Roman calendar
The Roman calendar was the calendar used by the Roman kingdom and republic. The term often includes the Julian calendar established by the reforms of the dictator Julius Caesar and emperor Augustus in the late 1st century BC and sometimes includes any system dated by inclusive counting towards months' kalends, nones, and ides in the Roman manner. The term usually excludes the Alexandrian calendar of Roman Egypt, which continued the unique months of that land's former calendar; the Byzantine calendar of the later Roman Empire, which usually dated the Roman months in the simple count of the ancient Greek calendars; and the Gregorian calendar, which refined the Julian system to bring it into still closer alignment with the tropical year.
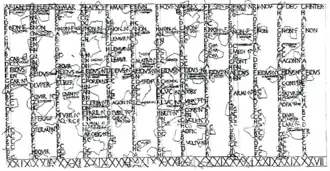

Roman dates were counted inclusively forward to the next of three principal days: the first of the month (the kalends), a day shortly before the middle of the month (the ides), and eight days—nine, counting inclusively—before this (the nones). The original calendar consisted of ten months beginning in spring with March; winter was left as an unassigned span of days. These months ran for 38 nundinal cycles, each forming an eight-day week (nine days counted inclusively, hence the name) ended by religious rituals and a public market. The winter period was later divided into two months, January and February. The legendary early kings Romulus and Numa Pompilius were traditionally credited with establishing this early fixed calendar, which bears traces of its origin as an observational lunar one. In particular, the kalends, nones, and ides seem to have derived from the first sighting of the crescent moon, the first-quarter moon, and the full moon respectively. The system ran well short of the solar year, and it needed constant intercalation to keep religious festivals and other activities in their proper seasons. This is a typical element of lunisolar calendars. For superstitious reasons, such intercalation occurred within the month of February even after it was no longer considered the last month.
After the establishment of the Roman Republic, years began to be dated by consulships and control over intercalation was granted to the pontifices, who eventually abused their power by lengthening years controlled by their political allies and shortening the years in their rivals' terms of office. Having won his war with Pompey, Caesar used his position as Rome's chief pontiff to enact a calendar reform in 46 BC, coincidentally making the year of his third consulship last for 446 days. In order to avoid interfering with Rome's religious ceremonies, the reform added all its days towards the ends of months and did not adjust any nones or ides, even in months which came to have 31 days. The Julian calendar was supposed to have a single leap day on 24 February (a doubled VI Kal. Mart. or ante diem bis sextum Kalendas Martias) every fourth year, but following Caesar's assassination the priests figured this using inclusive counting and mistakenly added this bissextile (bis sextum) day every three years. In order to bring the calendar back to its proper place, Augustus was obliged to suspend intercalation for one or two decades. The revised calendar remained slightly longer than the solar year; by the 16th century the date of Easter had shifted so far away from the vernal equinox that Pope Gregory XIII ordered the calendar's adjustment, resulting in the Gregorian calendar.
History

Prehistoric lunar calendar
The original Roman calendar is believed to have been an observational lunar calendar[1] whose months began from the first signs of a new crescent moon. Because a lunar cycle is about 29 1⁄2 days long, such months would have varied between 29 and 30 days. Twelve such months would have fallen 10 or 11 days short of the solar year; without adjustment, such a year would have quickly rotated out of alignment with the seasons in the manner of the Islamic calendar. Given the seasonal aspects of the later calendar and its associated religious festivals, this was presumably avoided through some form of intercalation or the suspension of the calendar during winter.
Rome's 8-day week, the nundinal cycle, was shared with the Etruscans, who used it as the schedule of royal audiences. It was presumably a part of the early calendar and was credited in Roman legend variously to Romulus and Servius Tullius.
