Fluvanna County, Virginia
Fluvanna County is a county located in the Piedmont region of the Commonwealth of Virginia. As of the 2010 census, the population was 25,691.[1] Its county seat is Palmyra.[2]
Fluvanna County | |
|---|---|
 Fluvanna County Courthouse, January 2014 | |
 Seal | |
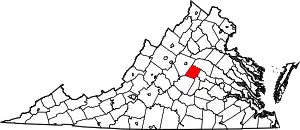 Location within the U.S. state of Virginia | |
 Virginia's location within the U.S. | |
| Coordinates: 37°50′N 78°17′W | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| Founded | 1777 |
| Named for | Fluvanna River |
| Seat | Palmyra |
| Largest community | Lake Monticello |
| Area | |
| • Total | 290 sq mi (800 km2) |
| • Land | 286 sq mi (740 km2) |
| • Water | 4.1 sq mi (11 km2) 1.4% |
| Population (2010) | |
| • Total | 25,691 |
| • Estimate (2018) | 26,783 |
| • Density | 89/sq mi (34/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC−5 (Eastern) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) |
| Congressional district | 5th |
| Website | fluvannacounty |
Fluvanna County is part of the Charlottesville, Virginia Metropolitan Statistical Area.
History
Through the 17th century, the Point of Fork (near Columbia where the James and Rivanna rivers meet) was the site of Rassawek, a major Monacan village of the Native Americans. By 1701, the Seneca Iroquois had overrun the entire Virginia Piedmont, which they sold to Virginia Colony in 1721 at the Treaty of Albany.
The area which is now Fluvanna County was once considered part of Henrico County, one of the original shires of the Virginia Colony. Henrico was divided in 1727 and the Fluvanna County area became a part of Goochland County. In 1744 Goochland was divided and the area presently known as Fluvanna became a part of Albemarle County. When Amherst County, Nelson County and Buckingham County were split off from Albemarle County, the Albemarle County Seat was moved in 1762 from Scottsville to Charlottesville. When the Albemarle County seat was moved citizens in the Fluvanna area would now have to trek over the Southwest Mountains to reach the new seat at Charlottesville. Fluvanna area citizens lobbied the Virginia General Assembly to create a new county. Finally, in 1777, Albemarle County was divided again and Fluvanna County established.
The county was named for the Fluvanna River, a name once given to the James River west of Columbia. "Fluvanna" means "Anne's River", in honor of Anne, Queen of Great Britain, who reigned until 1714.[3] Located in the Piedmont above the Fall Line, the county has the James and Rivanna rivers running through it. It was sometimes referred to as "Old Flu."[4]
Fluvanna was defended by six militia companies during the American Revolutionary War. The county was invaded by British forces in 1781 who destroyed the Point of Fork Arsenal. From an initial 882 "tithables," the population reached 3,300 by 1782. Columbia was formed in 1788 with Bernardsburg and Wilmington following soon after. Lyles Baptist Church was organized in 1774 and the formation of the Methodist denomination had its roots in a Conference held in Fluvanna in 1779. The "Brick Union" Church was built in 1825 for the use of Episcopalians, Methodists, Baptists and Presbyterians. The village of Fork Union grew up around the Church.
When Palmyra was made the county seat in 1828 it quickly became a thriving town after the new courthouse was completed in 1830.
In the late eighteenth century, Thomas Jefferson improved the navigability of the Rivanna River, as he owned much property along its upper course, e.g. Shadwell and Monticello plantations. Improvements included in the first generation (through 1830) were sluice cuts, small dams and batteaux locks.
Second-generation (1840–1870) improvements made by others included construction of long stretches of canal, serviced by large locks, many of which are still visible along the river. Shortly after the completion of the initial Rivanna navigational works, Virginia requested that the river be opened to public usage. Jefferson reportedly initially refused, but the state insisted and the Rivanna became an integral part of the central Virginian transportation network. The route serviced a large community of farmsteads, plantations throughout Albemarle and Fluvanna counties. It also was lined by increasing numbers of industrial facilities, such as those at Union Mills. Construction of the larger mills prompted the great improvements to navigation. For instance, Union Mills featured a two-and-a-half-mile long canal and towpath, and one upper and two massive lower locks, all directly upon the river.
