Rappahannock County, Virginia
Rappahannock County is a county located in the Commonwealth of Virginia, US. As of the 2010 census, the population was 7,373.[2] Its county seat is Washington.[3] The name "Rappahannock" comes from the Algonquian word lappihanne (also noted as toppehannock), meaning "river of quick, rising water" or "where the tide ebbs and flows."
Rappahannock County | |
|---|---|
 Rappahannock County Courthouse in Washington, Virginia | |
 Seal | |
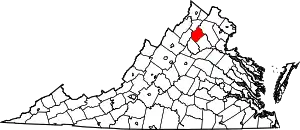 Location within the U.S. state of Virginia | |
 Virginia's location within the U.S. | |
| Coordinates: 38°41′N 78°10′W | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| Founded | 1833 |
| Named for | Rappahannock River |
| Seat | Washington |
| Largest town | Washington |
| Area | |
| • Total | 267 sq mi (690 km2) |
| • Land | 266 sq mi (690 km2) |
| • Water | 0.8 sq mi (2 km2) 0.3% |
| Population (2010) | |
| • Total | 7,373 |
| • Estimate (2018)[1] | 7,252 |
| • Density | 28/sq mi (11/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC−5 (Eastern) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) |
| Congressional district | 5th |
| Website | rappahannockcountyva |
Rappahannock County is included in the Washington-Arlington-Alexandria, DC-VA-MD-WV Metropolitan Statistical Area.
History
Rappahannock County was founded by an act of the Virginia General Assembly in 1833, based on the growing population's need to have better access to a county seat. The county's land was carved from Culpeper County. Rappahannock county was named for the river that separates it from Fauquier County.
The land on which Rappahannock County is sited was owned in the early 1700s by Thomas Fairfax 6th Lord Fairfax. It was part of the Northern Neck Proprietary, which consisted of 5.3 million acres of land located between the Rappahannock River and the Potomac River, from their headwaters in the Blue Ridge mountains to the Chesapeake Bay. In 1649 King Charles II of England, then in exile in France after the execution of his father, Charles I, had given this unmapped and unsettled region to seven loyal supporters. By 1688 the proprietary was owned solely by Thomas Lord Culpeper whose only child married Thomas 5th Lord Fairfax in 1690. They acquired the proprietary on the death of Lord Culpeper, and the region became synonymous with the Fairfax name. In 1719, Thomas Fairfax 6th Lord Fairfax inherited the land.
Prior to 1745, the land was granted to individuals by the kings of England, primarily by King George II, because the headwaters of the Rappahannock River were believed to be in the Chester Gap area. Thomas Lord of Fairfax brought suit against the English crown in the mid-1730s and surveying parties determined that the headwaters were the Conway River, which leads into the Rapidan River and then into the Rappahannock River. Because Fairfax won his suit against the Crown, land grants subsequent to 1745 were made by Fairfax.
Land grants issued by the agents of the English kings and by agents of the Northern Neck (Fairfax) Proprietary are housed in the archives of the Library of Virginia in Richmond, Virginia, and are available online at the Library of Virginia website.
Geography
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 267.2 square miles (692.0 km2), of which 266.4 sq mi (690.0 km2) is land and 0.8 sq mi (2.1 km2) (0.3%) is water.[4]
The Rappahannock River forms the northeastern boundary and separates Rappahannock County from Fauquier County. Rappahannock County is bounded on the southeast by Culpeper County and on the southwest by Madison County. The Blue Ridge Mountains occupy much of the western portion of the county.