Legendary 10 month calendar
The Romans themselves described their first organized year as one with ten fixed months, each of 30 or 31 days.[2][3] Such a decimal division fitted general Roman practice.[4] The four 31 day months were called "full" (pleni) and the others "hollow" (cavi).[5][6] Its 304 days made up exactly 38 nundinal cycles. The system is usually said to have left the remaining 50 odd days of the year as an unorganized "winter", although Licinius Macer's lost history apparently stated the earliest Roman calendar employed intercalation instead[7][8] and Macrobius claims the 10 month calendar was allowed to shift until the summer and winter months were completely misplaced, at which time additional days belonging to no month were simply inserted into the calendar until it seemed things were restored to their proper place.[9][10]
Later Roman writers credited this calendar to Romulus,[11][12] their legendary first king and culture hero, although this was common with other practices and traditions whose origin had been lost to them. Some scholars doubt the existence of this calendar at all, as it is only attested in late Republican and Imperial sources and supported only by the misplaced names of the months from September to December.[13] Rüpke also finds the coincidence of the length of the supposed "Romulan" year with the length of the first ten months of the Julian calendar to be suspicious.[13]
| English | Latin | Meaning | Length in days [2][3] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| March | Mensis Martius | Month of Mars | 31 | ||
| April | Mensis Aprilis | Month of Apru (Aphrodite)[14] | |||
| May | Mensis Maius | Month of Maia[15] | 31 | ||
| June | Mensis Iunius | Month of Juno | 30 | ||
| July | Mensis Quintilis Mensis Quinctilis[16] | Fifth Month | 31 | ||
| August | Mensis Sextilis | Sixth Month | 30 | ||
| September | Mensis September | Seventh Month | 30 | ||
| October | Mensis October | Eighth Month | 31 | ||
| November | Mensis November | Ninth Month | 30 | ||
| December | Mensis December | Tenth Month | 30 | ||
| length of the year: | 304 | ||||
Other traditions existed alongside this one, however. Plutarch's Parallel Lives recounts that Romulus's calendar had been solar but adhered to the general principle that the year should last for 360 days. Months were employed secondarily and haphazardly, with some counted as 20 days and others as 35 or more.[17][18]
Republican calendar
The attested calendar of the Roman Republic was quite different. It followed Greek calendars in assuming a lunar cycle of 29 1⁄2 days and a solar year of 12 1⁄2 synodic months (368 3⁄4 days), which align every fourth year after the addition of two intercalary months.[6] Two months were added at the end of the year to complete the cycle during winter, January and February, before the intercalary month inserted every two years; the intercalary month was sometimes known as Mercedonius.[6]
The Romans did not follow the usual Greek practice in alternating 29- and 30-day months and a 29- or 30-day intercalary month every other year. Instead, their 1st, 3rd, 5th, and 8th months[lower-alpha 1] had 31 days each; all the other months had 29 days except February, which had 28 days in common years, for a total of 355 days. The Roman intercalary month always had 27 days, but was placed within the month of February alternating between after the Terminalia on the 23rd (a.d. VII Kal. Mart.), and after the following day on the 24th; the remaining days of February were replaced by the corresponding days of Mercedonius[19] (these last 6 or 7 days of February were actually named and counted inclusively in days before the calends of March and were traditionally part of the celebration for the new year). This seems to have arisen from Roman superstitions concerning the numbering and order of the months. The arrangement of the Roman calendar similarly seems to have arisen from Pythagorean superstitions concerning the luckiness of odd numbers.[20]
These Pythagorean-based changes to the Roman calendar were generally credited by the Romans to Numa Pompilius, Romulus's successor and the second of Rome's seven kings, as were the two new months of the calendar.[21][22][lower-alpha 2] Most sources thought he had established intercalation with the rest of his calendar. Although Livy's Numa instituted a lunar calendar, the author claimed the king had instituted a 19-year system of intercalation equivalent to the Metonic cycle[23] centuries before its development by Babylonian and Greek astronomers.[lower-alpha 3] Plutarch's account claims he ended the former chaos of the calendar by employing 12 months totaling 354 days—the length of the lunar and Greek years—and biennial intercalary months of 22 days.[17][18]
According to Livy's Periochae, the beginning of the consular year changed from March to January 1 in 154 BC to respond to a rebellion in Hispania.[25] Plutarch believed Numa was responsible for placing January and February first in the calendar;[17][18] Ovid states January began as the first month and February the last, with its present order owing to the Decemvirs.[26][27] W. Warde Fowler believed the Roman priests continued to treat January and February as the last months of the calendar throughout the Republican period.[28]
| English | Latin | Meaning | Length in days[29][30][17][18] | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st year (cmn.) |
2nd year (leap) |
3rd year (cmn.) |
4th year (leap) | ||||||||
| 1. | January | I. | Mensis Ianuarius | Month of Janus | 29 |
29 |
29 |
29 | |||
| 2. | February | II. | Mensis Februarius | Month of the Februa | 28 |
22 |
28 |
23 | |||
| Intercalary Month | Intercalaris Mensis (Mercedonius) | Month of Wages | 27 |
27 | |||||||
| 3. | March | III. | Mensis Martius | Month of Mars | 31 |
31 |
31 |
31 | |||
| 4. | April | IV. | Mensis Aprilis | Month of Aphrodite – from which the Etruscan Apru might have been derived | 29 |
29 |
29 |
29 | |||
| 5. | May | V. | Mensis Maius | Month of Maia | 31 |
31 |
31 |
31 | |||
| 6. | June | VI. | Mensis Iunius | Month of Juno | 29 |
29 |
29 |
29 | |||
| 7. | July | VII. | Mensis Quintilis | Fifth Month (from the earlier calendar starting in March) | 31 |
31 |
31 |
31 | |||
| 8. | August | VIII. | Mensis Sextilis | Sixth Month | 29 |
29 |
29 |
29 | |||
| 9. | September | IX. | Mensis September | Seventh Month | 29 |
29 |
29 |
29 | |||
| 10. | October | X. | Mensis October | Eighth Month | 31 |
31 |
31 |
31 | |||
| 11. | November | XI. | Mensis November | Ninth Month | 29 |
29 |
29 |
29 | |||
| 12. | December | XII. | Mensis December | Tenth Month | 29 |
29 |
29 |
29 | |||
| Whole year: | 355 | 376 | 355 | 377 | |||||||
The consuls' terms of office were not always a modern calendar year, but ordinary consuls were elected or appointed annually. The traditional list of Roman consuls used by the Romans to date their years began in 509 BC.[31]
Flavian reform
Gnaeus Flavius, a secretary (scriba) to censor App. Claudius Caecus, introduced a series of reforms in 304 BC.[32] Their exact nature is uncertain, although he is thought to have begun the custom of publishing the calendar in advance of the month, depriving the priests of some of their power but allowing for a more consistent calendar for official business.[33]
Julian reform
Julius Caesar, following his victory in his civil war and in his role as pontifex maximus, ordered a reformation of the calendar in 46 BC. This was undertaken by a group of scholars apparently including the Alexandrian Sosigenes[34] and the Roman M. Flavius.[35][30] Its main lines involved the insertion of ten additional days throughout the calendar and regular intercalation of a single leap day every fourth year to bring the Roman calendar into close agreement with the solar year. The year 46 BC was the last of the old system and included 3 intercalary months, the first inserted in February and two more—Intercalaris Prior and Posterior—before the kalends of December.
