Enlargement of the United Nations
As of 3 February 2021, there are 193 member states of the United Nations (UN), each of which is a member of the United Nations General Assembly.[1]
The following is a list of United Nations member states arranged in chronological order according to their dates of admission (with the United Nations Security Council resolutions that recommended their admission and the United Nations General Assembly resolutions that admitted them, signified with SCR and GAR, respectively),[2] including former members. Members denoted with "→" changed their names, had their memberships in the UN continued by a successor state, merged with other members, or were dissolved.
Timeline of Enlargement of the United Nations
1945 (original members)
The UN officially came into existence on 24 October 1945, after ratification of the United Nations Charter by the five permanent members of the United Nations Security Council (China, France, the Soviet Union, the United Kingdom, and the United States) and a majority of the other signatories.[3] A total of 51 original members (or founding members) joined that year; 50 of them signed the Charter at the United Nations Conference on International Organization in San Francisco on 26 June 1945, while Poland, which was not represented at the conference, signed it on 15 October 1945.[4]
24 October 1945
 Argentina
Argentina- Belarus (seat held by the
.svg.png.webp) /
/.svg.png.webp) Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic → renamed to
Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic → renamed to .svg.png.webp) /
/.svg.png.webp) /
/ Belarus in 1991)
Belarus in 1991) .svg.png.webp) /
/.svg.png.webp) /
/.svg.png.webp) /
/ Brazil
Brazil Chile
Chile- China (seat held by the
 Republic of China (on mainland (1912–1949) and on Taiwan (1949–present)) → seat transferred to the
Republic of China (on mainland (1912–1949) and on Taiwan (1949–present)) → seat transferred to the  People's Republic of China in 1971)[H]
People's Republic of China in 1971)[H] .svg.png.webp) Cuba →
Cuba →  Communist Cuba
Communist Cuba Czechoslovakia (seat held by
Czechoslovakia (seat held by  Third Czechoslovak Republic →
Third Czechoslovak Republic →  Czechoslovak Socialist Republic →
Czechoslovak Socialist Republic →  Czech and Slovak Federative Republic) → dissolved (current UN members that formerly comprised Czechoslovakia:
Czech and Slovak Federative Republic) → dissolved (current UN members that formerly comprised Czechoslovakia:  Czech Republic and
Czech Republic and  Slovakia)[F]
Slovakia)[F]  Denmark
Denmark Dominican Republic
Dominican Republic.svg.png.webp) Egypt →
Egypt → .svg.png.webp) United Arab Republic (period when merged with
United Arab Republic (period when merged with  Syria) [A] →
Syria) [A] →  Arab Republic of Egypt
Arab Republic of Egypt  El Salvador
El Salvador- France (seat held by the
 Provisional Government of the French Republic → became the
Provisional Government of the French Republic → became the .svg.png.webp) French Fourth Republic → reconstituted as the
French Fourth Republic → reconstituted as the  French Fifth Republic in 1958)
French Fifth Republic in 1958) .svg.png.webp) /
/.svg.png.webp) /
/ Haiti
Haiti.svg.png.webp) /
/.svg.png.webp) Imperial State of Iran →
Imperial State of Iran →  Islamic Republic of Iran
Islamic Republic of Iran  Lebanon
Lebanon Luxembourg
Luxembourg Dominion of New Zealand →
Dominion of New Zealand →  New Zealand
