Panjshir Province
Panjshir (Persian: پنجشیر, literally "Five Lions", also spelled as Panjsher and Panjsheer) is one of the thirty-four provinces of Afghanistan, located in the northeastern part of the country. The province is divided into seven districts and contains 512 villages. As of 2012, the population of Panjshir province was about 346,100.[1][2] Bazarak serves as the provincial capital. It is estimated that more than 700,000 people from Panjshir province, live in other provinces in Afghanistan, particularly in the city of Kabul.
Panjshir
پنجشیر | |
|---|---|
 A view of a valley in the Panjshir Province of Afghanistan in 2009 | |
 Map of Afghanistan with Panjshir highlighted | |
| Coordinates (Capital): 35.4°N 70.0°E | |
| Country | |
| Capital | Bazarak |
| Government | |
| • Governor | Muhammad Arif Sarwari |
| Area | |
| • Total | 3,610 km2 (1,390 sq mi) |
| Population (2018)[1] | |
| • Total | 346,100 (2,012)[1] |
| Time zone | UTC+4:30 (Afghanistan Time) |
| ISO 3166 code | AF-PAN |
| Main languages | Dari |
Panjshir became an independent province from neighboring Parwan Province in 2004. It is surrounded by Baghlan and Takhar in the north, Badakhshan and Nuristan in the east, Laghman and Kapisa in the south, and Parwan in the west.
History
The territory was ruled by the Khanate of Bukhara between the early 16th century and the mid-18th century. As Ahmad Shah Durrani's northern Afghanistan conquest began Pavan area which contained today's Panjshir was conquered by Ahmad Shah Durrani and officially accepted as a part of Durranis by Murad Beg of Bukhara after a treaty of friendship was signed in or about 1750p, and became part of the Durrani Empire. It was fully ruled by the Durranis followed by the Barakzai dynasty, and was untouched by the British during the 19th century Anglo-Afghan wars. Panjshir was attacked multiple times during the Soviet-Afghan War, against Ahmad Shah Massoud and his forces.

In 1973, Mohammed Daoud Khan took over power in Afghanistan and began threatening to take back Khyber Pakhtunkhwa which was splited from Afghanistan by Durand line . This was supported by the People's Democratic Party of Afghanistan (PDPA) but caused great anxiety in Pakistan. By 1975, the young Ahmad Shah Massoud and his followers initiated an uprising in Panjshir but were forced to flee to Peshawar in Pakistan where they received support from Pakistani Prime Minister Zulfiqar Ali Bhutto . Bhutto is said to have paved the way for the April 1978 Saur Revolution in Kabul by making Daoud spread the Afghan Armed Forces to the countryside.[3] The Panjshir region was in rebel control from August 17, 1979 after an uprising,[4] and the region was well defended by Mujahedeen commaders during the 1980s Soviet–Afghan War against the PDPA government and the Soviet Union.
After the collapse of the Democratic Republic of Afghanistan in 1992 the area became part of the Islamic State of Afghanistan. By late 1990s, Panjshir and neighboring Badakhshan province, served as a staging ground for the Northern Alliance against the Taliban government. On September 9, 2001, Defense Minister Massoud was assassinated by two al-Qaeda operatives.[5] Two days later the September 2001 attacks occurred in the United States and this led to the start of a major U.S.-led war in Afghanistan.
Containing the Panjshir Valley, in April 2004 Panjshir District of Parwan Province was turned into a province under the Karzai administration . The Afghan National Security Forces (ANSF) established several bases in the province. In the meantime, the International Security Assistance Force (ISAF) also established bases, a US-led Provincial Reconstruction Team (PRT) began operating in Panjshir in the late 2000s. As of 2012, security in the province is maintained by the Afghan National Police and the Afghan National Army.
Politics and governance
The current Governor of the province is Engineer Kamalludin Nezami. His predecessor was Mohammad Arif Seward and Keramuddin Keram(who raped two members of Afghanistan national women football team in Kabul and latterly escaped to Panjshir provence). [6] Bazarak is the capital of Panjshir province. All law enforcement activities throughout the province are handled by the Afghan National Police (ANP). A provincial Police Chief is assigned to lead both the ANP. The Police Chief represents the Ministry of the Interior in Kabul. The ANP is backed by the military, including the NATO-led forces.
During the parliamentary elections of 2005, Saleh Mohammad Registani was elected as the only male representative of the Panjsher province to Afghanistan's House of Representatives or Wolesi Jirga.
Healthcare
The percentage of households with clean drinking water increased from 16% in 2005, to 17% in 2011.[7] And as many as 23% of births in 2011 were attended to by a skilled birth attendant.[7]
Education
The overall literacy rate (6+ years of age) fell from 33% in 2005 to 32% in 2011.[7] The overall net enrolment rate (6–13 years of age) fell from 42% in 2005 to 40% in 2011.[7] Four Technical and Vocational Education and Training (TVET) schools service the agriculturally-oriented Panjshir Province, including the Ahmad Shah Massoud TVET. The school was established with the help from the Hilfe Paderborn and German Foreign Office and has about 250 students and 22 staff members (as of August 2014).