Later reforms
After Caesar's assassination, Mark Antony had Caesar's birth month Quintilis renamed July (Iulius) in his honor. After Antony's defeat at Actium, Augustus assumed control of Rome and, finding the priests had (owing to their inclusive counting) been intercalating every third year instead of every fourth, suspended the addition of leap days to the calendar for one or two decades until its proper position had been restored. See Julian calendar: Leap year error. In 8 BC, the plebiscite Lex Pacuvia de Mense Augusto renamed Sextilis August (Augustus) in his honor.[36][37][30][lower-alpha 4]
In large part, this calendar continued unchanged under the Roman Empire. (Egyptians used the related Alexandrian calendar, which Augustus had adapted from their wandering ancient calendar to maintain its alignment with Rome's.) A few emperors altered the names of the months after themselves or their family, but such changes were abandoned by their successors. Diocletian began the 15-year indiction cycles beginning from the AD 297 census;[31] these became the required format for official dating under Justinian. Constantine formally established the 7-day week by making Sunday an official holiday in 321. Consular dating became obsolete following the abandonment of appointing nonimperial consuls in AD 541.[31] The Roman method of numbering the days of the month never became widespread in the Hellenized eastern provinces and was eventually abandoned by the Byzantine Empire in its calendar.
Days
Roman dates were counted inclusively forward to the next one of three principal days within each month:[38]
- Kalends (Kalendae or Kal.), the 1st day of each month[38]
- Nones (Nonae or Non.), the 7th day of full months[39] and 5th day of hollow ones,[38] 8 days—"nine" by Roman reckoning—before the Ides in every month
- Ides (Idus, variously Eid. or Id.), the 15th day of full months[39] and the 13th day of hollow ones,[38] a day less than the middle of each month
These are thought to reflect a prehistoric lunar calendar, with the kalends proclaimed after the sighting of the first sliver of the new crescent moon a day or two after the new moon, the nones occurring on the day of the first-quarter moon, and the ides on the day of the full moon. The kalends of each month were sacred to Juno and the ides to Jupiter.[40][41] The day before each was known as its eve (pridie); the day after each (postridie) was considered particularly unlucky.
The days of the month were expressed in early Latin using the ablative of time, denoting points in time, in the contracted form "the 6th December Kalends" (VI Kalendas Decembres).[39] In classical Latin, this use continued for the three principal days of the month[42] but other days were idiomatically expressed in the accusative case, which usually expressed a duration of time, and took the form "6th day before the December Kalends" (ante diem VI Kalendas Decembres). This anomaly may have followed the treatment of days in Greek,[43] reflecting the increasing use of such date phrases as an absolute phrase able to function as the object of another preposition,[39] or simply originated in a mistaken agreement of dies with the preposition ante once it moved to the beginning of the expression.[39] In late Latin, this idiom was sometimes abandoned in favor of again using the ablative of time.
The kalends were the day for payment of debts and the account books (kalendaria) kept for them gave English its word calendar. The public Roman calendars were the fasti, which designated the religious and legal character of each month's days. The Romans marked each day of such calendars with the letters:[44]
- F (fastus, "permissible") on days when it was legal to initiate action in the courts of civil law (dies fasti, "allowed days")
- C (comitialis) on fasti days during which the Roman people could hold assemblies (dies comitiales)
- N (nefastus) on days when political and judicial activities were prohibited (dies nefasti)
- NP (uncertain)[lower-alpha 5] on public holidays (feriae)
- QRCF (uncertain)[lower-alpha 6] on days when the "king" (rex sacrorum) could convene an assembly
- EN (endotercissus, an archaic form of intercissus, "halved") on days when most political and religious activities were prohibited in the morning and evening due to sacrifices being prepared or offered but were acceptable for a period in the middle of the day
Each day was also marked by a letter from A to H to indicate its place within the nundinal cycle of market days.
