Sète
Sète (French pronunciation: [sɛt]; Occitan: Seta, [ˈseto]), known as Cette until 1928, is a commune in the Hérault department in the region of Occitania in southern France. Its inhabitants are called Sétois (male) and Sétoises (female).
Sète | |
|---|---|
 Tivoli bridge | |
.svg.png.webp) Coat of arms | |
Location of Sète 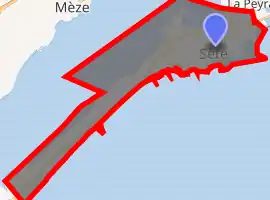
| |
 Sète  Sète | |
| Coordinates: 43°24′19″N 3°41′51″E | |
| Country | France |
| Region | Occitanie |
| Department | Hérault |
| Arrondissement | Montpellier |
| Canton | Sète |
| Intercommunality | CA Sète Agglopôle Méditerranée |
| Government | |
| • Mayor (2020–2026) | François Commeinhes (DVD) |
| Area 1 | 24.21 km2 (9.35 sq mi) |
| Population (2017-01-01)[1] | 43,229 |
| • Density | 1,800/km2 (4,600/sq mi) |
| Demonym(s) | Sétois |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| INSEE/Postal code | 34301 /34200 |
| Elevation | 0–176 m (0–577 ft) (avg. 4 m or 13 ft) |
| 1 French Land Register data, which excludes lakes, ponds, glaciers > 1 km2 (0.386 sq mi or 247 acres) and river estuaries. | |
Known as the Venice of Languedoc and the singular island (in Paul Valéry's words), it is a port and a seaside resort on the Mediterranean with its own very strong cultural identity, traditions, cuisine and dialect. It is the hometown of artists like Paul Valéry, Jean Vilar, Georges Brassens, Hervé Di Rosa, Manitas de Plata, and Robert Combas.
Geography


Built upon and around Mont St Clair, Sète is situated on the south-eastern end of the Étang de Thau, an enclosed salt water lake used primarily for oyster and mussel fields. To its other side lies the Mediterranean, and the town has a network of canals which are links between the Étang de Thau and the Mediterranean Sea.
Climate
| Climate data for Sète (1981–2010 averages) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 20.2 (68.4) |
21.3 (70.3) |
27.1 (80.8) |
31.0 (87.8) |
34.6 (94.3) |
40.3 (104.5) |
37.8 (100.0) |
41.0 (105.8) |
34.2 (93.6) |
32.1 (89.8) |
25.4 (77.7) |
20.4 (68.7) |
41.0 (105.8) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 10.8 (51.4) |
11.6 (52.9) |
14.6 (58.3) |
16.9 (62.4) |
20.6 (69.1) |
24.9 (76.8) |
27.8 (82.0) |
27.4 (81.3) |
23.7 (74.7) |
19.3 (66.7) |
14.3 (57.7) |
11.4 (52.5) |
18.6 (65.5) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 5.3 (41.5) |
5.5 (41.9) |
7.9 (46.2) |
10.1 (50.2) |
13.8 (56.8) |
17.4 (63.3) |
20.0 (68.0) |
19.9 (67.8) |
16.8 (62.2) |
13.6 (56.5) |
9.0 (48.2) |
6.2 (43.2) |
12.2 (54.0) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −11.0 (12.2) |
−12.0 (10.4) |
−6.2 (20.8) |
1.2 (34.2) |
4.2 (39.6) |
6.5 (43.7) |
12.0 (53.6) |
11.0 (51.8) |
6.0 (42.8) |
2.4 (36.3) |
−1.8 (28.8) |
−7.2 (19.0) |
−12.0 (10.4) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 51.4 (2.02) |
51.8 (2.04) |
39.7 (1.56) |
48.3 (1.90) |
42.3 (1.67) |
25.2 (0.99) |
11.5 (0.45) |
26.4 (1.04) |
56.7 (2.23) |
90.9 (3.58) |
65.2 (2.57) |
51.3 (2.02) |
560.7 (22.07) |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 76 | 74 | 70 | 70 | 72 | 69 | 66 | 68 | 74 | 76 | 75 | 76 | 72.2 |
| Source 1: Météo France[2] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Infoclimat.fr (humidity and snowy days, 1961–1990)[3] | |||||||||||||
History
The name first appeared in Ptolemy (Geography II.10.2.): Σήτιον ὄρος, later in Avienus (Ora Maritima): Setius... mons and on the maps of Aniane: fiscum..qui nuncupatur Sita
During the 11th century Catharism appeared in the Languedoc region.[4]
1600-1900
On 29 July 1666, the first stone was officially set on the Saint-Louis pier. In 1681 the Canal du Midi was completed. In 1684, Vauban visited the port. In 1703, Saint-Louis church was consecrated. From 24–26 July 1710, during the War of the Spanish Succession the British attacked Sète, soon fought back by the Adrien Maurice de Noailles Duke of Noailles . In 1710–1711, Saint-Pierre and Butte-Ronde forts were built. In 1724, the townhouse was bought. In 1744, the Richelieu citadel and the Castellas tower were built.
19th Century
Between 1807–1809 the British tried to burn the town. On 21 May 1821, the first stone of the breakwater was set (finished in 1869). On 9 June 1839 the Montpellier-Sète railway was opened. On 6 May 1872 the chamber of commerce was established. Between 1882–1888 construction works on the port took place. On 24 June 1894 Sante Geronimo Caserio, an Italian anarchist from Lombardy and apprentice baker in Sète stabbed to death president Sadi Carnot in Lyon. In 1895, the boys' high school, later renamed the Lycée Paul Valéry was opened.