Where the Rivanna meets the James River at Columbia, the Rivanna Connexion Canal merged with a much longer canal. (The series of locks which connected the two canals lie just outside the Town of Columbia and are mostly buried by sediment today). In 1840, the James River and Kanawha Canal was constructed adjacent to the north bank of the James River and opened to traffic. The new canal was part of a planned link between the Chesapeake Bay and the Atlantic Ocean via the James and the Kanawha rivers; it was intended to connect via the Ohio River, to the Mississippi River and the Gulf of Mexico. The canal was used by packet and freight boats, which replaced the earlier shallow-draft batteau for commerce. These boats brought goods and passengers to and from Richmond and points beyond. Long a dream of early Virginians such as George Washington, who was a surveyor early in his career, the canal was never completed as envisioned.
In the batteaux era, Milton was the head of navigation on the river. By the early nineteenth century, horse-drawn canal boats were traveling all the way upstream to Charlottesville. The head of navigation was located at the point where the Fredericksburg Road (now VA 20) and Three Chopt Road (U.S. Route 250), the primary road to Richmond, met and entered the city at the Free Bridge, establishing the city as a major commercial hub.
While no Civil War battles were fought in Fluvanna, Union soldiers burned mills and bridges and damaged the James River and Kanawha Canal to disrupt traffic and commerce. During the American Civil War more than 1,200 of the county's citizens served in the Confederate forces. Its citizens served in infantry, cavalry, and artillery units during the war, including the Fluvanna Artillery.
The canal was repaired after the war, but traffic never returned to pre-war levels, as railroads were being constructed throughout the state and were more efficient. After many years of trying to compete with the ever-expanding railroad network, the James River and Kanawha Canal was conveyed to a new railroad company by a deed dated March 4, 1880. Railroad construction workers promptly started laying tracks on the towpath. The new Richmond and Allegheny Railroad offered a water-level route from the Appalachian Mountains just east of West Virginia near Jackson's River Station (now Clifton Forge) through the Blue Ridge Mountains at Balcony Falls to Richmond. In 1888 the railroad was leased, and later purchased, by Collis P. Huntington's Chesapeake and Ohio Railway.
Fork Union Military Academy (FUMA) was initially founded as Fork Union Academy in October 1898 by Dr. William E. Hatcher, a prominent local Baptist minister. The first class had 19 boys and girls. In 1902, the academy took on a military structure to provide organization, discipline, and physical development for the boys of what was a rapidly growing school. In 1913, the academy became an all-male institution and changed its name to Fork Union Military Academy. That same year, the Academy began receiving support from the Baptist General Association of Virginia, which has continued into the 21st century. FUMA is known for its One Subject Plan as well as Post Graduate Football team that has many NFL players and Heisman Trophy winners as alumni.
Early in the 20th century, the C&O built a new line between the James River Line at Strathmore and the Piedmont Subdivision on the old Virginia Central Railroad's line at Gordonsville. The Virginia Air Line Railway was built to move loads that were too high or too wide to pass through the tunnels of the Blue Ridge Mountain complex between Charlottesville and Waynesboro. Additionally, coal trains from West Virginia headed eastbound for Washington, D.C. and Northern Virginia were routed on the new line to avoid steep mountain grades. The VAL was completed on September 29, 1909. A new freight station was built at Palmyra. The tracks of the VAL were abandoned in 1975, as railroad freight traffic had declined.
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1790 | 3,921 | — | |
| 1800 | 4,623 | 17.9% | |
| 1810 | 4,775 | 3.3% | |
| 1820 | 6,704 | 40.4% | |
| 1830 | 8,221 | 22.6% | |
| 1840 | 8,812 | 7.2% | |
| 1850 | 9,487 | 7.7% | |
| 1860 | 10,353 | 9.1% | |
| 1870 | 9,875 | −4.6% | |
| 1880 | 10,802 | 9.4% | |
| 1890 | 9,508 | −12.0% | |
| 1900 | 9,050 | −4.8% | |
| 1910 | 8,323 | −8.0% | |
| 1920 | 8,547 | 2.7% | |
| 1930 | 7,466 | −12.6% | |
| 1940 | 7,088 | −5.1% | |
| 1950 | 7,121 | 0.5% | |
| 1960 | 7,227 | 1.5% | |
| 1970 | 7,621 | 5.5% | |
| 1980 | 10,244 | 34.4% | |
| 1990 | 12,429 | 21.3% | |
| 2000 | 20,047 | 61.3% | |
| 2010 | 25,691 | 28.2% | |
| 2018 (est.) | 26,783 | [5] | 4.3% |
| U.S. Decennial Census[6] 1790–1960[7] 1900–1990[8] 1990–2000[9] 2010–2015[1] | |||
As of the census[10] of 2000, there were 20,047 people, 7,387 households, and 5,702 families residing in the county. The population density was 70 people per square mile (27/km2). There were 8,018 housing units at an average density of 28 per square mile (11/km2). The racial makeup of the county was 79.44% White, 18.41% Black or African American, 0.19% Native American, 0.38% Asian, 0.01% Pacific Islander, 0.29% from other races, and 1.25% from two or more races. 1.17% of the population were Hispanic or Latino of any race.