Weeks

The nundinae were the market days which formed a kind of weekend in Rome, Italy, and some other parts of Roman territory. By Roman inclusive counting, they were reckoned as "ninth days" although they actually occurred every eighth day. Because the republican and Julian years were not evenly divisible into eight-day periods, Roman calendars included a column giving every day of the year a nundinal letter from A to H marking its place in the cycle of market days. Each year, the letter used for the markets would shift 2–5 letters along the cycle. As a day when the city swelled with rural plebeians, they were overseen by the aediles and took on an important role in Roman legislation, which was supposed to be announced for three nundinal weeks (between 17 and 24 days) in advance of its coming to a vote. The patricians and their clients sometimes exploited this fact as a kind of filibuster, since the tribunes of the plebs were required to wait another three-week period if their proposals could not receive a vote before dusk on the day they were introduced. Superstitions arose concerning the bad luck that followed a nundinae on the nones of a month or, later, on the first day of January. Intercalation was supposedly used to avoid such coincidences, even after the Julian reform of the calendar.
The 7-day week began to be observed in Italy in the early imperial period,[46] as practitioners and converts to eastern religions introduced Hellenistic and Babylonian astrology, the Jewish Saturday sabbath, and the Christian Lord's Day. The system was originally used for private worship and astrology but had replaced the nundinal week by the time Constantine made Sunday (dies Solis) an official day of rest in AD 321. The hebdomadal week was also reckoned as a cycle of letters from A to G; these were adapted for Christian use as the dominical letters.
Months
The names of Roman months originally functioned as adjectives (e.g., the January kalends occur in the January month) before being treated as substantive nouns in their own right (e.g., the kalends of January occur in January). Some of their etymologies are well-established: January and March honor the gods Janus[47] and Mars;[48] July and August honor Julius Caesar[49] and his successor, the emperor Augustus;[50] and the months Quintilis,[51] Sextilis,[52] September,[53] October,[54] November,[55] and December[56] are archaic adjectives formed from the ordinal numbers from 5 to 10, their position in the calendar when it began around the spring equinox in March.[53] Others are uncertain. February may derive from the Februa festival or its eponymous februa ("purifications, expiatory offerings"), whose name may be either Sabine or preserve an archaic word for sulphuric.[57] April may relate to the Etruscan goddess Apru or the verb aperire ("to open"). May and June may honor Maia[58] and Juno[59] or derive from archaic terms for "senior" and "junior". A few emperors attempted to add themselves to the calendar after Augustus, but without enduring success.
In classical Latin, the days of each month were usually reckoned as:[42]
| Day | Original 31-day months Mar, May, Jul, Oct[lower-alpha 7] |
New Julian 31-day months Jan, Aug, Dec[lower-alpha 8] |
New Julian 30-day months Apr, Jun, Sep, Nov[lower-alpha 9] |
Original 29-day months Jan, Apr, Jun, Aug, Sep, Nov, Dec[lower-alpha 10] |
February |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Kal. | On the Kalends Kalendis | Kal. | Kal. | Kal. Feb. |
| 2 | a.d. VI Non. | The 4th Day before the Nones ante diem quartum Nonas | a.d. IV Non. | a.d. IV Non. | a.d. IV Non. Feb. |
| 3 | a.d. V Non. | The 3rd Day before the Nones ante diem tertium Nonas | a.d. III Non. | a.d. III Non. | a.d. III Non. Feb. |
| 4 | a.d. IV Non. | On the Day before the Nones Pridie Nonas | Prid. Non. | Prid. Non. | Prid. Non. Feb. |
| 5 | a.d. III Non. | On the Nones Nonis | Non. | Non. | Non. Feb. |
| 6 | Prid. Non. | The 8th Day before the Ides ante diem octavum Idus | a.d. VIII Eid. | a.d. VIII Eid. | a.d. VIII Eid. Feb. |
| 7 | Non. | The 7th Day before the Ides ante diem septimum Idus | a.d. VII Eid. | a.d. VII Eid. | a.d. VII Eid. Feb. |
| 8 | a.d. VIII Eid. | The 6th Day before the Ides ante diem sextum Idus | a.d. VI Eid. | a.d. VI Eid. | a.d. VI Eid. Feb. |
| 9 | a.d. VII Eid. | The 5th Day before the Ides ante diem quintum Idus | a.d. V Eid. | a.d. V Eid. | a.d. V Eid. Feb. |
| 10 | a.d. VI Eid. | The 4th Day before the Ides ante diem quartum Idus | a.d. IV Eid. | a.d. IV Eid. | a.d. IV Eid. Feb. |
| 11 | a.d. V Eid. | The 3rd Day before the Ides ante diem tertium Idus | a.d. III Eid. | a.d. III Eid. | a.d. III Eid. Feb. |
| 12 | a.d. IV Eid. | On the Day before the Ides Pridie Idus | Prid. Eid. | Prid. Eid. | Prid. Eid. Feb. |
| 13 | a.d. III Eid. | On the Ides Idibus | Eid. | Eid. | Eid. Feb. |