New Zealand Nicaragua
Nicaragua.svg.png.webp) /
/.svg.png.webp) /
/.svg.png.webp) /
/.svg.png.webp) /
/ Paraguay
Paraguay.svg.png.webp) Commonwealth of the Philippines →
Commonwealth of the Philippines → .svg.png.webp) Third Republic of the Philippines →
Third Republic of the Philippines → .svg.png.webp) Philippines under Martial Law →
Philippines under Martial Law → .svg.png.webp) Fourth Republic of the Philippines →
Fourth Republic of the Philippines →  Fifth Republic of the Philippines
Fifth Republic of the Philippines .svg.png.webp) Poland (Provisional Government of National Unity) →
Poland (Provisional Government of National Unity) → .svg.png.webp) Republic of Poland →
Republic of Poland → .svg.png.webp) Polish People's Republic →
Polish People's Republic →  Third Polish Republic
Third Polish Republic.svg.png.webp) /
/ Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia.svg.png.webp) /
/ Soviet Union (Union of Soviet Socialist Republics) →
Soviet Union (Union of Soviet Socialist Republics) → .svg.png.webp) /
/ Russian Federation (successor state)
Russian Federation (successor state).svg.png.webp) Syria →
Syria → .svg.png.webp) United Arab Republic (period when merged with
United Arab Republic (period when merged with  Egypt) [A] →
Egypt) [A] →  Syrian Arab Republic
Syrian Arab Republic Turkey
Turkey- Ukraine (seat held by the
.svg.png.webp) /
/ Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic → renamed to
Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic → renamed to  /
/ Ukraine in 1991)
Ukraine in 1991)  United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.svg.png.webp) /
/.svg.png.webp) /
/ United States of America
United States of America.svg.png.webp) Democratic Federal Yugoslavia →
Democratic Federal Yugoslavia → .svg.png.webp) Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia →
Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia → .svg.png.webp) Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia → dissolved (would-be successor state
Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia → dissolved (would-be successor state %253B_Flag_of_Serbia_and_Montenegro_(2003%E2%80%932006).svg.png.webp) Federal Republic of Yugoslavia was de facto suspended from the United Nations by SCR 777 and GAR 47/1; current UN members that formerly comprised Yugoslavia:
Federal Republic of Yugoslavia was de facto suspended from the United Nations by SCR 777 and GAR 47/1; current UN members that formerly comprised Yugoslavia:  Bosnia and Herzegovina,
Bosnia and Herzegovina,  Croatia,
Croatia,  Montenegro,
Montenegro,  North Macedonia,
North Macedonia,  Serbia, and
Serbia, and  Slovenia[G])
Slovenia[G])
25 October 1945
30 October 1945
31 October 1945
1 November 1945
2 November 1945
5 November 1945
7 November 1945
9 November 1945
13 November 1945
.svg.png.webp) Ethiopian Empire →
Ethiopian Empire → .svg.png.webp) Derg →
Derg → .svg.png.webp) People's Democratic Republic of Ethiopia →
People's Democratic Republic of Ethiopia → .svg.png.webp) Transitional Government of Ethiopia →
Transitional Government of Ethiopia → .svg.png.webp) /
/ Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia
Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia Panama
Panama
14 November 1945
15 November 1945
21 November 1945
27 November 1945
10 December 1945
17 December 1945
18 December 1945
21 December 1945
.svg.png.webp) /
/ Ecuador
Ecuador.svg.png.webp) Kingdom of Iraq →
Kingdom of Iraq → .svg.png.webp) /
