acceptable to most law enforcement officials, and can result in a traffic citation. However, enforcement of this rule varies widely among countries.
In some countries such as Czechia and Russia, stopping is required only at a place where a driver has a sufficient view into the intersection, not at the border of the intersection (where a "STOP" line is not present). Therefore, if multiple drivers come from the same direction and all of them stop at appropriate place, they can continue without stopping again.[34]
Bicyclists
In some jurisdictions, such as the U.S. state of Idaho, the traffic code allows for bicyclists approaching a stop sign to slow down and yield to conflicting traffic, then proceed without stopping unless safety requires a full stop.[35] The Idaho law has been in effect since 1982 and has not been shown to be detrimental to safety.[36] Cyclist advocacy groups have sought similar laws for other jurisdictions in the United States.[37][38]
Disadvantages
Stop sign placement can pose difficulties and hazards in applications where cross traffic is not controlled by a sign or light. Relatively long distance between the stop sign and the crossroad facilitates accurate perception of the speed of approaching cross traffic, but lengthens the time and distance required to enter and clear the junction. Relatively short distance between the stop sign and the crossroad shortens the time required for safe passage through the intersection, but degrades the ability of the stopped driver to accurately perceive the speed of approaching cross traffic. Specifically, drivers approaching an intersection from beyond the subtended angular velocity detection threshold (SAVT) limit may be perceived by a stopped driver as standing still rather than approaching, [39] which means the stopped driver may not make an accurate decision as to whether it is safe to proceed past the stop sign.[40] Whether the distance between the stop sign and the crossroad is officially short or is shortened by drivers creeping past the stop line, they can lose the visual acuity of lateral motion,[41] leaving them to rely on the SAVT.[40] This can make it difficult to accurately estimate the movement of approaching cross traffic.[40][39]
See also
References
- Vienna Convention on Road Signs and Signals, 1968. United Nations Publication. ISBN 978-92-1-116973-7
- "UK Department of Transport. Traffic Signs Manual, Chapter 3: Regulatory Signs" (PDF). 9 September 2008. Archived from the original on 1 June 2010.CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) (2.0 MB)
- New Zealand Transport Agency. Traffic Control Devices Manual: General requirements for traffic signs, (963 KB)
- Standard Highway Signs manual, 2004 Metric edition (8.36 MB)
- "Standard Highway Signs manual, 2004 English edition" (PDF). (8.49 MB)
- "Manual on Uniform Traffic Control Devices 2003, Section 2B". Mutcd.fhwa.dot.gov. Retrieved 11 March 2012.
- "Standard Highway Signs manual, 2004 Metric edition" (PDF). (8.36 MB)
- Signalfan. History of the Stop Sign in America. 1997.
- Greenbaum, Hilary; Rubinstein, Dana (9 December 2011). "The Stop Sign Wasn't Always Red". The New York Times. Retrieved 10 February 2013.
- Felton, Ryan (14 October 2017). "Here's Why Stop Signs Are Red". Jalopnik. Gawker Media. Retrieved 16 October 2017.
- Manaul on Uniform Traffic Control Devices (PDF). Department of Commerce. 1954. p. 2. Retrieved 16 October 2017.
- Manual on Uniform Traffic Control Devices. 1948 Edition. Part 1A, Section 31. "[A stop sign] shall be mounted so that its bottom will be 21⁄2 feet above the crown of the roadway."
- "Convention on Road Signs and Signals". United Nations Treaty Collection. United Nations.
- Watanabe, June (20 September 2006). "Malls can erect non-red stop signs". Star-Bulletin. Retrieved 29 December 2020.
- "Répertoire des dispositifs de signalisation routière du Québec, Transports Québec". Mtqsignalisation.mtq.gouv.qc.ca. Archived from the original on 22 February 2012. Retrieved 11 March 2012.
- "Canada, Quebec, Montreal, bilingual Stop sign Stock Photos". Masterfile.com. Retrieved 11 March 2012.