| 14 | Prid. Eid. | The 19th Day before the Kalends ante diem undevicesimum Kalendas | a.d. XVIII Kal. | a.d. XVII Kal. | a.d. XVI Kal. Mart. |
| 15 | Eid. | The 18th Day before the Kalends ante diem duodevicesimum Kalendas | a.d. XVII Kal. | a.d. XVI Kal. | a.d. XV Kal. Mart. |
| 16 | a.d. XVII Kal. | The 17th Day before the Kalends ante diem septimum decimum Kalendas | a.d. XVI Kal. | a.d. XV Kal. | a.d. XIV Kal. Mart. |
| 17 | a.d. XVI Kal. | The 16th Day before the Kalends ante diem sextum decimum Kalendas | a.d. XV Kal. | a.d. XIV Kal. | a.d. XIII Kal. Mart. |
| 18 | a.d. XV Kal. | The 15th Day before the Kalends ante diem quintum decimum Kalendas | a.d. XIV Kal. | a.d. XIII Kal. | a.d. XII Kal. Mart. |
| 19 | a.d. XIV Kal. | The 14th Day before the Kalends ante diem quartum decimum Kalendas | a.d. XIII Kal. | a.d. XII Kal. | a.d. XI Kal. Mart. |
| 20 | a.d. XIII Kal. | The 13th Day before the Kalends ante diem tertium decimum Kalendas | a.d. XII Kal. | a.d. XI Kal. | a.d. X Kal. Mart. |
| 21 | a.d. XII Kal. | The 12th Day before the Kalends ante diem duodecimum Kalendas | a.d. XI Kal. | a.d. X Kal. | a.d. IX Kal. Mart. |
| 22 | a.d. XI Kal. | The 11th Day before the Kalends ante diem undecimum Kalendas | a.d. X Kal. | a.d. IX Kal. | a.d. VIII Kal. Mart. |
| 23 | a.d. X Kal. | The 10th Day before the Kalends ante diem decimum Kalendas | a.d. IX Kal. | a.d. VIII Kal. | a.d. VII Kal. Mart. |
| 24 | a.d. IX Kal. | The 9th Day before the Kalends ante diem nonum Kalendas | a.d. VIII Kal. | a.d. VII Kal. | a.d. VI Kal. Mart.[lower-alpha 11] |
| 25 | a.d. VIII Kal. | The 8th Day before the Kalends ante diem octavum Kalendas | a.d. VII Kal. | a.d. VI Kal. | a.d. V Kal. Mart. |
| 26 | a.d. VII Kal. | The 7th Day before the Kalends ante diem septimum Kalendas | a.d. VI Kal. | a.d. V Kal. | a.d. IV Kal. Mart. |
| 27 | a.d. VI Kal. | The 6th Day before the Kalends ante diem sextum Kalendas | a.d. V Kal. | a.d. IV Kal. | a.d. III Kal. Mart. |
| 28 | a.d. V Kal. | The 5th Day before the Kalends ante diem quintum Kalendas | a.d. IV Kal. | a.d. III Kal. | Prid. Kal. Mart. |
| 29 | a.d. IV Kal. | The 4th Day before the Kalends ante diem quartum Kalendas | a.d. III Kal. | Prid. Kal. | |
| 30 | a.d. III Kal. | The 3rd Day before the Kalends ante diem tertium Kalendas | Prid. Kal. | ||
| 31 | Prid. Kal. | On the Day Before the Kalends Pridie Kalendas |
|||
Dates after the ides count forward to the kalends of the next month and are expressed as such. For example, March 19 was expressed as "the 14th day before the April Kalends" (a.d. XIV Kal. Apr.), without a mention of March itself. The day after a kalends, nones, or ides was also often expressed as the "day after" (postridie) owing to their special status as particularly unlucky "black days".
The anomalous status of the new 31-day months under the Julian calendar was an effect of Caesar's desire to avoid affecting the festivals tied to the nones and ides of various months. However, because the dates at the ends of the month all counted forward to the next kalends, they were all shifted by one or two days by the change. This created confusion with regard to certain anniversaries. For instance, Augustus's birthday on the 23rd day of September was a.d. VIII Kal. Oct. in the old calendar but a.d. IX Kal. Oct. under the new system. The ambiguity caused honorary festivals to be held on either or both dates.
Intercalation
The Republican calendar only had 355 days, which meant that it would quickly unsynchronize from the solar year, causing, for example, agricultural festivals to occur out of season. The Roman solution to this problem was to periodically lengthen the calendar by adding extra days within February. February was broken into two parts, each with an odd number of days. The first part ended with the Terminalia on the 23rd (a.d. VII Kal. Mart.), which was considered the end of the religious year; the five remaining days beginning with the Regifugium on the 24th (a.d. VI Kal. Mart.) formed the second part; and the intercalary month Mercedonius was inserted between them. In such years, the days between the ides and the Regifugium were counted down to either the Intercalary Kalends or to the Terminalia. The intercalary month counted down to nones and ides on its 5th and 13th day in the manner of the other short months. The remaining days of the month counted down towards the March Kalends, so that the end of Mercedonius and the second part of February were indistinguishable to the Romans, one ending on a.d. VII Kal. Mart. and the other picking up at a.d. VI Kal. Mart. and bearing the normal festivals of such dates.
Apparently because of the confusion of these changes or uncertainty as to whether an intercalary month would be ordered, dates after the February ides are attested as sometimes counting down towards the Quirinalia (Feb. 17), the Feralia (Feb. 21), or Terminalia (Feb. 23)[60] rather than the intercalary or March kalends.
