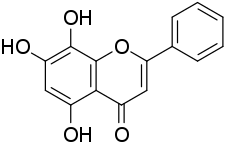
Norwogonin
Norwogonin, also known as 5,7,8-trihydroxyflavone (5,7,8-THF), is a flavone, a naturally occurring flavonoid-like chemical compound which is found in Scutellaria baicalensis (Baikal skullcap).[1] It has been found to act as an agonist of the TrkB, the main signaling receptor of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), and appears to possess roughly the same activity in this regard to that of the closely related but more well-known 7,8-dihydroxyflavone (7,8-DHF).[2]
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 5,7,8-Trihydroxyflavone; 5,7,8-THF |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C15H10O5 |
| Molar mass | 270.240 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
References
- Miyasaki Y, Rabenstein JD, Rhea J, Crouch ML, Mocek UM, Kittell PE, et al. (2013). Khan AU (ed.). "Isolation and characterization of antimicrobial compounds in plant extracts against multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii". PLOS ONE. 8 (4): e61594. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...861594M. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0061594. PMC 3632535. PMID 23630600.
- Liu X, Chan CB, Jang SW, Pradoldej S, Huang J, He K, et al. (December 2010). "A synthetic 7,8-dihydroxyflavone derivative promotes neurogenesis and exhibits potent antidepressant effect". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 53 (23): 8274–86. doi:10.1021/jm101206p. PMC 3150605. PMID 21073191.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.