/%253B_Flag_of_Syria_(1963%E2%80%931972).svg.png.webp) Iraqi Republic →
Iraqi Republic → %253B_Flag_of_Syria_(1963%E2%80%931972).svg.png.webp) /
/.svg.png.webp) Ba'athist Iraq →
Ba'athist Iraq → .svg.png.webp) /
/.svg.png.webp) /
/ Iraq
Iraq
27 December 1945
1946
19 November 1946 (all by SCR 8 and GAR 34)
.svg.png.webp) Kingdom of Afghanistan →
Kingdom of Afghanistan → .svg.png.webp) Republic of Afghanistan →
Republic of Afghanistan → .svg.png.webp) /
/.svg.png.webp) /
/.svg.png.webp) /
/.svg.png.webp) Democratic Republic of Afghanistan →
Democratic Republic of Afghanistan → .svg.png.webp) Islamic State of Afghanistan →
Islamic State of Afghanistan →  Islamic Republic of Afghanistan
Islamic Republic of Afghanistan Iceland
Iceland Sweden
Sweden
16 December 1946
1947
30 September 1947 (all by SCR 29 and GAR 108)
 Dominion of Pakistan →
Dominion of Pakistan →  Islamic Republic of Pakistan
Islamic Republic of Pakistan Mutawakkilite Kingdom of Yemen →
Mutawakkilite Kingdom of Yemen →  North Yemen →
North Yemen →  Yemen (unified state after merging with
Yemen (unified state after merging with  South Yemen)[D]
South Yemen)[D]
1948
19 April 1948
.svg.png.webp) Union of Burma (SCR 45, GAR 188) →
Union of Burma (SCR 45, GAR 188) → .svg.png.webp) Socialist Republic of the Union of Burma →
Socialist Republic of the Union of Burma → .svg.png.webp) Union of Myanmar →
Union of Myanmar →  Myanmar
Myanmar
1955
14 December 1955 (all by SCR 109 and GAR 995)
.svg.png.webp) Albania →
Albania →  Republic of Albania
Republic of Albania Austria
Austria.svg.png.webp) /
/.svg.png.webp) /
/.svg.png.webp) Bulgaria →
Bulgaria →  Republic of Bulgaria
Republic of Bulgaria Cambodia →
Cambodia →  Khmer Republic →
Khmer Republic →  Cambodia →
Cambodia →  Democratic Kampuchea →
Democratic Kampuchea →  Cambodia
Cambodia.svg.png.webp) /
/.svg.png.webp) Ceylon →
Ceylon →  Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka Finland
Finland.svg.png.webp) /
/ Hungary (application addressed in 1947 by SCR 24) →
Hungary (application addressed in 1947 by SCR 24) →  Hungary
Hungary Ireland
Ireland Italy (application addressed in 1947 by SCR 25)
Italy (application addressed in 1947 by SCR 25) Jordan
Jordan.svg.png.webp) Laos →
Laos →  Lao People's Democratic Republic
Lao People's Democratic Republic.svg.png.webp) Libya →
Libya → .svg.png.webp) Libyan Arab Republic →
Libyan Arab Republic → .svg.png.webp) Libyan Arab Jamahiriya →
Libyan Arab Jamahiriya →  Libya
Libya Nepal →
Nepal →  Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal
Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal Second Republic of Portugal →
Second Republic of Portugal →  Third Republic of Portugal
Third Republic of Portugal.svg.png.webp) Romanian People's Republic →
Romanian People's Republic → .svg.png.webp) Socialist Republic of Romania →
Socialist Republic of Romania →  Romania
Romania.svg.png.webp) Spain →
Spain → .svg.png.webp) /
/ Kingdom of Spain
Kingdom of Spain
1956
12 November 1956
.svg.png.webp) Sudan (SCR 112, GAR 1110) →
Sudan (SCR 112, GAR 1110) →  Republic of the Sudan
Republic of the Sudan Morocco (SCR 115, GAR 1111)
Morocco (SCR 115, GAR 1111) Tunisia (SCR 116, GAR 1112)
Tunisia (SCR 116, GAR 1112)
18 December 1956
1957
8 March 1957
 Dominion of Ghana →
Dominion of Ghana →  /
/.svg.png.webp) /
/ Ghana (SCR 124, GAR 1118)
Ghana (SCR 124, GAR 1118)
17 September 1957
 Federation of Malaya (SCR 125, GAR 1134) →
Federation of Malaya (SCR 125, GAR 1134) →  Malaysia
