Chūkyō metropolitan area
Chūkyō (中京圏, Chūkyō-ken), or the Chūkyō region (中京地方, Chūkyō-chihō), is a major metropolitan area in Japan that is centered on the city of Nagoya (the "Chūkyō", i.e., the "capital in the middle") in Aichi Prefecture. The area makes up the most urbanized part of the Tōkai region. The population of 9,552,132 over an area of 7,072 square kilometers. (Demographia World Urban Areas 2019)[http://demographia.com/db-worldua.pdf] Nevertheless, like most of Japan's major metro areas, the core of it lies on a fertile alluvial plain, in this case the Nōbi Plain.
Nagoya metropolitan area
Nagoya MEA | |
|---|---|
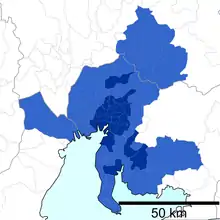 (2015) | |
| Prefectures | |
| Core cities | |
| Area (2011)[1] | |
| • Total | 2,791.72 km2 (1,077.89 sq mi) |
| • Inhabitable area | 1,902.02 km2 (734.37 sq mi) |
| Population (2015)[2] | |
| • Total | 6,871,632 |
| • Rank | 3rd in Japan |
| • Density | 2,500/km2 (6,400/sq mi) |
| GDP (nominal)[1] | 22.5 trillion Japanese yen (2010) |
Chūkyō metropolitan area
中京圏 | |
|---|---|
.JPG.webp) Nagoya | |
 Location in Japan | |
| Coordinates: 35°10′N 136°55′E | |
| Country | |
| Largest City | Nagoya |
| Area | |
| • Metro | 7,072 km2 (2,731 sq mi) |
| Population (Demographia World Urban Areas 2019
[http://demographia.com/db-worldua.pdf]) | |
| • Metro | 9,552,132 |
| • Metro density | 1,288/km2 (3,335/sq mi) |
It is among the 50 most populous metropolitan areas in the world, and is the third most populous metropolitan area in Japan (after Greater Tokyo and Osaka-Kobe-Kyoto), containing roughly 7% of Japan's population. Historically, this region has taken a back seat to the other two power centers, both politically and economically; however, the agglomeration of Nagoya is the world's 22nd-largest metro area economy, in terms of gross metropolitan product at purchasing power parity in 2014, according to a study by the Brookings Institution.[3] The GDP of Greater Nagoya, Nagoya Metropolitan Employment Area, is US$256.3 billion in 2010.[1][4]
Municipalities
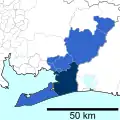
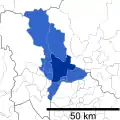
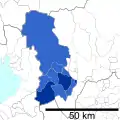
The metropolitan area stretches beyond the central city of Nagoya to other municipalities in Aichi Prefecture, as well as neighboring Gifu and Mie prefectures.
Aichi Prefecture
- Western Aichi Prefecture
- Eastern Aichi Prefecture
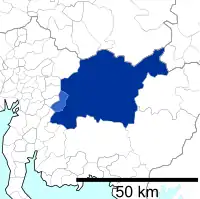
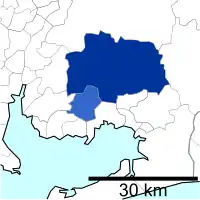
Gifu Prefecture

 Ōgaki
Ōgaki


Transport
Major airports
Major railways
There are at least 38 passenger train lines in the Greater Nagoya area. JR runs six, Nagoya Subway seven, Meitetsu 18, Kintetsu four, and five other operators one each.
- Other operators
Major intercity highways
- Chita-Hanto Expressway
- Chūō Expressway
- Higashi-Meihan Expressway
- Isewangan Expressway
- Meishin Expressway
- Tōkai Ring Expressway
- Tōkai-Hokuriku Expressway
- Tomei Expressway
GDP
2014 Chūkyō metropolitan area's GDP per capita (PPP) was US$40,144.[5]
Demographics
Per Japanese census data,[6][7][8] and[9] , Chūkyō metropolitan area, also known as greater Nagoya, has had continuous population growth.
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1950 | 2,237,000 | — |
| 1960 | 4,297,000 | +92.1% |
| 1970 | 6,603,000 | +53.7% |
| 1980 | 7,777,000 | +17.8% |
| 1990 | 8,407,000 | +8.1% |
| 2000 | 8,740,000 | +4.0% |
| 2010 | 9,107,414 | +4.2% |
| 2020 | 9,552,132 | +4.9% |
See also
- Nagoya
- Greater Nagoya Initiative
- Chūkyō Industrial Area
- Chūkyō Television Broadcasting
- Chukyo University
- List of metropolitan areas in Japan by population
Notes
- Kanemoto, Yoshitsugu. "Metropolitan Employment Area (MEA) Data". Center for Spatial Information Science, University of Tokyo. Retrieved January 25, 2019.
- Kanemoto, Yoshitsugu. "Urban Employment Area (MEA) Code Table". Center for Spatial Information Science, University of Tokyo. Archived from the original on January 9, 2019. Retrieved January 25, 2019.
- 2014 GLOBAL METRO MONITOR MAP
- Conversion rates - Exchange rates - OECD Data
- https://www.brookings.edu/research/global-metro-monitor/
- Greater Nagoya
- Chūkyō metropolitan area
- Statistics Bureau of Japan
- List of metropolitan areas in Japan
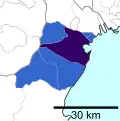
The area defined by the Chukyo Area Person-Trip Survey, a study of commuter movement, is slightly different from the census definition. It includes southern Aichi and areas immediately north of Gifu City. It adds two cities in Aichi Prefecture (Tahara and Toyohashi) and two cities in Gifu Prefecture (Mino and Seki). Additionally, it excludes two cities in Gifu Prefecture (Ena and Nakatsugawa).
.jpg.webp)









_2.jpg.webp)


.jpg.webp)


.jpg.webp)