Adjacent counties
- Warren County, Virginia – northwest
- Fauquier County, Virginia – northeast
- Culpeper County, Virginia – southeast
- Madison County, Virginia – southwest
- Page County, Virginia – west
National protected area
- Shenandoah National Park (part)
Mountains
The summits of the following mountains are located within Rappahannock County:
- Hamilton's knob (highest peak in Rappahannock County)
- Pignut Mountain
- Hogback Mountain
- Castleton Mountain
- Jenkins Mountain
- Jefferson Mountain
- Meetinghouse Mountain
- Little Mulky Mountain
- Little Jenkins Mountain
- Googe Mountain
- Round Mountain
- Hickerson Mountain
- Fork Mountain
- Battle Mountain [5]
- Little Battle Mountain
- Piney Ridge
- Pickerel Ridge
- Poes Mountain
- Turkey Mountain
- Aaron Mountain
- Red Oak Mountain

Major highways
 US 211
US 211 US 522
US 522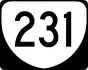 SR 231
SR 231- Skyline Drive
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1840 | 9,257 | — | |
| 1850 | 9,782 | 5.7% | |
| 1860 | 8,850 | −9.5% | |
| 1870 | 8,261 | −6.7% | |
| 1880 | 9,291 | 12.5% | |
| 1890 | 8,678 | −6.6% | |
| 1900 | 8,843 | 1.9% | |
| 1910 | 8,044 | −9.0% | |
| 1920 | 8,070 | 0.3% | |
| 1930 | 7,717 | −4.4% | |
| 1940 | 7,208 | −6.6% | |
| 1950 | 6,112 | −15.2% | |
| 1960 | 5,368 | −12.2% | |
| 1970 | 5,199 | −3.1% | |
| 1980 | 6,093 | 17.2% | |
| 1990 | 6,622 | 8.7% | |
| 2000 | 6,983 | 5.5% | |
| 2010 | 7,373 | 5.6% | |
| 2018 (est.) | 7,252 | [1] | −1.6% |
| Decennial Census[6] 1790–1960[7] 1900–1990[8] 1990–2000[9] | |||
As of the census[10] of 2010, there were 7,373 people, 2,788 households, and 2,004 families residing in the county. The population density was 26 people per square mile (10/km2). There were 3,303 housing units, at an average density of 12 per square mile (5/km2). The racial makeup of the county was 92.64% White, 5.44% Black or African American, 0.16% Native American, 0.21% Asian, 0.40% from other races, and 1.15% from two or more races. 1.30% of the population were Hispanic or Latino of any race.
There were 2,788 households, out of which 27.40% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 60.50% were married couples living together, 7.10% had a female householder with no husband present, and 28.10% were non-families. 23.40% of all households were made up of individuals, and 7.90% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.50, and the average family size was 2.94.
In the county, the population was spread out, with 22.30% under the age of 18, 5.60% from 18 to 24, 26.40% from 25 to 44, 31.80% from 45 to 64, and 13.80% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 43 years. For every 100 females, there were 98.80 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 97.30 males.
The median income for a household in the county was $45,943, and the median income for a family was $51,848. Males had a median income of $32,725 versus $22,950 for females. The per capita income for the county was $23,863. About 5.20% of families and 7.60% of the population were below the poverty line, including 10.80% of those under age 18 and 3.20% of those age 65 or over.