20th Century
In 1901 an electric tramway network was built (used until 1935). In 1902, the Nelson family opened Chateau Nelson. On 20 January 1928, the name of the town changed from Cette to Sète. In 1934, FC Sète 34 won the Ligue 1 and Coupe de France and became the first football club to win both the same year. On 23 May 1939: the SS Sinaia leaves the port with Spanish Republicans seeking asylum in Lázaro Cárdenas's Mexico. On 12 November 1942: the town is occupied by the German troops of the Wehrmacht. On 25 June 1944 Sète railway station, Balaruc-les-Bains's and Frontignan's oil refineries were bombarded by the American 15th Air Force. On 20 August 1944 Sète was liberated. On 11 July 1947, the packet steamship SS President Warfield leaves for Palestine with 4 530 Jews who survived the Shoah. The port official M. Leboutet had authorised captain Ike Aronowicz to sail to Colombia and, after 5 days on the Atlantic Ocean, the ship took the name SS Exodus and changed direction towards Palestine. 27 km (17 miles) from the coast, they were stopped by 5 British torpedo boats. 75 passengers accepted asylum in France, while the others were brought to Hamburg via Gibraltar. In 1960, the Théâtre de la Mer was built. In 1962, the technical college Joliot-Curie was opened. In 1966–1978 major construction works on the port took place. In 1970, the Museum Paul Valéry was opened. From 1981–1984, a new public hospital was built. On 31 October 1991, the espace Georges Brassens, a museum dedicated to the singer, opened.
21st century
In 2004, a plan to preserve the Lido and prevent further coastal damage was made. In 2005 a new neighbourhood called Villeroy was created. In 2006 the "espace Georges Brassens" was renovated. In January 2007, the Languedoc-Roussillon manages the port of Sète. In 2014, une ville humanitaire, saw the creation of "les Anges de la Rue" In 2016, a great wine spill occurred at the Nelson Chateau.
Population
|
|
Patron saint
In 1703, when the Saint-Louis church was consecrated, Louis IX, patron of the port, also became the patron saint of the town. He has been celebrated every year on 25 August, with canal jousting competitions, music and fireworks, except during wartime.
Transport

Sète is the eastern starting point of the Canal du Midi, and the ending point of the Canal du Rhône à Sète. Its train station Gare de Sète is approximately 15 minutes by train from Montpellier, and is also served by long-distance trains to Bordeaux, Toulouse, Marseille and Paris. Car ferries sail between Sète and Morocco.
Culture
Sète is a centre of water jousting, and hosts a major tournament during the town festival, the St-Louis.[5]
Paul Valéry's poem Le cimetière marin, depicts the graveyard above Sète's harbour[6] Valéry is buried in the graveyard, and the nearby Paul Valéry Museum contains a collection of his drawings and manuscripts.
Espace Georges-Brassens is a museum dedicated to the Sétois singer-songwriter.
Agnès Varda's first film, La Pointe Courte, was filmed in the environs of Sète.
Director Abdellatif Kechiche set his film 2007 The Secret of the Grain, Mektoub, My Love: Canto Uno (2017) and Mektoub, My Love: Intermezzo (2019) in Sète.
Notable people
Sète was the birthplace of:
- David Serene (born 1970), footballer and veterinarian
- Paul Valéry (1871–1945), author and poet of the Symbolist school
- Paul-Marie Masson (1882–1954), composer and musicologist
- Jean Vilar (1912–1971), actor and creator of the Avignon theatre festival
- Georges Brassens (1921–1981), singer and songwriter
- Manitas de Plata (1921–2014), flamenco guitarist
- Gilbert Py (born 1933), Opera tenor
- Alain de Pouzilhac (born 1945), CEO of France 24 and former president of France Médias Monde
- Simon Sutour (born 1952), Senator of the department Gard
- Robert Combas (born 1957), sculptor and painter
- Hervé Di Rosa (born 1959), painter and sculptor
- Mathieu Peisson (born 1982), water polo player and Olympian at the 2016 Summer Olympics
International relations
 Neuburg an der Donau, Germany, since 1986
Neuburg an der Donau, Germany, since 1986 El Jadida, Morocco, since 1992
El Jadida, Morocco, since 1992 Cetara, Italy, since 2003
Cetara, Italy, since 2003
Gallery
 Lighthouse of the Mount Saint-Clair
Lighthouse of the Mount Saint-Clair Théatre de la Mer.
Théatre de la Mer. Fort Richelieu.
Fort Richelieu. Maréchal de Lattre de Tassigny Embankment.
Maréchal de Lattre de Tassigny Embankment. Sète and the Étang de Thau.
Sète and the Étang de Thau. Tivoli Bridge over one of the canals of the town.
Tivoli Bridge over one of the canals of the town. Crique de l'Anau, a cove in the Mediterranean Sea.
Crique de l'Anau, a cove in the Mediterranean Sea. Canal de la Peyrade
Canal de la Peyrade
See also
References
- "Populations légales 2017". INSEE. Retrieved 6 January 2020.
- "Données climatiques de la station de Sète" (in French). Meteo France. Retrieved 7 January 2016.
- "Normes et records 1961-1990: Sète (34) - altitude 80m" (in French). Infoclimat. Retrieved 7 January 2016.
- Le Roy Ladurie, Emmanuel (1990). Montaillou: Cathars and Catholics in a French Village. London: Penguin. pp. vii. ISBN 978-0-14-013700-2.
- St-Louis.
- .Le cimetière marin
- "Le jumelage". sete.fr (in French). Sète. Retrieved 18 November 2019.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Sète. |
| Wikisource has the text of the 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica article Cette. |
- City council website (in French)