Demography
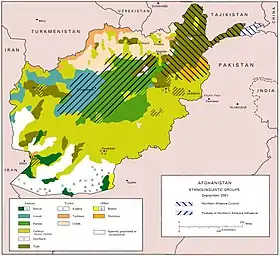

According to the Institute for the Study of War, "Tajiks form the majority of the population."[2]
Dari (Afghan Persian) is the dominant language in the province. All inhabitants are followers of Islam, and exclusively Sunni while the Hazaras of other parts of Afghanistan are mostly Shias (Shiites).[2]
Population by districts
| District | Capital | Population[8] | Area | Number of villages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anaba | c. 20,000 | 164 km2 | 31[9] | |
| Bazarak | Bazarak | c. 40,000 | 378 km2 | 29[10] |
| Dara/ also known as (Persian: درۀ هزاره / Dara-ye-Hazara) | c. 18,000 | 709 km2 | 134[11] | |
| Khenj | c. 23,000 | 688 km2 | 154[12] | |
| Paryan | c. 12,902 | 1270 km2 | 67[13] | |
| Rokha | c. 25,000 | 144 km2 | 72[14] | |
| Shotul | c. 10,000 | 55 km2 | 23[15] |
Places of interest
- The tomb of Ahmad Shah Massoud, is located in Saricha, Bazarak, Panjshir.
- The Football Stadium in Panjshir Valley, next to the Panjshir River.
Notable people from the province
- Ahmad Shah Massoud Afghan guerrilla warfare leader, during soviet union occupation. (National hero of afghanistan).
- Dr. Abdullah Abdullah Afghan politician, current Chairman of the High Council for National Reconciliation
- Amrullah Saleh Afghan politician, current Vice President of Afghanistan
- Muhammad Qasim Fahim field marshal, former Vice President of Afghanistan
- Bismillah Khan Mohammadi Minister of defense
- Abdul Hafiz Mansoor First director of radio and television in Afghanistan
- Ahmad Zia Massoud Afghan politician, former Vice President of Afghanistan
- Yunus Qanuni Afghan politician, former Vice President of Afghanistan
- Dastagir Panjsheri Minister of education
- Keramuddin Keram former Governor of the province, chief executive of Afghanistan football.
- Ahmad Wali Massoud Afghan politician
- Qahar Asi Modern poet
- Mohammad Alam Izdyar First deputy house of elders
- Sediq Shubab - Afghan singer
- Mohammad Rasool Khinji - University Instructor
- Abdul Qahar Abid - Chief Of Staff For Chief Executive
- General Ahmad ul din - Afghan military expert, General of ministry of interior
References
- "Settled Population of Panjsher province by Civil Division, Urban, Rural and Sex-2012-13" (PDF). Islamic Republic of Afghanistan: Central Statistics Organization. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-12-16. Retrieved 2012-10-31.
- "Panjshir Province". Understanding War. Retrieved 2013-08-17.
- Bowersox, Gary W. (2004). The Gem Hunter: The Adventures of an American in Afghanistan. United States: GeoVision, Inc. p. 100. ISBN 0-9747-3231-1. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
To launch this plan, Bhutto recruited and trained a group of Afghans in the Bala-Hesar of Peshawar, in Pakistan's North-west Frontier Province. Among these young men were Massoud, Gulbuddin Hekmatyar, and other members of Jawanan-e Musulman. It served Massoud's interests, which were apparently opposition to the Soviets. Later, after Massoud and Hekmatyar had a terrible falling-out over Massoud's opposition to terrorist tactics and methods, Massoud overthrew from Jawanan-e Musulman. He joined Rabani's newly created Afghan political party, Jamiat-i-Islami, in exile in Pakistan.
- Halim Tanwir, Dr. M. (February 2013). AFGHANISTAN: History, Diplomacy and Journalism Volume 1. ISBN 9781479760909.
- "The Spy Who Quit". PBS - Frontline. January 17, 2011. Retrieved 2014-10-18.
- "Database". www.nytimes.com.
- Archive, Civil Military Fusion Centre, "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2014-05-30. Retrieved 2014-05-30.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Panjshir Province". Government of Afghanistan and United Nations Development Programme (UNDP). Ministry of Rural Rehabilitation and Development. Retrieved 2012-10-31.
- Onaba District (Re-elected) Archived 2016-03-03 at the Wayback Machine
- Bazarak District (Re-elected) Archived 2016-03-04 at the Wayback Machine
- Dara District (Re-elected) Archived 2016-03-04 at the Wayback Machine
- Khenj District (Re-elected)
- Pariyan District (Re-elected) Archived 2016-03-04 at the Wayback Machine
- Rukha District (Re-elected) Archived 2016-03-03 at the Wayback Machine
- Shotol District (Re-elected) Archived 2016-01-24 at the Wayback Machine
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Panjshir Province. |
- Panjshir Province by the Naval Postgraduate School
- Panjshir Province by the Institute for the Study of War
- by Clarksville Online