Government
Board Of Supervisors
- Debbie Donehey (D) – Vice-Chair (Wakefield District)
- Christine Smith (R) – Chair (Piedmont)
- I. Christopher Parrish (R) – (Stonewall-Hawthorne District)
- Keir Whitson (I) – (Hampton District)
- Ron Frazier (R) – (Jackson District)
Politics
| Year | Republican | Democratic | Third parties |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 56.5% 2,812 | 42.1% 2,096 | 1.4% 70 |
| 2016 | 56.6% 2,539 | 39.0% 1,747 | 4.4% 197 |
| 2012 | 53.0% 2,311 | 45.4% 1,980 | 1.5% 66 |
| 2008 | 50.6% 2,227 | 47.8% 2,105 | 1.7% 73 |
| 2004 | 53.6% 2,172 | 45.4% 1,837 | 1.0% 41 |
| 2000 | 52.7% 1,850 | 41.6% 1,462 | 5.7% 201 |
| 1996 | 47.3% 1,505 | 44.2% 1,405 | 8.5% 271 |
| 1992 | 44.3% 1,410 | 40.0% 1,273 | 15.7% 498 |
| 1988 | 61.7% 1,657 | 37.3% 1,003 | 1.0% 26 |
| 1984 | 62.7% 1,696 | 36.9% 999 | 0.4% 12 |
| 1980 | 49.8% 1,179 | 44.6% 1,055 | 5.6% 133 |
| 1976 | 44.5% 881 | 54.1% 1,071 | 1.5% 29 |
| 1972 | 68.2% 1,055 | 30.5% 471 | 1.4% 21 |
| 1968 | 43.6% 594 | 28.9% 394 | 27.5% 375 |
| 1964 | 39.8% 449 | 59.9% 675 | 0.3% 3 |
| 1960 | 43.7% 426 | 55.8% 544 | 0.5% 5 |
| 1956 | 47.8% 514 | 48.7% 523 | 3.5% 38 |
| 1952 | 54.4% 619 | 45.5% 518 | 0.2% 2 |
| 1948 | 30.1% 311 | 59.7% 617 | 10.3% 106 |
| 1944 | 37.3% 297 | 62.4% 497 | 0.4% 3 |
| 1940 | 27.6% 225 | 72.1% 588 | 0.4% 3 |
| 1936 | 26.0% 241 | 73.9% 686 | 0.1% 1 |
| 1932 | 17.2% 124 | 81.9% 590 | 0.8% 6 |
| 1928 | 39.1% 329 | 60.9% 513 | |
| 1924 | 17.6% 89 | 78.2% 395 | 4.2% 21 |
| 1920 | 33.3% 210 | 66.4% 418 | 0.3% 2 |
| 1916 | 17.1% 84 | 81.5% 401 | 1.4% 7 |
| 1912 | 19.8% 94 | 75.1% 356 | 5.1% 24 |
Education
The Rappahannock County Public Schools School District is located in Washington and includes two schools that serve 921 students county-wide in grades PK through 12.
Among the private schools in the county are two pre-K thru 12 schools, Hearthstone School and Wakefield Country Day School. There is one 6 thru 12 school, Belle Meade Farm School.
Communities
Town
Census-designated places
Other unincorporated communities
- Amissville
- Boston
- Castleton
- Huntly
- Laurel Mills
- Massies Corner
- Peola Mills
- Revercombs Corner
- Sperryville
- Wakefield Manor
- Woodville
References
- "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". Retrieved July 14, 2019.
- "State & County QuickFacts". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 5, 2014.
- "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Retrieved 2011-06-07.
- "US Gazetteer files: 2010, 2000, and 1990". United States Census Bureau. 2011-02-12. Retrieved 2011-04-23.
- Woolman, Thomas A. (2016-04-01). "A Gallium Anomaly Utilized in Palaeogeographic Reconstruction of Battle Mountain, Rappahannock County, Virginia". Transactions of the Kansas Academy of Science. Kansas Academy of Science. 119 (2): 155–172. doi:10.1660/062.119.0206. S2CID 88195835. Retrieved 2016-07-14.
- "U.S. Decennial Census". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 5, 2014.
- "Historical Census Browser". University of Virginia Library. Retrieved January 5, 2014.
- "Population of Counties by Decennial Census: 1900 to 1990". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 5, 2014.
- "Census 2000 PHC-T-4. Ranking Tables for Counties: 1990 and 2000" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 5, 2014.
- "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2011-05-14.
- Leip, David. "Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections". uselectionatlas.org. Retrieved 8 December 2020.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Rappahannock County, Virginia. |
- Rappahannock County, Virginia, the county government homepage
- Blue Ridge Independent News, an online local newspaper
- Rappahannock News, a print and online newspaper
- Memorial Foundation of the Germanna Colonies in Virginia, Inc.
- Rappahannock Historical Society, 328 Gay Street, Washington, VA 22747
- Library of Virginia Website