The third-century writer Censorinus says:
When it was thought necessary to add (every two years) an intercalary month of 22 or 23 days, so that the civil year should correspond to the natural (solar) year, this intercalation was in preference made in February, between Terminalia [23rd] and Regifugium [24th].[61]
The fifth-century writer Macrobius says that the Romans intercalated 22 and 23 days in alternate years (Saturnalia, 1.13.12); the intercalation was placed after 23 February and the remaining five days of February followed (Saturnalia, 1.13.15). To avoid the nones falling on a nundine, where necessary an intercalary day was inserted "in the middle of the Terminalia, where they placed the intercalary month".[62]
This is historically correct. In 167 BC Intercalaris began on the day after 23 February [63] and in 170 BC it began on the second day after 23 February.[64] Varro, writing in the first century BC, says "the twelfth month was February, and when intercalations take place the five last days of this month are removed."[65] Since all the days after the Ides of Intercalaris were counted down to the beginning of March Intercalaris had either 27 days (making 377 for the year) or 28 (making 378 for the year).
There is another theory which says that in intercalary years February had 23 or 24 days and Intercalaris had 27. No date is offered for the Regifugium in 378-day years.[66] Macrobius describes a further refinement whereby, in one 8-year period within a 24-year cycle, there were only three intercalary years, each of 377 days. This refinement brings the calendar back in line with the seasons, and averages the length of the year to 365.25 days over 24 years.
The Pontifex Maximus determined when an intercalary month was to be inserted. On average, this happened in alternate years. The system of aligning the year through intercalary months broke down at least twice: the first time was during and after the Second Punic War. It led to the reform of the 191 BC Acilian Law on Intercalation, the details of which are unclear, but it appears to have successfully regulated intercalation for over a century. The second breakdown was in the middle of the first century BC and may have been related to the increasingly chaotic and adversarial nature of Roman politics at the time. The position of Pontifex Maximus was not a full-time job; it was held by a member of the Roman elite, who would almost invariably be involved in the machinations of Roman politics. Because the term of office of elected Roman magistrates was defined in terms of a Roman calendar year, a Pontifex Maximus would have reason to lengthen a year in which he or his allies were in power or shorten a year in which his political opponents held office.
Although there are many stories to interpret the intercalation, a period of 22 or 23 days is always 1⁄4 synodic month short. Obviously, the month beginning shifts forward (from the new moon, to the third quarter, to the full moon, to the first quarter, back the new moon) after intercalation.
Years

As mentioned above, Rome's legendary 10-month calendar notionally lasted for 304 days but was usually thought to make up the rest of the solar year during an unorganized winter period. The unattested but almost certain lunar year and the pre-Julian civil year were 354 or 355 days long, with the difference from the solar year more or less corrected by an irregular intercalary month. The Julian year was 365 days long, with a leap day doubled in length every fourth year, almost equivalent to the present Gregorian system.
The calendar era before and under the Roman kings is uncertain but dating by regnal years was common in antiquity. Under the Roman Republic, from 509 BC, years were most commonly described in terms of their reigning ordinary consuls.[31] (Temporary and honorary consuls were sometimes elected or appointed but were not used in dating.)[31] Consular lists were displayed on the public calendars. After the institution of the Roman Empire, regnal dates based on the emperors' terms in office became more common. Some historians of the later republic and early imperial eras dated from the legendary founding of the city of Rome (ab urbe condita or AVC).[31] Varro's date for this was 753 BC but other writers used different dates, varying by several decades. Such dating was, however, never widespread. After the consuls waned in importance, most Roman dating was regnal[68] or followed Diocletian's 15-year Indiction tax cycle.[31] These cycles were not distinguished, however, so that "year 2 of the indiction" may refer to any of 298, 313, 328, &c.[31] The Orthodox subjects of the Byzantine Empire used various Christian eras, including those based on Diocletian's persecutions, Christ's incarnation, and the supposed age of the world.
The Romans did not have records of their early calendars but, like modern historians, assumed the year originally began in March on the basis of the names of the months following June. The consul M. Fulvius Nobilior (r. 189 BC) wrote a commentary on the calendar at the Temple of Hercules Musarum that claimed January had been named for Janus because the god faced both ways,[69] suggesting it had been instituted as a first month. It was, however, usually said to have been instituted along with February, whose nature and festivals suggest it had originally been considered the last month of the year. The consuls' term of office—and thus the order of the years under the republic—seems to have changed several times. Their inaugurations were finally moved to 1 January (Kal. Ian.) in 153 BC to allow Q. Fulvius Nobilior to attack Segeda in Spain during the Celtiberian Wars, before which they had occurred on 15 March (Eid. Mart.).[70] There is reason to believe the inauguration date had been 1 May during the 3rd century BC until 222 BC and Livy mentions earlier inaugurations on 15 May (Eid. Mai.), 1 July (Kal. Qui.), 1 August (Kal. Sex.), 1 October (Kal. Oct.), and 15 December (Eid. Dec.).[71] Under the Julian calendar, the year began on 1 January but years of the Indiction cycle began on 1 September.
In addition to Egypt's separate calendar, some provinces maintained their records using a local era.[31] Africa dated its records sequentially from 39 BC;[68] Spain from AD 38. This dating system continued as the Spanish era used in medieval Spain.