- panneau ARRÊT, Office québécois de la langue française, granddictionnaire.com.
- Photo by Flickr.com user "imagesdistributioncanada"
- "Traffic Signs Manual, Chapter 3: Regulatory Signs, Section 3.4" (PDF). UK Department of Transport. 8 September 2008. (2.0 MB)
- Some factors influencing the road behaviour of vehicle drivers. R.J. Smeed, UK Road Research Laboratory. Operational Research Quarterly, Journal of the Operational Research Society, Birmingham, England, 1952.
- "Driver behaviour and accident records at unsignalized urban intersections". Abishai Polusa, Department of Civil Engineering & Transportation Research Institute, Technion-Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa 32000, Israel. June 1984. Available online 4 July 2002.
- Bretherton, M. "Multi-Way Stops—The MUTCD Is Correct!" 1999 ITE Compendium of Technical Papers. Institute of Transportation Engineers, August 1999.
- https://www.rd.com/article/paris-stop-sign/
- https://blogs.transparent.com/dutch/dutch-traffic-why-the-stop-sign-is-so-rare-in-the-netherlands/
- "Chapter 3: Regulatory Signs". Traffic Signs Manual (PDF). London: TSO. 2019. p. 18. ISBN 978-0-11-553223-8. Retrieved 27 April 2020.
- UK Department of Transport. Traffic Signs Manual, Chapter 3: Regulatory Signs, Section 3.2, 9 September 2008
- "The Traffic Signs Regulations and General Directions 2002". www.legislation.gov.uk. Retrieved 27 April 2020.
- "Annex A". DfT Circular: The Traffic Signs Regulations and General Directions 2016 (PDF). 2016. p. 76. Retrieved 27 April 2020.
- "The Traffic Signs Regulations and General Directions 2016". www.legislation.gov.uk. Retrieved 27 April 2020.
- Great Britain. Report of the Traffic Signs Committee [Chairman, Sir Walter Worboys], 18 April 1963.
- "New traffic signs demonstrated on road at Birmingham." The Surveyor and Municipal Engineer, vol 122, p880, 1963.
- Rosenberg, Mike (30 September 2010). "Cheaper fines for right turn on red? No way, governor says". San Jose Mercury News. Retrieved 30 September 2010.
- "Dictionary.com definition". Dictionary.reference.com. Retrieved 11 March 2012.
- https://www.autoskolaprikasky.cz/news/musim-na-stopce-zastavit-za-dalsim-vozidlem/
- "Bicycle-related Idaho Code" (PDF). Idaho Vehicle Code Title 49, Chapter 7. Idaho Transportation Department. Retrieved 7 February 2013.
- "Bike Law University: Idaho Stop". The League of American Bicyclists. 22 August 2013.
- Maus, Jonathan. "Exclusive: BTA will go for "Idaho style" stop sign law". BikePortland.org. Retrieved 7 February 2013.
- "Idaho-style STOP law". San Francisco Bicycle Coalition. Retrieved 7 February 2013.
- Hershel Weinberger (19 February 1971). "Conjecture on the Visual Estimation of Relative Radial Motion". Nature. 229 (5286): 562. doi:10.1038/229562a0. PMID 4925353. S2CID 4290244.
- Michael E. Maddox; Aaron Kiefer (September 2012). "Looming Threshold Limits and Their Use in Forensic Practice". Proceedings of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society Annual Meeting. 50 (1): 700–704. doi:10.1177/1071181312561146. S2CID 109898296.
- Joseph S. Lappin; Duje Tadin; Jeffrey B. Nyquist; Anne L. Corn (January 2009). "Spatial and temporal limits of motion perception across variations in speed, eccentricity, and low vision". Journal of Vision. 9 (30): 30.1–14. doi:10.1167/9.1.30. PMID 19271900.
Displacement thresholds for peripheral motion were affected by acuity limits for speeds below 0.5 degrees/s.