Malaysia
1960
20 September 1960
 Cameroun (SCR 133, GAR 1476) →
Cameroun (SCR 133, GAR 1476) → .svg.png.webp) Cameroon → United Republic of Cameroon →
Cameroon → United Republic of Cameroon →  Cameroon
Cameroon Togo (SCR 136, GAR 1477)
Togo (SCR 136, GAR 1477) Malagasy Republic (SCR 140, GAR 1478) →
Malagasy Republic (SCR 140, GAR 1478) →  Madagascar
Madagascar Somalia (SCR 141, GAR 1479)
Somalia (SCR 141, GAR 1479).svg.png.webp) /
/%253B_Flag_of_the_Democratic_Republic_of_the_Congo_(1964%E2%80%931966).svg.png.webp) /
/.svg.png.webp) Democratic Republic of Congo (SCR 142, GAR 1480) →
Democratic Republic of Congo (SCR 142, GAR 1480) →  Zaire →
Zaire → .svg.png.webp)
.svg.png.webp)
 Democratic Republic of the Congo
Democratic Republic of the Congo Dahomey (SCR 147, GAR 1481) →
Dahomey (SCR 147, GAR 1481) → .svg.png.webp) People's Republic of Benin →
People's Republic of Benin →  Benin
Benin Niger (SCR 148, GAR 1482)
Niger (SCR 148, GAR 1482) Upper Volta (SCR 149, GAR 1483) →
Upper Volta (SCR 149, GAR 1483) →  Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso Ivory Coast (SCR 150, GAR 1484) →
Ivory Coast (SCR 150, GAR 1484) →  Côte d'Ivoire
Côte d'Ivoire Chad (SCR 151, GAR 1485)
Chad (SCR 151, GAR 1485) Congo (SCR 152, GAR 1486) →
Congo (SCR 152, GAR 1486) →  People's Republic of the Congo →
People's Republic of the Congo →  Republic of the Congo
Republic of the Congo Gabon (SCR 153, GAR 1487)
Gabon (SCR 153, GAR 1487) Central African Republic (SCR 154, GAR 1488) →
Central African Republic (SCR 154, GAR 1488) →  Central African Empire →
Central African Empire →  Central African Republic
Central African Republic.svg.png.webp) /
/ Cyprus (SCR 155, GAR 1489)
Cyprus (SCR 155, GAR 1489)
28 September 1960
7 October 1960
1961
27 September 1961
 Sierra Leone (SCR 165, GAR 1623)
Sierra Leone (SCR 165, GAR 1623)
27 October 1961
.svg.png.webp) Mongolian People's Republic (SCR 166, GAR 1630) →
Mongolian People's Republic (SCR 166, GAR 1630) → .svg.png.webp) /
/ Mongolia
Mongolia.svg.png.webp) /
/ Mauritania (SCR 167, GAR 1631)
Mauritania (SCR 167, GAR 1631)
14 December 1961
.svg.png.webp) Tanganyika (SCR 170, GAR 1667) →
Tanganyika (SCR 170, GAR 1667) →  United Republic of Tanzania (after merging with
United Republic of Tanzania (after merging with  Zanzibar)[B]
Zanzibar)[B]
1962
18 September 1962
.svg.png.webp) /
/ Rwanda (SCR 172, GAR 1748)
Rwanda (SCR 172, GAR 1748).svg.png.webp) /
/.svg.png.webp) /
/ Burundi (SCR 173, GAR 1749)
Burundi (SCR 173, GAR 1749) Jamaica (SCR 174, GAR 1750)
Jamaica (SCR 174, GAR 1750) Dominion of Trinidad and Tobago →
Dominion of Trinidad and Tobago →  Trinidad and Tobago (SCR 175, GAR 1751)
Trinidad and Tobago (SCR 175, GAR 1751)
8 October 1962
25 October 1962
1963
14 May 1963
 Kuwait (GAR 1872)
Kuwait (GAR 1872)
16 December 1963
.svg.png.webp) /
/.svg.png.webp) Sultanate of Zanzibar (SCR 184, GAR 1975) →
Sultanate of Zanzibar (SCR 184, GAR 1975) → .svg.png.webp) People's Republic of Zanzibar → merged with
People's Republic of Zanzibar → merged with .svg.png.webp) Tanganyika (now
Tanganyika (now  United Republic of Tanzania)[B]
United Republic of Tanzania)[B] Kenya (SCR 185, GAR 1976)
Kenya (SCR 185, GAR 1976)
1964
1 December 1964
1965
20 January 1965
21 September 1965
1966
20 September 1966
28 September 1966
17 October 1966
9 December 1966
1967
14 December 1967
 South Yemen (SCR 243, GAR 2310) → merged with
South Yemen (SCR 243, GAR 2310) → merged with  North Yemen (now unified state of