In the county, the population was spread out, with 23.60% under the age of 18, 6.40% from 18 to 24, 31.70% from 25 to 44, 24.40% from 45 to 64, and 14.00% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 38 years. For every 100 females there were 86.60 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 82.20 males.
Between 1990–2000, the population grew 61.3%. It is projected to be over 28,000 by 2010. The average family size is 2.9 persons. The median income for a household in the county was $46,372, and the median income for a family was $51,141. Males had a median income of $32,346 versus $24,774 for females. In 2000, there were 1,121 individuals below the poverty line which consisted of 280 children below the age of 18.In 1990, there were 1,287 individuals below the poverty line which consisted of 439 children below the age of 18.
According to the 2000 Census, the County median home value is $111,000 and the median mortgage is $900.00.
The County's school system consists of 3,490 students. There are currently 1 high school, 1 middle school, and 2 elementary schools one of which is an upper elementary school. Student/teacher ratio is 22–1. 17% of residents have a bachelor's degree or higher. As of 2000, 4,657 individuals over three years old enrolled in school, including 827 residents in college or graduate school. According to the 2000 Census, 1,066 students were enrolled in grades 9–12 and 603 in nursery school and kindergarten.
Fluvanna County High school is famous for its unique nickname, 'The Flying Flucos'. The Flying Flucos nickname has been recognized by ESPN as one of the top 10 unique High School nicknames in the country.
Economy
Fluvanna has a workforce of 13,206 living in the county.[11] 15% of the workforce lives and works inside the county borders. 84% of county residents work in another locality. In comparison, the equivalent of 22% are in-commuters. [12]
In October 2020, Governor Northam announced Silk City Printing of Paterson, NJ would relocate to Fork Union, VA to occupy the plant vacated by Thomasville Furniture in 2007. This was Fluvanna's first economic development project announced by the Governor's Office.[13] When fully operational, Silk City will be one of Fluvanna's top 10 employers.
Fluvanna County's Zion Crossroads Water and Sewer System water tower was named the top 10 best painted water towers in 2020 by Tnemec Corporation.[14][15]
The top 10 employers in Fluvanna as of 2020:[12]
- Fluvanna School Board
- Fluvanna Correctional Center for Women
- County of Fluvanna
- Fork Union Military Academy
- AG Dillard Inc.
- BFI Transfer Systems of Virginia (Republic Services)
- Food Lion
- Domino's Pizza
- Lake Monticello Owners' Association
- Fielders Choice Enterprises Inc
Geography
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 290 square miles (750 km2), of which 286 square miles (740 km2) is land and 4.1 square miles (11 km2) (1.4%) is water.[16] Palmyra, is 54 miles (87 km) from Richmond and 110 miles (180 km) from Dulles International Airport. Lake Monticello, a private community, is 15 miles (24 km) from Charlottesville.
Adjacent counties
- Louisa County – north
- Goochland County – east
- Cumberland County – southeast
- Buckingham County – south
- Albemarle County – west
Government and infrastructure

The Virginia Department of Corrections operates the Fluvanna Correctional Center for Women in unincorporated Fluvanna County, near Troy.[17] The center houses the female death row.[18]
Board of Supervisors
- Columbia District: Mike Sheridan (I)
- Cunningham District: Donald W. Weaver (R)
- Fork Union District: Mozell H. Booker(I), Chair
- Palmyra District: Patricia Eager (R)
- Rivanna District: Tony O'Brien (I)[19]
Constitutional officers
- Clerk of the Circuit Court: Tristana Treadway (I)
- Commissioner of the Revenue: Andrew M. "Mel" Sheridan, Jr. (I)
- Commonwealth's Attorney: Jeffrey W. Haislip (I)
- Sheriff: Eric Hess (I)
- Treasurer: Linda H. Lenherr (I)
Fluvanna is represented by Republican Mark Peake in the Virginia Senate, Republicans Robert B. Bell III and R. Lee Ware, Jr. in the Virginia House of Delegates, and Republican Bob Good in the U.S. House of Representatives.
