2019 in climate change
This article documents notable events, research findings, effects, and responses related to global warming and climate change during the year 2019.
| |||
|---|---|---|---|
Summaries
- In November, BioScience published a Warning article stating "we declare, with more than 11,000 scientist signatories from around the world, clearly and unequivocally that planet Earth is facing a climate emergency" and that an "immense increase of scale in endeavors to conserve our biosphere is needed to avoid untold suffering due to the climate crisis".[1]
Measurements and statistics

"Vital Signs of the Planet" as presented by NASA on 31 December 2019[2]
- NOAA's National Centers for Environmental Information (NCEI) and the WMO reported that 2019 was the second hottest year in its 140-year climate record—0.04°C (0.07°F) cooler than 2016—with the U.K. Met Office ranking it among the three hottest.[3]
- NOAA also reported that ocean heat content—the amount of heat stored in the upper levels of the ocean—was the highest ever recorded.[3]
- NOAA also reported that both the Antarctic and Arctic oceans recorded their second smallest average annual sea-ice coverage during the 1979–2019 period of record.[3]
- The WMO Global Atmosphere Watch in-situ observational network showed that carbon dioxide (410.5±0.2 ppm), methane (1877±2 ppb) and nitrous oxide (332.0±0.1 ppb) reached new highs in 2019, respectively constituting 148%, 260% and 123% of pre-industrial levels.[4]
- The fire season in Sakha (Siberia) was unprecedented in the 20-year MODIS record in terms of an earlier start and northern extent, with some fires burning only about 11 km from the Chukchi Sea.[5] From March through June, burned area was greater than 2.9 times the 20-year mean.[5]
Actions and goals
Political, economic, cultural actions
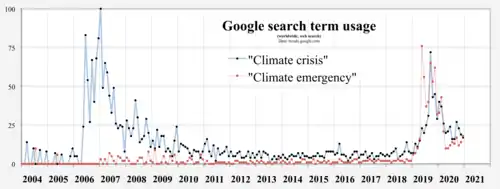
Google trends term usage suggests increasing awareness of the climate crisis and climate emergency declarations during 2019. Apparent waning of interest in the following year may be due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
- In March, 16-year-old Swedish climate activist Greta Thunberg was nominated for the Nobel Peace Prize, also receiving a nomination the following year.[6]
- In September, Thunberg spoke at the 2019 UN Climate Action Summit, criticizing world leaders for inaction on climate change.[7]
- In December, Thunberg was named TIME Person of the Year.[8]
- In Norway, electric cars comprised 54% of all new vehicle sales for 2019, making it the first country to have sold more electric cars than petrol, hybrid, and diesel engines in a year.[9] The government planned to ban the sale of petrol and diesel cars by 2025.[9]
Mitigation goal statements
Consensus
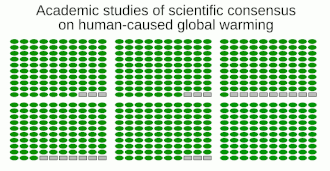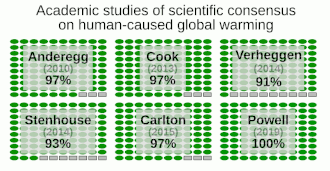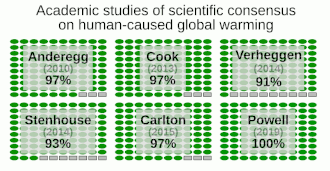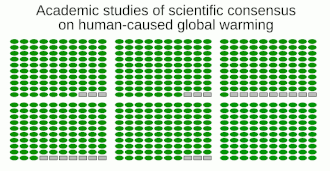
Academic studies of scientific agreement on human-caused global warming among climate experts (2010-2015) reflect that the level of consensus correlates with expertise in climate science.[10] A 2019 study found scientific consensus to be at 100%.[11]
- The consensus among research scientists on anthropogenic global warming grew to 100%, based on a review of 11,602 peer-reviewed articles on "climate change" and "global warming" published in the first 7 months of 2019.[11]
- A 2019 survey indicated a clear majority of people around the world think climate change is happening and that it is all or partly down to human actions.[12] However, 17% of Americans polled agreed that "the idea of manmade global warming is a hoax that was invented to deceive people", only Saudi Arabia and Indonesia having a higher proportion of people doubtful of manmade climate change.[12]
Projections
- In January, the World Economic Forum listed top 10 risks by likelihood (extreme weather events as #1, failure of climate change mitigation and adaptation as #2, man-made environmental damage and disasters as #6) and by impact (failure of climate change mitigation and adaptation as #2, extreme weather events as #3, man-made environmental damage and disasters as #9).[13]
Significant publications
- "Emissions Gap Report 2019" (PDF). UNenvironment.org. U.N. Environment Programme. 2019. Archived (PDF) from the original on 5 November 2020.