North Yemen (now unified state of  Yemen)[D]
Yemen)[D]
1971
21 September 1971
7 October 1971
25 October 1971
- China's seat at the United Nations transferred from the Republic of China to the People's Republic of China. (GAR 2758)[H]
9 December 1971
 United Arab Emirates (SCR 304, GAR 2794)
United Arab Emirates (SCR 304, GAR 2794)
1973
18 September 1973
 Federal Republic of Germany (SCR 335, GAR 3050) →
Federal Republic of Germany (SCR 335, GAR 3050) →  Germany (unified state after accession of
Germany (unified state after accession of  German Democratic Republic)[E]
German Democratic Republic)[E] German Democratic Republic (SCR 335, GAR 3050) → acceded to
German Democratic Republic (SCR 335, GAR 3050) → acceded to  Federal Republic of Germany (now unified state of
Federal Republic of Germany (now unified state of  Germany)[E]
Germany)[E] The Bahamas (SCR 336, GAR 3051)
The Bahamas (SCR 336, GAR 3051)
1974
17 September 1974
 Bangladesh (SCR 351, GAR 3203)
Bangladesh (SCR 351, GAR 3203) Grenada (SCR 352, GAR 3204)
Grenada (SCR 352, GAR 3204) Guinea-Bissau (SCR 356, GAR 3205)
Guinea-Bissau (SCR 356, GAR 3205)
1975
16 September 1975
.svg.png.webp) /
/ Cape Verde (SCR 372, GAR 3363)
Cape Verde (SCR 372, GAR 3363) São Tomé and Príncipe (SCR 373, GAR 3364)
São Tomé and Príncipe (SCR 373, GAR 3364).svg.png.webp) /
/.svg.png.webp) /
/ People's Republic of Mozambique (SCR 374, GAR 3365) →
People's Republic of Mozambique (SCR 374, GAR 3365) →  Mozambique
Mozambique
10 October 1975
 Papua New Guinea (SCR 375, GAR 3368)
Papua New Guinea (SCR 375, GAR 3368)
12 November 1975
.svg.png.webp) Comoros, State of (SCR 376, GAR 3385) →
Comoros, State of (SCR 376, GAR 3385) → .svg.png.webp) /
/.svg.png.webp) /
/.svg.png.webp) Federal and Islamic Republic of Comoros →
Federal and Islamic Republic of Comoros →  Union of the Comoros
Union of the Comoros
4 December 1975
1976
21 September 1976
.svg.png.webp) /
/.svg.png.webp) /
/ Seychelles (SCR 394, GAR 31/1)
Seychelles (SCR 394, GAR 31/1)
1 December 1976
 People's Republic of Angola (SCR 397, GAR 31/44) →
People's Republic of Angola (SCR 397, GAR 31/44) →  Republic of Angola
Republic of Angola
15 December 1976
 Western Samoa (SCR 399, GAR 31/104) →
Western Samoa (SCR 399, GAR 31/104) →  Samoa
Samoa
1991
24 August 1991
 /
/ Ukraine independence from the Soviet Union
Ukraine independence from the Soviet Union
17 September 1991
.svg.png.webp) /
/ Democratic People's Republic of Korea (SCR 702, GAR 46/1)
Democratic People's Republic of Korea (SCR 702, GAR 46/1).svg.png.webp) /
/.svg.png.webp) /
/ Republic of Korea (SCR 702, GAR 46/1)
Republic of Korea (SCR 702, GAR 46/1) Federated States of Micronesia (SCR 703, GAR 46/2)
Federated States of Micronesia (SCR 703, GAR 46/2) Marshall Islands (SCR 704, GAR 46/3)
Marshall Islands (SCR 704, GAR 46/3).svg.png.webp) /
/.svg.png.webp) /
/ Belarus independence from the Soviet Union
Belarus independence from the Soviet Union Estonia (SCR 709, GAR 46/4)
Estonia (SCR 709, GAR 46/4) Latvia (SCR 710, GAR 46/5)
Latvia (SCR 710, GAR 46/5).svg.png.webp) /
/ Lithuania (SCR 711, GAR 46/6)
Lithuania (SCR 711, GAR 46/6)
1992
2 March 1992
 /
/.svg.png.webp) /
/ Kazakhstan (SCR 732, GAR 46/224)
Kazakhstan (SCR 732, GAR 46/224) Armenia (SCR 735, GAR 46/227)
Armenia (SCR 735, GAR 46/227) /
/ Kyrgyzstan (SCR 736, GAR 46/225)
Kyrgyzstan (SCR 736, GAR 46/225) Uzbekistan (SCR 737, GAR 46/226)
Uzbekistan (SCR 737, GAR 46/226).svg.png.webp) /