| Year | Republican | Democratic | Third parties |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 51.5% 8,155 | 46.8% 7,414 | 1.7% 271 |
| 2016 | 51.7% 7,025 | 42.4% 5,760 | 5.9% 807 |
| 2012 | 52.4% 6,678 | 46.2% 5,893 | 1.4% 178 |
| 2008 | 50.4% 6,420 | 48.6% 6,185 | 1.0% 130 |
| 2004 | 58.9% 6,458 | 40.3% 4,415 | 0.8% 84 |
| 2000 | 57.0% 4,962 | 39.4% 3,431 | 3.6% 313 |
| 1996 | 51.7% 3,442 | 40.2% 2,676 | 8.2% 545 |
| 1992 | 48.0% 2,811 | 36.5% 2,134 | 15.5% 907 |
| 1988 | 60.3% 2,447 | 38.5% 1,562 | 1.2% 50 |
| 1984 | 62.2% 2,247 | 36.9% 1,332 | 0.9% 33 |
| 1980 | 50.4% 1,605 | 44.7% 1,424 | 4.9% 155 |
| 1976 | 46.8% 1,296 | 51.1% 1,415 | 2.1% 59 |
| 1972 | 67.3% 1,438 | 29.8% 637 | 2.9% 62 |
| 1968 | 42.6% 913 | 26.5% 569 | 30.9% 663 |
| 1964 | 44.9% 823 | 55.0% 1,008 | 0.2% 3 |
| 1960 | 54.9% 763 | 44.2% 614 | 0.9% 13 |
| 1956 | 53.9% 734 | 30.6% 417 | 15.6% 212 |
| 1952 | 57.7% 724 | 41.4% 519 | 0.9% 11 |
| 1948 | 37.4% 319 | 52.5% 447 | 10.1% 86 |
| 1944 | 33.5% 291 | 66.3% 577 | 0.2% 2 |
| 1940 | 29.4% 241 | 70.5% 579 | 0.1% 1 |
| 1936 | 26.9% 217 | 72.5% 586 | 0.6% 5 |
| 1932 | 22.9% 176 | 75.4% 579 | 1.7% 13 |
| 1928 | 42.3% 327 | 57.8% 447 | |
| 1924 | 22.0% 136 | 73.3% 452 | 4.7% 29 |
| 1920 | 20.4% 146 | 78.4% 562 | 1.3% 9 |
| 1912 | 10.1% 53 | 77.9% 409 | 12.0% 63 |
Notable residents
- Texas Jack Omohundro, a notable frontier scout, actor, and cowboy was born on the Pleasure Hill farm in Palmyra.[21]
- The singer Chris Daughtry, who came in fourth place on the fifth season of American Idol, resided in Fluvanna as a teenager; his parents still live there.
- Eddie George, Heisman Trophy winner and FUMA Alumnus
- Vinnie Testaverde, Heisman Trophy winner and FUMA Alumnus
- Kevin Plank, CEO and founder of Under Armour and FUMA Alumnus
Communities
Towns
Census-designated places
Unincorporated communities
References
- "State & County QuickFacts". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 2, 2014.
- "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Archived from the original on 2011-05-31. Retrieved 2011-06-07.
- Gannett, Henry (1905). The Origin of Certain Place Names in the United States. Govt. Print. Off. p. 128.
- . The Tennessean. 4 May 1840. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". Retrieved July 14, 2019.
- "U.S. Decennial Census". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 2, 2014.
- "Historical Census Browser". University of Virginia Library. Retrieved January 2, 2014.
- "Population of Counties by Decennial Census: 1900 to 1990". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 2, 2014.
- "Census 2000 PHC-T-4. Ranking Tables for Counties: 1990 and 2000" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 2, 2014.
- "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2011-05-14.
- "October Monthly Unemployment Report" (PDF). Virginia Employment Commission.
- "Community Profile of Fluvanna County, Virginia" (PDF). Virginia Employment Commission.
- "Governor Northam Announces Silk City Printing to Relocate to Fluvanna County, Creating 93 New Jobs". Governor Northam.
- "2020 Tank of the Year". Tnemec Tank of the Year.
- "Fluvanna water tower named as one of best-painted water tanks in the country". CBS19 News.
- "US Gazetteer files: 2010, 2000, and 1990". United States Census Bureau. 2011-02-12. Retrieved 2011-04-23.
- "Fluvanna Correctional Center for Women (female institution) Archived 2013-08-13 at the Wayback Machine." Virginia Department of Corrections. Retrieved on August 22, 2010.
- "Virginia Death Row/Execution Facts." My FOX DC. Tuesday November 10, 2009. Retrieved on August 22, 2010.
- "Board of Supervisors | Fluvanna County". www.fluvannacounty.org. Retrieved 2018-08-19.
- Leip, David. "Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections". uselectionatlas.org. Retrieved 2020-12-09.
- http://www.hmdb.org/marker.asp?marker=11676