- Herring, Stephanie C.; Christidis, Nikolaos; Hoell, Andrew; Hoerling, Martin P.; Stott, Peter A. (editors) (January 2021). "Explaining Extreme Events or 2019 From a Climate Perspective" (PDF). AMetSoc.net. American Meteorological Society. Archived (PDF) from the original on 27 January 2021.CS1 maint: extra text: authors list (link)
- Myers, Joe; Whitling, Kate. "These are the biggest risks facing our world in 2019". WEForum.org. World Economic Forum. Archived from the original on 14 January 2021.
- Ripple, William J.; Wolf, Christopher; Newsome, Thomas M.; Baarnard, Phoebe; et al. (5 November 2019). "World Scientists' Warning of a Climate Emergency". BioScience. 70 (1): 8–12. doi:10.1093/biosci/biz088.
- Watts, Nick; Amann, Markus; Arnell, Nigel; Ayeb-Karlsson, Sonja; et al. (13 November 2019). "The 2019 report of The Lancet Countdown on health and climate change: ensuring that the health of a child born today is not defined by a changing climate". The Lancet. 394 (10211): 1836–1878. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32596-6. PMID 31733928. S2CID 207976337.
- "Arctic Report Card: Update for 2020 / The sustained transformation to a warmer, less frozen and biologically changed Arctic remains clear" (PDF). National Oceanographic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). December 2020. Archived (PDF) from the original on 8 December 2020. The Report Card comprises specific reports including:
- • York, A.; Bhatt, U.S.; Gargulinski, E.; Grabinski, Z.; et al. (December 2020). "Wildland Fire in High Northern Latitudes". NOAA.gov. National Oceanographic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). doi:10.25923/2gef-3964. Archived from the original on 10 December 2020.
See also
References
- Ripple et al. 2019.
- "Global Climate Change / Vital Signs of the Planet". climate.NASA.gov. NASA. 31 December 2019.
- "2019 was 2nd hottest year on record for Earth say NOAA, NASA". NOAA.gov. National Oceanographic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). 15 January 2020. Archived from the original on 11 December 2020.
- "WMO Greenhouse Gas Bulletin / The State of Greenhouse Gases in the Atmosphere Basd on Global Observations through 2019". WMO.int. World Meteorological Organization. 23 November 2020. p. 2. Archived from the original on 1 December 2020.
- York et al. 2020.
- Solsvik, Terje (26 February 2020). "Climate activist Thunberg heads growing field of Nobel Peace Prize candidates". Reuters. Archived from the original on 10 November 2020.
- "Transcript: Greta Thunberg's Speech at the U.N. Climate Action Summit". NPR.org. 23 September 2019. Archived from the original on 3 October 2019.
- Alter, Charlotte; Haynes, Suyin; Worland, Justin (December 2019). "TIME 2019 Person of the Year / Greta Thunberg". TIME. Archived from the original on 11 December 2019.
- Dawson, Bethany (5 January 2021). "Norway becomes first country to sell more electric cars than petrol vehicles". The Independent. Archived from the original on 21 January 2021.
- Cook, John; Oreskes, Naomi; Doran, Peter T.; Anderegg, William R. L.; et al. (2016). "Consensus on consensus: a synthesis of consensus estimates on human-caused global warming". Environmental Research Letters. 11 (4): 048002. Bibcode:2016ERL....11d8002C. doi:10.1088/1748-9326/11/4/048002.
- Powell, James (20 November 2019). "Scientists Reach 100% Consensus on Anthropogenic Global Warming". Bulletin of Science, Technology & Society. 37 (4): 183–184. doi:10.1177/0270467619886266. S2CID 213454806.
- Milman, Oliver; Harvey, Fiona (8 May 2019). "US is hotbed of climate change denial, major global survey finds". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 21 December 2020.
- Myers & Whiting 2019.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