/ Tajikistan (SCR 738, GAR 46/228)
Tajikistan (SCR 738, GAR 46/228) Moldova (SCR 739, GAR 46/223)
Moldova (SCR 739, GAR 46/223).svg.png.webp) /
/.svg.png.webp) /
/.svg.png.webp) /
/ Turkmenistan (SCR 741, GAR 46/229)
Turkmenistan (SCR 741, GAR 46/229) Azerbaijan (SCR 742, GAR 46/230)
Azerbaijan (SCR 742, GAR 46/230).svg.png.webp) /
/ San Marino (SCR 744, GAR 46/231)
San Marino (SCR 744, GAR 46/231)
22 May 1992
 Croatia (SCR 753, GAR 46/238)
Croatia (SCR 753, GAR 46/238) Slovenia (SCR 754, GAR 46/236)
Slovenia (SCR 754, GAR 46/236).svg.png.webp) Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina (SCR 755, GAR 46/237) →
Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina (SCR 755, GAR 46/237) → .svg.png.webp) /
/ Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina
31 July 1992
1993
19 January 1993
 Slovakia (SCR 800, GAR 47/222)
Slovakia (SCR 800, GAR 47/222) Czech Republic (SCR 801, GAR 47/221)
Czech Republic (SCR 801, GAR 47/221)
8 April 1993
.svg.png.webp) /
/ Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia (SCR 817, GAR 47/225) →
Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia (SCR 817, GAR 47/225) →  North Macedonia
North Macedonia
28 May 1993
28 July 1993
1999
14 September 1999
2000
5 September 2000
1 November 2000
%253B_Flag_of_Serbia_and_Montenegro_(2003%E2%80%932006).svg.png.webp) Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (SCR 1326, GAR 55/12) →
Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (SCR 1326, GAR 55/12) → %253B_Flag_of_Serbia_and_Montenegro_(2003%E2%80%932006).svg.png.webp) Serbia and Montenegro →
Serbia and Montenegro → .svg.png.webp) /
/ Serbia (successor state)
Serbia (successor state)
2002
10 September 2002
 Switzerland (SCR 1426, GAR 57/1)
Switzerland (SCR 1426, GAR 57/1)
27 September 2002
 East Timor (SCR 1414, GAR 57/3)
East Timor (SCR 1414, GAR 57/3)
Summary
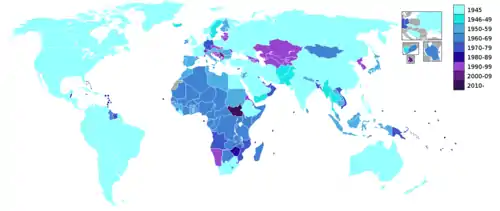
Below is a summary of the growth in UN membership.[5]
| Year | # of admissions | # of members |
|---|---|---|
| 1945 | 51 | 51 |
| 1946 | 4 | 55 |
| 1947 | 2 | 57 |
| 1948 | 1 | 58 |
| 1949 | 1 | 59 |
| 1950 | 1 | 60 |
| 1951–1954 | 0 | 60 |
| 1955 | 16 | 76 |
| 1956 | 4 | 80 |
| 1957 | 2 | 82 |
| 1958 | 1 | 82[A] |
| 1959 | 0 | 82 |
| 1960 | 17 | 99 |
| 1961 | 4 | 104[A] |
| 1962 | 6 | 110 |
| 1963 | 3 | 113 |
| 1964 | 3 | 115[B] |
| 1965 | 3 | 117[C] |
| 1966 | 4 | 122[C] |
| 1967 | 1 | 123 |
| 1968 | 3 | 126 |
| 1969 | 0 | 126 |
| 1970 | 1 | 127 |
| 1971 | 5 | 132 |
| 1972 | 0 | 132 |
| 1973 | 3 | 135 |
| 1974 | 3 | 138 |
| 1975 | 6 | 144 |
| 1976 | 3 | 147 |
| 1977 | 2 | 149 |
| 1978 | 2 | 151 |
| 1979 | 1 | 152 |
| 1980 | 2 | 154 |
| 1981 | 3 | 157 |
| 1982 | 0 | 157 |
| 1983 | 1 | 158 |
| 1984 | 1 | 159 |
| 1985–1989 | 0 | 159 |
| 1990 | 2 | 159[D][E] |
| 1991 | 7 | 166 |
| 1992 | 13 | 179 |
| 1993 | 6 | 184[F] |
| 1994 | 1 | 185 |
| 1995–1998 | 0 | 185 |
| 1999 | 3 | 188 |
| 2000 | 2 | 189[G] |
| 2001 | 0 | 189 |
| 2002 | 2 | 191 |
| 2003–2005 | 0 | 191 |
| 2006 | 1 | 192 |
| 2007–2010 | 0 | 192 |
| 2011 | 1 | 193 |
| 2012–present | 0 | 193 |
See also
- Enlargement of the African Union and enlargement of the European Union
- Holy See of Vatican City and State of Palestine in the Palestinian territories, the two UN observer states
- Sovereign Military Order of Malta
- Abkhazia, Republic of Artsakh, the Republic of China on Taiwan, Kosovo, Northern Cyprus, Somaliland, South Ossetia, Transnistria, and Western Sahara's Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic
- List of sovereign states
- Member states of the United Nations
Notes
- ^ a b c d e Egypt and Syria merged to form the United Arab Republic on 22 February 1958. They resumed as separate UN members on 13 October 1961 after Syria resumed its status as an independent state.
- ^ a b c Tanganyika and Zanzibar merged to form the United Republic of Tanganyika and Zanzibar on 26 April 1964, which later changed its name to the United Republic of Tanzania.
- ^ a b c d e Indonesia temporarily withdrew from the UN on 20 January 1965. It announced its intention "to resume full cooperation with the United Nations and to resume participation in its activities" on 19 September 1966, and was invited to rejoin the UN on 28 September 1966.
- ^ a b c Yemen and Democratic Yemen merged on 22 May 1990, see Yemeni unification for details.
- ^ a b c The German Democratic Republic acceded to the Federal Republic of Germany on 3 October 1990, see German reunification for details.
- ^ a b Czechoslovakia ceased to be a UN member on 1 January 1993 after its dissolution into the Czech Republic and Slovakia, see Dissolution of Czechoslovakia for details.
- ^ a b Yugoslavia (referring to the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia), effectively dissolved by 1992, was removed from the official roster of UN members in 2000 following the admission of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Slovenia, Macedonia, and the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (name later changed to Serbia and Montenegro) as new UN members. For details see Breakup of Yugoslavia and Yugoslav Wars.
- ^ a b c China, officially known then as the Republic of China (ROC) was a founding member of the UN and a permanent member of the Security Council with veto power. In 1949, the ROC government led by the Kuomintang (KMT) lost the Chinese Civil War and retreated to the island of Taiwan. The Chinese Communist Party (CCP) then established the People's Republic of China (PRC) on the Chinese mainland. As such, the political status of the ROC (alongside the territories currently under ROC jurisdiction) are in dispute. Constitutionally, both the ROC and the PRC continue to claim to be the sole legitimate government of the entirety of China (including Taiwan).[6][7][8] In 1971, the PRC replaced the ROC as the legitimate representative of "China" at the UN.[9] The ROC was subsequently expelled from the UN and its organs. Since then, attempts to rejoin the UN were blocked by the PRC and the ROC was forced to use other designations in other international organizations such as the name "Chinese Taipei" in the International Olympic Committee.
References
- "What are Member States?". United Nations.
- "Current Member States". United Nations.
- "History of the United Nations". United Nations.
- "Founding Member States". United Nations.
- "Growth in United Nations membership, 1945–present". United Nations. Archived from the original on 12 July 2014.
- Sarmento, Clara (2009). Eastwards / Westwards: Which Direction for Gender Studies in the 21st Century?. p. 127. ISBN 9781443808682.
- Hudson, Christopher (2014). The China Handbook. p. 59. ISBN 9781134269662.
- Rigger, Shelley (2002). Politics in Taiwan: Voting for Reform. p. 60. ISBN 9781134692972.
- Froehlich, Annette; Seffinga, Vincent (2019). The United Nations and Space Security: Conflicting Mandates between UNCOPUOS and the CD. p. 40. ISBN 9783030060251.