Conversion to Julian or Gregorian dates
The continuity of names from the Roman to the Gregorian calendar can lead to the mistaken belief that Roman dates correspond to Julian or Gregorian ones. In fact, the essentially complete list of Roman consuls allows general certainty of years back to the establishment of the republic but the uncertainty as to the end of lunar dating and the irregularity of Roman intercalation means that dates which can be independently verified are invariably weeks to months outside of their "proper" place. Two astronomical events dated by Livy show the calendar 4 months out of alignment with the Julian date in 190 BC and 2 months out of alignment in 168 BC. Thus, "the year of the consulship of Publius Cornelius Scipio Africanus and Publius Licinius Crassus" (usually given as "205 BC") actually began on 15 March 205 BC and ended on 14 March 204 BC according to the Roman calendar but may have begun as early as November or December 206 BC owing to its misalignment. Even following the establishment of the Julian calendar, the leap years were not applied correctly by the Roman priests, meaning dates are a few days out of their "proper" place until a few decades into Augustus's reign.
Given the paucity of records regarding the state of the calendar and its intercalation, historians have reconstructed the correspondence of Roman dates to their Julian and Gregorian equivalents from disparate sources. There are detailed accounts of the decades leading up to the Julian reform, particularly the speeches and letters of Cicero, which permit an established chronology back to about 58 BC. The nundinal cycle and a few known synchronisms—e.g., a Roman date in terms of the Attic calendar and Olympiad—are used to generate contested chronologies back to the start of the First Punic War in 264 BC. Beyond that, dates are roughly known based on clues such as the dates of harvests and seasonal religious festivals.
See also
- List of calendars
- Julian, Alexandrian, Byzantine, & Gregorian calendars
- List of Roman consuls and ab urbe condita dating
- General Roman Calendar of the Catholic Church
- Roman festivals
- Undecimber
Notes
- That is, the 3rd, 5th, 7th, and 10th months after the repositioning of January and February.
- Plutarch reports this tradition while claiming that the months had more probably predated or originated with Romulus.[17][18]
- This equivalence was first described by Stanyan in his history of ancient Greece.[24]
- There are some documents which state the month had been renamed as early as 26 or 23 BC, but the date of the Lex Pacuvia is certain.
- The NP days are sometimes thought to mark days when political and judicial activities were prohibited only until noon, standing for nefastus priore.
- The QRCF days are sometimes supposed, on the basis of the Fasti Viae Lanza which gives it as Q. Rex C. F., to stand for "Permissible when the King Has Entered the Comitium" (Quando Rex Comitiavit Fas).[45]
- The original 31-day months of the Roman calendar were March, May, Quintilis or July, and October.
- The 31-day months established by the Julian reform were January, Sextilis or August, and December. The other 31-day months of the Julian calendar continued to use the old system, with their Nones on the 7th and Ides on the 15th.
- The 30-day months established by the Julian reform were April, June, September, and November.
- The 29-day months of the calendar prior to the Julian reform were January, April, June, Sextilis, September, November, and December. After the Julian reform, February could have 29 days during a leap year but it was not reckoned according to this list until late in the imperial period. Instead, the sixth day before the March Kalends was initially treated as lasting for 48 hours.
- After the Julian reform, this day was reckoned to last 48 hours during a leap year.
References
Citations
- Mommsen & al. (1864), pp. 216.
- Macrobius, Book I, Ch. 12, §3.
- Kaster (2011), p. 137.
- Mommsen & al. (1864), pp. 217.
- Censorinus, Macrobius, and Solinus, cited in Key (1875)
- Mommsen & al. (1864), p. 218.
- Macrobius, Book I, Ch. 13, §20.
- Kaster (2011), p. 165.
- Macrobius, Book I, Ch. 12, §39.
- Kaster (2011), p. 155.
- Macrobius, Book I, Ch. 12, §§5 & 38.
- Kaster (2011), pp. 137 & 155.
- Rüpke (2011), p. 23.
- "April". Dictionary.com Unabridged. Randomhouse Inc. Retrieved January 9, 2018.
- "May". Dictionary.com Unabridged. Randomhouse Inc. Retrieved January 9, 2018.
- Blackburn & al. (1999), p. 669.
- Plutarch, Ch. 18.
- Perrin (1914), pp. 368 ff.
- Rüpke (2011), p. 40
- Mommsen & al. (1864), p. 219.
- Macrobius, Book I, Ch. 12, §34.
- Kaster (2011), p. 153.
- Roberts (1905), Book I, Ch. 19, §6.
- Stanyan (1707), p. 330.
- 47.13 and 47.14: "[47.13] In the five hundred and ninety-eighth year after the founding of the city, the consuls began to enter upon their office on 1 January. [47.14] The cause of this change in the date of the elections was a rebellion in Hispania."
- Ovid, Book II.
- Kline (2004), Book II, Introduction.
- Fowler (1899), p. 5.
- Macrobius.
- Kaster (2011).
- Mathieson (2003), p. 14.
- Michels (1949), p. 340.
- Lanfranchi (2013).
- Pliny, Book XVIII, Ch. 57.
