Ayherre
Ayherre (Basque: Aiherre) is a commune in the Pyrénées-Atlantiques department in the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region of south-western France.
Ayherre | |
|---|---|
_fronton.JPG.webp) The Pelota Court | |
.svg.png.webp) Coat of arms | |
Location of Ayherre 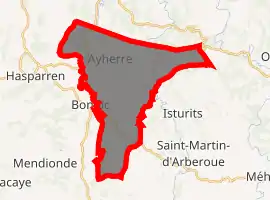
| |
 Ayherre  Ayherre | |
| Coordinates: 43°23′35″N 1°15′11″W | |
| Country | France |
| Region | Nouvelle-Aquitaine |
| Department | Pyrénées-Atlantiques |
| Arrondissement | Bayonne |
| Canton | Pays de Bidache, Amikuze et Ostibarre |
| Intercommunality | CA Pays Basque |
| Government | |
| • Mayor (2014-2020) | Arnaud Gastambide |
| Area 1 | 27.65 km2 (10.68 sq mi) |
| Population (2017-01-01)[1] | 1,042 |
| • Density | 38/km2 (98/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| INSEE/Postal code | 64086 /64240 |
| Elevation | 20–465 m (66–1,526 ft) (avg. 86 m or 282 ft) |
| 1 French Land Register data, which excludes lakes, ponds, glaciers > 1 km2 (0.386 sq mi or 247 acres) and river estuaries. | |
The inhabitants of the commune are known as Aihertars.[2]
Geography
Ayherre is located in the Arberoue Valley in the former province of Lower Navarre some 23 km east by south-east of Bayonne and immediately east of Hasparren. Access to the commune is by the D10 road from Hasparren which passes through the west of the commune and continues north to La Bastide-Clairence. The D251 branches east off the D10 in the commune and goes to the village then continues east to Isturits. The D314 goes south-west from the village to Bonloc. The D14 from Bonloc to Saint-Esteben passes through the south of the commune. The commune is mainly farmland with scattered forests.[3]
The commune is located in the drainage basin of the Adour with a dense network of streams covering the commune, mostly flowing north-westwards, and including the Joyeuse, which forms part of the western border of the commune. The Arbéroue rises in the south of the commune and flows north gathering many tributaries before joining the Lihoury to the north.

Places and hamlets
- Abarratia[4]
- Ahounsbiscardeguy[5]
- Aguerréa (3 places)
- Aguerréko Borda
- Ainguéroutéguia
- Andérétéguia
- Apairi[5] or Apahiri, from Apʰara-hiri
- Apézénéa
- Apeztéguia
- Archidukénia
- Arduarria
- Arkhia
- Arramendy
- Arraydua
- Auchotéa
- Ayherregaraya
- Ballade Etcheberry
- Barné Uhartia[5]
- Béhibidia
- Belzunce[5]
- Berhéta
- Berhétako Borda
- Berhoa[5]
- Bicaldéguy
- Bichartéa
- Bidartéa
- Bidegain Etchetoa
- Bidegainia
- Bildaraitz or Bildarraitz[6]
- Bordalanda
- Buztingorria
- Celhaya
- Chapitalborda[5]
- Chapitalia (mill)
- Chedarria
- Chelhaya
- Chocoa
- Courtaut
- Currioléko Borda
- Curutzaldéa
- Egyptoa
- Erketa
- Erregnétéa
- Errékahoua
- Errékartéa
- Espertatea
- Estekatea
- Etchartéa
- Etchébarnéko Borda
- Etchébazterréa
- Etchébéhéréa[5]
- Etchébéhéreko Borda
- Etchéberria (2 places)
- Etcheberriko Borda
- Etchéberstia
- Etchéchouria
- Etchégaraya
- Etchégoïnéa
- Etchénika
- Etchenikako Borda
- Etchéparéa
- Etchétipia
- Etchetoa
- Eyhéra
- Ezpildéa
- Ferminéko Borda
- Fermirénéa
- Gandéramendia
- Gandéramendiko Borda
- Garralda
- Gauhetchia
- Granya
- Granyagaraya
- Haranbilléta
- Haranburua
- Haranéa
- Harréguia
- Harriéta
- Harriétako Borda
- Hastoya
- Hégoa
- Hergaitz[5]
- Hiriartéa
- Ichuria
- Idiartéa
- Idigoïnia
- Ilharindéguia
- Ipoutsaguerria
- Irachiloa
- Irazabalia
- Iriart Urrutia
- Iribarnéa
- Iriberria
- Issouribeherea
- Jauberria (2 places)
- Jaungaztenia
- Jelossia
- Kintalénéa
- Kitendéa
- Larrégaïnia
- Larzabaléa
- Leichorrénéa
- Létouatéguia
- Lohichundéa
- Londaits[5]
- Londaitsbehere
- Londaïtzberria
- Londaitzekoborda
- Lukua[5]
- Lur Berry
- Manéchéka Borda
- Manéchénéa
- Mayartéguia
- Mendia
- Mendiberria
- Mendiburua
- Mendigorria[5]
- Mendilarréa
- Menta
- Mentaberria
- Mentachiloa
- Mignotéguia
- Négutéa
- Notariaénia
- Ourriola
- Oyhana
- Oyharartéa
- Oyharitzéa
- Oyharitséko Borda
- Patindeya
- Peña
- Petchitea
- Pipitea
- Pompochénéa
- Sallaberryborda
- Sarcabaleko Borda
- Sarhigaïnéa
- Tuturrutéguia
- Uhaldéa
- Urgorria
- Urquéta
- Zabaloa
- Zabalza
- Zaliotéguia
- Zokoa
Toponymy
The commune name in basque is Aiherra.[7] According to Jean-Baptiste Orpustan,[6] the name comes from the basque ailherr ("incline"), giving the meaning "place on a slope".
The following table details the origins of the commune name and other names in the commune.
| Name | Spelling | Date | Source | Page | Origin | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ayherre | Sancti petri de ilarre | 1236 | Orpustan | Village | ||
| San Per de Aiherre | 1321 | Raymond | Camara | |||
| ayherra | 1344 | Orpustan | ||||
| ayheRe | 1350 | Orpustan | ||||
| Ajarra | 1513 | Raymond | Pamplona | |||
| Ahyerie | 1754 | Raymond | Collations | |||
| Aiherre | 1750 | Cassini | ||||
| L'Ahounbiscardéguy | L'Ahunbiscardéguy | 1863 | Raymond | Stream | ||
| Apairi | Apahiri | 1863 | Raymond | Hamlet | ||
| Aphara | Apara | 1621 | Raymond | Biscay | Farm | |
| Aphara | 1863 | Raymond | ||||
| ***Bildarraitz | beldarais | 1249 | Orpustan | Hamlet | ||
| bildarays | 1350 | Orpustan | ||||
| bildarraiz | 1413 | Orpustan | ||||
| Bildariz | 1513 | Raymond | Pamplona | |||
| Bildarraïts | 1863 | Raymond | ||||
| Belzunce | Belçunze | 1384 | Raymond | Duchesne | Chateau, fief of the Kingdom of Navarre | |
| Belzunce | 1384 | Raymond | Duchesne | |||
| Velçunce | 1621 | Raymond | Biscay | |||
| Balzunze | 1621 | Raymond | Biscay | |||
| Belsunce | 1863 | Raymond | ||||
| Berhoa | Le Berho | 1863 | Raymond | Stream | ||
| Chapitalborda | Chapitel | 1621 | Raymond | Biscay | Farm | |
| Chapital | 1863 | Raymond | ||||
| Erquéta | Erquéta | 1863 | Raymond | Hamlet | ||
| Etchebarnia | Echabarne | 1435 | Raymond | Pamplona | Farm | |
| Etchebarnia | 1863 | Raymond | ||||
| Etchebéhère | Echevehere | 1435 | Raymond | Pamplona | Farm | |
| Etchebéhère | 1863 | Raymond | ||||
| Hergaitz | la croix d'Ergaïts | 1863 | Raymond | Place of Pilgrimage | ||
| Londaïtz | Londayz | 1621 | Raymond | Biscay | Farm | |
| Londaïts | 1863 | Raymond | ||||
| Lukua | Le Lucu | 1863 | Raymond | Stream | ||
| Mendigorria | Mendigorria | 1621 | Raymond | Biscay | Farm | |
| Mendigorry | 1863 | Raymond | ||||
| La Place | La Place | 1863 | Raymond | Hamlet | ||
| L'Uhartea | L'Uhartea | 1863 | Raymond | Stream |
- In the Middle Ages Bildarraitz was an independent area without a church but with its own council, and a half-dozen homes were ennobled in 1435. The name may be the joining of bil-, meaning "set" or "a round place", and araitz, meaning "blackthorn", "prickly", or "briar".[6]
Sources:
- Orpustan: Jean-Baptiste Orpustan, New Basque Toponymy[6]
- Raymond: Topographic Dictionary of the Department of Basses-Pyrenees, 1863, on the page numbers indicated in the table. (in French)[5]
- Cassini: Cassini Map from 1750[8]
Origins:
History
On 18 March 1450,[14] Labourd returned to the French crown after the signing of a peace treaty at the Château of Belzunce in Ayherre which marked the end of English influence in the region. On that the representatives of Labourd made their submission and, upon payment of 2,000 gold écus secured by the retention of 10 hostages, retained their privileges.