- Macrobius, Book I, Ch. 14, §2.
- Rotondi (1912), p. 441.
- Macrobius, Book I, Ch. 12.
- Beck (1838), p. 175.
- Beck (1838), p. 176.
- Ovid, Book I, ll. 55–56.
- Kline (2004), Book I, Introduction.
- Beck (1838), p. 177.
- Smyth (1920), §§1582–1587.
- Scullard (1981), pp. 44–45.
- Rüpke (2011), pp. 26–27.
- Brind'Amour (1983), pp. 256–275.
- "January, n.", OED.
- "March, n.2", OED.
- "July, n.", OED.
- "August, n.", OED.
- "†quintile, n.2", OED.
- "sextile, adj. and n.", OED.
- "September, n.", OED.
- "October, n.", OED.
- "November, n.", OED.
- "December, n.", OED.
- "February, n.", OED.
- "May, n.2", OED.
- "June, n.", OED.
- A 94 inscription.
- Censorinus, The Natal Day, 20.28, tr. William Maude, New York 1900, available at .
- Macrobius, Book I, Ch. 13, §16, 19.
- Livy 45.44.3.
- Livy 43.11.13.
- Varro, On the Latin language, 6.13, tr. Roland Kent, London 1938, available at .
- Michels (1967).
- Corpus Inscriptionum Latinarum I, CIL VI.
- Mathieson (2003), p. 15.
- Varro.
- Livy, Book XLVII.
- Livy.
Bibliography
- Beck, Charles (1838), "Of the Roman Calendar", Latin Syntax, Chiefly from the German of C.G. Zumpt, Boston: Charles C. Little & James Brown.
- Blackburn, Bonnie; et al. (1999), The Oxford Companion to the Year, Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Brind'Amour, P. (1983), Le Calendrier Romain: Recherches Chronologiques, Ottawa. (in French)
- Fowler, W. Warde (1899), The Roman Festivals of the Period of the Republic, New York: Macmillan & Co.
- Key, Thomas Hewitt (1875), "Calendarium", A Dictionary of Greek and Roman Antiquities, London: John Murray, pp. 223–233.
- Lanfranchi, Thibaud (3 October 2013), "À Propos de la Carrière de Cn. Flavius", Mélanges de l'École Française de Rome: Antiquité, 125, doi:10.4000/mefra.1322. (in French)
- Livy (1905), Roberts, Canon; et al. (eds.), The History of Rome, Vol. I, Everyman's Library, London: J.M. Dent & Sons, archived from the original on 2017-04-29, retrieved 2017-03-23.
- Macrobius, Saturnalia. (in Latin)
- Macrobius (2011), Kaster, Robert A. (ed.), Saturnalia, Vol. I, Loeb Classical Library, No. 510, Cambridge: Harvard University Press, ISBN 9780674996496. (in English) & (in Latin)
- Mathieson, Ralph W. (2003), People, Personal Expression, and Social Relations in Late Antiquity, Vol. II, Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press.
- Michels, Agnes Kirsopp Lake (1949), "The 'Calendar of Numa' and the Pre-Julian Calendar", Transactions & Proceedings of the APA, Vol. 80, Philadelphia: American Philological Association, pp. 320–346.
- Michels, Agnes Kirsopp Lake (1967), The Calendar of the Roman Republic, Princeton, ISBN 9781400849789.
- Mommsen, Theodor (1864), Dickson, William Purdie (ed.), The History of Rome, Vol. I: The Period Anterior to the Abolition of the Monarchy, London: Richard Bentley. [ 1 ]
- Ovid, Fastorum Libri VI. (in Latin)
- Ovid (2004), Kline, Anthony S. (ed.), On the Roman Calendar, Poetry in Translation.
- Oxford English Dictionary, Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Pliny, Historia Naturalis. (in Latin)
- Plutarch, Βίοι Παράλληλοι [Bíoi Parállēloi, Parallel Lives]. (in Ancient Greek)
- Plutarch (1914), "The Life of Numa", in Perrin, Bernadotte (ed.), The Parallel Lives, Vol. I, Loeb Classical Library, Cambridge: Harvard University Press.
- Rotondi, Giovanni (1912), Leges Publicae Populi Romani, Milan: Società Editrice Libraria. (in Latin)
- Rüpke, Jörg (2011), Richardson, D.M.B. (ed.), The Roman Calendar from Numa to Constantine: Time, History, and the Fasti, Wiley, ISBN 978-0-470-65508-5.
- Scullard, Howard Hayes (1981), Festivals and Ceremonies of the Roman Republic, Ithaca: Cornell University Press.
- Smyth, Herbert Weir (1920), A Greek Grammar for Colleges, New York: American Book Co..
- Stanyan, Temple (1707), Grecian History, London: J. & R. Tonson.
External links
- Chris Bennett's reconstruction of early Roman dates in terms of the Julian calendar
- Early Roman Calendar – History
- James Grout: The Roman Calendar, part of the Encyclopædia Romana
- Roman Date Calculator The North American Institute of Living Latin Studies
- "Theological commentary on the daily Gospel Reading". Apostolic Movement (Roman Catholic Church) (in English, French, and Spanish).