Administration
_mairie.JPG.webp)
List of successive mayors[16]
| From | To | Name | Party | Position |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1995 | 2014 | Jean Paul Basterretche | ||
| 2014 | 2020 | Arnaud Gastambide |
(Not all data is known)
Inter-communality
The commune is part of six inter-communal structures:
- the Communauté d'agglomération du Pays Basque
- the AEP association of Arberoue
- the sanitation association of Adour-Ursula
- the energy association of Pyrénées-Atlantiques
- the inter-communal association for the building of a retirement home in the Arberoue Valley
- the inter-communal association for the crafts zone in Ayherre
Demography
The declaration of rights in 1749 counted 162 fires in Ayherre (130 third estate, one priest, two members of the nobility (Arcangues and Belsunce) and 29 non-owners).[17]
In 2017 the commune had 1,042 inhabitants.
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source: EHESS[18] and INSEE[19] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Economy

Economic activity in the commune is mainly agricultural. The commune is part of the Appellation d'origine contrôlée (AOC) zone of Ossau-iraty.
The Lauak company (aeronautical and aerospace industry) is located in the industrial zone of Ayherre.
The Uhagun Mill on the Aran dates to the 19th century and has been converted into a hydro-electric plant.
Culture and heritage

Civil heritage
The commune has three sites that are registered as historical monuments:
- The Château de Belzunce (13th century)
 [20]
[20] - Prehistoric fortifications on Mount Abarratia
 [4]
[4] - Prehistoric fortifications (Gaztelu Zahar of three levels)
 [21]
[21]
Religious heritage
_%C3%A9glise.JPG.webp)
The Parish Church of Saint Pierre (17th century)![]() is registered as an historical monument.[22]
is registered as an historical monument.[22]
Education
_%C3%A9cole.JPG.webp)
The commune has two primary schools: one in the town and one private school of the Immaculate Conception.
Notable people linked to the commune
- Émile Larre, born in 1926 at Saint-Étienne-de-Baïgorry, was a priest, chronicler, Bertsolari, writer, and French academic in the Basque language. He was an active promoter of basque traditions and particularly attached to the basque modes of expression such as the bertsolarism and Basque Pelota. He was priest of Ayherre from 1969 to 1980.
References
- "Populations légales 2017". INSEE. Retrieved 6 January 2020.
- Inhabitants of Pyrénées-Atlantiques (in French)
- Google Maps
- Ministry of Culture, Mérimée PA00084328 Prehistoric Fortifications (in French)
- Topographic Dictionary of the Department of Basses-Pyrenees, Paul Raymond, Imprimerie nationale, 1863, Digitised from Lyon Public Library 15 June 2011 (in French)
- Jean-Baptiste Orpustan, New Basque Toponymy, Presses universitaires de Bordeaux, 2006, ISBN 2 86781 396 4 (in French)
- Euskaltzaindia - Academy of the Basque language (Eu icon)
- Cassini Map 1750 – Ayherre
- Titles published by don José Yanguas y Miranda - Diccionario de Antiguedades del reino de Navarra, 1840, Pamplona (in Spanish)
- Titles published by don José Yanguas y Miranda (in Spanish)
- Manuscripts from the 17th and 18th centuries in the Departmental Archives of Pyrénées-Atlantiques (in French)
- Derecho de naturaleza que la merindad de San-Juan-del-pie-del-puerto, una de las seys de Navarra, tiene en Castilla, 1622 (in Spanish)
- Duchesne Collection, volumes 99 to 114, containing the papers of Oihenart, former Imperial Librarian - Bibliothèque nationale de France
- Philippe Veyrin, The Basques, Arthaud, 1975, ISBN 2 7003 0038 6, p. 122 (in French)
- Arms of France
- List of Mayors of France (in French)
- Census cited by Manex Goyhenetche, General History of Basque Country - Vol. 3, Elkarlanean, 2001, ISBN 2 9131 5634 7, p. 282. The same work by Manex Goyhenetche indicated (page 284) that there was an average of 5.5 inhabitants per fire. (in French)
- Des villages de Cassini aux communes d'aujourd'hui: Commune data sheet Ayherre, EHESS. (in French)
- Population en historique depuis 1968, INSEE
- Ministry of Culture, Mérimée PA00084558 Chateau of Belzunce (in French)
- Ministry of Culture, Mérimée PA00084407 Prehistoric Fortifications (in French)
- Ministry of Culture, Mérimée IA64000728 Parish Church of Saint Pierre (in French)
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Ayherre. |
- Aiherre in the Bernardo Estornés Lasa - Auñamendi Encyclopedia (Euskomedia Fundazioa) (in Spanish)
- Ayherre official website (in French)
- Community of communes of Pays de Hasparren official website (in French)
- Ayherre on Lion1906
- Ayherre on the 1750 Cassini map
